Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a big health problem worldwide. TBI happens when something outside the body changes how the brain works. This can be from a head injury, a blow, or a penetrating wound.
TBI can really change someone’s life. It messes with how the brain works and affects not just the person but their loved ones too. It’s very important to understand what TBI does to help those who are hurt.
Key Takeaways
- Traumatic brain injury is a major global health concern.
- TBI can result from external forces causing alterations in brain function.
- Understanding TBI is key for giving the right care.
- TBI can deeply affect someone’s life quality.
- Support is needed for patients, families, and caregivers.
The Nature of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is key to helping those affected and society. TBI is a complex condition caused by external forces that damage the brain.
Definition and Classification of TBI
TBI is divided into three main types: mild (concussion), moderate, and severe. Knowing the type helps decide the right care and what to expect.
Diagnosing TBI involves checking symptoms, medical history, and injury details. Symptoms can range from cognitive issues to physical and behavioral changes, depending on the injury’s severity.
The Global Impact of TBI
Every year, over 50 million people suffer from TBI, leading to 30 to 40 percent of injury-related deaths globally. Falls cause nearly half of TBI hospitalizations.
The impact of TBI is huge, affecting individuals, families, and healthcare systems worldwide. Knowing the causes and effects is vital for prevention and better care.
|
TBI Severity |
Common Symptoms |
Typical Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
|
Mild TBI |
Headache, dizziness, confusion |
Usually recovers within weeks |
|
Moderate TBI |
Cognitive impairments, emotional changes |
May have lasting cognitive and emotional effects |
|
Severe TBI |
Significant cognitive and physical impairments |
Often results in long-term disability |
TBI Statistics: A Growing Public Health Concern
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a big problem worldwide. It causes a lot of sickness and death. Knowing the numbers helps us understand how big this issue is. It also helps us find ways to prevent and treat it.
Global Prevalence and Incidence Rates
TBI is a major cause of death and disability globally. The World Health Organization (WHO) says TBI will soon be the third biggest cause of death and disability. It’s hard to know how many people get TBI every year because of different ways of reporting.
But it’s clear that TBI affects not just the person who gets it. It also hurts their family and community. The cost of TBI is huge, including medical bills, lost work time, and long-term care.
TBI in the United States: By the Numbers
In the U.S., TBI is a big health issue. In 2020, there were about 214,110 hospital visits for TBI. In 2021, there were 69,473 TBI-related deaths. That’s about 190 deaths every day.
People over 65 are most at risk for serious TBI. Knowing these numbers is key for doctors, lawmakers, and everyone to tackle TBI’s challenges.
|
Year |
TBI-related Hospitalizations |
TBI-related Deaths |
|---|---|---|
|
2020 |
214,110 |
– |
|
2021 |
– |
69,473 |
The numbers show we need to keep working on preventing, diagnosing, and treating TBI. By understanding the trends, we can try to lower the number of TBI cases and their effects.
Common Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury
It’s important to know what causes Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) to lower its numbers and help patients get better. TBI can happen in many ways, and its causes change with age.
Falls and Blunt Trauma
Falls are the top reason for TBI hospital visits. Blunt trauma to the head can come from falls, fights, or accidents with objects. Falls are a big problem for kids aged 0 to 4, so we need to act fast to prevent them.
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Car crashes are another big cause of TBI. Being in a car accident can lead to TBI, based on how bad the crash is and if safety gear was used. Knowing the dangers of car accidents helps us find ways to make them safer.
Sports-Related Injuries and Concussions
Sports injuries, like concussions, are a big worry for athletes. Concussions happen when the head or body hits something hard, causing the brain to shake inside the skull. Spotting concussion signs early and acting fast is key to avoiding lasting harm.
By learning about TBI causes, we can make places safer and lower TBI rates in all ages and activities.
Types of Traumatic Brain Injuries
It’s important to know about the different types of Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI). TBI can show up in many ways, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment needs.
Mild TBI vs. Moderate to Severe TBI
TBIs are divided into mild, moderate, and severe based on how bad they are. Mild TBI, or a concussion, might cause short-term symptoms like confusion and headaches. But moderate to severe TBI can lead to lasting problems with thinking, feeling, and moving.
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) helps figure out how severe a TBI is. A score of 14-15 means it’s mild. Scores of 9-13 are moderate, and 8 or less is severe.
