Atrial fibrillation (afib) affects millions worldwide. Ablation for afib is a key medical procedure for managing it. Even with the progress in afib ablation, not everyone with atrial fibrillation can have this procedure. The length of afib, overall health, and other medical conditions are important. They help decide if someone is eligible.
Learn who is not eligible for ablation. Understand the contraindications for ablation for afib clearly.
Key Takeaways
- The suitability for afib ablation depends on several health and medical factors.
- Understanding the criteria for eligibility is key for patients considering this procedure.
- Atrial fibrillation medical procedures are continually evolving.
- Patient selection for afib ablation involves a detailed assessment.
Understanding Cardiac Ablation Procedures

For those with atrial fibrillation (afib), cardiac ablation is a hopeful solution. It aims to bring back a normal heart beat. This procedure scars or destroys heart tissue that causes irregular rhythms.
What is Cardiac Ablation?
Cardiac ablation is a treatment that fixes heart rhythm problems, like afib. It uses a catheter to send energy to the heart. This creates lesions that stop the abnormal signals.
Types of Ablation Techniques
There are several ways to do cardiac ablation for atrial fibrillation:
- Radiofrequency Ablation: This method uses heat from radiofrequency energy to make lesions.
- Cryoballoon Ablation: It uses a cold liquid-filled balloon to freeze the tissue, creating lesions.
- Laser Ablation: This technique uses laser energy to make lesions.
Each method has its benefits. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s preference.
General Success Rates and Outcomes
The success of cardiac ablation for afib depends on many factors. These include the ablation technique, the patient’s health, and the severity of afib. Studies show that many patients see their heart rhythm return to normal.
Recent data shows a success rate of 60% to 80% for patients with paroxysmal afib. But, the success rate is lower for those with persistent or long-standing afib.
Surgery for atrial fibrillation, including ablation, is a key treatment for those who don’t respond to other treatments. Knowing about the different ablation techniques and their success rates helps patients make better choices.
Ablation for Afib: Patient Selection Overview
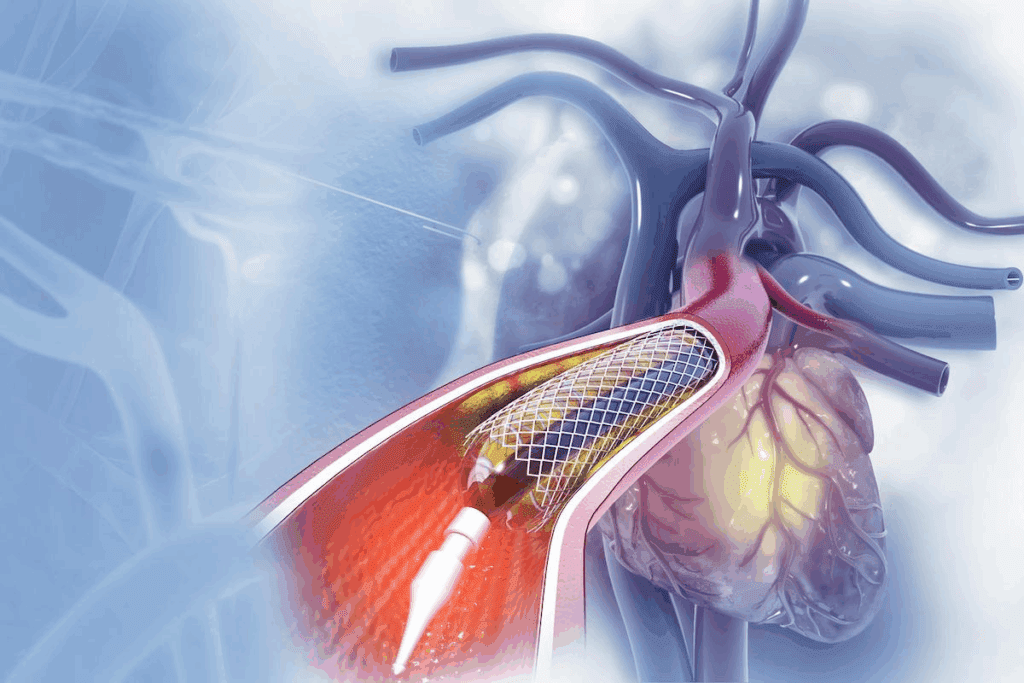
Choosing the right patients is key to successful Afib ablation. It’s about finding those who will benefit most and who are at the least risk. This careful selection is what makes the treatment work well.
