A stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) can be the first sign of carotid artery disease. This disease often develops slowly over time.Learn what are the warning signs of a blocked carotid artery. Understand symptoms like TIA, dizziness, and sudden weakness clearly.
Carotid artery blockage happens when the carotid arteries narrow or get blocked. This can lead to a stroke.
It’s important to recognize the warning signs of a blocked carotid artery. This can help prevent a stroke and its severe consequences.
Key Takeaways
- Carotid artery disease can develop slowly without noticeable symptoms.
- A stroke or TIA can be the first sign of the condition.
- Blocked carotid artery can lead to severe consequences if left untreated.
- Recognizing warning signs is key for prevention.
- Understanding carotid artery symptoms can help in seeking timely medical attention.
The Carotid Artery System: Location and Function
The carotid arteries are vital blood vessels. They supply the brain with oxygenated blood. Located on each side of the neck, these arteries are key to brain health.
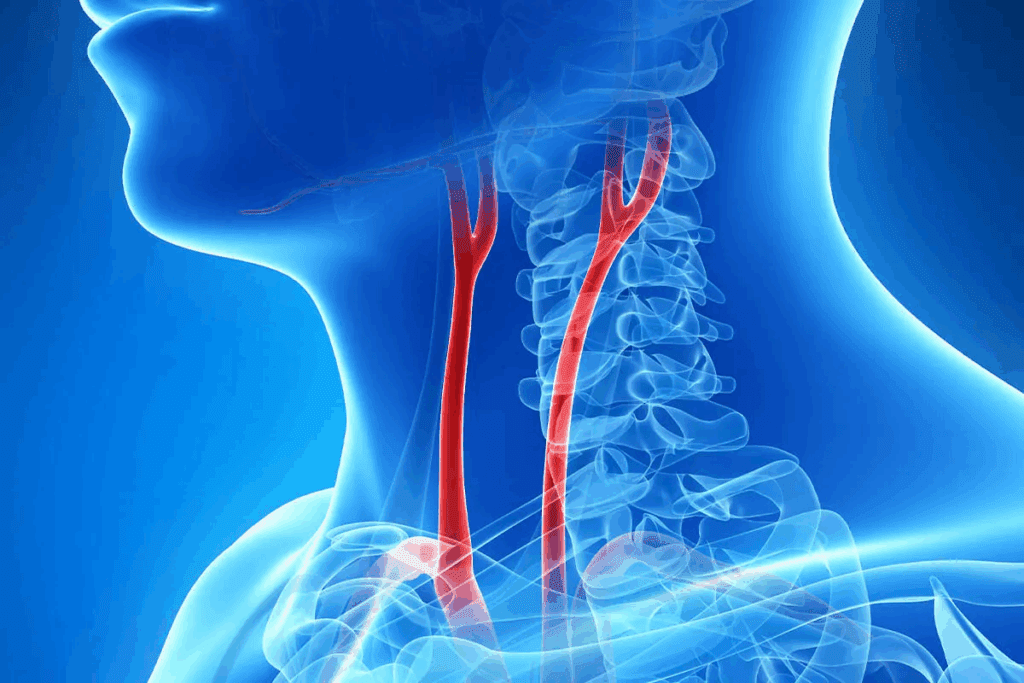
What are carotid arteries and where are they located?
The carotid arteries are two major blood vessels in the neck. They deliver blood to the brain, neck, and face. They are located on either side of the trachea and can be felt on the sides of the neck, just below the jawline. Starting from the aortic arch, they ascend through the neck, dividing into internal and external branches.
The critical role in blood supply to the brain
The carotid arteries are vital for the brain’s blood supply. The brain needs a constant flow of oxygen and nutrients, which these arteries provide. Any disruption can lead to serious neurological issues, including stroke.
Differences between internal and external carotid arteries
The carotid arteries split into two main branches: the internal and external carotid arteries. The internal carotid artery goes straight to the brain. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. Knowing the difference is key for diagnosing and treating carotid artery issues.
What Causes Blockages in the Carotid Artery?
