Discover LIV Hospital’s personalized pediatric treatment. We cover medications, minimally invasive surgery, rehabilitation, and full recovery support.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
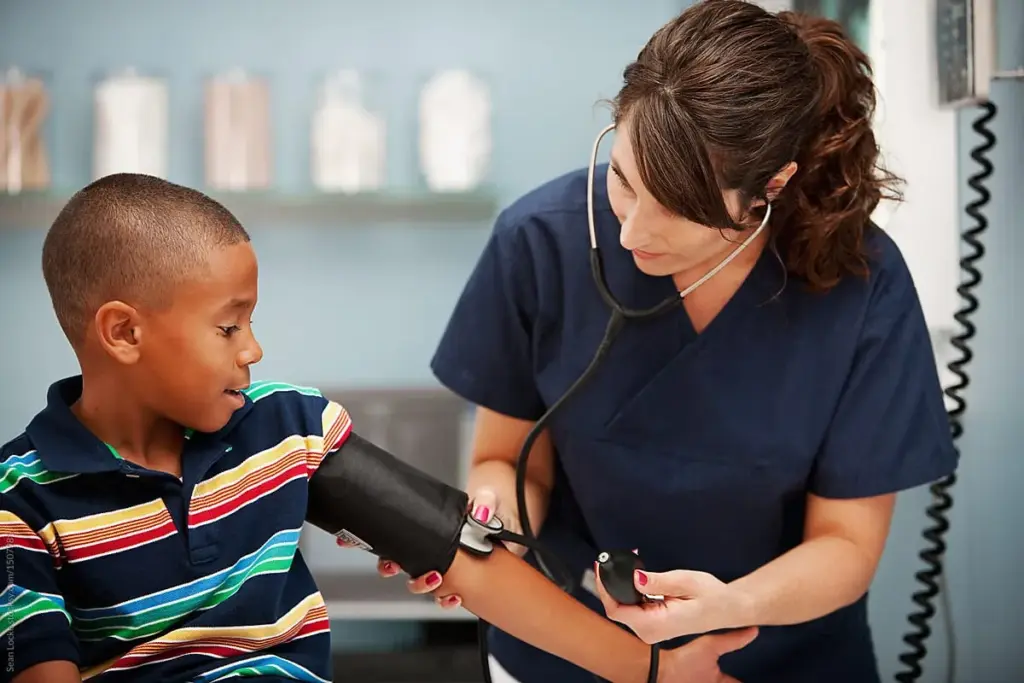

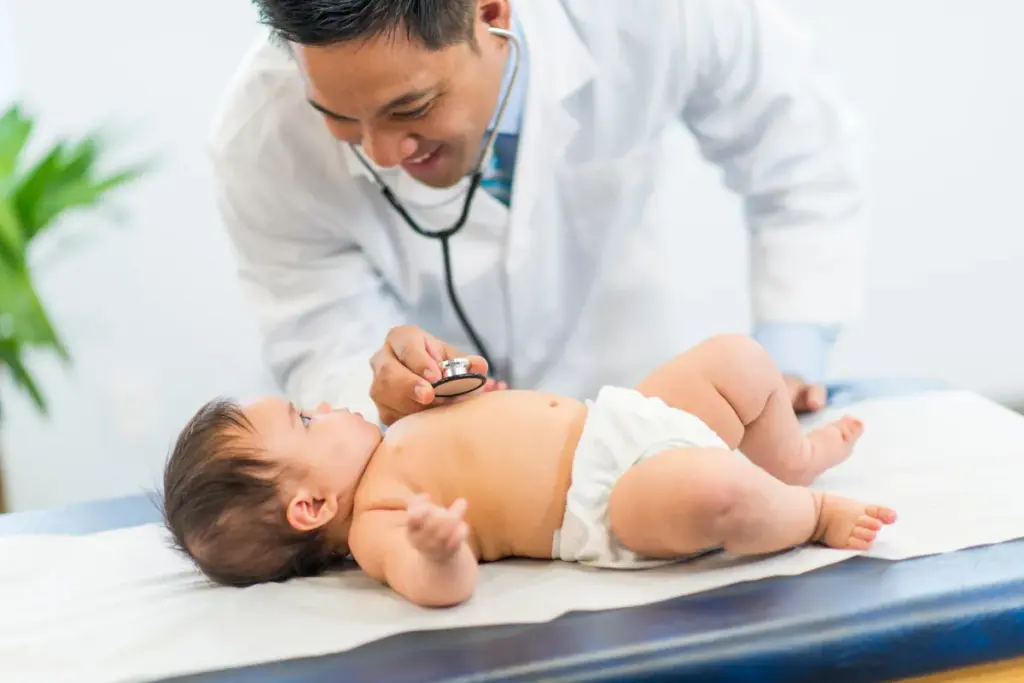
Medication dosing in children is an exact science. Unlike adult doses, which are often fixed, pediatric doses are calculated based on weight or body surface area. This ensures safety and efficacy.