Ideal Candidates for Afib Ablation
Those who might benefit from Afib ablation are often those who can’t manage their symptoms with medicine. They might feel tired, have trouble breathing, or feel irregular heartbeats. Careful evaluation is needed to see if they’re good candidates.
Doctors look at a patient’s history, including how long they’ve had Afib and any other health issues. They might also use advanced imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans to check the heart’s shape and how it works.
The Importance of Proper Patient Selection
Choosing the right patients is vital for the success of Afib ablation. It helps doctors pick those most likely to get better and avoid complications. Risk stratification is important here, as it helps spot and manage risks.
Doctors consider many things when picking patients, like their overall health and how severe their Afib symptoms are. Multidisciplinary teams often work together to decide the best treatment for each patient.
Risk Stratification Process
The risk stratification process is about figuring out the risks of Afib ablation for each patient. Doctors look at age, health conditions, and any reasons a patient might not be a good candidate. Advanced risk assessment tools help spot patients at higher risk.
Understanding the risks and benefits helps doctors make better choices about who to treat.
Absolute Contraindications for Cardiac Ablation
Some conditions make cardiac ablation too risky. These can affect the treatment’s safety and success.
Left Atrial Thrombus
A blood clot in the left atrium is a big no-no for ablation. It could break loose and cause a stroke. Before ablation, patients with this issue need blood thinners.
Active Infection or Sepsis
Having an active infection or sepsis is a clear no-go for ablation. It could make things worse, like spreading the infection. Patients must get their infection under control first.
Severe Uncontrolled Heart Failure
Heart failure that’s not well-managed is also a big risk. It can make the heart too weak for the procedure. Before ablation, heart failure needs to be better managed.
| Contraindication | Description | Pre-Ablation Management |
| Left Atrial Thrombus | Blood clot in the left atrium that can dislodge during ablation | Anticoagulation therapy |
| Active Infection or Sepsis | Ongoing infection that can spread or worsen with the procedure | Treatment with antibiotics, clearance by healthcare provider |
| Severe Uncontrolled Heart Failure | Compromised heart function that increases procedural risk | Optimization of heart failure management |
It’s key for doctors to know these no-go’s. This helps pick the right patients for ablation and manage risks.
Relative Contraindications: When Ablation May Be Risky
Relative contraindications are important when deciding if cardiac ablation is right for patients. This treatment can help many heart conditions. But, some health issues might make the procedure riskier.
Severe Pulmonary Hypertension
Severe pulmonary hypertension means high blood pressure in the lungs’ arteries. It’s a relative contraindication for cardiac ablation. This is because it can make the procedure harder and raise the chance of complications after.
Patients with severe pulmonary hypertension need careful evaluation and management before ablation.
Uncontrolled Thyroid Disorders
Uncontrolled thyroid disorders can affect the heart and increase the risk of complications during and after ablation. It’s important to manage thyroid conditions well before the procedure.
Recent Stroke or TIA
A recent stroke or TIA is another relative contraindication for cardiac ablation. The risk of more neurological problems or complications during the procedure is higher. A detailed assessment and the right timing of the ablation are key to reduce risks.
In conclusion, while cardiac ablation is a valuable treatment for many, it’s vital to understand and manage relative contraindications. This ensures patient safety and the success of the procedure.
