deep brain stimulation
Parkinson’s disease affects over 1 million people in the United States. Symptoms significantly impact quality of life. For many, Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) has emerged as a revolutionary treatment, offering new hope for managing this condition.
DBS involves implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain to deliver electrical impulses. These impulses help regulate abnormal brain activity. This neurosurgical procedure is used to treat movement disorders associated with Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia.
By understanding how DBS works, we can better appreciate its benefits and potential applications. We will explore the procedure and its applications, providing insights into this advanced treatment.
Key Takeaways
- DBS is a neurosurgical procedure for treating movement disorders.
- It involves implanting electrodes to deliver electrical impulses.
- DBS is used to treat Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia.
- The procedure helps regulate abnormal brain activity.
- DBS offers new hope for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
The Fundamentals of Deep Brain Stimulation
A detailed, high-resolution medical illustration showcasing the fundamentals of deep brain stimulation. In the foreground, a cross-section of the human brain reveals the intricately woven neural pathways, with a deep implanted electrode emitting soft pulses of electrical energy. The middle ground features a close-up view of the DBS device, its metallic casing and connectors meticulously rendered. In the background, a minimalist diagram illustrates the surgical placement of the DBS system, from the implanted electrodes to the subcutaneous neurostimulator. The overall scene is bathed in a cool, clinical lighting that enhances the technical precision and medical nature of the procedure.
DBS is about putting electrodes in certain brain areas to change bad neural activity. It’s a detailed process that needs to know the brain’s neural pathways well. Also, placing the electrodes right is key.
Definition and Basic Concept
DBS is a surgery that puts a device called a “brain pacemaker” in the brain. This device sends electrical signals to certain brain spots. It helps treat movement and mental health issues.
The idea behind DBS is to change brain activity. Doctors can adjust the electrical signals to help patients feel better. This makes DBS a tailored therapeutic approach.
Historical Development of DBS
The start of DBS goes back to the early 1900s. Back then, doctors were studying how electricity affects the brain. With new tech and better brain surgery skills, DBS has grown into a powerful treatment.
In the 1980s, DBS really took off. There were big steps forward in electrode placement and better neurostimulators. Now, DBS is a key treatment for many brain diseases, like Parkinson’s and dystonia.
The Science Behind Deep Brain Stimulation
A detailed cross-section of intricate neural circuits, illuminated by a soft, warm glow. The foreground showcases the complex web of interconnected neurons, their delicate axons and dendrites winding through the brain’s intricate landscape. In the middle ground, the pulsing synaptic connections between cells create a mesmerizing dance of electrical activity, while the background fades into a hazy, ethereal realm, hinting at the vast, mysterious nature of the human mind. Captured with a high-resolution lens, the image conveys the elegance and precision of the brain’s inner workings, a testament to the remarkable complexity of deep brain stimulation.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) works by sending electrical impulses to the brain. This helps patients with neurological disorders find relief. It’s a therapy that changes brain activity in a targeted way.
Neural Circuits and Brain Signaling
The brain has a complex network of neural circuits. These circuits control movement, thinking, and more. In diseases like Parkinson’s, these circuits can get mixed up, causing odd brain signals.
DBS aims at certain brain spots like the subthalamic nucleus. It sends electrical impulses to these areas. This helps bring back normal brain signals.
How Electrical Stimulation Affects Brain Activity
DBS changes brain activity with electrical stimulation. This can lessen the odd brain signals seen in movement disorders.
Studies show DBS can tweak brain function in many ways. It can make neural activity sync better and affect neurotransmitter release. Doctors can fine-tune the treatment for each patient.
Grasping how DBS impacts brain activity is key. It helps make treatments better and opens up new uses for DBS in other conditions.
Components of a DBS System
A high-quality, detailed medical illustration of the key components of a deep brain stimulation (DBS) system. Showcase a patient’s head in the foreground, with a cutaway view revealing the implanted pulse generator, the electrodes precisely placed in the brain, and the connecting leads. Depict the system in a clean, technical style using soft, neutral lighting to emphasize the medical and scientific nature of the subject. Ensure accurate anatomical details and precise engineering of the device components. The overall mood should be informative and educational, conveying the sophisticated technology of modern DBS treatment.
