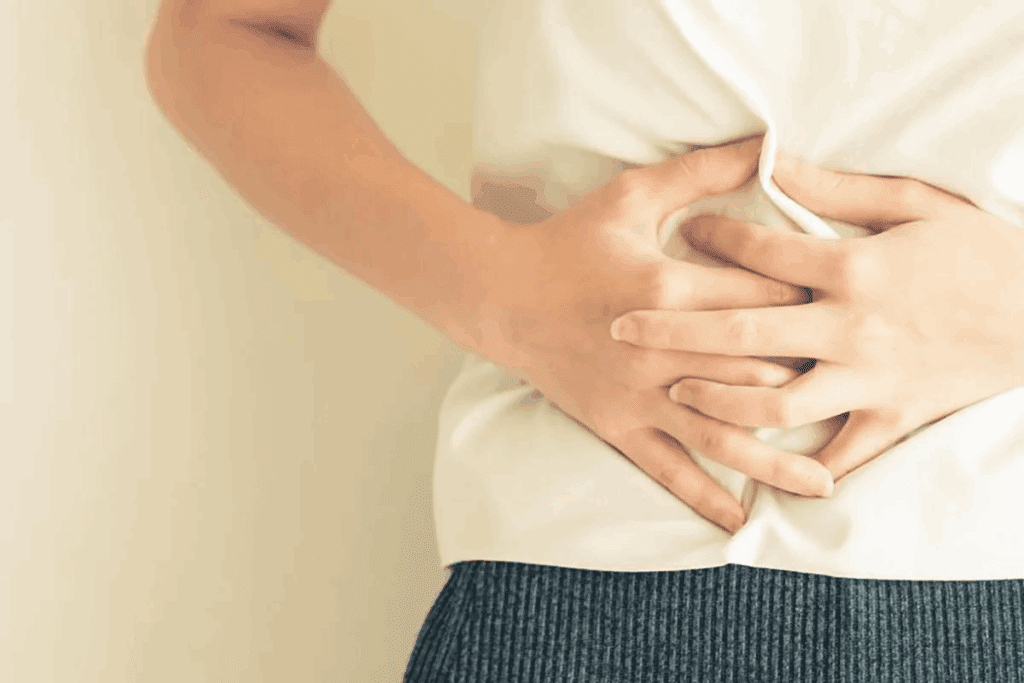
What’s the big deal about a hernia? While many aren’t life-threatening, some can turn serious fast. A simple hernia can quickly become a big problem, needing quick medical help.The ultimate, critical list of emergency hernia signs. These 5 shocking symptoms mean you must go to the hospital immediately.
Knowing the signs is key. A strangulated hernia can hurt a lot. If not treated, it can cause serious issues. An incarcerated hernia might need surgery right away to avoid more harm.
Dealing with hernia emergencies can be tough. At our medical center, we focus on top-notch care and personal attention. We aim to help you understand when a hernia is an emergency and what to do next.
Key Takeaways
- Not all hernias are emergencies, but some can become severe.
- Recognizing warning signs is critical for timely medical help.
- A strangulated hernia can cause severe pain and needs immediate care.
- Urgent surgery might be needed for an incarcerated hernia.
- Our medical center offers personalized care for hernia emergencies.
Understanding Hernias: An Overview

A hernia is when parts of the belly bulge through a weak spot in the lining. We’ll explain what hernias are, their types, and why they happen. Knowing this helps us spot when a hernia is an emergency.
What is a Hernia?
A hernia happens when something bulges through a weak spot in the muscle. This can cause pain and serious problems, like a hernia causing bowel blockage, if not treated. The bulge can hurt, mainly when you cough, lift heavy, or bend over.
Types of Hernias
There are many types of hernias, each with its own issues and risks.
- Inguinal Hernia: This is when tissue bulges through a weak spot in the muscles in the groin.
- Umbilical Hernia: It’s when part of the intestine bulges through a weak spot near the belly button.
- Femoral Hernia: This happens when tissue bulges through the femoral canal in the groin.
- Incisional Hernia: It occurs through a scar or incision from previous surgery.
Each hernia type has its own risks, like strangulation, where blood supply is cut off.
Common Causes
Hernias can be caused by several things, including:
- Weakness in the abdominal wall: This can be from birth or develop over time due to aging or strain.
- Increased abdominal pressure: Things like heavy lifting, chronic coughing, or being overweight can cause hernias.
- Previous surgeries: Incisions from surgery can weaken the area and lead to hernias.
Knowing the causes and signs of a hernia, like sudden swelling or unbearable pain, is key. If you have a sudden swelling hernia emergency, you need to act fast to avoid serious problems.
Recognizing Emergency Hernia Signs
A hernia can quickly become a medical emergency if certain symptoms are not recognized and addressed promptly. We are here to guide you through the critical signs that indicate a hernia has turned into an emergency, requiring immediate medical attention.