Age-Related Eligibility Concerns
Age is a big factor when it comes to Afib ablation procedures. As people get older, more of them develop atrial fibrillation (Afib). It’s important to check if older patients can safely have this treatment.
Elderly Patients (Over 75)
Deciding if older patients should have Afib ablation is tough. It’s not just about their age. Doctors also look at their health, any other health issues they might have, and if the treatment will help them.
| Age Group | Success Rate of Afib Ablation | Complication Rate |
| 75+ | 60-70% | Higher due to comorbidities |
| 65-74 | 70-80% | Moderate |
| <65 | 80-90% | Lower |
Very Young Patients with Afib
Young patients with Afib face their own challenges. Afib is rare in the young and often caused by different things than in older people. Doctors have to think carefully about the long-term effects and if they might need to do it again.
Comorbidities That May Exclude Ablation Candidates
Some health conditions can make it hard for patients to get afib ablation. These conditions happen along with atrial fibrillation (afib). They can change how well the ablation works.
Severe Kidney Disease
Severe kidney disease can make it tough for patients to get afib ablation. It raises the risk of problems during and after the procedure. Kidney disease can also mess with heart rhythm because of electrolyte imbalances.
Key considerations for patients with severe kidney disease:
- Increased risk of bleeding due to anticoagulation therapy
- Potential for electrolyte imbalances affecting heart rhythm
- Higher risk of complications during the ablation procedure
Advanced Liver Dysfunction
Advanced liver disease can make afib ablation tricky. Liver problems can cause bleeding issues during and after the procedure. They can also mess with how medicines work.
Important factors for patients with advanced liver dysfunction:
- Risk of bleeding due to coagulopathy
- Potential for medication interactions and altered metabolism
- Increased risk of complications during and after the procedure
Significant Respiratory Conditions
Conditions like COPD can also affect a patient’s chance for afib ablation. These issues can lead to breathing problems during and after the procedure.
Notable considerations for patients with significant respiratory conditions:
- Increased risk of respiratory complications during the procedure
- Potential need for adjusted anesthesia and sedation strategies
- Higher risk of post-procedure respiratory issues
Anatomical and Structural Heart Issues
Having certain heart problems can affect if you’re a good candidate for afib ablation. The heart’s shape and structure play a big role in how well the procedure works.
Complex Congenital Heart Defects
People with complex heart defects face challenges with afib ablation. These defects, like holes in the heart or odd chamber shapes, need careful checking. This helps decide if ablation is right for them.
Severe Valve Disease
Severe valve disease also matters when considering afib ablation. Problems like leaky valves or narrowed passages can make the procedure harder. It’s important to know how bad the disease is to see if ablation is a good option.
Unusual Pulmonary Vein Anatomy
The shape of the pulmonary veins is key for afib ablation. Odd shapes or numbers can make the procedure tricky. Doctors use special imaging to look at these veins before starting.
| Anatomical Issue | Impact on Afib Ablation | Considerations |
| Complex Congenital Heart Defects | Complicates procedure due to abnormal heart structure | Requires detailed pre-procedure evaluation |
| Severe Valve Disease | May affect outcome or complicate procedure | Assess severity of valve disease |
| Unusual Pulmonary Vein Anatomy | Complicates ablation targeting | Use advanced imaging for assessment |
It’s vital to know about these heart issues to figure out if afib ablation is right.
Blood Clotting and Anticoagulation Challenges
Blood clotting and anticoagulation challenges are key for patients with afib ablation. Ablation for atrial fibrillation depends on safe anticoagulation therapy. This therapy is vital for preventing strokes and other blood clots.
Bleeding Disorders
Patients with bleeding disorders face unique challenges with afib ablation. Conditions like hemophilia or other blood clotting issues raise the risk of the procedure. Careful assessment of the patient’s bleeding risk is essential.
The Isolator Synergy Clamps are designed to treat atrial fibrillation. They might offer benefits in some cases. But, their use in patients with bleeding disorders needs careful thought.
