Learn warning signs for illness and developmental delays, and understand modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors for pediatric diseases. (pediatric symptoms)
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

Fever is one of the most common reasons parents seek medical advice. In children, a fever is a sign that the body is fighting an infection. It is a symptom, not a disease itself. The severity of the fever does not always correlate with the severity of the illness.
Viral infections are the leading cause of fevers in the pediatric population. These include the common cold, influenza, and roseola. Bacterial infections, such as urinary tract infections or pneumonia, also present with fever and require specific treatment.
Monitoring the child’s behavior is as important as tracking the thermometer. A playful child who is drinking fluids is generally less concerning than a lethargic child, regardless of the exact temperature.

Respiratory issues are frequent in childhood due to smaller airways. Recognizing signs of distress is crucial. Rapid breathing, or tachypnea, is often the first indicator of a problem.
Retractions occur when the muscles between the ribs or at the neck pull in with each breath. This indicates the child is working hard to breathe. Grunting and nostril flaring are also warning signs.
Conditions like Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), croup, and asthma are common culprits. Urgent care pediatrics facilities frequently manage these acute respiratory presentations during the winter months.

Children’s digestive systems are sensitive and prone to disruption. Vomiting and diarrhea are common symptoms of gastroenteritis, often caused by viruses like Rotavirus or Norovirus. Dehydration is the primary risk associated with these illnesses.
Chronic abdominal pain can be a complex symptom. It may relate to constipation, food intolerances, or functional abdominal pain disorders. Reflux in infants is another frequent concern, often presenting as spitting up and fussiness.
Identifying the difference between a surgical emergency, such as appendicitis, and a viral illness depends on the location of pain and associated symptoms.
A child’s skin is susceptible to various rashes. Viral exanthems produce widespread rashes accompanied by fever. Examples include chickenpox, hand, foot, and mouth disease, and fifth disease.
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, presents as dry, itchy, red patches. It is often chronic and requires long-term skin care management. Contact dermatitis can result from irritants such as soaps or from plants such as poison ivy.
Fungal infections, such as ringworm, and bacterial infections, such as impetigo, are also common. Visual inspection is usually sufficient for diagnosis, but sometimes cultures are needed.

Ear infections (otitis media) are a hallmark of early childhood. Fluid builds up behind the eardrum, causing pain and fever. Recurrent infections may impact hearing and speech development.
Sore throats are often caused by viruses, but can also be caused by Group A Streptococcus (strep throat). Differentiating between the two requires a swab test.
Allergic rhinitis causes a chronic runny nose, sneezing, and congestion. It can significantly impact sleep quality and school performance.
Parents often notice subtle changes in behavior that warrant evaluation. Delays in reaching milestones such as walking or talking are early indicators of developmental disorders.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) may present as difficulties with social interaction and communication. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) involves patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
Pediatric news today frequently highlights the importance of early intervention for these conditions. The sooner therapies begin, the better the child’s long-term outcomes.
Seizures can occur in children, ranging from febrile seizures triggered by fever to epilepsy. Staring spells or rhythmic twitching require immediate neurological assessment.
Headaches are common but can sometimes signal underlying issues. Migraines do occur in children and often present with nausea and light sensitivity.
Concussions from sports or falls are a significant concern. Proper evaluation and management of head injuries are essential to prevent long-term cognitive damage.