It’s important to know what makes up a DBS system. This knowledge helps us see how it can help with different brain conditions. A DBS system has several key parts that work together. They send electrical signals to specific brain areas.
Electrodes and Lead Wires
The electrodes, or leads, are placed in the brain. They are connected to lead wires. These wires are thin and carry electrical signals from the neurostimulator to the electrodes.
Neurostimulator (IPG) and Programming Device
The neurostimulator, or Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG), makes the electrical signals. It’s placed under the skin in the chest. The programming device lets doctors adjust the signals. They make sure the treatment fits each patient’s needs.
The parts of the DBS system work together to control the brain’s electrical stimulation. Here’s a quick look at the main parts and what they do:
Component | Function |
Electrodes (Leads) | Implanted in the brain to deliver electrical stimulation |
Lead Wires | Carry electrical impulses from the neurostimulator to the electrodes |
Neurostimulator (IPG) | Generates electrical impulses; implanted under the skin in the chest area |
Programming Device | Used to adjust stimulation parameters and tailor therapy to individual patient needs |
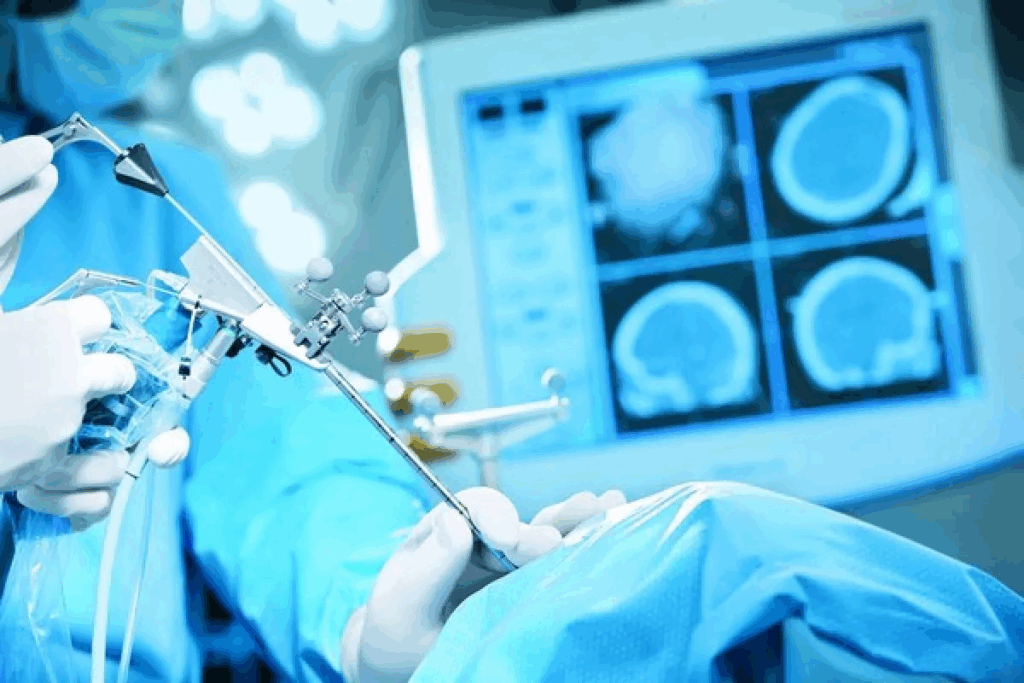
The Deep Brain Stimulation Surgical Procedure
A high-resolution, detailed medical illustration depicting the surgical procedure of deep brain stimulation electrode implantation. The foreground shows a cross-section of the human head, with the skull opened to reveal the brain structure. The electrode is visible, precisely placed within the target region of the brain. The middle ground includes surgical tools, such as scalpels and forceps, used by the neurosurgeon during the operation. The background showcases a modern operating theater, with bright, clean lighting and advanced medical equipment. The overall scene conveys a sense of clinical precision, expertise, and the delicate nature of the neurosurgical procedure.
