Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
The philosophy of modern rheumatology is “Treat to Target.” This means setting a specific goal, usually remission (absence of symptoms) or low disease activity, and adjusting medication aggressively until that goal is reached. The era of simply managing pain with aspirin is over; today, we use sophisticated biologic therapies to halt the immune attack and prevent joint destruction.
Targeted Synthetic DMARDs (JAK Inhibitors): A newer class of oral medications that block signaling pathways inside the cell.
Medication alone is rarely enough. A holistic approach is required.

Rheumatic diseases are systemic. Treatment involves monitoring for associated risks:
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
While the Anti-inflammatory Diet (like the Mediterranean diet) is broad and focuses on adding Omega-3s and antioxidants to fight systemic inflammation, the Gout Diet is restrictive. It specifically targets the reduction of purines (found in red meat, organ meats, and beer) and fructose to prevent the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints.
No. A steroid shot is a powerful anti-inflammatory that acts quickly to stop pain. Viscosupplementation (hyaluronic acid) acts more like a “lubricant” or gel for the knee. It is used specifically for Osteoarthritis to improve joint “cushioning” rather than just suppressing the immune system.
Rheumatic diseases are systemic, meaning inflammation isn’t just in your joints—it’s in your blood vessels too. This chronic inflammation significantly increases the risk of heart disease. Managing cardiovascular health is a standard part of modern rheumatologic care to prevent long-term complications like heart attacks.
It depends. Your rheumatologist must coordinate with your surgeon. Often, Conventional DMARDs (like Methotrexate) are continued, but Biologics or JAK Inhibitors might be paused briefly before and after surgery to ensure your immune system can properly heal the surgical site and prevent infection.
They are the newest class of Targeted Synthetic DMARDs. Unlike Biologics, which are large proteins given by injection to block inflammation outside the cells, JAK Inhibitors are oral pills that work inside the cell to block the signaling pathways that tell the cell to produce inflammation.

Crystalline arthropathy is a group of diseases, including gout and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD). These diseases happen when crystals build up in the joints,
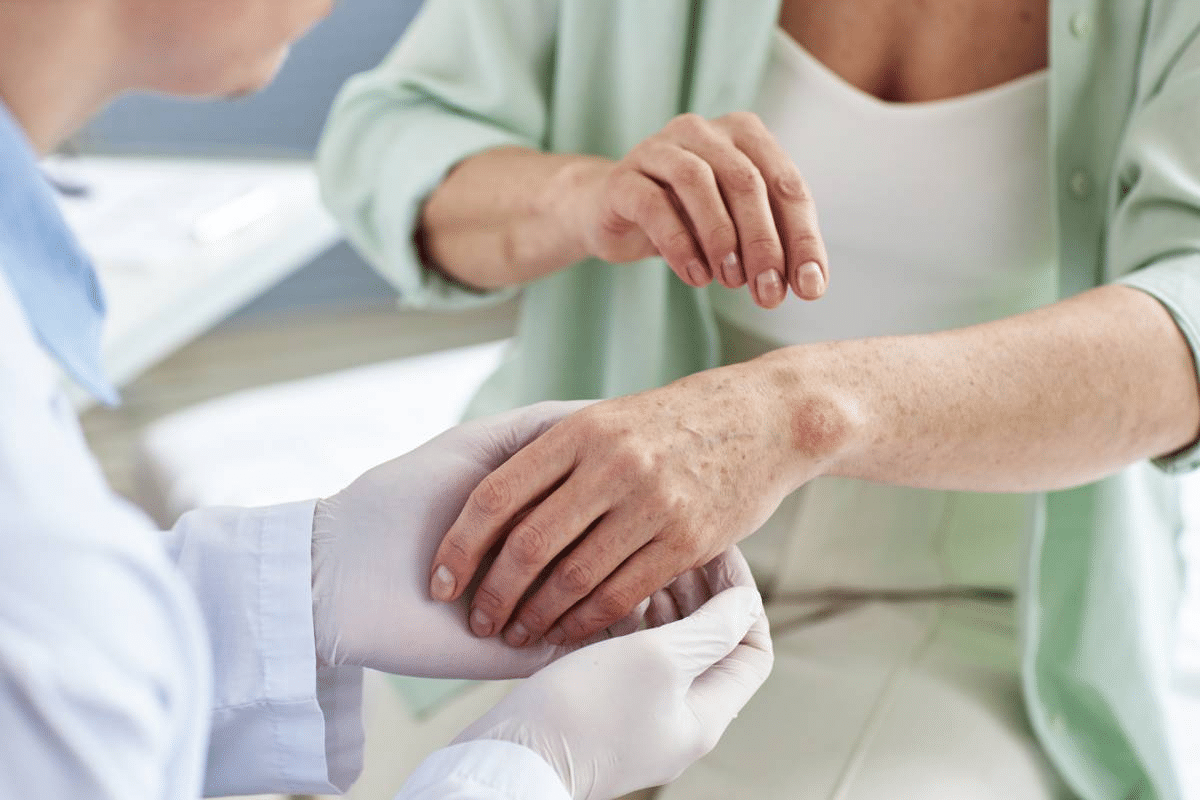
Autoimmune conditions can show up in many ways, including skin rashes. A rash on the neck might mean you have an autoimmune disease that needs
Arthritis affects millions worldwide. What we eat plays a big role in managing its symptoms. Some foods can make arthritis worse by causing inflammation. Identifying

Best spine strengthening exercises for osteoporosis. This essential guide explains how to build bone density and prevent injury safely. Osteoporosis affects over 40 million people

Arthritis affects millions worldwide, causing a lot of pain and trouble. Research shows that what we eat can help manage the inflammation and pain in

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)