Liquid formulations are commonly used for younger children who cannot swallow pills. Flavoring is often added to improve compliance.
Safety is paramount. Physicians educate parents on the proper use of dosing syringes and cups to prevent overdose. Double-checking calculations is a standard of practice.
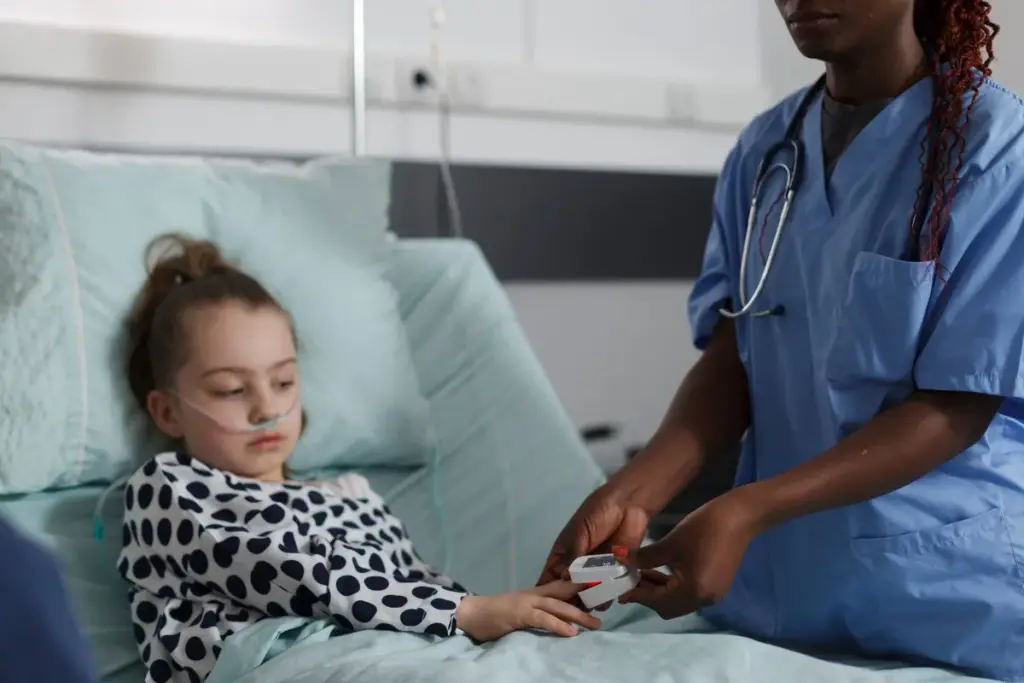

Antibiotics are powerful tools, but they must be used wisely. Viral infections, which cause most childhood illnesses, are not treated with antibiotics. Overuse leads to resistant bacteria.
Pediatricians practice stewardship by prescribing antibiotics only for confirmed bacterial infections, such as strep throat or urinary tract infections.
Watchful waiting is often used for ear infections in older children, giving the body’s immune system a chance to fight the disease before medication is introduced.
Chronic diseases like asthma require long-term management plans. This involves maintenance medications to prevent flares and rescue medications for acute symptoms.
Diabetes management involves insulin administration and continuous glucose monitoring. It requires a close partnership between the family, the school, and the medical team.
Care plans are dynamic. They are adjusted as the child grows and their physiological needs change. Alpine Pediatrics and similar clinics emphasize this adaptive approach to chronic care.
