Nearly 800,000 Americans suffer from strokes each year. Carotid artery disease is a big reason for these strokes. carotid artery disease happens when plaque builds up in the carotid arteries. This can lead to a stroke.

A CT scan is a key tool for finding blockages in the carotid arteries. It shows detailed images of the arteries. Doctors can then see how bad the blockage is.Get the definitive answer: does a CT scan show blocked carotid artery? Understand the use of CT angiography clearly.
Knowing how CT scans help find carotid artery blockages is important. It helps doctors act fast to prevent strokes.
Key Takeaways
- Carotid artery disease is a big risk for stroke.
- CT scans help find blockages in the carotid arteries.
- Early diagnosis is key to prevent stroke.
- CT scans give clear images of the carotid arteries.
- Quick medical action can stop a stroke.
Understanding the Carotid Artery and Its Function
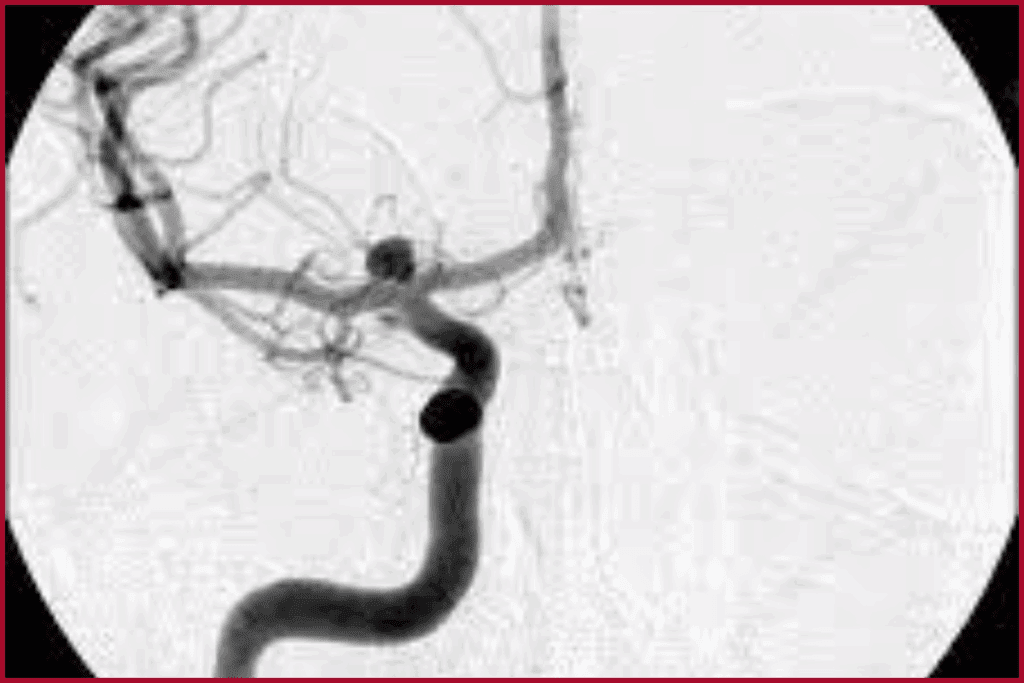
The carotid arteries are key to the circulatory system. They carry blood to the brain. You can find these important blood vessels on each side of your neck.
Anatomy of the Carotid Artery
The carotid arteries have a complex anatomy. This complexity is vital for their function.
Location and Structure
The carotid arteries are in the neck. They are built to handle blood pressure. They have three layers: the intima, media, and adventitia.
Common and Internal Carotid Branches
The common carotid artery splits into the internal and external carotid arteries. The internal carotid artery goes straight to the brain. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck.
Role in Blood Supply to the Brain

The carotid arteries are vital for the brain’s blood supply. They bring oxygenated blood to the brain.
Importance for Cerebral Circulation
Cerebral circulation is essential for brain function. The carotid arteries are key to keeping this circulation going.
