Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Diagnosing conditions in older adults requires a detective’s mindset. The classic “textbook” presentation of disease is the exception rather than the rule. A comprehensive approach is needed to uncover the root causes of health decline.
The diagnostic process begins with a shift in perspective. Instead of focusing solely on the chief complaint, the physician evaluates the patient’s entire life context.
This journey often takes more time than a standard medical visit. It involves gathering history from multiple sources and reviewing years of medical records to build a complete picture.

The core tool of the specialty is the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA). This is a systematic evaluation of health, function, and psychosocial status. It is the gold standard for diagnosing complex frailty.
The CGA assesses physical health, functional ability, psychological state, and socio-environmental factors. It is an interdisciplinary process often involving nurses, social workers, and therapists.
The output of a CGA is a coordinated plan for treatment and long-term follow-up. It has been shown to reduce hospitalization and improve survival.
Evaluating memory and thinking is a routine part of the exam. Short screening tools like the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) or the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) are commonly used.
These tests evaluate different domains of cognition, including memory, attention, language, and visuospatial skills. They help establish a baseline and track changes over time.
If screening indicates a problem, more in-depth neuropsychological testing may be ordered to differentiate between types of dementia or other causes of cognitive impairment.
Functional status is often a better predictor of health outcomes than disease diagnosis. Doctors evaluate Activities of Daily Living (ADLs), such as bathing, dressing, and eating.
They also assess Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs), which are more complex tasks like managing finances, cooking, and using the phone.
Decline in these areas often precedes a medical diagnosis. Observing a patient’s ability to rise from a chair or walk a short distance provides immediate data on strength and balance.
A “brown bag” review is a critical diagnostic step. Patients are asked to bring all their current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to the appointment.
The doctor reviews each item for indication, dosage, and potential interactions. This helps identify polypharmacy and medication-related symptoms.
Many “symptoms” in the elderly are actually side effects of drugs. Identifying and removing the offending agent can cure the problem without further testing.

The physical exam for geriatric doctors near me is tailored to the aging body. It focuses on areas often overlooked in general exams, such as feet, hearing, and vision.
Orthostatic blood pressure is checked to see if pressure drops when standing, a common cause of falls. Skin is examined for pressure ulcers or signs of abuse.
The exam also looks for signs of frailty, such as weak handgrip or slow gait speed. These physical biomarkers help stratify risk.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Health does not exist in a vacuum. The evaluation includes a detailed look at the patient’s social network. Who helps with shopping? Is there a caregiver at home?
Social isolation is a significant health risk. Identifying a lack of support allows the team to connect the patient with community resources.
This assessment also screens for signs of elder abuse or neglect. Ensuring a safe living environment is a diagnostic priority.
Malnutrition is prevalent and often underdiagnosed. The evaluation includes tracking weight history and asking about dietary habits.
Dentition and swallowing are checked, as problems here can lead to food avoidance. Lab tests may be used to check for specific vitamin deficiencies such as B12 or D.
The “Mini Nutritional Assessment” is a validated tool used to identify older adults at risk of malnutrition.
Because depression presents atypically in the elderly, specific screening tools are used. The Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) removes somatic questions (like fatigue) that might be related to physical illness.
It focuses on mood, interest, and life satisfaction. Screening is vital because depression worsens outcomes for all other medical conditions.
Identifying depression allows for treatment that can significantly improve cognition and functional status.
Falls are a significant threat. The “Timed Up and Go” (TUG) test is a simple diagnostic measure. The patient stands from a chair, walks 10 feet, turns, and sits back down.
The time it takes to complete this task predicts fall risk. Observing the gait quality helps diagnose underlying neurological or musculoskeletal issues.
Balance testing helps determine whether physical therapy or assistive devices, such as canes or walkers, are needed.
Lab interpretations must be adjusted for age. Creatinine levels, used to assess kidney function, can be misleading in patients with low muscle mass. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is a better metric.
Thyroid function tests are routine, as disorders here can mimic dementia or heart disease. Anemia workups are standard to explain fatigue.
Urinalysis is used carefully; asymptomatic bacteria in the urine is common in the elderly and does not always require treatment.
Diagnosis of heart issues often requires more than an EKG. Echocardiograms assess heart valve function and left ventricular muscle function.
Holter monitors track heart rhythm over time to catch intermittent irregularities like atrial fibrillation, a significant stroke risk.
Stress tests may be modified for those who cannot run on a treadmill, using medication to simulate stress on the heart.
Hearing and vision are formally tested—a whisper test or handheld audioscope screens for hearing loss. Snellen charts check visual acuity.
Detecting sensory loss is crucial for accurate cognitive testing. If a patient cannot hear the questions, they may falsely appear confused.
Correcting these deficits is part of the diagnostic treatment plan to improve engagement and safety.
The American Geriatrics Societyprovides the Beers Criteria, a list of medications that are potentially inappropriate for older adults. This guideline is a key diagnostic tool for identifying drug-related problems.
They also provide guidelines for screening and prevention tailored to life expectancy. This helps avoid over-testing in frail patients where the burden outweighs the benefit.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures that care is evidence-based and age-appropriate.
The diagnostic phase concludes with aligning medical findings with patient goals. A diagnosis of cancer, for example, is discussed in the context of the patient’s values.
Does the patient want aggressive treatment or symptom management? These discussions frame all future diagnostic and therapeutic decisions.
This shared decision-making process is the hallmark of the specialty.
It is a simple physical test where a doctor observes you standing up from a chair, walking a short distance, turning around, and sitting back down to evaluate your balance and fall risk.
Seeing the actual bottles allows the doctor to check for expired medications, duplicate prescriptions from different doctors, and ensure you are taking the correct dosages.
Doctors use standardized questionnaires, such as the Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE) or the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which ask you to recall words, draw a clock, and perform simple mental tasks.
No, sudden confusion is often a sign of delirium caused by an infection (like a UTI), dehydration, or medication side effects, and it is often reversible when the cause is treated.
It is an evaluation of your ability to perform daily tasks necessary for independence, such as bathing, dressing, cooking, and managing finances, to determine what support you might need.


