Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Aging well is not just the absence of disease. It involves maintaining physical function, cognitive ability, and active engagement with life. This concept shifts the focus from deficit to asset.
It emphasizes resilience and adaptation. Successful aging means being able to do the things you value for as long as possible.
Strategies focus on maximizing reserve capacity in all organ systems. It is a proactive approach to the later years.

Exercise is the closest thing we have to a fountain of youth. Guidelines recommend a mix of aerobic, strength, balance, and flexibility training.
Aerobic activity, like walking or swimming, supports heart and brain health. Resistance training combats sarcopenia (muscle loss).
Balance exercises, such as standing on one foot, are critical for fall prevention. Flexibility keeps joints moving freely. Even small amounts of movement have significant benefits.

A nutrient-dense diet supports immune function and energy levels. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, is strongly supported by evidence.
Protein intake should often be higher in older adults to maintain muscle mass. Hydration is critical, as the thirst mechanism dampens with age.
Vitamin D and Calcium are emphasized for bone health. Limiting processed foods and sugars reduces inflammation.
Vaccinations are a primary prevention tool. As the immune system weakens, vaccines provide a necessary boost. The high-dose flu vaccine is specifically designed for older adults.
Pneumococcal vaccines protect against pneumonia. The shingles vaccine (Shingrix) prevents a painful and debilitating condition.
Tetanus boosters and COVID-19 vaccinations are also standard. Staying up to date prevents severe illness and hospitalization.

“Use it or lose it” applies to the brain. Engaging in mentally stimulating activities builds cognitive reserve. This helps the brain cope with pathology, such as Alzheimer’s plaques, without showing symptoms.
Learning new skills, such as a language or an instrument, is more effective than passive activities. Social interaction is also a potent cognitive stimulator.
Managing vascular risk factors (blood pressure, cholesterol) is arguably the most effective way to prevent dementia.
Loneliness is toxic to health. Wellness involves nurturing relationships and community ties. Volunteering, joining clubs, or participating in religious groups provides purpose.
Intergenerational connection benefits both the young and the old. Technology can help bridge the gap for those with mobility issues.
Maintaining a sense of purpose is linked to longer life expectancy and better health outcomes.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Preventing falls preserves independence. This involves modifying the home environment: removing throw rugs, installing grab bars, and improving lighting.
Wearing proper footwear with non-slip soles is essential. Regular vision checks ensure hazards are seen.
Reviewing medications to remove those that cause dizziness is a key medical intervention. Tai Chi is an evidence-based practice for balance.
Medical science is constantly evolving. Following reputable geriatrics news sources keeps patients and families informed about the latest research on longevity.
New findings on diet, exercise, and supplements can inform wellness strategies. Awareness of fraud and scams targeting older people is also part of staying informed.
Education empowers older adults to advocate for their own health and make evidence-based decisions.
Oral health is often neglected, but it is vital for nutrition and heart health. Poor dentition can lead to malnutrition and social withdrawal.
Gum disease is linked to cardiovascular inflammation. Regular dental check-ups prevent pain and infection.
For those with dentures, a proper fit is essential for comfortable eating and speaking.
Aging skin is thinner, drier, and more fragile. Wellness involves protecting the skin barrier. Daily moisturizing prevents itching and tearing.
Sun protection prevents skin cancer, which is common in this demographic. Regular skin checks allow for early detection of malignancies.
Proper wound care is essential, as healing in older adults takes longer.
Protecting remaining hearing and vision is a wellness priority. Wearing hearing protection in noisy environments prevents further damage.
Regular eye exams catch glaucoma and macular degeneration early, when they are treatable. Using sunglasses protects against cataracts.
Maintaining sensory input keeps the brain active and engaged with the world.
Driving represents independence, but safety is paramount. Wellness involves regular self-assessment of driving skills.
Reaction times and vision change with age. Refresher courses for older drivers can update skills.
Planning for “driving retirement” enables a smooth transition to other transport options, preserving mobility without risk.
Financial stress impacts physical health. Wellness includes planning for the costs of long-term care.
Understanding insurance coverage and potential out-of-pocket costs prevents crises. Protecting assets from fraud is a significant concern.
Having a financial power of attorney ensures bills are paid if the patient becomes incapacitated.
For many, spirituality or a sense of meaning becomes more important with age. This can be a source of great comfort and resilience.
Engaging in spiritual practices, whatever they may be, supports mental health. It helps individuals cope with loss and mortality.
Providers respect and support these beliefs as part of the holistic care plan.
Good sleep is not a luxury; it is a pillar of health. Establishing a consistent sleep routine helps regulate the body clock.
Exposure to natural light during the day improves sleep at night. Avoiding caffeine and large meals before bed is helpful.
Creating a safe, comfortable sleep environment helps prevent insomnia and promotes restful sleep.
While a balanced diet is best, Vitamin D is often considered critical because it supports bone health, muscle function, and the immune system, and deficiency is very common in older adults.
The CDC recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity (like brisk walking) per week, plus muscle-strengthening activities on 2 days a week.
It is never too late; quitting smoking at any age improves circulation, lung function, and heart health almost immediately, and reduces the risk of stroke and cancer.
Remove throw rugs, improve lighting (especially night lights), install grab bars in the bathroom, and wear sturdy, non-slip shoes inside the house.
As we age, our sense of thirst diminishes, putting seniors at high risk of dehydration, which can lead to confusion, urinary tract infections, constipation, and kidney problems.

