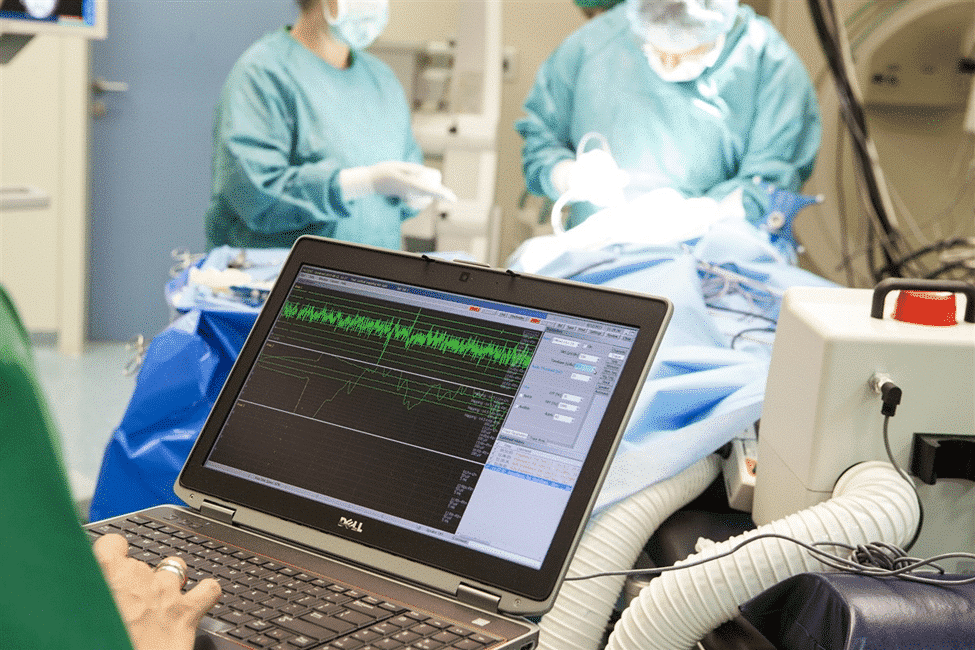
Nearly 20 million surgeries in the United States each year risk nerve damage. This makes intraoperative testing very important for surgical care. Learn what is intraoperative testing. Understand the techniques used in intraoperative neuromonitoring clearly.
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) is a key tool. It watches neural structures during surgery to prevent damage.
This method is very important in surgeries with a high risk of nerve injury. It helps keep neural pathways safe and improves patient results.
Key Takeaways
- Intraoperative testing is key in surgeries with a high risk of nerve damage.
- IONM prevents nerve injuries in complex surgeries.
- Intraoperative neuromonitoring is now a big part of surgery.
- It keeps neural structures safe during surgery.
- This testing makes surgical care better.
The Fundamentals of Intraoperative Testing

Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) has changed surgery by giving feedback in real-time. This tech has greatly improved patient care by letting surgeons make smart choices during tough surgeries.
Definition and Clinical Significance
Intraoperative testing, or IONM, uses neurophysiological monitoring during surgery. It checks if the nervous system is working right. This is key because it can spot nerve damage early, helping avoid lasting harm.
A top expert says,
“IONM has become an indispensable tool in modern surgery, making patients safer and surgeries more precise.”
IONM is very important in surgeries that risk the nervous system, like spine and brain surgeries. It keeps an eye on nerve paths, lowering the chance of nerve problems. This leads to better results for patients.
Historical Development and Evolution
IONM has come a long way, from basic tests to complex systems. Its growth is thanks to tech advances and better understanding of the nervous system. What started as a simple tool is now a must-have in many surgeries.
With better neurophysiological monitoring, more surgeries use IONM. Its growth shows our drive to make surgery safer and more effective. It’s a key part of surgical neurophysiology.
Understanding Intraoperative Neuromonitoring
Intraoperative neuromonitoring is key to making surgeries safer and more effective. It uses neurophysiological principles to watch the nervous system during surgery. This helps doctors make better decisions in real-time.