DBS surgery is a detailed process that needs careful planning and execution. It includes several key steps. These are pre-surgical evaluation and planning, electrode implantation, and the placement of the neurostimulator.
Pre-surgical Evaluation and Planning
Before DBS surgery, patients go through a detailed pre-surgical evaluation. This includes a full medical check-up, imaging studies like MRI, and neurological tests. These steps help decide if DBS is right for the patient.
Key components of pre-surgical evaluation:
- Medical history review
- Neurological examination
- Imaging studies (MRI, CT scans)
- Psychological assessment
Planning is key for DBS surgery success. Our team uses advanced imaging to find the best spot for electrode placement. This ensures the stimulation is precise and effective.
Electrode Implantation Process
The electrode implantation is a crucial step in DBS surgery. It involves placing electrodes in specific brain areas. This is done under local anesthesia, allowing for feedback from the patient to ensure accurate placement.
A leading neurosurgeon notes, “The accuracy of electrode placement is crucial for DBS therapy success.”
“The precision of electrode implantation directly influences the outcome of DBS treatment, making it a critical factor in the surgical process.”
Placement of the Neurostimulator
After placing the electrodes, the neurostimulator is put under the skin, usually in the chest. The neurostimulator sends electrical impulses to the brain. This helps control abnormal brain activity.
Component | Function |
Electrodes | Deliver electrical impulses to the brain |
Neurostimulator | Generates and delivers electrical impulses |
Lead Wires | Connect electrodes to the neurostimulator |
The neurostimulator’s programming is customized for each patient. This requires careful adjustments to achieve the best results.
Brain Mapping and Target Selection
High-detailed, photorealistic image of brain mapping techniques, showing a human brain with a grid-like pattern overlaid on the surface, illustrating different regions and connections. The brain is shown in a stark, clinical setting with a minimalist background, highlighting the technical and scientific nature of the process. Bright, diffused lighting casts a serene, contemplative mood, emphasizing the precision and complexity of the brain mapping procedure. The image conveys a sense of depth and scale, allowing the viewer to clearly understand the various components and techniques involved in this specialized field of neuroscience.
Effective Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) needs precise brain mapping to find the best spots for stimulation. This is key for DBS therapy to work well. It helps doctors target the brain areas linked to the patient’s condition.
Finding the right target selection is crucial for DBS to work best and avoid side effects. The brain’s complex structure and the differences in people make this hard.
Identifying the Optimal Stimulation Sites
Finding the best stimulation sites means understanding the brain’s neural circuits and the areas causing symptoms. For Parkinson’s Disease, the subthalamic nucleus (STN) and globus pallidus internus (GPi) are often chosen.
We use advanced imaging and neurophysiological methods to map the brain. This way, we tailor DBS therapy to each patient’s needs.
Imaging Techniques Used in DBS Planning
Several imaging techniques are vital for DBS planning, like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans. They give detailed brain images, helping pinpoint target areas.
By mixing these imaging methods with neurophysiological recordings, we pinpoint the best stimulation sites. This guides the electrode placement during DBS surgery.
The use of advanced imaging in DBS planning is a big step forward. It leads to better treatment outcomes and a better life for patients.
Programming and Adjusting DBS Parameters
A close-up view of a medical professional’s hands carefully manipulating a handheld programming device connected to a deep brain stimulation (DBS) implant. The device’s display shows a detailed graphical interface with adjustable parameters and settings. The background is a clean, sterile medical environment, with clean white walls and bright, diffused lighting creating a sense of precision and clinical professionalism. The overall atmosphere conveys the meticulous and technical nature of DBS programming, emphasizing the importance of carefully customizing the treatment to the patient’s unique needs.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) therapy needs precise programming for the best results. We adjust the DBS device’s settings to improve therapy and reduce side effects.