Open vs. Closed Head Injuries
TBI can also be open or closed. An open head injury happens when something goes through the skull, like a bullet. Closed head injuries happen when the brain hits the skull, often from falls or car accidents.
Primary vs. Secondary Brain Injuries
There are also primary and secondary brain injuries. Primary brain injury is the damage right away from the accident, like a skull fracture. Secondary brain injury is the damage that happens later, like swelling in the brain.
Knowing about these types of TBI helps doctors make better plans for treatment. It also helps patients and their families understand what to expect during recovery.
What Does Brain Damage Do to Neural Function?
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) affects the brain in many ways. It changes how the brain works and its chemistry. TBI can lead to changes in thinking, feeling, and behavior.
The Mechanics of Brain Trauma
TBI can cause injuries in two ways. Focal injuries affect one area of the brain. Diffuse injuries damage more areas. Knowing how TBI works is key to understanding its effects.
The forces that hit the brain during TBI can move it inside the skull. This can stretch or tear brain fibers. The injury’s severity and where it happens affect the damage.
Cellular and Chemical Changes After Injury
After a TBI, the brain goes through big changes. These changes can lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, and disrupt normal brain function. Knowing these changes helps in finding treatments.
Some important changes include:
- Inflammation: The body’s natural injury response, which can sometimes make things worse.
- Oxidative Stress: An imbalance that causes cell damage.
- Disruptions in Neurotransmitter Balance: Changes in chemicals that affect how brain cells talk to each other.
|
Change |
Description |
Impact on Neural Function |
|---|---|---|
|
Inflammation |
Body’s response to injury |
Can make damage worse, affect recovery |
|
Oxidative Stress |
Imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants |
Causes cell damage, hampers brain function |
|
Neurotransmitter Imbalance |
Changes in neurotransmitter levels |
Affects communication between brain cells, impacts thinking and feelings |
Understanding TBI’s effects on the brain is complex. It involves knowing how trauma works and the brain’s changes. This knowledge is essential for creating better treatments for TBI.
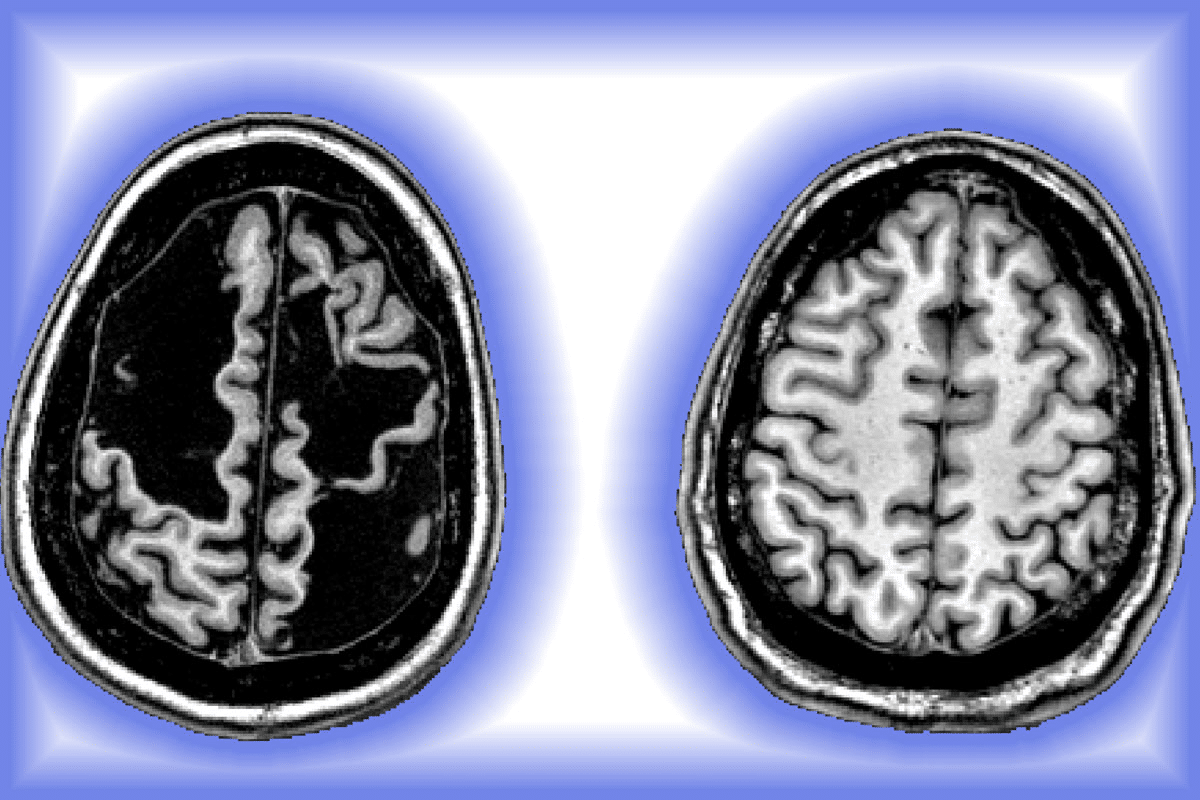
Normal Brain vs. TBI Brain: Understanding the Differences
It’s important to know how a normal brain differs from one with a Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). TBI can change the brain’s structure and how it works. This leads to changes in thinking, feeling, and behavior.