Consequences of Disrupted Blood Flow
When blood flow through the carotid arteries is disrupted, serious conditions can occur. These include stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
| Artery | Location | Function |
| Common Carotid Artery | Neck | Supplies blood to the head and neck |
| Internal Carotid Artery | Inside the skull | Supplies blood directly to the brain |
| External Carotid Artery | Face and neck | Supplies blood to the face and neck |
Carotid Artery Disease: Causes and Risk Factors
It’s important to know what causes and increases the risk of carotid artery disease. This disease happens when the carotid arteries, which carry blood to the brain, get narrowed or blocked.
Atherosclerosis and Plaque Formation
Atherosclerosis, or the buildup of plaque in artery walls, is the main cause of carotid artery disease. This buildup includes fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances. These can harden and narrow the arteries. Plaque formation is key because it can cut down blood flow to the brain.
Common Risk Factors
There are many risk factors for carotid artery disease. These can be split into two groups: modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Smoking: Smoking harms the inner lining of blood vessels, making them more likely to block.
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can damage artery walls, speeding up atherosclerosis.
- High Cholesterol: High levels of LDL cholesterol can cause plaque to form.
- Diabetes: Diabetes increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
Non-modifiable Risk Factors
- Age: The risk of carotid artery disease goes up with age.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease raises your risk.
- Gender: Men are generally at higher risk, but women’s risk goes up after menopause.
Progression of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease can progress slowly, over years or decades. It’s vital to manage risk factors to stop the disease from getting worse. As Early detection and treatment can greatly lower the risk of stroke and other complications from carotid artery disease.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Blockage
Knowing the signs of carotid artery blockage is key to getting help fast. Carotid artery disease shows itself through specific symptoms that need quick action.
Warning Signs of Carotid Stenosis
Carotid stenosis, or the narrowing of the carotid arteries, can cause various symptoms. These include:
- Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), also known as mini-strokes
- Stroke symptoms, such as sudden weakness or numbness in the face or limbs
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden vision changes, including blurred vision or loss of vision in one eye
Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs)
TIAs are brief disruptions in brain blood flow, often due to carotid artery blockage. Symptoms are like a stroke but usually go away in 24 hours.
Stroke Symptoms
Stroke symptoms can differ based on the brain area affected. Common signs include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty with speech or understanding language
- Sudden vision changes
- Dizziness or loss of balance
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical help right away if you or someone else shows symptoms of carotid artery blockage.
Emergency Situations
If you have any of these symptoms, call emergency services immediately:
- Sudden severe headache
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Weakness or numbness in the face or limbs
- Vision changes or difficulty walking
Discussing Symptoms with Your Doctor
If you’re worried about symptoms, talk to your doctor. Describe your symptoms in detail, including when they started and how long they’ve lasted.
Diagnostic Methods for Carotid Artery Disease
To find carotid artery disease, doctors use many methods. First, they do a physical check. Then, they do initial tests and might use advanced imaging if needed.
Physical Examination Techniques
Checking the body is the first step in finding carotid artery disease. Doctors use special ways to look at the carotid arteries.
Listening for Carotid Bruits
They listen for carotid bruits with a stethoscope. A bruit is a sound that means the artery might be narrowed or blocked.
Pulse Assessment
They also check the pulse in the neck. This helps find if the pulse is weak or irregular.
Initial Screening Tests
After the physical check, initial dtests are done. These tests are non-invasive and look for carotid artery problems.
- Carotid ultrasound
- Doppler studies
Advanced Imaging Options
For a closer look, advanced imaging options are used. These give a clear view of the carotid arteries and any blockages.
| Imaging Technique | Description | Benefits |
| CT Angiography (CTA) | Uses CT scans and contrast dye to visualize the carotid arteries | High-resolution images, detailed view of artery blockages |
| Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) | Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to image the carotid arteries | No radiation, detailed images of arteries |
| Conventional Angiography | Involves injecting contrast dye into the arteries to visualize blockages | Highly detailed images, can be used for interventions |
CT Scans for Detecting Blocked Carotid Arteries
CT scans are key in finding blocked carotid arteries. They give detailed views of artery health. This tool has changed how we find and treat carotid artery disease.