Inability to Tolerate Anticoagulation
Some patients can’t handle anticoagulation therapy for various reasons. This inability makes managing afib harder, as anticoagulation is key to preventing blood clots.
For these patients, other strategies might be needed. This could include different anticoagulant drugs or treatments to lower stroke risk.
History of Major Bleeding Events
A history of major bleeding events is a big factor in afib ablation eligibility. Patients who have had big bleeds before might be at higher risk during the procedure.
| Risk Factor | Consideration for Afib Ablation | Management Strategy |
| Bleeding Disorders | Increased risk; careful assessment needed | Alternative treatments or adjusted anticoagulation |
| Inability to Tolerate Anticoagulation | Complicated management; alternative strategies required | Different anticoagulants or non-anticoagulant treatments |
| History of Major Bleeding Events | Increased procedural risk; thorough evaluation necessary | Risk-benefit analysis; possible adjustment of anticoagulation regimen |
In conclusion, blood clotting and anticoagulation challenges are critical in deciding if afib ablation is right for patients. A detailed evaluation of these factors is vital for the best patient outcomes.
Long-standing Persistent Afib Considerations
Understanding long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation (afib) is key to finding the right treatment. The success of treatments like cardiac ablation depends on how long afib lasts and how much the left atrium has changed.
Duration of Afib and Success Rates
The length of afib affects how well cardiac ablation works. Patients with afib that lasts a long time face a bigger challenge. This is because their heart may have changed a lot.
Key considerations for patients with long-standing persistent afib include:
- The extent of atrial remodeling
- The presence of underlying heart disease
- The patient’s overall health status
Left Atrial Remodeling
Left atrial remodeling is a big worry for those with long-standing persistent afib. As afib goes on, the left atrium can change a lot, like getting bigger and scarred. These changes can make ablation harder and less effective.
Doctors use advanced imaging like cardiac MRI or CT scans to check the heart. These tools help see the heart’s shape and find any problems with ablation.
Pregnancy and Reproductive Considerations
For women with atrial fibrillation, pregnancy brings unique challenges. It’s a delicate balance to manage the arrhythmia and protect both the mother and the fetus.
Risks During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can make atrial fibrillation worse due to changes in blood volume and hormones. These changes raise the risk of arrhythmia episodes. Afib during pregnancy also increases the risk of complications like preeclampsia and preterm labor.
Effective management strategies are key to reduce these risks. This might include medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Choosing the right medication is important because of the risks to the fetus.
Radiation Exposure Concerns
Cardiac ablation, a common treatment, uses fluoroscopy, exposing patients to radiation. This is a concern for women of childbearing age. Minimizing radiation exposure is important to protect future pregnancies.
Planning Ablation Around Family Planning
For women planning to get pregnant, the timing of cardiac ablation is critical. Planning ablation around family planning is important. It’s best to avoid ablation during pregnancy to avoid radiation risks and complications.
Pre-pregnancy counseling is vital for women with Afib. It should cover managing Afib during pregnancy, risks, and planning for after pregnancy.
Psychological and Compliance Factors
Looking at psychological factors and compliance is key when checking if afib patients are ready for ablation. The success of the ablation isn’t just about the technical side. It also depends on the patient’s well-being and following instructions after the procedure.
Mental Health Considerations
Mental health is very important for patients getting afib ablation. Issues like depression and anxiety can affect a patient’s life quality. Healthcare providers must check a patient’s mental health before ablation.
Research shows that untreated mental health issues can raise the risk of problems or lower success rates after ablation. So, improving mental health treatment is a big part of getting ready for ablation.
Medication Adherence Issues
Following medication is also very important for afib ablation success. Patients must take anticoagulation therapy and other meds as told to avoid risks like stroke or bleeding. Not taking medication as directed can greatly affect the procedure’s outcome.