Structural Changes
TBI can cause several changes in the brain’s structure, including:
- Bleeding: Hemorrhages can occur due to the rupture of blood vessels.
- Swelling: Edema can lead to increased intracranial pressure.
- Tearing of nerve fibers: Diffuse axonal injury can disrupt normal brain function.
These changes can greatly affect how the brain works. Doctors say, “The extent of structural damage often correlates with the severity of TBI symptoms.”
Functional Alterations
Functional changes after TBI are just as important as structural ones. These changes can impact:
- Cognitive processes: Attention, memory, and executive functions can be impaired.
- Emotional regulation: Mood swings, depression, and anxiety are common.
- Behavioral changes: Impulsivity and aggression can occur due to frontal lobe damage.
Understanding these changes is key to creating effective rehabilitation plans. Research shows, “Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with TBI.”
By knowing the differences between a normal brain and a TBI brain, healthcare providers can tailor care. This improves the quality of care and support for each patient.
Immediate Effects of TBI on the Brain
It’s key to know how TBI affects the brain right away. This knowledge helps us give the right care to those hurt. A TBI, from a concussion to a serious injury, messes up how the brain works.
TBI stands for Traumatic Brain Injury. It covers many injuries that can harm the brain’s function and shape. The first effects of TBI can differ a lot, based on how bad and what kind of injury it is.
Cognitive Impairments
One big effect of TBI is problems with thinking. People might feel confused, lost, and have trouble focusing. These issues are tough in the first days after getting hurt.
Common thinking problems include:
- Memory loss
- Difficulty with problem-solving
- Slowed thinking
- Attention deficits
Physical Symptoms
Right after a TBI, people often feel physical symptoms. These can be mild or serious. They might have headaches, feel dizzy, feel sick, or get very tired. Some might even have seizures or trouble with balance and movement.
|
Symptom |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Headache |
Pain or discomfort in the head or neck region |
|
Dizziness |
Feeling of imbalance or lightheadedness |
|
Nausea |
Feeling of queasiness or sickness |
Behavioral and Emotional Changes
TBI can also cause big changes in how people act and feel. They might get moody, irritable, or frustrated. These changes can upset both the person and their loved ones.
It’s important to remember these changes come from the injury, not because of anything wrong with the person. Support and understanding from family and caregivers are key in helping people deal with these changes.
Knowing how TBI affects the brain right away helps us support those with brain damage better. This includes understanding thinking problems, physical symptoms, and mood changes.
Long-Term Consequences of Brain Damage
It’s important to know the long-term effects of TBI to help those affected. Traumatic Brain Injury can change a person’s life a lot. It can affect their thinking, physical abilities, and mood.
Chronic Cognitive Deficits
One big effect of TBI is chronic cognitive deficits. This means memory loss, trouble focusing, and hard time processing info. These problems can make daily tasks hard and affect independence.
Everyone recovers differently from TBI. The extent of these cognitive problems varies. Rehabilitation aims to help people adapt and improve their life quality.
Physical Disabilities and Limitations
TBI can cause physical disabilities and limitations. These include chronic pain, headaches, seizures, and vision problems. In severe cases, it can affect motor skills, making movement and coordination hard.
Physical therapy is key in rehab. It helps people regain physical function and adapt to disabilities. We create personalized plans to meet each patient’s needs and goals.
Psychological and Social Impacts
The psychological and social effects of TBI are significant. People may feel depression, anxiety, and mood swings. These can be tough for the person and their family. Social interactions might also change due to personality or behavior shifts.