Initial Programming Session
The first programming session is key in DBS therapy. We use the programming device to tweak settings like amplitude, pulse width, and frequency. Our aim is to find the right balance for symptom relief without side effects.
We start by checking the patient’s condition and medical history. Then, we pick the best settings based on this information. The patient helps by sharing how different settings affect them.
Fine-tuning Stimulation Settings Over Time
After the first session, we often need to fine-tune the settings. As the patient’s condition changes, we adjust to keep symptoms under control. We work with the patient to monitor how they’re doing and make changes as needed.
These adjustments might be small, like tweaking the amplitude or frequency. We might also change the electrode setup to better deliver the therapy. Regular check-ups help keep the therapy effective and side effects low.
By carefully adjusting the DBS settings, we aim to improve our patients’ lives. Our goal is to offer personalized care that boosts the quality of life for those with neurological disorders.
Primary Applications of Deep Brain Stimulation
A close-up view of a human head with the brain exposed, revealing the surgical implantation of deep brain stimulation electrodes. The electrodes are connected to a medical device, casting subtle shadows across the surrounding tissue. The lighting is soft and directional, highlighting the intricate details of the brain’s surface and the precision of the surgical procedure. The scene conveys a sense of medical intervention, with a clinical yet thoughtful atmosphere. The angle and composition draw the viewer’s attention to the key elements of deep brain stimulation for essential tremor.
DBS is becoming more popular for treating various movement disorders. It’s especially helpful for those who don’t respond well to other treatments.
DBS is great because it can be customized for each patient. This personalized treatment can greatly improve their life quality. It’s mainly used for Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia.
Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
DBS is a top choice for advanced Parkinson’s disease. It helps those with big motor issues and side effects from medicines. It targets specific brain areas to lessen symptoms like tremors and stiffness.
The benefits of DBS for Parkinson’s include:
- Improved motor function
- Reduced medication side effects
- Better quality of life
A leading neurologist says, “DBS has changed how we treat Parkinson’s. It gives patients a new chance at life.”
“DBS is a game-changer for many patients with advanced Parkinson’s, providing them with significant symptom relief and improved functional ability.”
Essential Tremor Management
DBS is also good for essential tremor. This condition causes ongoing and severe tremors. By targeting the thalamus, DBS can greatly reduce tremors and help with daily tasks.
Dystonia and Other Movement Disorders
DBS is also used for dystonia and other movement disorders. Dystonia causes involuntary muscle contractions, leading to odd movements or postures. DBS can help by changing how the brain works.
While DBS isn’t a cure, it offers a lot of relief. It improves life quality for many. Research and new DBS technologies are making it even more effective.
Patient Selection and Candidacy for DBS
Choosing the right patients for DBS therapy is key to success. We carefully check many factors to see if a patient will do well with DBS.
Ideal Candidates for DBS Therapy
Finding the best candidates for DBS is important. These are people with neurological problems that haven’t gotten better with usual treatments. They might have Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, or dystonia.
Other things that make someone a good candidate include:
- Their condition really affects their daily life and how well they can do things.
- They have symptoms like tremors or rigidity that DBS can help with.
- They understand the good and bad things that can happen with DBS.
- They have the right hopes about how DBS will change their life.
Contraindications and Exclusion Criteria
DBS is not right for everyone. There are some things that make it not a good choice. These include:
Contraindication | Description |
Cognitive Impairment | Big problems with thinking or dementia that make it hard to manage after surgery. |
Psychiatric Conditions | Severe mental health issues that make it hard to work with DBS therapy. |
Medical Comorbidities | Other serious health problems that make surgery riskier or affect overall health. |
We look at these things to find out who will really benefit from DBS. It’s also important to have a team of experts to make sure we’re making the right choice.
Emerging Applications of DBS
DBS is showing promise for treating conditions that traditional methods can’t handle. It’s being explored for psychiatric and neurological disorders, beyond just movement issues.
Psychiatric Conditions: OCD and Depression
DBS might help those with severe OCD and depression. For those with OCD, it could lessen symptoms and improve life quality. It’s also being looked at for treating depression that other treatments can’t fix.