Doctors should check if a patient can follow their medication plan before ablation. This might mean looking at the patient’s past with meds, understanding their current regimen, and any challenges they might face.
By focusing on both mental health and medication issues, doctors can better decide if a patient is right for afib ablation. This can also help make the procedure more likely to succeed.
Pre-Ablation Testing: Red Flags and Exclusions
To make sure Afib ablation works well, doctors do a lot of testing before the procedure. They look for any problems that might stop the treatment from working. This helps find out who might face more risks and who might not get much benefit from it.
Cardiac Imaging Findings
Cardiac imaging is key in checking if someone can have Afib ablation. Tools like transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) and cardiac MRI show how the heart works and looks. TEE is great for finding left atrial thrombi, which means you can’t have the treatment.
- Checking the left atrium’s size and how it works
- Looking at the pulmonary veins’ shape
- Finding any heart problems
| Imaging Modality | Key Findings | Clinical Implication |
| TEE | Left atrial thrombus | Contraindication for Afib ablation |
| Cardiac MRI | Left atrial size and function | Predictive of ablation success |
| CT Angiography | Pulmonary vein anatomy | Guides ablation strategy |
Laboratory Test Abnormalities
Labs are also very important before Afib ablation. They check for things like:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Renal dysfunction
- Coagulopathy
Fixing electrolyte imbalances is key before the treatment. It helps the heart work right.
ECG and Monitoring Findings
ECG and monitoring tell a lot about the heart’s rhythm and electrical activity. They can spot:
- Atrial fibrillation burden
- Other arrhythmias
- How well antiarrhythmic meds work
Long-term monitoring is great for seeing how well treatments work. It also finds Afib episodes that don’t show symptoms.
Doctors use all this testing info to decide if someone can have Afib ablation. They make a plan that’s just right for each patient.
Alternative Treatments When Ablation Is Contraindicated
Afib ablation may not be right for everyone. Other treatments are needed when ablation is not an option. Atrial fibrillation (afib) is complex and needs a treatment plan that fits each person.
Healthcare providers use different treatments to help manage symptoms. This improves the quality of life for those with afib.
Rate Control Strategies
Rate control strategies aim to keep the heart rate in check. This method is used for those with mild symptoms. Medications like beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and digoxin are used.
| Medication Class | Examples | Primary Use |
| Beta-blockers | Metoprolol, Propranolol | Control heart rate |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | Diltiazem, Verapamil | Control heart rate |
| Digoxin | Lanoxin | Control heart rate in heart failure |
Rhythm Control Medications
Rhythm control medications aim to keep the heart in a normal rhythm. Antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) help prevent afib from coming back. The right AAD depends on the patient’s heart condition and symptoms.
Non-Ablation Procedures
Other procedures can also manage afib. Cardioversion converts the heart rhythm back to normal. The maze procedure is a surgery that creates scar tissue to block bad signals.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are key in managing afib. Keeping a healthy weight, exercising, and limiting alcohol and caffeine are important. Managing stress also helps reduce symptoms and improves well-being.
When to Seek a Second Opinion
Getting a second opinion can give you clarity and confidence, which is key when thinking about afib ablation. This is very important for complex heart conditions that need precise treatment plans.
Conflicting Medical Advice
Getting conflicting medical advice can be confusing and stressful. When different doctors give different opinions on afib ablation, it’s important to understand why.
It’s a good idea to get a second opinion from a specialist with lots of experience in afib ablation. This can help make sure you’re getting the best treatment and exploring all your options.
Specialized Afib Centers
Specialized afib centers offer top-notch care and the latest treatments for atrial fibrillation. These centers have the latest technology and teams with lots of experience in managing complex afib cases.
Going to a specialized afib center can give you access to new therapies and advanced ablation techniques.
Clinical Trial Opportunities
For some, clinical trial opportunities can offer new treatments not yet widely available. Joining a clinical trial might be a good choice for those who haven’t seen results from usual treatments or are looking for other options.