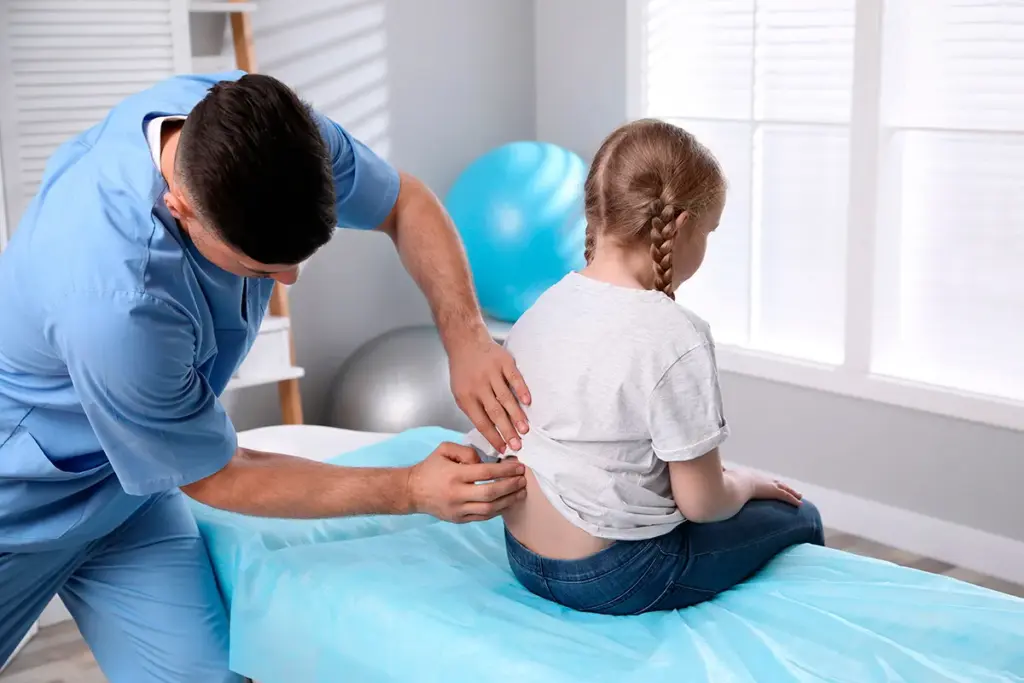

When illness strikes suddenly, urgent care pediatrics provides a bridge between the office and the emergency room. These facilities handle high fevers, dehydration, minor fractures, and lacerations.
Rapid testing for flu, strep, and RSV allows for immediate treatment decisions. Intravenous fluids can be administered for dehydration.
The goal is to stabilize the child and provide relief quickly while keeping them out of the intimidating hospital environment if possible.
Pediatric surgery ranges from routine procedures to complex reconstructions. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are standard for sleep apnea and recurrent infections.
Ear tube placement (myringotomy) helps drain fluid and improve hearing. Hernia repairs and circumcisions are other frequent procedures.
Preoperative preparation involves reducing anxiety. Pediatric anesthesiologists monitor the child’s vital signs meticulously during procedures.
Treatment for mental health often involves a combination of therapy and medication. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is effective for anxiety and depression.
Behavioral therapy is the first-line treatment for ADHD in young children. Parent Management Training (PMT) helps parents develop strategies to manage problematic behaviors.
Medications like stimulants or SSRIs are prescribed when necessary, with careful monitoring for side effects.

Nutrition is a powerful treatment modality. For infants with allergies, specialized hydrolyzed formulas are prescribed.
Children with failure to thrive may require high-calorie supplementation. Ketogenic diets are used as a medical treatment for intractable epilepsy.
Dietitians work with families to manage obesity through lifestyle changes rather than restrictive dieting, focusing on healthy relationships with food.
Clinics like PM Pediatrics represent the shift towards accessible, after-hours care designed specifically for children. These models prioritize convenience without sacrificing specialized expertise.
Tribeca Pediatrics is known for a low-intervention, high-accessibility philosophy, often communicating directly with parents via email.
These varied models allow parents to choose a care style that aligns with their values and schedule.