DBS targets specific brain areas for these conditions. For OCD, it often goes to the anterior limb of the internal capsule. For depression, it might target the subcallosal cingulate gyrus or the ventral capsule/ventral striatum.
Epilepsy and Other Neurological Disorders
DBS is also being tested for epilepsy and other neurological issues. For epilepsy, it aims at areas like the anterior thalamus or hippocampus that cause seizures.
The table below shows some new uses of DBS and their targets:
Condition | DBS Target | Potential Benefit |
OCD | Anterior limb of the internal capsule | Reduction in OCD symptoms |
Depression | Subcallosal cingulate gyrus or ventral capsule/ventral striatum | Improvement in depressive symptoms |
Epilepsy | Anterior thalamus or hippocampus | Reduction in seizure frequency |
As research grows, DBS might help more people with tough conditions. It could offer new hope for those facing complex health challenges.
DBS Compared to Alternative Treatments
DBS is often compared to medication therapy and other surgical methods for treating neurological disorders. We will look at the good and bad sides of DBS compared to these options.
DBS vs. Medication Therapy
Medication is usually the first choice for many neurological issues. But, long-term use can cause problems like tolerance and side effects. DBS stands out because it offers adjustable and reversible therapy. This can help reduce the need for medication or make it work better when used together.
Treatment Aspect | DBS | Medication Therapy |
Adjustability | Highly adjustable | Limited by dosage and side effects |
Reversibility | Reversible | Not reversible |
Side Effects | Generally fewer systemic side effects | Can have significant systemic side effects |
DBS vs. Other Surgical Approaches
Other surgical treatments for neurological disorders include lesioning and other surgeries. DBS is unique because it’s reversible and adjustable. This makes it a better choice for many patients.
When comparing DBS to other surgeries, several things matter:
- Reversibility: DBS can be reversed, unlike some surgeries.
- Adjustability: DBS’s settings can be changed after surgery, tailoring treatment.
- Invasiveness: DBS requires implanting electrodes and a neurostimulator, a big surgery.
In summary, while DBS has its downsides and risks, its benefits often make it a better choice for some patients. Understanding how DBS compares to other treatments helps healthcare providers make better decisions for their patients.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
DBS offers big benefits for those with movement disorders. But, it’s important to know the risks and side effects. These can affect a patient’s quality of life.
Surgical Complications
Surgical risks with DBS are serious. These include:
- Infection at the site of the implanted device
- Bleeding or hemorrhage in the brain
- Stroke or other cerebrovascular events
- Seizures
- Hardware-related complications, such as lead migration or breakage
To lower these risks, careful planning is key. This means checking the patient’s health and the condition’s severity before surgery.
Surgical Complication | Risk Factors | Prevention/Management Strategies |
Infection | Poor wound care, compromised immune system | Proper wound care, antibiotic prophylaxis |
Bleeding/Hemorrhage | Anticoagulant use, hypertension | Careful management of anticoagulants, blood pressure control |
Stroke/Cerebrovascular Events | Vascular disease, hypertension | Preoperative vascular evaluation, blood pressure management |
Stimulation-Related Side Effects
Side effects from DBS’s electrical stimulation can happen. These include:
- Dyskinesia or involuntary movements
- Speech disturbances, such as dysarthria
- Mood changes, including depression or mania
- Cognitive changes, such as confusion or memory issues
Changing the stimulation settings can help. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are key to adjusting the DBS and reducing side effects.
Knowing the risks and side effects of DBS is vital for patients. This knowledge helps them make informed choices and work with their healthcare team to avoid complications.
Advances in DBS Technology
DBS technology has made big strides in recent years. These improvements make it safer and more effective. They help patients get better results and open up new ways to use DBS.
Directional and Adaptive Stimulation
One big step forward is directional and adaptive stimulation. Old DBS systems send out electrical signals in all directions. But, directional DBS leads can target specific brain spots more accurately. This could lead to fewer side effects and better results.