Psychological support and counseling are vital in care plans. They help individuals with TBI and their families deal with emotional challenges. This way, we can support them through the tough times of recovery.
In summary, TBI’s long-term effects are complex. They need a complete care approach that covers thinking, physical, and emotional aspects. Understanding these challenges helps us support those with TBI better and improve their life quality.
Diagnosing and Treating TBI
Managing TBI well needs a detailed diagnosis and treatment plan. Doctors use clinical checks, imaging, and brain tests to see how bad the injury is.
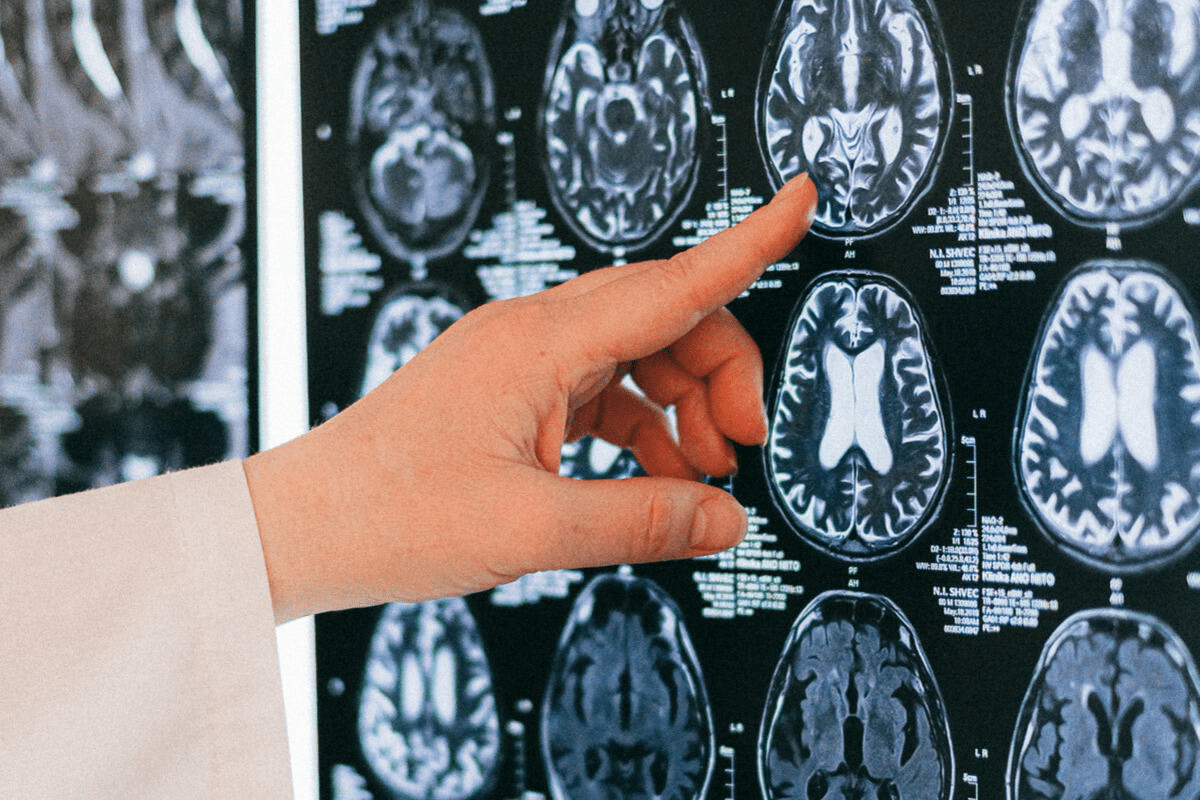
Assessment and Imaging Techniques
The first step in checking for TBI is a neurological exam. This checks how awake and aware the patient is, their thinking skills, and physical strength. Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are key for finding out where and how bad the brain damage is.
CT scans are quick and good for finding bleeding in the brain. MRI gives more detailed views of the brain. It’s great for spotting small injuries and seeing how much damage there is.
Acute Medical Interventions
Quick medical actions for TBI aim to keep the patient stable and prevent more harm. This might include intracranial pressure monitoring to watch for and manage high pressure in the skull.
Surgery might be needed to fix blood vessel damage, remove blood clots, or ease brain pressure.