Neurophysiological Principles
This method is based on how the nervous system reacts to surgery. It looks at neurophysiological signals to check if nerves are working right. The main idea is to catch and understand these signals quickly to help surgeons.
The main neurophysiological principles are:
- The generation and movement of electrical signals in the nervous system.
- How nerves react to surgery.
- Using special techniques to get clear responses.
Signal Detection and Interpretation
Good intraoperative neuromonitoring needs precise signal detection and understanding. It uses advanced tools and methods to get and study these signals. The IONM technologist is key in making sure the data is good and useful.
Understanding signals means knowing what’s normal, spotting changes during surgery, and linking them to what’s happening in the operating room. This helps doctors avoid harming nerves.
Important parts of signal understanding are:
- Spotting big changes in signal strength or speed.
- Linking signal changes to specific surgical steps.
- Telling the surgical team important findings right away.
Types of Intraoperative Monitoring Techniques

Intraoperative neuromonitoring uses several methods to check the nervous system during surgery. These methods are key for checking how well the nerves are working and for avoiding damage during complex surgeries.
Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEP)
SSEP checks the health of sensory pathways. It works by stimulating nerves and recording signals from the brain or spinal cord. SSEP monitoring is very helpful during surgeries that might harm the spinal cord or nerves. It lets surgeons keep an eye on SSEP signals to avoid nerve damage.
Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP)
MEP checks the motor pathways by stimulating the brain and recording muscle responses. It’s very important for surgeries that could affect motor function, like spine surgery. MEP monitoring helps surgeons spot motor pathway damage right away, so they can change their approach.
Electromyography (EMG)
EMG records the electrical activity of muscles. It’s used to find nerve irritation or damage during surgery. EMG is great for surgeries in the face, neck, or other areas with complex nerves. It lets surgeons catch nerve stress or damage early and take action.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
EEG records the brain’s electrical activity. It’s used during surgeries that might harm the brain, like carotid endarterectomy. EEG monitoring gives feedback on brain activity in real-time. This helps surgeons and anesthesiologists quickly respond to any signs of brain trouble.
These monitoring techniques – SSEP, MEP, EMG, and EEG – are vital in today’s surgery. They give real-time info on nerve function, helping to reduce the risk of nerve damage and improve patient results.
Equipment Used in Neuromonitoring
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) uses advanced tools to monitor during surgeries. The quality of these tools is key to IONM’s success.
Monitoring Systems and Platforms
Monitoring systems are the heart of IONM. They help capture and analyze brain signals. These systems are easy to use but also have advanced features.
Key Features of Monitoring Systems:
- High-resolution displays for clear signal visualization
- Advanced signal processing algorithms for noise reduction
- Multimodal monitoring capabilities to assess various neurological functions
- Real-time data analysis for immediate feedback during surgery
Electrodes and Sensors
Electrodes and sensors are vital in IONM. They pick up and send brain signals to the monitoring systems. The accuracy of monitoring depends on these components.
Types of Electrodes Used:
- Surface electrodes for non-invasive monitoring
- Subdermal electrodes for more precise signal detection
- Intracranial electrodes for direct neural activity monitoring
The choice of electrodes and sensors varies by surgery type and patient condition. Correct placement and care of these tools are essential for good data.
Surgical Procedures Requiring Intraoperative Monitoring
Surgical procedures that need precise neural function monitoring greatly benefit from intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM). This technology is key in surgeries where there’s a high risk of neurological damage. It helps surgeons make better decisions during the surgery, which can lower the chance of neurological problems after the operation.
Spine Surgery Applications
Spine surgery is a major use of IONM. It helps in correcting spinal deformities, removing spinal tumors, and treating spinal stenosis. Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEP) and Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP) are used to watch the spinal cord during these surgeries.
Brain Surgery Protocols
Brain surgery uses IONM to protect important brain areas. Electrocorticography and EEG are used to check brain activity. They help spot risky areas during tumor removals or epilepsy surgery.