Adaptive stimulation is another big improvement. It lets the DBS system change how it sends signals based on the patient’s brain activity. For example, it can adjust the signal strength when symptoms get worse.
Rechargeable and MRI-Compatible Systems
Rechargeable DBS systems are another big win. They mean patients don’t have to get their batteries replaced as often. This lowers the risk of problems from more surgeries. Patients can charge their devices themselves, usually every day or week.
MRI compatibility is also key. New DBS systems can work with MRI scans under certain conditions. This is important for patients who might need MRI scans for other health reasons.
Feature | Traditional DBS | Advanced DBS |
Stimulation Pattern | Omnidirectional | Directional |
Adaptability | Fixed Parameters | Adaptive Stimulation |
Power Source | Non-Rechargeable | Rechargeable |
MRI Compatibility | Limited | Conditional Compatibility |
These new DBS technologies are changing how we treat neurological disorders. They make DBS more precise, adaptable, and safe. These changes are likely to lead to better results for patients and open up new uses for DBS.
Conclusion: The Future of Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is growing fast, with new research and tech. The future looks bright, with big steps in understanding brain signals and pathways.
DBS has changed how we treat diseases like Parkinson’s and dystonia. With better tech, patients will see even better results from DBS therapy.
New advancements like directional and adaptive stimulation are exciting. These changes make DBS more effective. As we learn more about the brain, DBS will keep getting better.
DBS could change how we treat many diseases. It’s set to lead in neuroscientific research and treatment. We’re excited to see what DBS can do next, offering top healthcare to patients worldwide.
FAQ
What is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) and how does it work?
DBS is a treatment that involves putting electrodes in the brain. These electrodes send electrical impulses to help control brain activity. It helps people with Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia.
What are the components of a DBS system?
A DBS system has several parts. These include electrodes, lead wires, a neurostimulator, and a programming device. Together, they send electrical stimulation to the brain.
How is DBS surgery performed?
DBS surgery starts with planning and evaluation. Then, electrodes are implanted in the brain. Finally, a neurostimulator is placed. This requires precise placement and programming for the best results.
What is the role of brain mapping in DBS?
Brain mapping is key in DBS. It helps find the best places to put the electrodes. Imaging like MRI and CT scans guide the placement to target the right brain areas.
How are DBS parameters programmed and adjusted?
DBS parameters are set during the first programming session. They are then adjusted over time. This ensures the treatment works well and with minimal side effects.
What are the primary applications of DBS?
DBS mainly treats Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. It helps manage motor symptoms and improves life quality for those with these conditions.
Who is a candidate for DBS therapy?
The best candidates for DBS are those with neurological conditions that haven’t improved with other treatments. They must have significant motor symptoms and no certain contraindications.
What are the potential risks and side effects of DBS?
DBS can have risks and side effects. These include surgical complications like infection and bleeding. Stimulation side effects like paresthesia and dyskinesia can be managed with careful programming and monitoring.
How does DBS compare to alternative treatments?
DBS is compared to other treatments like medication and surgery. DBS offers big benefits for certain conditions. However, the right treatment depends on the individual’s needs and situation.
What are the emerging applications of DBS?
DBS is being explored for treating psychiatric conditions like OCD and depression, and epilepsy. Research is ongoing to understand its benefits and limitations in these areas.
What advances have been made in DBS technology?
DBS technology has improved with directional and adaptive stimulation, and rechargeable and MRI-compatible systems. These advancements make DBS safer and more effective, opening up new possibilities.
How does electrode placement affect DBS outcomes?
Where the electrodes are placed is very important in DBS. Accurate placement in the right brain area is crucial for the best results. Incorrect placement can reduce effectiveness or increase side effects.
What is the role of neurostimulation in DBS?
Neurostimulation is the core of DBS. It sends electrical impulses to specific brain areas to control abnormal activity. Adjusting the stimulation parameters is key to achieving the best results.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4871171/




