Rehabilitation Strategies and Emerging Therapies
Rehab is key in treating TBI. It helps patients get back lost skills and adjust to any lasting effects. A team of physical, occupational, and speech therapists creates a custom rehab plan.
New treatments like cognitive rehabilitation and pharmacological interventions are being looked into. They aim to improve recovery and results for TBI patients.
Knowing how to diagnose and treat TBI helps doctors give full care to patients with brain injuries.
TBI Across the Lifespan: Special Considerations
It’s important to know how TBI affects people at different ages. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) impacts everyone, but kids and older adults face unique challenges.
Pediatric TBI: Impacts on Developing Brains
TBI in kids can stop them from doing well in school and other activities. Their brains are very sensitive to injury. TBI can harm their thinking, feelings, and physical skills.
Effects on Developing Brains:
- Cognitive impairments, including difficulties with attention and memory
- Emotional and behavioral changes, such as increased irritability
- Physical developmental delays or difficulties with coordination
Parents and caregivers need to know these effects. They should work with doctors to create a good care plan.
TBI in Older Adults: Unique Challenges
Older people are more likely to get hurt from a TBI, often from falls. Their brains change with age, making them more vulnerable to TBI’s effects.
Key Considerations for Older Adults:
|
Challenge |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Increased Risk of Complications |
Older adults are more likely to experience complications, such as subdural hematomas. |
|
Slower Recovery |
Recovery from TBI can be slower in older adults due to decreased physiological reserve. |
|
Cognitive Decline |
TBI can accelerate cognitive decline in older adults, potentially exacerbating dementia. |
Doctors need to think differently when treating TBI in older adults. They often need a more detailed and team-based approach.
Knowing the special needs for TBI at all ages helps us give better care. This way, we can support those affected by TBI more effectively.
Conclusion: Living with and Understanding TBI
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a big health problem worldwide. In 2021, there were about 20.84 million new cases and 37.93 million people living with TBI. It’s key to know what TBI is and how it affects the brain to give top-notch care to patients from around the world.
TBI can change a person’s life a lot. It can affect their thinking, movement, and feelings. We’ve looked at the different kinds of TBI and how they happen, like from falls or car accidents.
Figuring out and treating TBI needs a full plan. This includes tests, scans, quick medical help, and rehab. It’s vital to give the right care and support, even more so for patients from other countries who need special help.
Knowing about TBI helps us make life better for those who have it. Our goal is to offer the best healthcare and support to patients from everywhere. Understanding TBI is a big part of reaching this goal.
FAQ
What is Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)?
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a complex injury. It has a wide range of symptoms and outcomes. It happens when a blow or jolt to the head disrupts normal brain function.
What are the common causes of TBI?
TBI can be caused by falls, car accidents, sports injuries, and assaults. Knowing these causes helps in preventing them.
What are the different types of TBI?
TBI can be mild, moderate, or severe. It can also be open or closed head injuries. There are primary and secondary brain injuries too.
What are the immediate effects of TBI on the brain?
TBI can cause cognitive, physical, and emotional changes. These effects vary based on the injury’s severity and type.
What are the long-term consequences of brain damage from TBI?
Long-term effects of TBI include chronic cognitive deficits and physical disabilities. It also affects psychological and social well-being. Understanding these effects is key to proper care.
How is TBI diagnosed?
TBI diagnosis involves assessment and imaging techniques. This includes CT scans, MRI scans, and neurological exams. Accurate diagnosis is vital for effective treatment.
What are the treatment options for TBI?
TBI treatment includes acute medical care, rehabilitation, and new therapies. The goal is to lessen the injury’s impact and aid recovery.
What are the special considerations for TBI across the lifespan?
TBI affects developing brains in children and presents unique challenges in older adults. Comorbidities and age-related changes play a role.
What is the difference between a normal brain and a TBI brain?
A TBI brain shows structural and functional changes compared to a normal brain. Understanding these differences is essential for care and support.
What is the global impact of TBI?
TBI is a major global health issue. In 2021, it affected 20.84 million people worldwide. It’s important to understand its global impact for prevention and treatment.
What is post-TBI syndrome?
Post-TBI syndrome includes cognitive, emotional, and physical symptoms after a TBI. It’s important to understand it for proper care and support.
Can TBI be prevented?
While not all TBI can be prevented, knowing the causes helps reduce risk. Wearing protective gear and using safety equipment are important steps.
Reference
World Health Organization. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/traumatic-brain-injury