How CT Scanning Technology Works
CT scanning uses X-rays to make detailed images of the body’s inside. For carotid artery disease, CT scans show the arteries and any blockages or narrowing.
CT Angiography (CTA) of the Neck
CT Angiography (CTA) is a special CT scan for blood vessels. It uses contrast material to make arteries stand out, helping spot blockages.
Contrast-Enhanced Imaging
Contrast-enhanced imaging makes blood vessels more visible during CTA. A contrast agent is injected into the blood. This helps show the arteries clearly against other tissues.
3D Reconstruction Capabilities
CTA can make 3D models of the carotid arteries. This lets doctors see blockages or stenosis in more detail.
Accuracy and Limitations of CT Scans
CT scans are great for finding carotid artery disease, but they have limits. Knowing both the good and bad points is key for accurate diagnosis.
Sensitivity and Specificity Rates
Research shows CT scans are very good at finding big carotid artery stenosis. But, how well they do can change based on the technology and the doctor’s skill.
Situations Where CT May Miss Blockages
CT scans might not catch all blockages, like in severe calcification or small blockages. Knowing these limits helps in fully checking patients.
| Diagnostic Method | Sensitivity | Specificity |
| CT Angiography | 95% | 92% |
| Carotid Ultrasound | 90% | 85% |
| MRA | 93% | 90% |
The table shows how different methods compare for finding carotid artery disease. It highlights CT Angiography’s strong points.
The Patient Experience During Carotid Artery CT Scans
Carotid artery CT scans are quick and painless. Knowing what to expect can help reduce anxiety. This test is key for checking the carotid arteries’ health.
Preparation for the Procedure
Before the scan, patients must remove metal objects and jewelry. Wearing comfortable clothes is also recommended. Some may get contrast dye to see the arteries better.
What to Expect During the Scan
The scan takes place in a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The process is painless and quick. Patients must stay very quiet and might need to hold their breath for clear images.
Potential Risks and Complications
CT scans are mostly safe, but there are risks. These include radiation and reactions to contrast dye.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
CT scans use a small amount of radiation. The risk is low, but telling doctors about past radiation is important.
Contrast Dye Reactions
Some might react to the contrast dye, from mild to severe. Telling the doctor about allergies is key.
| Aspect | Description | Precaution |
| Radiation Exposure | Small amount of radiation | Inform doctor about previous exposure |
| Contrast Dye | Enhances artery visibility | Report any allergies |
| Scan Duration | A few minutes | Remain very quiet during the scan |
Alternative Imaging Techniques for Carotid Artery Assessment
CT scans are good for finding blocked carotid arteries. But, other methods can also help. These are key for people who can’t have CT scans or need more info for a full diagnosis.
Carotid Ultrasound and Doppler Studies
Carotid ultrasound uses sound waves to see the carotid arteries. It’s often paired with Doppler studies to check blood flow.
Non-invasive Nature and Limitations
The non-invasive nature of carotid ultrasound makes it safe and a first choice. But, its accuracy depends on the person doing it. It might not show the artery’s inner layers well.
Real-time Blood Flow Assessment
Doppler studies add to ultrasound by showing blood flow in real-time. This helps spot stenosis or blockages. It’s key for knowing how bad the artery disease is.
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) is great for looking at carotid artery disease. It uses magnetic fields and radio waves to get clear images of the arteries. This helps find stenosis, aneurysms, and other problems.
Conventional Angiography
Conventional angiography, or digital subtraction angiography (DSA), uses a contrast agent to see the arteries on an X-ray. It’s top-notch for finding vascular diseases. But, it’s invasive and riskier than non-invasive methods like ultrasound and MRA.
These other imaging methods give doctors many ways to diagnose and treat carotid artery disease. Each has its own good points and downsides. Knowing these helps doctors pick the best test for their patients.