Did you know that pluripotent stem cells can turn into almost any cell in the human body? This makes them very important for medical research

It’s important to know the symptoms of bone marrow cancer early. This helps get the right care quickly. Early detection can greatly improve treatment results.Multiple

Tooth bone loss is a big problem in dentistry today. It affects millions worldwide and hurts both your mouth and overall health. It happens when the
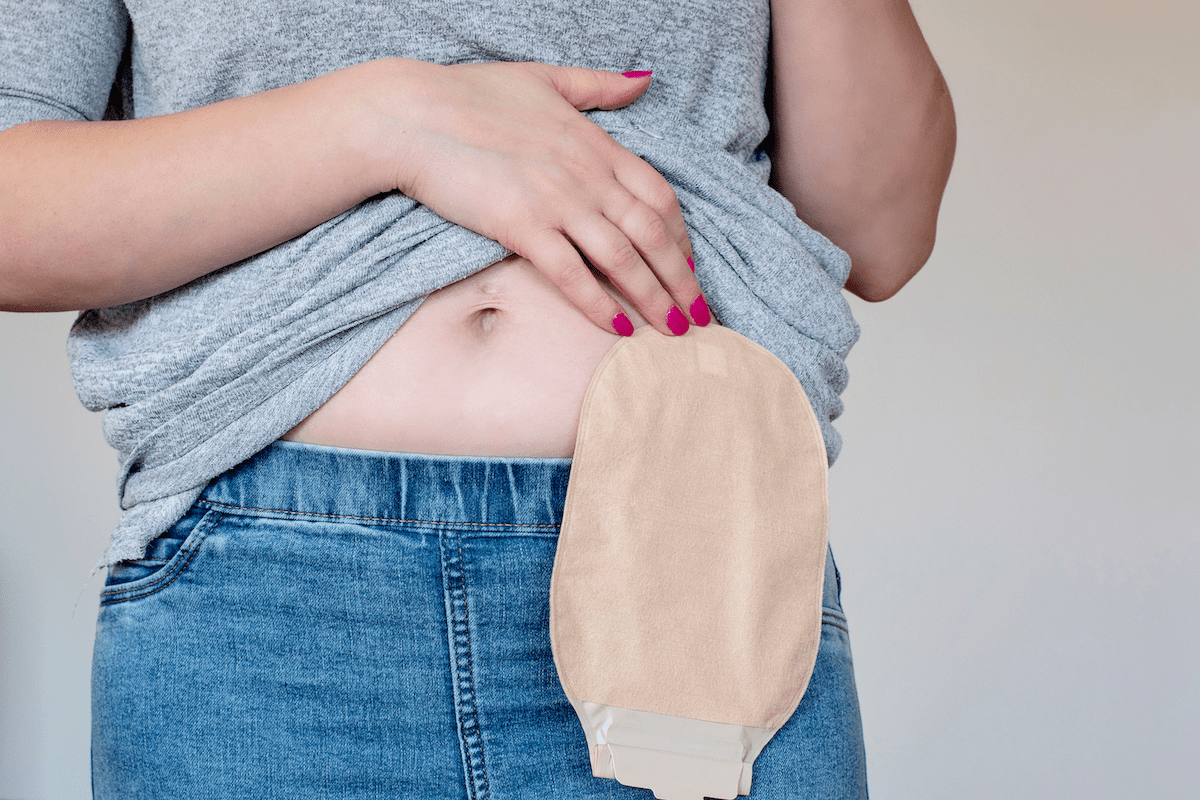