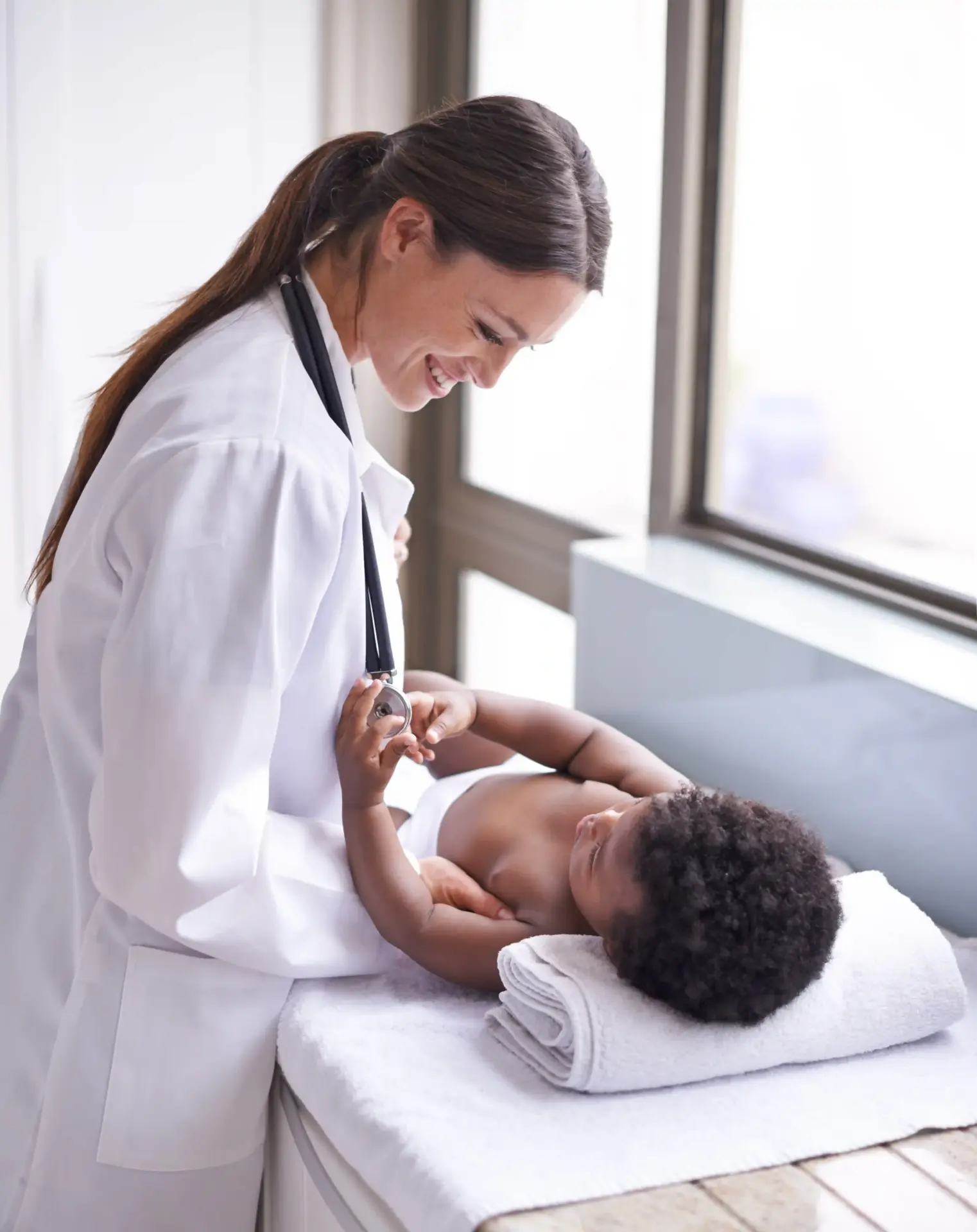
When a child is admitted to the hospital, they are cared for by pediatric hospitalists. These are specialists dedicated to inpatient care.
They coordinate the complex needs of hospitalized children, managing IV medications, oxygen therapy, and post-surgical recovery.
They communicate with the child’s primary care doctor to ensure a smooth transition back to home care upon discharge.
The NICU provides critical care for premature and ill newborns. Treatment involves respiratory support, from supplemental oxygen to mechanical ventilation.
Nutritional support is provided via IV (TPN) or feeding tubes until the baby can eat. Temperature regulation is maintained in incubators.
Developmental care in the NICU focuses on minimizing stress and noise to support the fragile brain’s development.
Treating pain in children requires specific assessment tools like the faces pain scale. Treatment uses a multimodal approach.
Pharmacological options include acetaminophen and ibuprofen. Opioids are used sparingly and are strictly monitored.
Non-pharmacological techniques are vital. These include distraction (bubbles, videos), sucrose for infants, and topical numbing creams for needle procedures.

Integrative pediatrics combines conventional medicine with evidence-based complementary therapies. This may include acupuncture for pain or nausea.
Mind-body therapies like yoga and biofeedback help with stress and chronic pain. Herbal supplements are evaluated for safety and efficacy.
This approach treats the whole child and offers families more options for managing chronic conditions.
Pediatric palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for children with life-limiting conditions. It is not just end-of-life care; it provides symptom management alongside curative treatment.
The team addresses pain, anxiety, and spiritual needs. They support the family in making difficult medical decisions.
Hospice care provides compassionate comfort care at the end of life, allowing the child to remain at home surrounded by family.
Selecting a provider involves looking for quality indicators. Preferred pediatric groups often boast board-certified physicians and recognition as Patient-Centered Medical Homes.
Parents should look for practices that offer family-centered pediatric approaches, prioritizing access and communication.
Finding a practice that aligns with the family’s philosophy on vaccination, antibiotics, and sleep training is crucial for a long-term partnership.