Vascular Procedures
Vascular procedures, like clipping aneurysms and fixing AVMs, use IONM to watch cerebral blood flow. Electroencephalography (EEG) is very helpful in these cases.
Other Surgical Applications
IONM is also used in other surgeries. It’s used in peripheral nerve surgery to check nerve function. It’s also used in some ENT procedures to watch cranial nerve function.
Benefits of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) has changed surgery for the better. It makes surgeries safer and more successful. IONM lets doctors watch the nervous system in real time. This helps them make better choices and avoid harming the nerves.
Improved Patient Outcomes
IONM has led to improved patient outcomes in many surgeries. It keeps an eye on the nerves, helping doctors catch and fix problems early. This is very important in complex surgeries where nerve damage is a big risk.
- Enhanced detection of neural dysfunction
- Real-time feedback for surgical decision-making
- Reduced risk of postoperative neurological deficits
Risk Reduction During Surgery
IONM is key in risk reduction during surgery. It watches the nerves closely, spotting problems early. This is super important in surgeries of the spine, brain, or big blood vessels.
A surgical neurophysiologist is also very important. They help understand the IONM data and guide the team. Their skills are essential in keeping the surgery safe and effective.
Limitations and Challenges in IONM
IONM has made big strides, but it’s not without its challenges. It’s a complex field that needs precision and accuracy. This ensures patient safety during surgeries.
Technical Limitations
Technical issues are a big problem in IONM. These include equipment failures, signal interference, and getting clear signals. These problems can cause false results, which can harm patients.
Interpretation Challenges
Understanding IONM data is tough. It needs a strong grasp of neurophysiology. It’s hard to tell real changes from noise, even for experts.
Because of this, IONM experts need constant training. This helps them stay sharp and make accurate calls.
The Role of the IONM Technologist
The IONM technologist is key in the operating room. They help make complex surgeries a success. They use advanced monitoring to guide surgical decisions.
IONM technologists have special training. They give surgeons real-time feedback to avoid nerve damage.
Responsibilities and Duties
They set up and run monitoring gear. They interpret signals and share important info with the team. They must make fast decisions under pressure.
- Setting up and calibrating monitoring equipment
- Interpreting neurophysiological signals in real-time
- Communicating with surgeons and other surgical team members
- Troubleshooting technical issues during surgery
Collaboration with Surgical Team
Working well with the surgical team is vital. IONM technologists team up with surgeons and others to give the best care.
|
Team Member |
Role in IONM |
|---|---|
|
Surgeon |
Uses IONM data to inform surgical decisions |
|
Anesthesiologist |
Collaborates with IONM technologist to manage anesthesia levels |
|
IONM Technologist |
Provides real-time neurophysiological monitoring data |
Becoming an IONM Professional
To become an IONM professional, you need the right education and certification. Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM) is a specialized field. It requires a deep understanding of neurophysiology and its use in surgeries.
Education Requirements
Aspiring IONM professionals should get a degree in neurophysiology, neuroscience, or a related field. Classes in neuroanatomy, neurophysiology, and electrophysiology are key. They lay the groundwork for a career in IONM.
Certification Process
Getting certified is a big step for IONM professionals. The Certified Intraoperative Neurophysiologic Monitoring (CINM) credential is a recognized standard. It shows you’re an expert and is often needed to practice.
Career Opportunities and Job Outlook
IONM professionals have many career paths in healthcare, like hospitals and surgical centers. The need for skilled IONM professionals is rising. This is due to better surgical techniques and a focus on patient safety.
With the right education, certification, and keeping up with new developments, you can have a fulfilling career in IONM.
Training Programs for Neuromonitoring
Intraoperative neuromonitoring is becoming more important. This means we need better training programs. These programs help professionals learn the skills needed for IONM.
Academic Programs and Degrees
There are many academic programs for neuromonitoring. They offer degrees or certifications. These programs mix theory with practical training, getting students ready for IONM.
Coursework includes neurophysiology, signal processing, and surgical techniques. This gives students a deep understanding of the field.