Sudden Pain and Discomfort
Sudden pain or discomfort in the area of the hernia is a significant indicator of a possible emergency. This pain can be sharp and intense, often signaling that the hernia has become incarcerated or strangulated. Severe localized pain is a symptom that should never be ignored.
Medical professionals say, “The onset of severe pain, accompanied by nausea or vomiting, is a red flag that requires immediate action.”
“Pain is the body’s alarm signal; when it’s persistent and severe, it’s a sign that something is seriously wrong.”
Medical Expert
Changes in Appearance
Changes in the appearance of the hernia, such as redness, swelling, or discoloration, are also critical signs of an emergency. These changes can indicate that the hernia is compromised, potentially cutting off blood supply to the affected area.
Signs | Description |
Redness | Indicates inflammation or infection |
Swelling | Signifies increased fluid or trapped tissue |
Discoloration | May indicate compromised blood supply |
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are systemic symptoms that can accompany a hernia emergency, specially if the hernia is obstructing the intestine. Vomiting with hernia symptoms is a dangerous sign that requires immediate medical evaluation.
We emphasize that nausea and vomiting, when combined with other symptoms like severe pain or changes in the hernia’s appearance, are indicative of a serious condition. Nausea and vomiting as hernia complications should be taken very seriously.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs of a hernia emergency is critical for timely intervention. If you or someone you know is experiencing sudden pain, changes in the hernia’s appearance, or systemic symptoms like nausea and vomiting, seek medical help immediately.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Knowing when to get help for a hernia can save lives. We’ll show you the signs that mean you need to see a doctor fast.
Severe Localized Pain
Severe pain in the hernia area is a big warning sign. It could mean your hernia is trapped or cut off, which is a serious emergency. Don’t wait if you have sudden and severe pain.
Difficulty in Bowel Movements
Having trouble with bowel movements or constipation can be a sign of a blockage. This can cause serious problems if not treated quickly. Look for these signs and get medical help right away:
- Severe constipation
- Vomiting
- Abdominal distension
Signs of Infection
Signs of infection, like fever, redness, or swelling around the hernia, mean you need to see a doctor fast. Infection can be very dangerous and needs quick treatment. If you have a fever and hernia pain, get medical help right away.
If you think you have an emergency like an incarcerated or strangulated hernia, don’t call your doctor, go straight to the ER or call 911. We’re here to help you through this tough time.
Differentiating Between Types of Hernia Emergencies
Hernias can seem similar but have unique traits that can turn into emergencies. It’s key to know these differences for quick and right medical help.
Inguinal Hernia Signs
Inguinal hernias happen in the groin. Look out for sudden, sharp pain and swelling in the groin or scrotum. If the hernia gets stuck or cut off, it can cause serious problems like bowel blockage or tissue death. This often needs urgent surgery.
Femoral Hernia Indicators
Femoral hernias are in the thigh and are less common but can be serious. About 20 to 30% of these hernias can get stuck if not treated, making them a big emergency. Signs include severe pain in the groin or thigh, nausea, vomiting, and a tender lump in the upper thigh.
Umbilical Hernia Complications
Umbilical hernias are near the navel and are common in babies and obese adults. If the hernia gets stuck or cut off, it can cause a lot of pain, nausea, and vomiting. In adults, these hernias can lead to bowel blockage and need urgent surgery.
To understand the risks and complications of different hernias, let’s look at a comparison table:
Hernia Type | Risk of Strangulation | Common Complications |
Inguinal Hernia | Moderate | Bowel Obstruction, Tissue Death |
Femoral Hernia | High | Strangulation, Bowel Obstruction |
Umbilical Hernia | Moderate to High in Adults | Incarceration, Strangulation, Bowel Obstruction |
It’s vital to know the specific signs and risks of each hernia type. This ensures quick medical help and prevents serious issues.
Risk Factors for Hernias
Hernias can happen due to lifestyle, genetics, and age. Knowing these factors helps us prevent them and get medical help when needed.
Lifestyle Factors
Some lifestyle choices raise hernia risk. For example, severe constipation puts more pressure on the belly, increasing hernia risk. Heavy lifting, chronic coughing, and straining also play a part.
- Smoking, which can lead to chronic coughing
- Poor diet, potentially leading to constipation
- Engaging in heavy physical labor or activities
Changing these habits can lower risk. Eating a fiber-rich diet helps prevent constipation and reduces hernia risk.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetics also affect hernia risk. If your family has a history of hernias, you’re more likely to get one. This is because of muscle or tissue weaknesses passed down.
“Genetic predisposition is a significant risk factor for hernias, highlighting the importance of awareness and preventive measures for those with a family history.”