Selecting a provider involves looking for quality indicators. Preferred pediatric groups often boast board-certified physicians and recognition as Patient-Centered Medical Homes.
Parents should look for practices that offer family-centered pediatric approaches, prioritizing access and communication.
Finding a practice that aligns with the family’s philosophy on vaccination, antibiotics, and sleep training is crucial for a long-term partnership.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Aim the syringe toward the inside of the cheek, not the back of the throat, and give small amounts at a time; you can also gently blow on the face to trigger a swallow reflex.
Yes, if your doctor approves them for persistent fever or pain, you can alternate them to maintain coverage. Still, you must track the timing carefully to avoid overdosing on either medication.
For children over 2 years old with mild symptoms, doctors may wait 48 hours before prescribing antibiotics because many ear infections are viral or resolve on their own, sparing the child from unnecessary drugs.
Asthma treatment involves two main types of medication: long-term control medicines (taken daily to prevent flare-ups) and quick-relief medicines (used only when symptoms suddenly get worse). These are usually given through an inhaler or a breathing machine for effective and fast delivery.
A nebulizer turns liquid medication into a fine mist that the child inhales through a mask or mouthpiece, allowing the medication to reach deep into the lungs to treat asthma or croup.
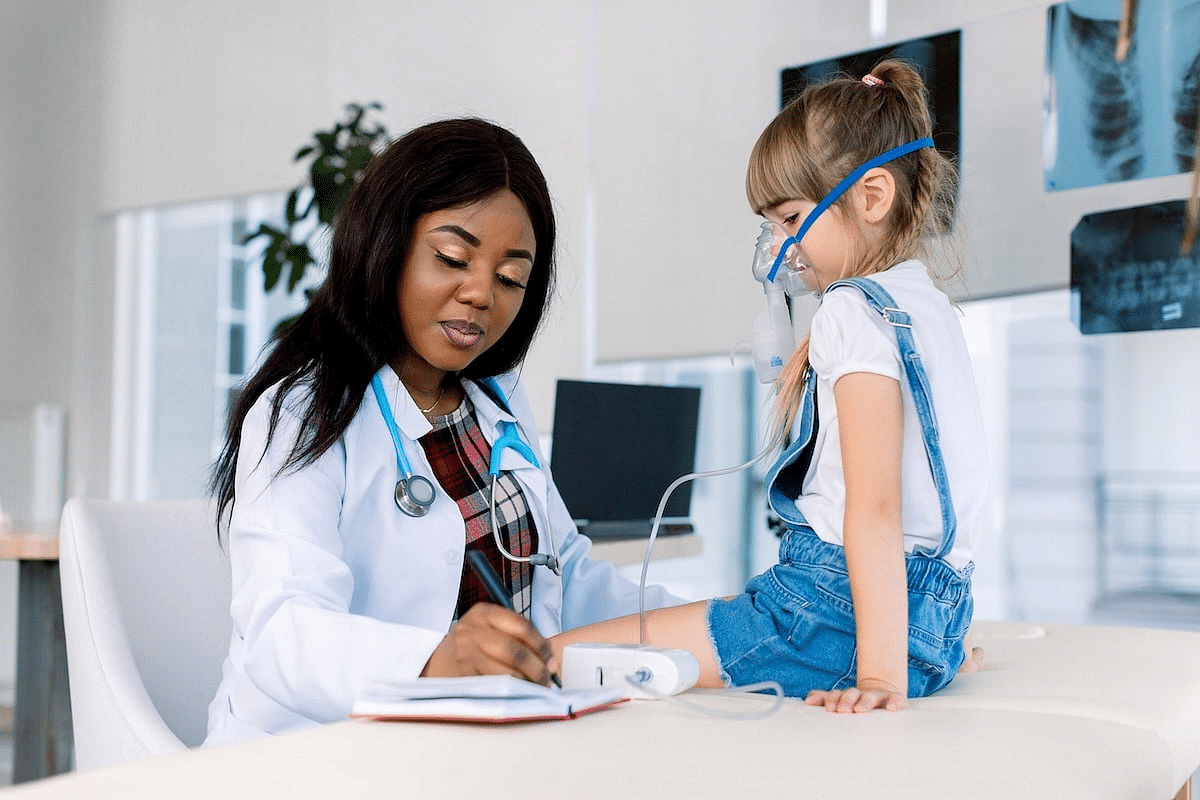


Millions of people worldwide suffer from allergies. Over 25 million Americans experience allergic rhinitis, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). We look
Asthma affects millions worldwide, and knowing what triggers symptoms is key. Did you know that asthma triggers can vary a lot from person to person?