Talking to your doctor about the benefits and risks of clinical trials is important. This will help you decide if it’s right for you.
Future Developments That May Expand Eligibility
The future of afib ablation looks bright, with new technologies coming. Medical tech is getting better, which means big changes for treating atrial fibrillation.
Emerging Technologies
One exciting area is emerging technologies that aim to make afib ablation better. These could help more people get the treatment they need.
New mapping systems, different ablation energies, and better catheters are some of these innovations. They could make afib ablation available to more patients.
Low-Risk Ablation Approaches
There’s also a focus on low-risk ablation approaches. These aim to lower the chance of problems and make recovery faster. New techniques, energy sources, and imaging tools are being explored.
These low-risk methods could help more people get treated. Even those who were thought to be too high-risk before.
Personalized Medicine Advances
Personalized medicine advances are key in afib ablation’s future. Tailoring treatments to each patient can lead to better results and fewer side effects.
Genetic tests, biomarkers, and other tools help doctors plan treatments better. This could mean more people can get afib ablation, even if they weren’t considered good candidates before.
As these advancements keep coming, we’ll see more people able to get afib ablation. This brings hope to those with atrial fibrillation.
Conclusion
Choosing the right patients is key for afib ablation success. This procedure treats atrial fibrillation. Several factors, like health conditions and blood clotting issues, affect who can get it.
Knowing how to pick the right patients helps doctors get better results. This improves patients’ lives a lot.
The future of afib ablation is bright. New technologies and personalized medicine will help more people. It’s important for doctors to keep up with these changes.
FAQ
What is cardiac ablation, and how is it used to treat atrial fibrillation (afib)?
Cardiac ablation is a procedure that uses energy to destroy abnormal heart pathways. It aims to fix irregular heartbeats by removing the problem areas.
Who is not eligible for ablation?
Some people can’t have ablation due to health issues. This includes those with heart failure, severe lung problems, or infections. Age and other health problems also play a role.
What are the different types of ablation techniques used for afib?
There are several methods, like radiofrequency, cryoablation, and laser ablation. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the doctor’s preference.
What is the success rate of afib ablation?
Success rates vary. They depend on how long afib has lasted, the heart’s size, and other health issues. Rates can be between 50% to 80% or more.
Can ablation cure afib?
Ablation can greatly improve life for many with afib. But, whether it “cures” it depends on the cause and other health issues.
What are the risks associated with afib ablation?
Risks include bleeding, infection, stroke, and heart problems. Doctors assess risks to identify those at higher danger.
How is patient selection done for afib ablation?
Doctors look at the patient’s health, afib symptoms, and other health issues. This helps decide if ablation is safe and likely to work.
What pre-ablation testing is done to identify red flags and exclusions?
Tests include heart imaging, blood work, and ECGs. These check heart function and find issues that might make ablation risky.
Are there alternative treatments for afib when ablation is contraindicated?
Yes, there are other ways to manage symptoms. This includes medications, cardioversion, and lifestyle changes to improve life quality.
When should I seek a second opinion regarding afib ablation?
Get a second opinion if you’re unsure about treatment or have different advice. It’s also good for exploring new treatments or clinical trials.
Can emerging technologies expand eligibility for afib ablation?
Yes, new technologies and personalized medicine might make more people eligible. This could lead to better results for more patients.
How do comorbidities affect eligibility for afib ablation?
Serious health issues like kidney or liver problems can affect eligibility. They might increase risks or affect how well the procedure works.
What are the considerations for patients with long-standing persistent afib?
Long-standing afib requires careful consideration. Factors like how long afib has lasted and heart changes are important. They help decide if ablation will work.
How do pregnancy and reproductive considerations affect afib ablation?
Pregnancy and family planning are key factors. Risks during pregnancy and concerns about radiation are important. Planning is needed for women of childbearing age.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5724842/