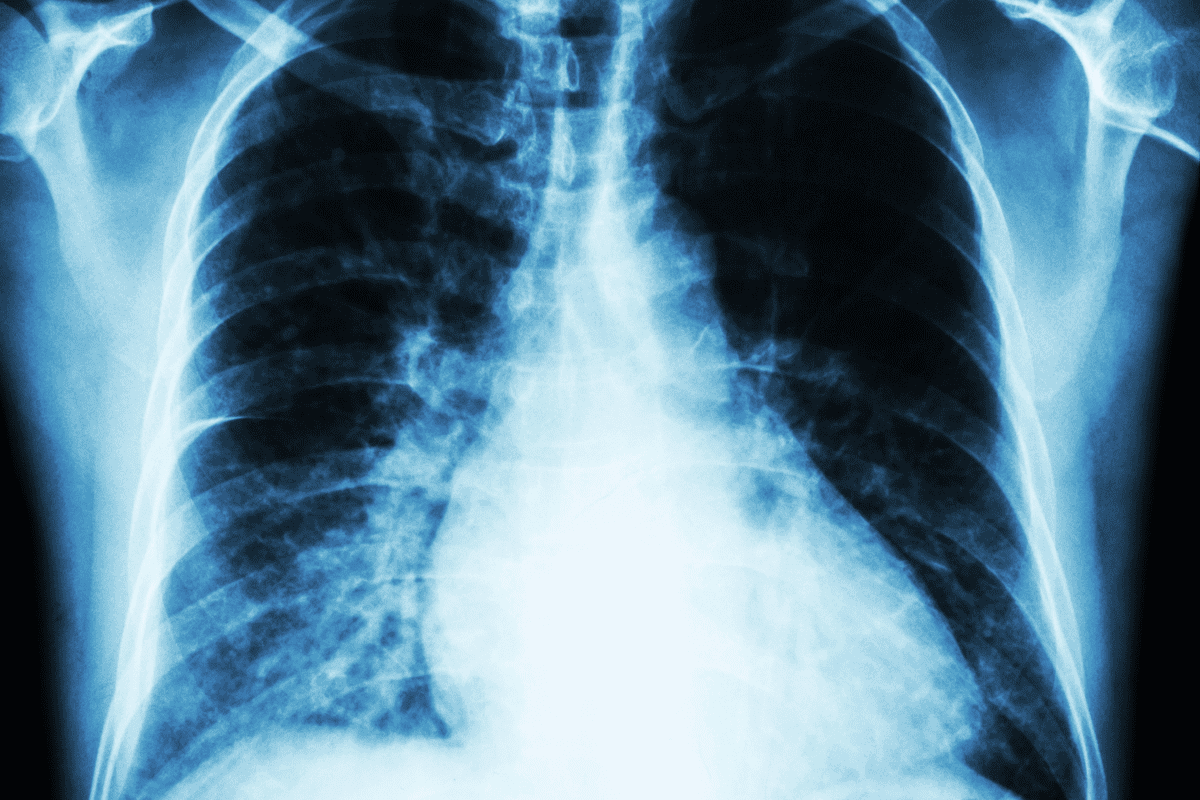
At Liv Hospital, we know how key it is to tell cardiomegaly and cardiac hypertrophy apart. Cardiomegaly, or an enlarged heart, happens when the heart
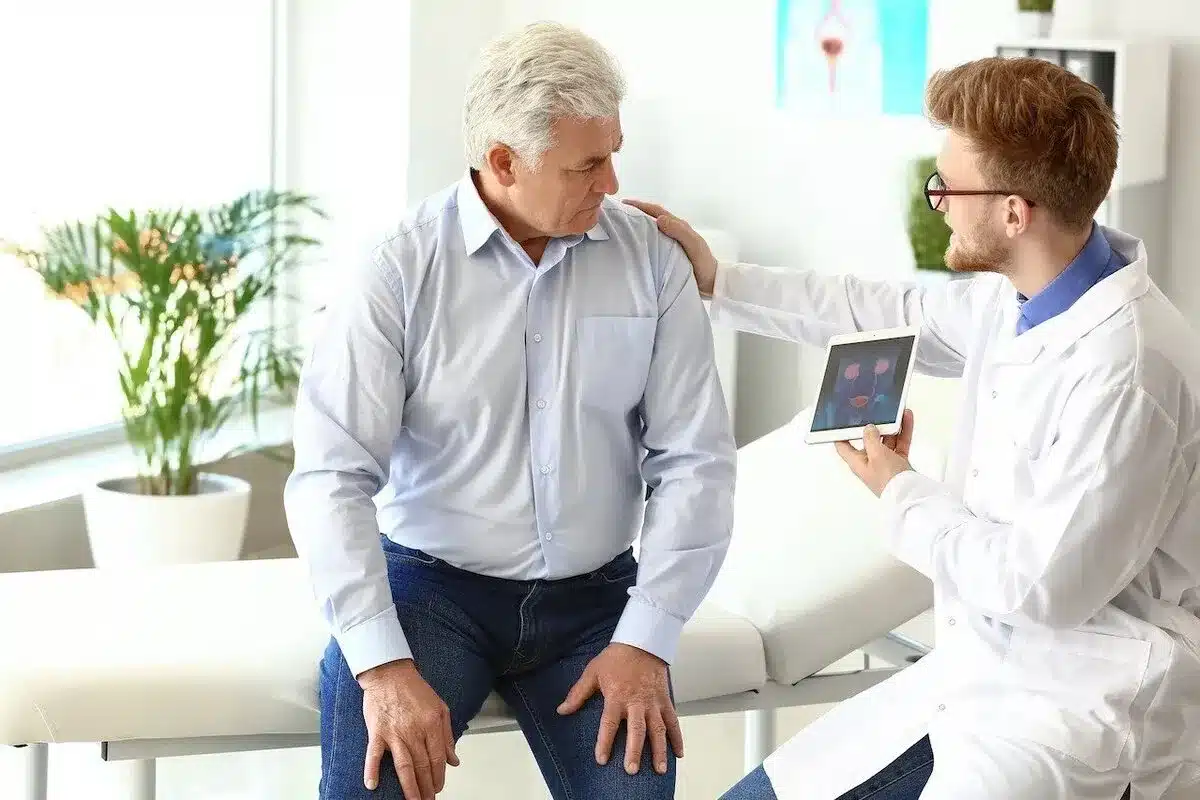

Prostate issues and urinary tract problems are big health worries for men. They often need to see a urologist. A lot of men over 50

Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition in women of childbearing age. It’s marked by many small ovarian follicles. This can affect fertility and
Men who have had a vasectomy often wonder if they can reverse it. This choice is complex and emotional. It raises many questions about success
Feeling a sore chest and headache at the same time can be scary and confusing. At Liv Hospital, we get how worried you must be
It’s important to spot the signs of bone marrow malfunction and insufficiency early. This can lead to better health outcomes. Bone marrow dysfunction affects the

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)