Treatment Options for Carotid Artery Disease
There are many ways to treat carotid artery disease. These include medicine, surgery, and new techniques. The right treatment depends on how bad the disease is and the patient’s health.
Medical Management
Medical management is key in treating carotid artery disease. It aims to lower risk factors and stop the disease from getting worse.
Antiplatelet Medications
Doctors often give patients aspirin and clopidogrel. These medicines stop platelets from clumping together. This helps prevent strokes by stopping blood clots.
Cholesterol Management
Statins and other drugs help control high cholesterol. High cholesterol is a big risk factor for carotid artery disease. These drugs lower bad cholesterol, slowing down artery damage.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is needed for serious carotid artery stenosis.
Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy removes plaque from the artery. It’s for those with very narrow arteries. This surgery greatly lowers stroke risk.
Recovery and Outcomes
After carotid endarterectomy, patients usually stay in the hospital briefly. They then need a few weeks to recover. The surgery is safe when done by skilled surgeons.
Endovascular Procedures
Endovascular procedures are a less invasive option for some.
Carotid Artery Stenting
Carotid artery stenting puts a stent in the artery to improve blood flow. It’s for those at high risk for surgery or with previous neck issues.
Candidate Selection
Choosing who gets carotid artery stenting depends on several things. These include how bad the stenosis is, the patient’s health, and other factors.
Conclusion
Carotid artery disease is a serious condition that can lead to stroke if left untreated. It happens when the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain, narrow or block. A CT scan is key in finding blockages and figuring out the best treatment.
A summary of carotid artery disease shows how important early diagnosis and treatment are. CT scans help spot blocked arteries. This lets doctors create effective treatment plans. Early action can greatly improve patient outcomes and lower stroke risk.
Knowing about carotid artery disease can help you protect your health. If you’re at risk, talk to your doctor about the best tests and treatments for you.
FAQ
What is carotid artery disease?
Carotid artery disease happens when the main blood vessels to the brain get narrowed or blocked. This is due to a buildup of plaque, known as atherosclerosis.
How do I check my carotid artery for blockage at home?
You can’t check for blockages at home for sure. But, watch for signs like transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or stroke symptoms. If you notice these, get medical help right away. A doctor can do a physical check and suggest tests like a carotid ultrasound or CT angiography.
What are the symptoms of carotid artery blockage?
Signs include TIAs or mini-strokes, stroke symptoms, dizziness, confusion, and weakness or numbness in the face or limbs. Also, trouble speaking or understanding speech. If you see these signs, get help fast.
Can a CT scan detect blocked carotid arteries?
Yes, a CT scan, like CT angiography (CTA), can spot blocked or narrowed carotid arteries. It uses dye and X-rays to show detailed images of the neck’s blood vessels.
What is the difference between a carotid ultrasound and a CT scan?
A carotid ultrasound uses sound waves to see the carotid arteries. A CT scan uses X-rays and dye for detailed images. Both can find carotid artery disease. But, CT angiography is often better at showing how bad the blockages are.
How long does a carotid ultrasound take?
A carotid ultrasound usually takes 15-30 minutes. This time can vary based on the test’s complexity and where it’s done.
What are the treatment options for carotid artery disease?
Treatments include medicines, lifestyle changes, and surgeries like carotid endarterectomy or stenting. The right treatment depends on how severe the disease is and the patient’s situation.
Can carotid artery disease be prevented?
Some risk factors, like age and family history, can’t be changed. But, you can manage others with lifestyle changes. Quit smoking, exercise, and control blood pressure and cholesterol.
What are the risks associated with carotid artery CT scans?
Risks include radiation and allergic reactions to dye. But, these risks are low. The test’s benefits usually outweigh the risks.
How accurate are CT scans in detecting carotid artery disease?
CT angiography is very accurate in finding carotid artery disease. But, accuracy depends on the imaging quality and the doctor’s skill.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10978047/




