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender considerations for hernias are key. Hernias can happen at any age but some types are more common in certain groups. For example, men often get inguinal hernias, while women, mainly the elderly, get femoral hernias.
Demographic Factor | Hernia Type | Risk Level |
Men over 40 | Inguinal Hernia | High |
Women, specially elderly | Femoral Hernia | High |
Individuals with family history | Various | Moderate to High |
Knowing these risk factors helps us understand our own risk. We can then take steps to lower our chance of getting a hernia.
Diagnosis of Hernias
To find out if someone has a hernia, doctors use different methods. They do physical checks and use advanced imaging tests. This way, they make sure they get the diagnosis right and plan the best treatment.
Physical Examination Techniques
Checking for hernias starts with a physical exam. Doctors look for bulges or swelling in the area. They might ask the patient to cough or strain to see the hernia better.
They also check the size and where the hernia is. They look for tenderness or pain. This helps them figure out how serious the hernia is and what to do next.
Key aspects of physical examination include:
- Visual inspection for bulges or swelling
- Palpation to assess tenderness and size
- Cough test to observe changes in the hernia
Imaging Tests Used
Imaging tests are also key in diagnosing hernias. They help confirm if there’s a hernia and how bad it is. They also check for other possible causes of symptoms.
Some common tests are:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to see inside the body.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan: Gives detailed pictures of the body to spot hernias and complications.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Shows detailed images of soft tissues, helping with hernia diagnosis and tissue damage checks.
Doctors pick the right test based on the patient’s situation and the type of hernia they think it is. By combining what they find in the physical exam with imaging results, they can make a precise diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treatments for Hernias
It’s important to know the different ways to treat hernias. At our place, we focus on care that fits each person’s needs.
Non-Surgical Options
Some people might not need surgery right away. This is true for small hernias that don’t hurt much. Options include:
- Watchful Waiting: Keeping an eye on the hernia for any changes.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Changing daily habits to ease the strain.
- Supportive Devices: Using things like trusses or binders for support.
These choices are good for those who don’t need surgery yet or who don’t want it.
Surgical Interventions
For bigger or painful hernias, surgery is usually the best option. We offer several types of surgery, like:
- Open Hernia Repair: A traditional method with one big cut.
- Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: A less invasive method with small cuts and a camera.
- Robotic Hernia Repair: A high-tech laparoscopic method for better precision.
Our doctors help pick the best surgery for each patient.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovering from hernia surgery can take time. It depends on the surgery and your health. Patients usually need:
- Pain Management: Ways to handle pain after surgery.
- Activity Restrictions: Rules on what activities to avoid and when to start again.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups to see how you’re healing.
Following the doctor’s instructions is key for a good recovery. Surgery done on your own schedule is often safer and works better.
Complications of Untreated Hernias
If left untreated, hernias can cause severe and life-threatening problems. It’s vital to seek medical help quickly to avoid these issues.
Strangulation Risks
Strangulation is a serious problem with untreated hernias. It happens when the blood supply to the hernia is cut off, causing tissue death. This is a medical emergency that needs immediate surgery.
Symptoms of strangulation include:
- Severe pain at the hernia site
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- A tender or painful lump in the groin or abdomen
Bowel Obstruction Concerns
Hernias can also cause bowel obstruction if the intestine gets trapped. This leads to severe abdominal pain, constipation, and vomiting. Bowel obstruction is a serious issue that needs quick treatment.
Signs of bowel obstruction:
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping
- Abdominal distension
- Vomiting
- Constipation or inability to pass gas
Long-term Health Implications
Ignoring hernia treatment can harm your health in the long run. It can lead to chronic pain, discomfort, and serious complications.
Complication | Symptoms | Consequences if Untreated |
Strangulation | Severe pain, nausea, fever, tender lump | Tissue death, surgical emergency |
Bowel Obstruction | Abdominal pain, distension, vomiting, constipation | Severe abdominal pain, possible bowel death |
Chronic Pain | Ongoing discomfort or pain at the hernia site | Reduced quality of life, risk of more problems |
We urge you to get medical help if symptoms get worse or don’t go away. Quick action can prevent these problems and improve your health.
Preventive Measures for Hernias
To lower the chance of getting hernias, making lifestyle changes and doing specific exercises is key. By choosing wisely and adding certain habits to your day, you can greatly cut down your risk of hernias.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Changing your lifestyle can help a lot in preventing hernias. Here are some important changes:
- Keeping a healthy weight to ease pressure on your belly
- Avoiding heavy lifting and bending to prevent straining your belly muscles
- Eating a diet full of fiber to avoid constipation and reduce straining
- Not smoking, as it can cause chronic coughing and increase belly pressure
Also, managing stress with techniques like meditation or deep breathing can help relax your muscles, including your belly.