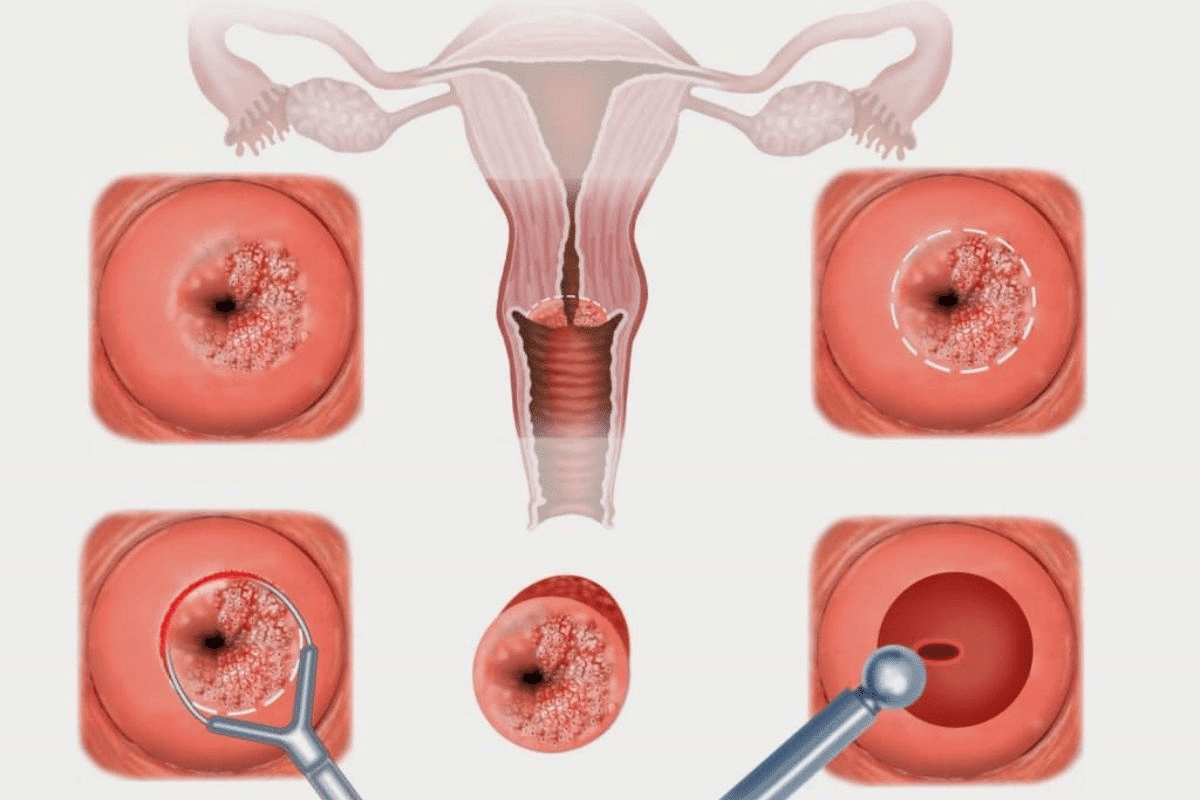
The 7 5 3 rule tonsillectomy guide defines need. specific surgery criteria. Learn the infection frequency that qualifies a child for surgery. Recurrent throat infections
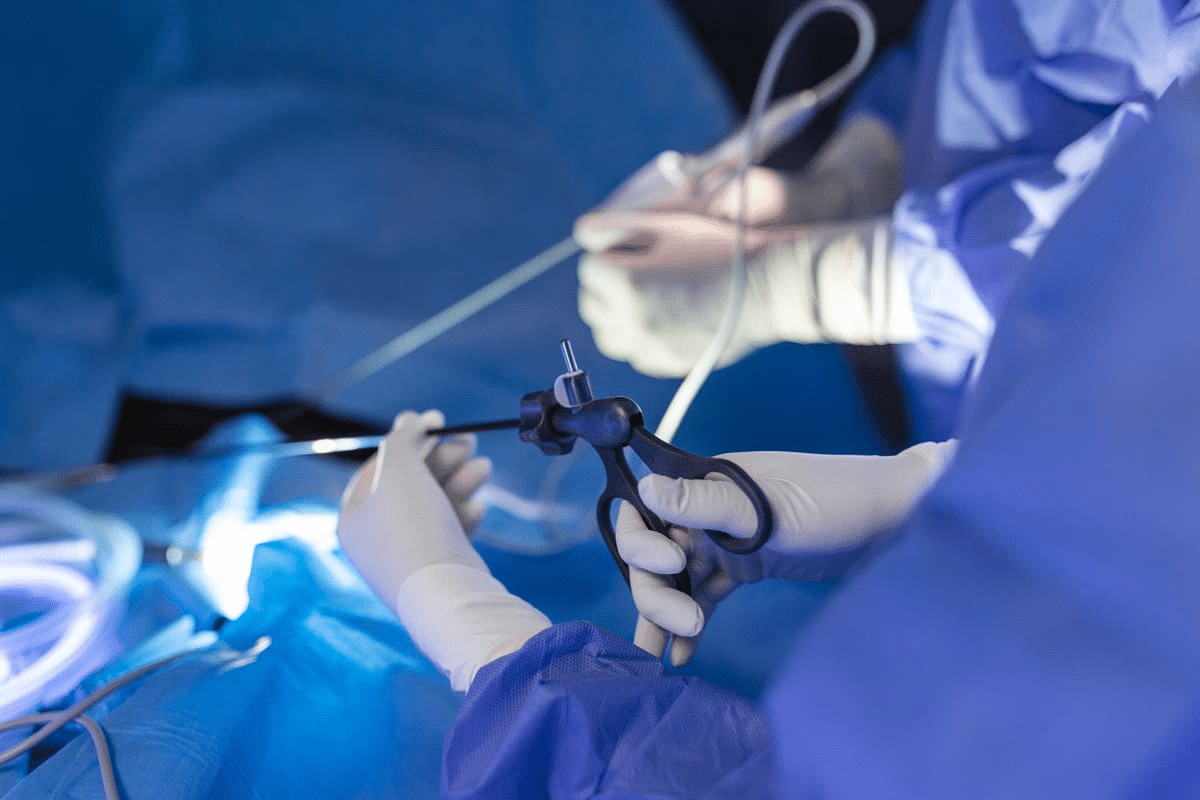