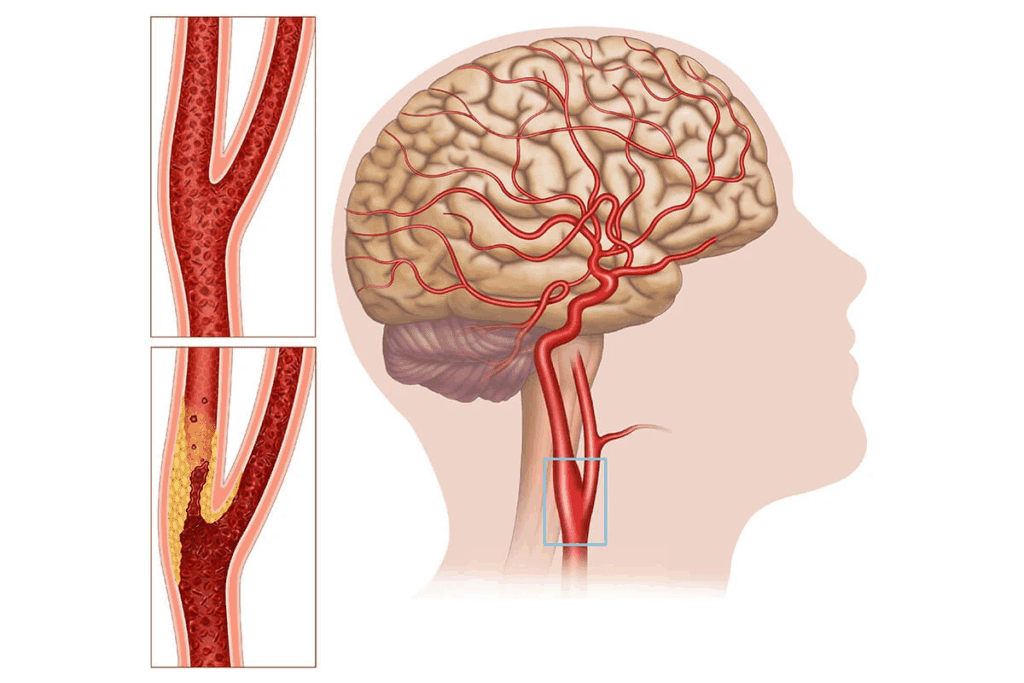
Knowing what causes blockages in the carotid artery is key to preventing strokes and heart problems. The carotid arteries are major paths for blood to the brain. They can narrow or block due to several conditions.
Atherosclerosis: The Primary Culprit
Atherosclerosis is the main reason for carotid artery blockages. It’s when plaque, a mix of fat, cholesterol, and more, builds up in artery walls. This buildup narrows the arteries, cutting down blood flow to the brain.
How Plaque Builds Up and Narrows the Artery
Plaque buildup happens slowly. It starts with fatty deposits on artery walls. Over time, these deposits harden into plaques. They can rupture, causing blood clots that block the artery.
High blood pressure, smoking, and high cholesterol speed up this process. Other factors include:
- High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- A family history of atherosclerosis
Other Causes of Carotid Stenosis
While atherosclerosis is the main cause, other factors can also narrow the carotid arteries. These include:
- Dissection: A tear in the artery wall
- Radiation therapy to the neck
- Certain inflammatory conditions
Understanding these causes is vital for diagnosing and treating carotid artery disease. By tackling the root causes, people can lower their risk of severe carotid stenosis and its serious effects.
Early Warning Signs That Are Often Missed
Spotting early signs of carotid artery blockage can be tricky. Yet, it’s key to avoid serious problems. These signs often start quietly, so staying alert to your health is important.
Subtle symptoms that precede major events
Before a big stroke or serious event, people might feel slight numbness or weakness. They might also have minor speech issues or brief dizziness.
These small symptoms can signal bigger issues. Knowing them can help you get medical help early. This might stop a bigger problem from happening.
Transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes)
A Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), or “mini-stroke,” is a short brain function problem. It’s caused by brief blood flow stop in the brain. Symptoms are like a stroke but usually go away in 24 hours.
TIAs are a big warning sign of carotid artery disease. Having a TIA means you’re at higher risk for a real stroke. So, getting medical help right away is very important.
Distinguishing carotid symptoms from other conditions
Symptoms of carotid artery blockage can look like other health issues. For example, dizziness might seem like an ear problem, not a carotid artery issue.
Seeing a doctor is key if you have strange or lasting symptoms. A doctor can figure out what’s wrong and what to do next.
| Symptom | Description | Possible Misdiagnosis |
| Numbness or Weakness | Slight numbness or weakness in the face or limbs | Multiple Sclerosis, Peripheral Neuropathy |
| Speech Difficulties | Minor speech difficulties or slurring | Dysarthria, Anxiety |
| Dizziness | Brief episodes of dizziness or vertigo | Inner Ear Problems, Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) |
It’s important to know the early signs of carotid artery blockage. This helps get medical help fast. If you notice any symptoms, don’t wait to see a doctor.