Growth is a sensitive indicator of overall health. Failure to thrive describes a child who is not gaining weight or growing as expected. This can be due to metabolic issues, malabsorption, or insufficient caloric intake.
Short stature may be familial or due to growth hormone deficiencies. Conversely, precocious puberty involves the onset of sexual development at an unusually early age.
Diabetes Type 1 is a major endocrine condition in children, presenting with excessive thirst, urination, and weight loss.
Children’s bones are growing and have open growth plates, making them susceptible to specific injuries. Fractures in children heal differently from those in adults.
Scoliosis is a curvature of the spine that often develops during the adolescent growth spurt. Early screening allows for bracing if necessary.
“Growing pains” is a diagnosis of exclusion, but it can cause real discomfort in the legs of young children, typically at night. Limbs should always be evaluated to rule out infection or hip disorders.
Sleep is vital for growth and brain development. Insomnia or resistance to bedtime is a frequent behavioral complaint.
Obstructive sleep apnea can occur in children, often due to enlarged tonsils and adenoids. It presents as snoring, pauses in breathing, and restless sleep.
Parasomnias like night terrors and sleepwalking are common in childhood and usually resolve with time, but can be distressing for families.
Despite abundant food, nutritional deficiencies persist. Iron-deficiency anemia is common among toddlers who drink excessive amounts of cow’s milk. It can lead to fatigue and developmental delays.
Vitamin D deficiency is a concern, particularly in northern climates, and it affects bone health. Calcium intake is crucial during the bone-building years of childhood.
Picky eating is a normal developmental stage, but it can lead to parental stress and nutrient gaps if it is severe or prolonged.
Food allergies are on the rise. Reactions can range from mild hives to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Common triggers include peanuts, milk, eggs, and tree nuts.
Seasonal allergies affect a large portion of the pediatric population, while immune deficiencies, though rare, present with recurrent, severe, or unusual infections.
A to Z pediatrics resources often include comprehensive guides on managing allergic reactions and creating safe environments for children with sensitivities.
Anxiety and depression are increasingly diagnosed in children and adolescents. Symptoms may include withdrawal, changes in sleep or appetite, and a decline in academic performance.
Somatic complaints, such as frequent stomach aches or headaches with no physical cause, are often manifestations of psychological distress.
Eating disorders like anorexia and bulimia typically emerge in adolescence and require a multidisciplinary treatment approach.
Some conditions are present from birth. Congenital heart defects may present with murmurs, cyanosis, or poor feeding. Genetic syndromes like Down syndrome have specific physical and developmental features.
Metabolic disorders are often screened for at birth, but may present later with acute decompensation. Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs and digestive system and requires lifelong management.
Early recognition of these conditions allows for proactive management and genetic counseling for the family.
Children are uniquely vulnerable to environmental toxins. Lead poisoning remains a risk in older housing, causing irreversible cognitive damage.
Exposure tosecondhandd smoke increases the risk of asthma, ear infections, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Access to the concept of pleasant pediatrics involves creating an environment—both medical and domestic—that minimizes stress and toxic exposure to support optimal health.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
A rectal temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher is considered a fever; measurements from other methods, like axillary or oral, may vary slightly in accuracy.
Signs of dehydration include a dry mouth, no tears when crying, sunken eyes, lethargy, and fewer than six wet diapers in 24 hours for infants.
While many viral rashes are accompanied by fever, a rash that does not fade when pressed (petechiae) with a fever can indicate a severe bacterial infection, such as meningitis, and requires immediate care.
Headaches that wake a child from sleep, are accompanied by vomiting (especially in the morning), or follow a head injury should be evaluated by a doctor immediately.
Toddlers with asthma may not wheeze; instead, they might have a chronic cough that worsens at night or with activity, rapid breathing, or visible chest retractions.