Some places offer master’s programs or postgraduate certificates in neuromonitoring. These are for those who want to learn more. These programs are key in training the next IONM professionals.
On-the-Job Training and Mentorship
On-the-job training is also essential. Many learn by doing, with experienced technologists guiding them. This mentorship is very valuable, giving real-world insights and practical skills.
Hospitals and neuromonitoring providers offer in-house training. This lets staff improve their skills in a supportive setting. These programs include workshops, seminars, and simulation training. They keep professionals updated with new techniques and technologies.
Anesthesia and Neuromonitoring Interactions
The relationship between anesthetic agents and neuromonitoring is complex. It requires teamwork. Anesthesiologists and neuromonitoring experts must work together closely. This is because anesthetic agents can change how neuromonitoring data is read.
Effects of Anesthetic Agents on Monitoring
Anesthetic agents can alter neuromonitoring signals. This can lead to wrong readings if not understood. For example, some anesthetics can reduce cortical signals. This affects the accuracy of EEG and SSEP.
Table: Effects of Common Anesthetic Agents on Neuromonitoring
|
Anesthetic Agent |
Effect on SSEP |
Effect on MEP |
Effect on EEG |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Propofol |
Minimal effect |
Significant suppression |
Suppresses activity |
|
Isoflurane |
Amplitude reduction |
Latency prolongation |
Alters frequency |
|
Etomidate |
Enhances amplitude |
Minimal effect |
Increases activity |
Collaborative Approach Between Specialties
Teamwork between anesthesiologists and neuromonitoring experts is key. They must understand how anesthetics impact neuromonitoring. This knowledge helps them adjust anesthesia plans and ensure accurate monitoring.
This teamwork makes surgeries safer. It also helps patients by reducing the risk of brain damage.
Advancements in Intraoperative Monitoring Technology
New technology in intraoperative neuromonitoring is changing how we do surgery. It helps doctors and anesthesiologists get feedback in real time. This makes surgeries safer and more effective.
IONM technology is getting better fast. This is thanks to new ways of processing signals, designing electrodes, and analyzing data. These changes make neuromonitoring more accurate and reliable during surgery.
Recent Innovations
In recent years, IONM has seen some big changes. Some key innovations include:
- Advanced signal processing algorithms that improve signal quality and reduce noise.
- Miniaturized electrodes and sensors that enhance patient comfort and reduce setup time.
- Real-time data analytics and machine learning capabilities that provide predictive insights during surgery.
These new technologies have made IONM better in many ways. They’ve also made it useful for more types of surgeries.
|
Innovation |
Description |
Impact on IONM |
|---|---|---|
|
Advanced Signal Processing |
Improved algorithms for better signal quality |
Enhanced accuracy and reliability |
|
Miniaturized Electrodes |
Smaller, more comfortable electrodes |
Reduced setup time and improved patient comfort |
|
Real-time Data Analytics |
Machine learning for predictive insights |
Better decision-making during surgery |
Future Directions and Research
The future of IONM looks bright. Researchers are working on making it even better. They’re exploring:
- Using artificial intelligence (AI) for smarter data analysis.
- Creating non-invasive monitoring methods.
- Using IONM in more surgical areas.
As research keeps moving forward, IONM will become even more important. It will help make surgeries safer and better for patients.
Neuromonitoring Service Providers
Neuromonitoring service providers are key in today’s healthcare. They offer different models to meet various needs. These services are vital for precise intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) in complex surgeries.
Service Models and Delivery Options
Neuromonitoring service providers offer different models to fit various healthcare needs. These models include:
- In-house monitoring teams: Some hospitals choose to have their own IONM teams.
- Remote monitoring services: Many providers offer remote IONM services for real-time monitoring from afar.
- Hybrid models: A mix of in-house and remote services, providing flexibility and expertise.
The choice of service model depends on several factors. These include the type of surgeries, available resources, and patient needs.
Cost and Insurance Considerations
It’s important to know the costs of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM) for both hospitals and patients. The price of IONM services changes based on the surgery type, monitoring complexity, and if it’s done in-house or remotely.