Major Symptoms of Carotid Artery Blockage
The main signs of carotid artery blockage include neurological, visual, and physical symptoms. These signs can be serious and need quick medical help to avoid worse problems.
Neurological Symptoms: Weakness, Numbness, and Speech Changes
Neurological symptoms are a key sign of carotid artery blockage. You might feel weakness or numbness in the face or limbs on one side. Also, you could have speech changes, like slurred speech or trouble finding words.
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face or limbs
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Trouble with coordination and balance
Visual Disturbances and Their Significance
Visual problems are another important symptom. You might see transient blindness in one eye or double vision. These signs are often short-lived but can lead to serious vision loss if not treated.
Other Physical Manifestations
Carotid artery blockage can also cause other physical symptoms. You might feel dizziness and balance problems, which can really affect your life.
Dizziness and Balance Problems
Dizziness and balance issues happen because of less blood to the brain. This raises the chance of falls and accidents. So, it’s important to get medical help fast.
Severe Headaches
In some cases, you might get severe headaches from carotid artery blockage. These headaches are different from usual headaches. They show the body’s effort to deal with less blood flow.
Spotting these symptoms early is key to managing them well and preventing stroke. If you or someone you know has these signs, getting medical help right away is critical.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Care
If you’re feeling symptoms of a blocked carotid artery, every minute counts. Knowing when to get help can make a big difference.
Red Flag Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
Some symptoms mean you’re at high risk for stroke and need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden vision changes, including double vision or loss of vision
- Severe headache with no known cause
Acting quickly when these symptoms show up can stop a stroke or lessen its effects.
The Importance of Rapid Response for Stroke Prevention
Quick action is key to stopping stroke damage. Emergency services can start treatments fast, which can greatly improve your chances.
What to Tell Emergency Responders
When you call for emergency help, tell them about your symptoms. Share when they started and any health issues you have. This helps them get ready and make fast decisions.
Even if symptoms last just a bit, getting emergency care is vital. Quick action can save lives and prevent serious harm.
Risk Factors That Increase Your Chances of Blockage
Carotid artery blockage risk comes from lifestyle, medical conditions, and genes. Knowing these factors helps prevent and manage the condition.
Modifiable Lifestyle Factors
Choices like smoking and diet affect your risk. These can be changed to lower your risk.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking greatly increases your risk. Quitting smoking can greatly reduce this risk.
Diet and Physical Activity
Eating too much saturated fat and cholesterol can harm your arteries. Exercise improves heart health and reduces risk.
Medical Conditions That Accelerate Blockage
Some health issues can speed up blockage. These include high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and obesity.
Hypertension and Diabetes
High blood pressure strains arteries, making them more likely to block. Diabetes also harms blood vessels and the heart.
High Cholesterol and Obesity
High LDL cholesterol causes artery plaque. Obesity increases risk due to its link with high blood pressure and diabetes.
Age, Gender, and Genetic Factors
Some risks can’t be changed, like age and gender. Age increases risk, and men are more at risk than women. A family history of heart disease also raises your risk.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Carotid Artery Blockage |
| Smoking/Tobacco Use | Increases plaque buildup and damages arteries | High |
| Hypertension | Puts extra strain on arteries | High |
| Diabetes | Affects blood vessels and cardiovascular health | High |
| High Cholesterol | Leads to plaque buildup in arteries | High |
| Obesity | Associated with other risk factors like hypertension and diabetes | High |
A study found that having many risk factors increases your chance of carotid artery disease.
“Managing modifiable risk factors is key to preventing carotid artery blockage.”
Diagnostic Methods for Detecting Carotid Blockages
Diagnosing carotid artery blockages requires a mix of physical checks and advanced imaging. A healthcare expert might use several methods to find and measure carotid stenosis.
Physical examination and carotid auscultation
A physical check is the first step in finding carotid artery disease. A doctor might listen to the carotid arteries with a stethoscope, called carotid auscultation. Abnormal sounds, or bruits, can show turbulent blood flow due to stenosis.