Nearly 1.5 million laparoscopic procedures are done every year in the United States. Many of these involve students who must return to school after their
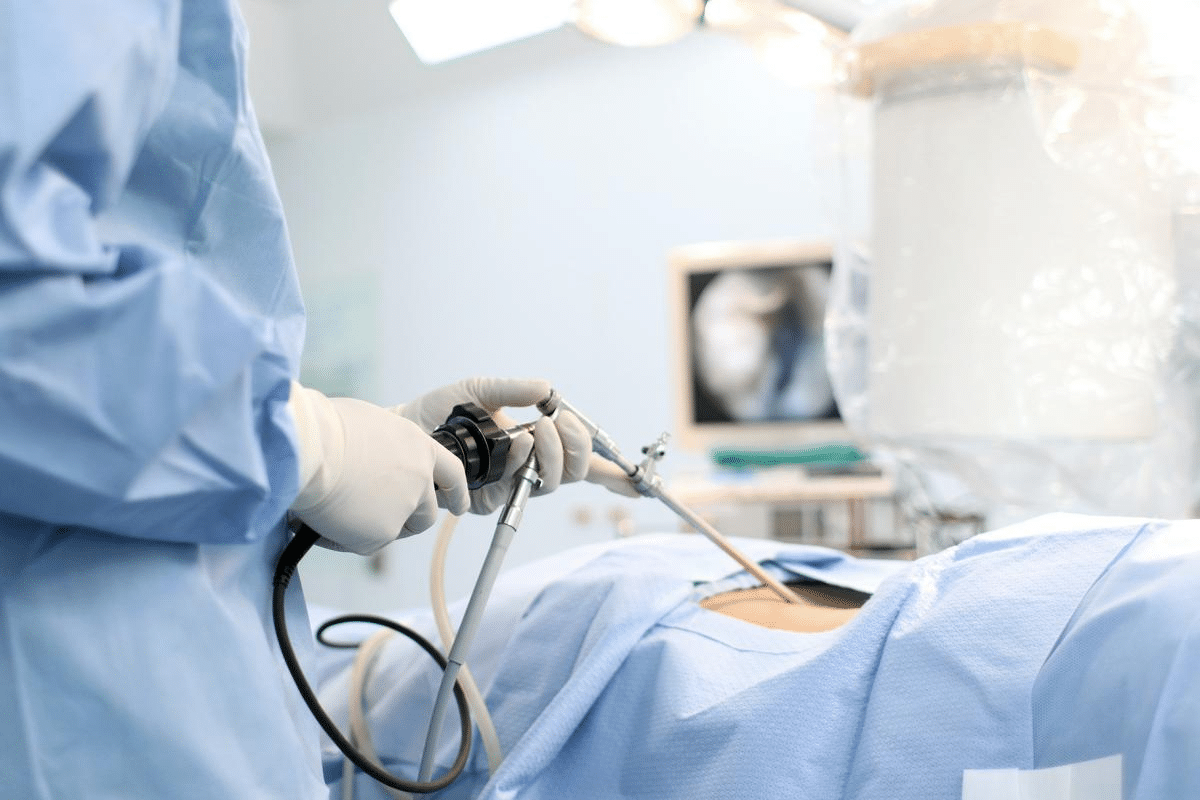
Nearly 1 in 100 patients who have diagnostic laparoscopy might face some complications. This shows why it’s important to know about the risks involved.The diagnostic