Exercises to Strengthen Abdominal Muscles
Doing exercises that make your belly muscles stronger can also help. Here are some good ones:
- Planks: They work your core, including your belly and back muscles
- Bridges: They target your belly muscles and improve your core stability
- Leg raises: They strengthen your lower belly muscles
- Pelvic tilts: They help strengthen your core and improve your posture
Start these exercises slowly and get better at them over time. It’s a good idea to talk to a doctor or fitness expert for advice.
Exercise | Benefits | Precautions |
Planks | Strengthens core muscles, improves posture | Avoid if you have lower back issues; ensure proper form |
Bridges | Targets abdominal muscles, improves core stability | Be cautious with neck and back alignment |
Leg Raises | Strengthens lower abdominal muscles | Avoid straining; start with lower repetitions |
Pelvic Tilts | Strengthens core, improves posture | Perform slowly and controlledly |
Talking to your doctor if you think you might have a hernia is the best step. By making lifestyle changes and doing exercises, you can prevent hernias and keep your belly healthy.
FAQs About Hernias and Emergencies
Hernias are a common health issue that raises many questions, including about emergencies. Understanding hernias can be tough. It’s key to have clear, simple information to make good choices.
Common Questions Answered
Many ask if all hernias need surgery. The answer is no. But, if a hernia hurts a lot or really affects your life, surgery might be needed.
People also wonder when a hernia is an emergency. Severe pain, trouble with bowel movements, and signs of infection mean you need to see a doctor right away.
- Severe localized pain: Sudden, severe pain in the hernia area might mean trouble.
- Difficulty in bowel movements: A hernia can block bowel movements, causing constipation or vomiting.
- Signs of infection: Redness, swelling, and warmth around the hernia could mean an infection.
Misconceptions Clarified
Some think all hernias are easy to see. But, not all are visible. It’s important to watch for other symptoms too.
Another myth is that hernias only happen in older people. While older people are at higher risk, anyone can get a hernia. This can happen due to genetics or lifestyle.
We aim to clear up these myths and answer your questions about hernias and emergencies. If you’re worried about a hernia, always talk to a doctor for advice tailored to you.
Resources for Further Information
If you’re looking for more info on hernias or need support, we’ve got you covered. Knowing where to find resources can help you make better choices about your health.
Support and Guidance
Many groups offer help and advice for those with hernias. They provide important materials and support groups. These can guide you through your situation.
Looking into these resources can give you more insight into managing and treating hernias. Our team is here to answer any questions and offer personal support to our patients.
Educational Resources
There are many educational materials on hernias. They cover the condition, its signs, and how to treat it. Using these resources can help you understand your condition better.
To book a consultation with one of our surgeons or to learn more about our services, please get in touch. We’re dedicated to providing top-notch care and supporting you every step of the way.
FAQ
What are the signs that a hernia has become an emergency?
Signs of a hernia emergency include severe pain and nausea. You might also vomit or have a fever. If your hernia looks red or swollen, get help right away.
Can a hernia cause bowel obstruction?
Yes, a hernia can trap the intestine, causing a bowel obstruction. This is a serious issue that needs quick medical care to avoid more harm.
How is a strangulated hernia treated?
A strangulated hernia is a serious emergency. It needs urgent surgery to fix the blood flow and prevent tissue death.
Are all hernias painful?
Not all hernias hurt, but sudden or severe pain is a warning sign. If you’re in pain, see a doctor for a check-up.
Can lifestyle changes prevent hernias?
While you can’t prevent all hernias, a healthy lifestyle helps. Avoid heavy lifting and manage coughing or constipation to lower your risk.
What is the difference between an incarcerated and a strangulated hernia?
An incarcerated hernia is trapped but not cut off from blood. A strangulated hernia is more serious, needing emergency surgery because it’s cut off from blood.
How are hernias diagnosed?
Doctors usually diagnose hernias by feeling them. Sometimes, they use tests like an ultrasound or CT scan to confirm the diagnosis.
Can I manage a hernia without surgery?
Some hernias might not need surgery right away. But, always follow your doctor’s advice. Small, painless hernias might be watched, but surgery is often needed for bigger or painful ones.
What are the risks of not treating a hernia?
Untreated hernias can lead to serious problems like bowel obstruction or strangulation. Getting medical help quickly is key to avoiding these issues.
How can I reduce the risk of hernia complications?
To avoid hernia complications, seek medical help if you have symptoms. Stay healthy and follow your doctor’s treatment and care advice.
What is the recovery process like after hernia surgery?
Recovery from hernia surgery varies. You might feel some discomfort, which can be managed with pain meds. It usually takes a few weeks to get back to normal.
References
BMJ (British Medical Journal). Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.bmj.com/content/336/7638/269




