Carotid ultrasound
Carotid ultrasound uses sound waves to see the carotid arteries. This non-invasive test can spot blockages and check blood flow. It’s great for diagnosing carotid disease and tracking its progress.
CT angiography and MRA
CT angiography and Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) give detailed views of the carotid arteries. CT angiography uses X-rays and dye to see the arteries, while MRA uses a magnetic field and radio waves. Both can find stenosis and measure its severity.
Advanced diagnostic procedures
Sometimes, more tests are needed. Digital subtraction angiography is a more invasive test that injects dye into the arteries. Advanced imaging helps doctors make accurate diagnoses and plan treatments.
Diagnosing carotid blockages is key to preventing strokes and heart problems. By using physical checks and non-invasive imaging, doctors can manage carotid artery disease well.
Treatment Approaches for Blocked Carotid Arteries
Dealing with blocked carotid arteries needs a detailed plan. This plan might include medicine, lifestyle changes, and surgery. The right treatment depends on how bad the blockage is, the patient’s health, and other things.
Medical Management Strategies
For blocked carotid arteries, doctors often start with medicine. This method aims to lower risks and slow down artery damage. Medications like blood thinners, clot preventers, and cholesterol-lowering drugs are used to prevent strokes and manage related issues.
- Antiplatelet therapy to prevent blood clots
- Statins to lower cholesterol levels
- Medications to manage hypertension and diabetes
Surgical Interventions: Endarterectomy and Stenting
When blockages are severe, surgery might be needed. There are two main surgeries: carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting.
| Procedure | Description | Benefits |
| Carotid Endarterectomy | Surgical removal of plaque from the carotid artery | Effective for severe blockages, reduces stroke risk |
| Carotid Artery Stenting | Minimally invasive procedure where a stent is placed to keep the artery open | Less invasive than endarterectomy, suitable for high-risk patients |
Recovery and Follow-up Care
After surgery, recovery and follow-up care are key for the best results. Patients are watched for any problems and told how to live healthier to avoid future blockages.
Managing blocked carotid arteries needs a team effort. Doctors, cardiologists, and vascular surgeons all play a part. Knowing the treatment options helps patients make better choices for their health.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Arterial Health
Keeping a healthy lifestyle is key to avoiding carotid artery disease. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and not smoking help a lot. These actions can lower the risk of blockages in the carotid artery.
By knowing the warning signs and acting early, you can protect your arteries. This helps prevent strokes. It’s all about being proactive.
Protecting your arteries is a big job. It means managing blood pressure, checking cholesterol, and keeping a healthy weight. These habits can greatly lower your risk of carotid artery disease.
Being aware of risks and taking steps to reduce them is important. This includes watching your family’s health history, managing stress, and staying up-to-date with new research. This way, you can control your carotid artery health.
FAQ
What is the carotid artery and what is its function?
The carotid arteries are major blood vessels in the neck. They supply blood to the brain, neck, and face. They are key in delivering oxygenated blood to the brain.
What are the symptoms of carotid artery blockage?
Symptoms include weakness, numbness, or paralysis in the face, arm, or leg. Difficulty speaking or swallowing is also a sign. Vision changes, dizziness, or loss of balance can occur too.
What causes blockages in the carotid artery?
Atherosclerosis is the main cause. It’s when plaque builds up in the artery. This narrows it and restricts blood flow.
What are the risk factors for carotid artery blockage?
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are big risks. Smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a family history also increase the risk.
How is carotid artery blockage diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams and imaging tests like ultrasound or angiography. Other diagnostic procedures are also used.
What are the treatment options for blocked carotid arteries?
Treatment includes medications to control blood pressure and cholesterol. Surgical options like endarterectomy or stenting are also available.
What is the difference between internal and external carotid arteries?
The internal carotid artery goes to the brain. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the neck and face.
Can carotid artery blockage be prevented?
Some risk factors can’t be changed, like age and genetics. But, quitting smoking, exercising, and eating healthy can help.
What are the signs of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or mini-stroke?
Signs include sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg. Difficulty speaking or understanding speech is also a sign. Vision changes, dizziness, or loss of balance can occur too.
Why is it important to seek emergency medical care if symptoms of carotid artery blockage occur?
Quick action is key if symptoms happen. Timely treatment can prevent a stroke or lessen its impact.
References
National Institutes of Health. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/carotid-artery-disease




