Healthcare Coverage for IONM
In the United States, insurance coverage for IONM is a big deal. This is because it helps patients and lowers surgery risks. But, how much they cover can differ, and some surgeries might need approval first.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Hospitals and Patients
Looking at IONM’s costs and benefits is key. Here’s a table that shows some important points:
|
Cost Factors |
Benefit Factors |
|---|---|
|
Equipment and maintenance costs |
Improved patient outcomes |
|
Technologist fees and training |
Reduced risk of surgical complications |
|
Insurance reimbursement variability |
Potential reduction in long-term healthcare costs |
While IONM has costs, its benefits often make it worth it. This is true, mainly for complex surgeries where brain injury risks are high. Knowing the costs and insurance can help healthcare providers decide when to use IONM.
Comparing In-House vs. Remote Neuromonitoring
Hospitals can choose between in-house and remote neuromonitoring services. Each has its own benefits. The choice depends on the hospital’s size, the surgeries done, and the staff available.
In-house teams work directly for the hospital, helping right away during surgeries. Remote services, on the other hand, come from outside companies. They use telecommunication to monitor patients.
Benefits of In-House Monitoring Teams
In-house teams bring several advantages, including:
- Quick response to emergencies
- Smooth work with the hospital’s surgical team
- Consistent quality in monitoring
Having a team on site also helps with better communication and teamwork. This can lead to better care for patients.
Advantages of Remote Monitoring Services
Remote services have their own benefits, such as:
- Access to more experienced professionals
- Cost savings from not needing in-house staff
- Flexibility in handling different surgeries
Conclusion
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) has changed surgery a lot. It makes surgeries safer and better for patients. Surgeons use new ways to watch the brain during surgery, cutting down on brain damage risks.
IONM gives surgeons feedback right when they need it. This is super helpful in tricky surgeries like spine and brain operations. It helps protect important brain parts.
As IONM gets better, so will patient care. It’s already making a big difference. IONM will keep being key in surgery, helping make patients safer and surgeries more successful.
FAQ
What is intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM)?
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) is a medical field. It watches the nervous system during surgery. This helps avoid nerve damage and ensures the best results for patients.
What are the different types of intraoperative monitoring techniques?
There are several types of intraoperative monitoring. These include Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEP), Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP), Electromyography (EMG), and Electroencephalography (EEG).
What is the role of an IONM technologist?
An IONM technologist sets up and runs the equipment for monitoring. They also interpret the data and talk to the surgical team.
What are the benefits of intraoperative neuromonitoring?
IONM improves patient outcomes and lowers the risk of nerve damage. It also makes surgeries safer for patients.
What are the limitations and challenges associated with IONM?
IONM faces technical issues and complex data interpretation. It also needs specialized training and expertise.
How does anesthesia affect neuromonitoring?
Anesthesia can change the signals picked up by monitoring equipment. It’s important for anesthesiologists and neuromonitoring experts to work together for accurate monitoring.
What are the education and certification requirements for becoming an IONM professional?
To be an IONM professional, you need a degree in neurophysiology or a related field. You also need to get certified by a recognized organization.
What are the different service models offered by neuromonitoring service providers?
Neuromonitoring providers offer various services. These include in-house teams and remote monitoring. They meet the needs of different healthcare places.
How does intraoperative neuromonitoring impact healthcare costs?
IONM can lower healthcare costs. It reduces complications and improves outcomes. This saves money for hospitals and patients.
What are the advantages of remote neuromonitoring services?
Remote neuromonitoring offers flexibility and access to experts. It’s also cost-effective. These benefits make it appealing to healthcare institutions.
What is the significance of intraoperative neuromonitoring in spine surgery?
In spine surgery, IONM is key. It prevents nerve damage and ensures the best results. It monitors the nervous system during the surgery.
What is the future of intraoperative neuromonitoring technology?
The future of IONM technology looks promising. It will see better signal detection and new monitoring methods. These advancements will improve patient care.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22742764/

