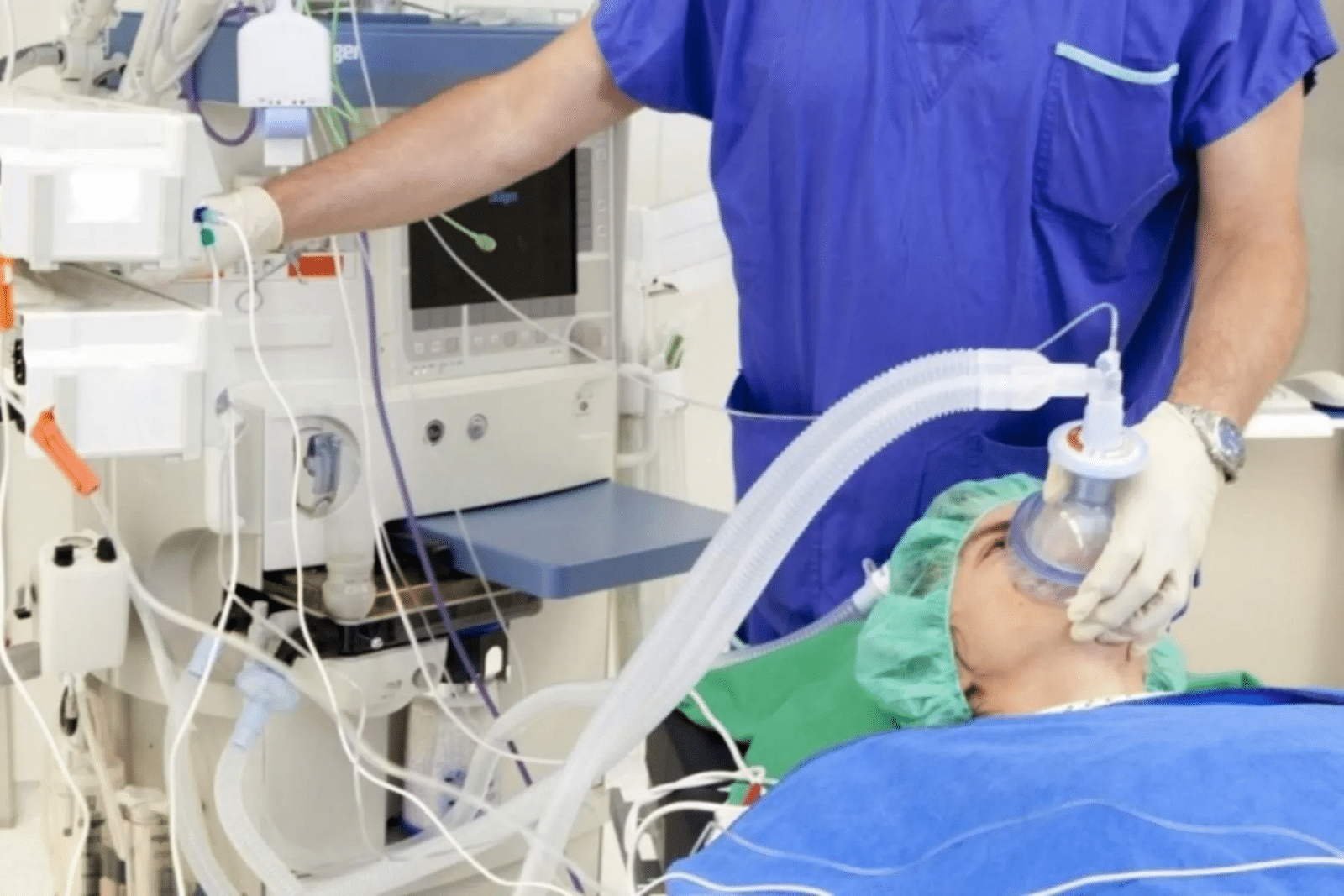
Did you know that advances in medical technology have made anesthesia safer? Recent studies show a big drop in anesthesia-related deaths. Now, we can better

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)