Creating a precise ostomy hole is key for those with ostomies. It affects their comfort and confidence. Liv Hospital focuses on accurate ostomy care, aiming
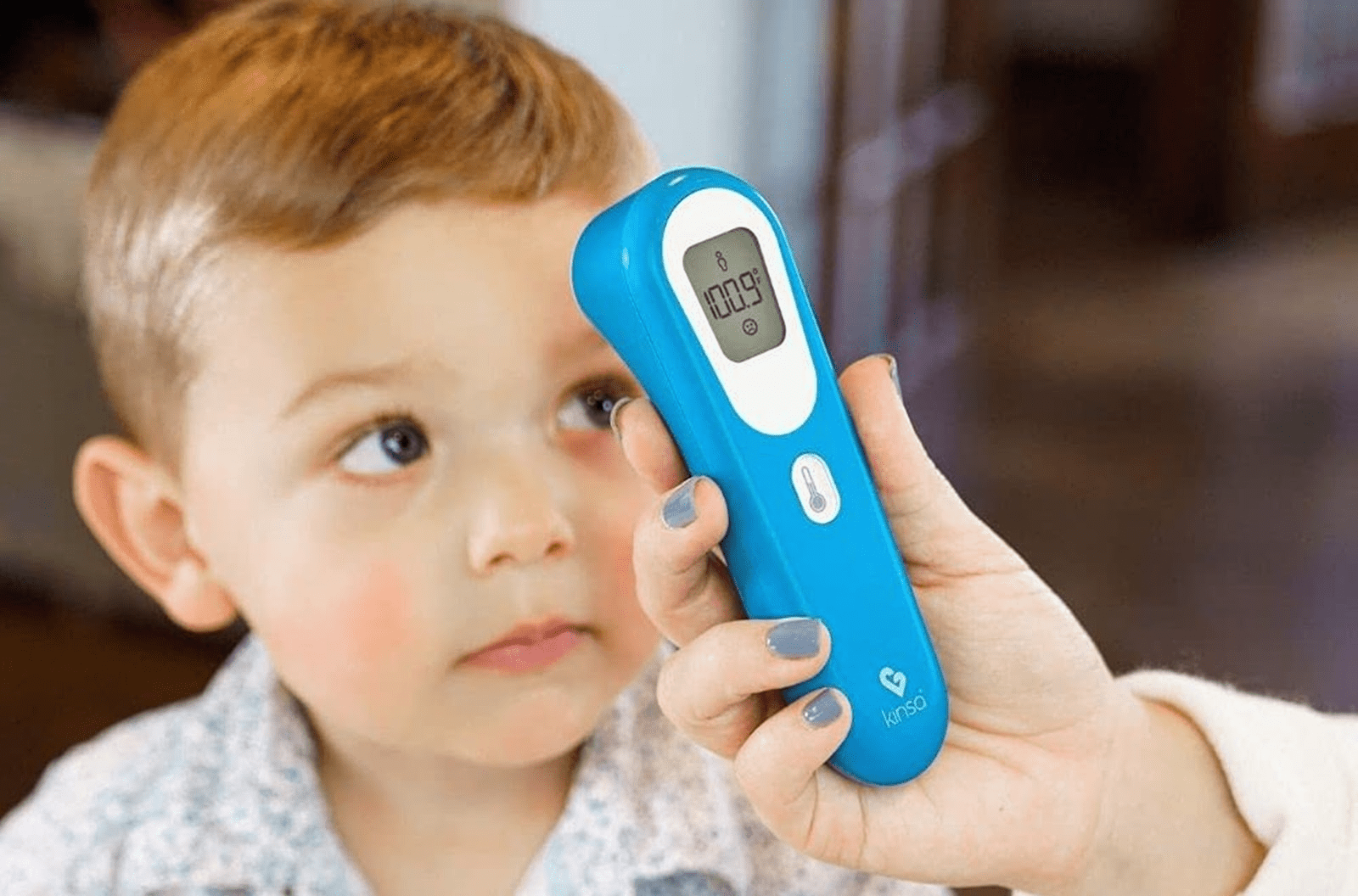
A forehead thermometer is popular because it’s easy to use and noninvasive. Forehead thermometers measure body temperature with infrared sensors, making them a fast and

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)