Millions of people worldwide suffer from allergies. Over 25 million Americans experience allergic rhinitis, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). We look
Asthma affects millions worldwide, and knowing what triggers symptoms is key. Did you know that asthma triggers can vary a lot from person to person?
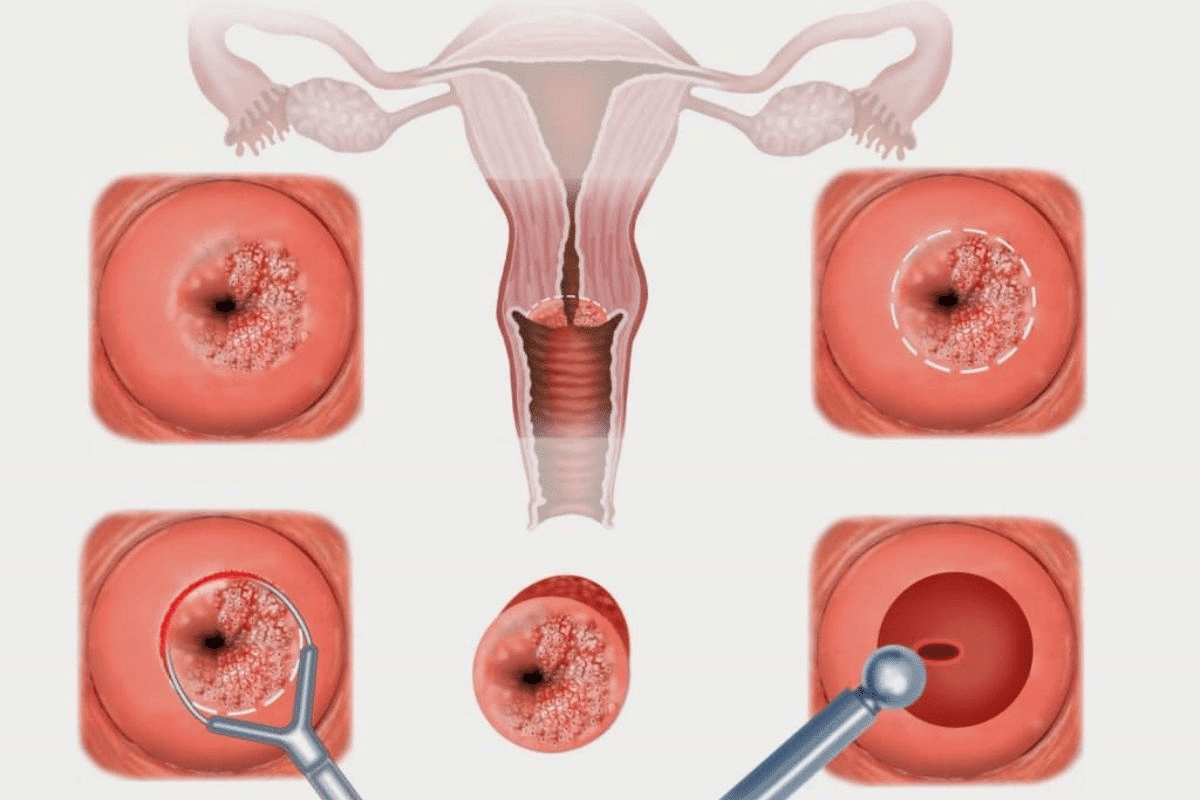
The 7 5 3 rule tonsillectomy guide defines need. specific surgery criteria. Learn the infection frequency that qualifies a child for surgery. Recurrent throat infections
Nearly 1.5 million laparoscopic procedures are done every year in the United States. Many of these involve students who must return to school after their
Nearly 1 in 100 patients who have diagnostic laparoscopy might face some complications. This shows why it’s important to know about the risks involved.The diagnostic
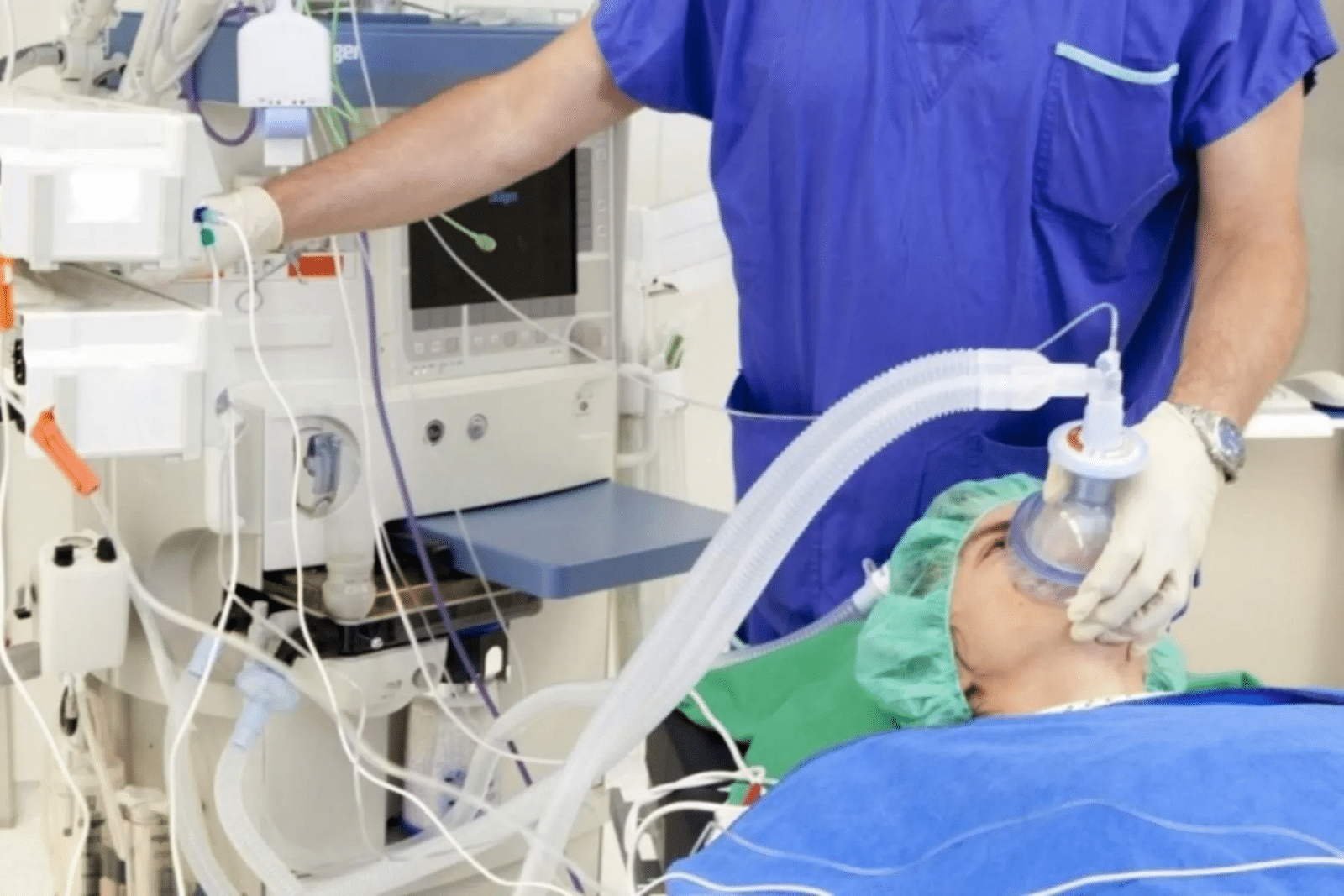
Did you know that advances in medical technology have made anesthesia safer? Recent studies show a big drop in anesthesia-related deaths. Now, we can better

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)