Learn about pediatric growth and disease prevention at LIV Hospital. Find expert advice on nutrition, exercise, stress management, and regular health checkups.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

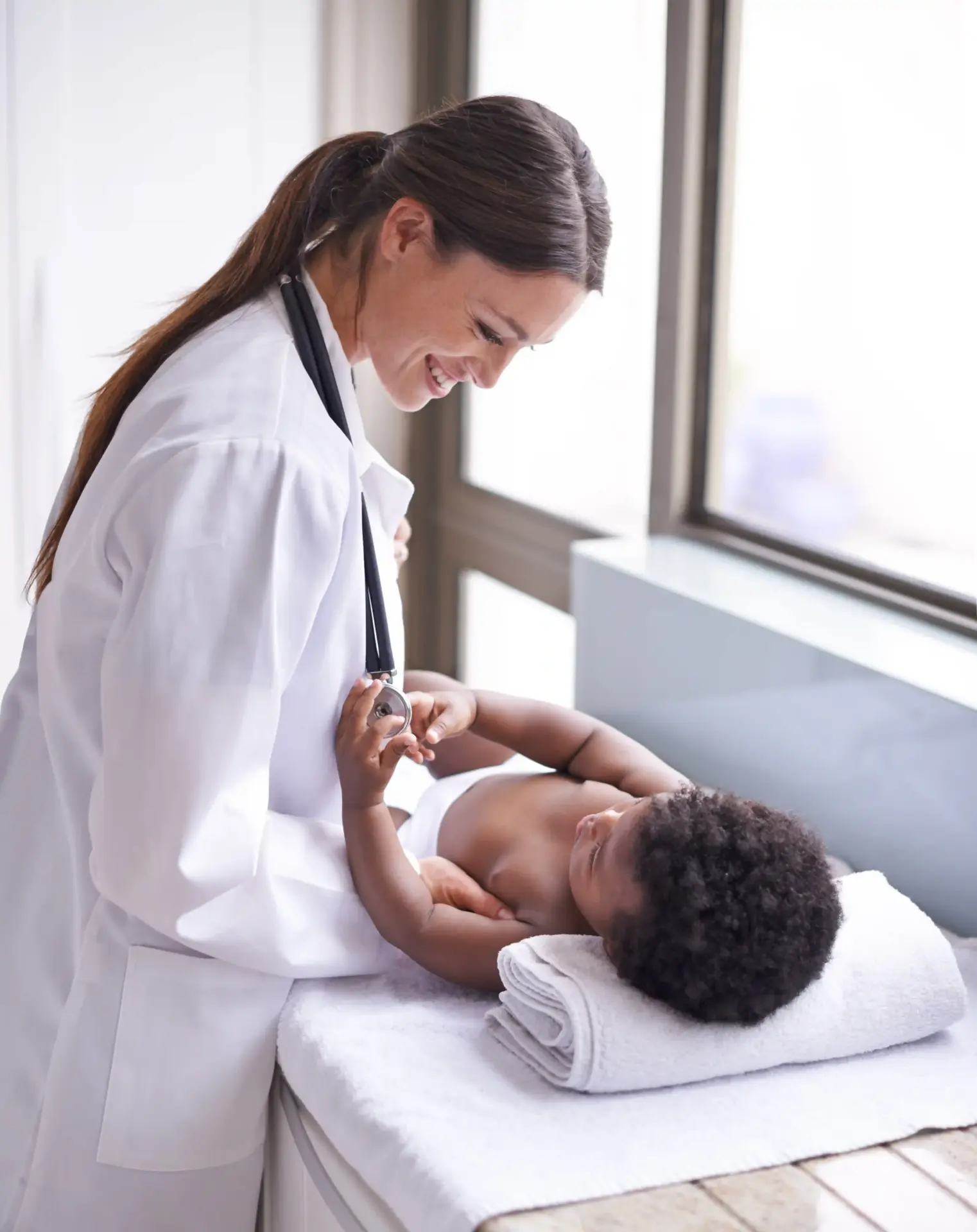
Preventive care follows a strict periodicity schedule designed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. These visits are frequent in the first two years of life to monitor rapid growth.
Visits occur at 1 week, 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 24, and 30 months. After age 3, visits typically become annual.
Each visit has a specific focus, from breastfeeding support in infancy to school readiness in early childhood and risk reduction in adolescence.

Vaccines are the most successful public health intervention in history. They prevent devastating diseases like polio, measles, meningitis, and whooping cough.
The schedule is carefully designed to protect at a time when children are most vulnerable. Combination vaccines reduce the number of shots needed.
Pediatricians spend significant time educating parents on vaccine safety and efficacy, addressing hesitancy with scientific facts.
Growth charts are essential tools. They plot height, weight, and head circumference against population averages. The goal is not for every child to be “average,” but to follow their own consistent curve.
Deviations from the curve—crossing percentiles upwards or downwards—can signal nutritional or hormonal issues.
BMI (Body Mass Index) is tracked starting at age 2 to screen for obesity risks. Head circumference in infants is a measure of brain growth.
Prevention of chronic disease starts with nutrition. Pediatricians advise parents on introducing solids, emphasizing vegetables and a variety of textures.
As children grow, the focus shifts to creating a healthy food environment. This means limiting sugary beverages and processed foods.
Obesity prevention involves family-based changes. The goal is to establish a relationship with food that is nourishing and positive, avoiding restrictive dieting.
Sleep is crucial for physical growth and emotional regulation. Prevention involves establishing healthy sleep habits from a young age.
This includes “back to sleep” protocols for infants to prevent SIDS. For older children, it involves setting consistent bedtimes and limiting screen time before sleep.
Adequate sleep prevents behavioral issues, improves academic performance, and supports the immune system.

Injuries are the leading cause of death in children. Anticipatory guidance is tailored to the child’s age. This covers car seat safety, childproofing the home, and water safety.
For adolescents, safety discussions shift to driving, substance use, and internet safety. Helmet use for bikes and sports is a constant message.
Physicians provide resources on poison control and safe storage of firearms and medications.

Oral health is systemic health. Pediatricians recommend establishing a “dental home” by age one. They apply fluoride varnish to teeth during well visits to prevent cavities.
Advice includes avoiding “bottle rot” by not putting babies to bed with milk and encouraging cup use.
Good oral hygiene habits prevent pain and infection that can affect eating and school attendance.

Regular screening prevents long-term sensory loss. Catching amblyopia (lazy eye) early allows for correction before the brain ignores the visual input.
Hearing protection education is increasingly important with the use of headphones. Protecting ears from noise induced hearing loss preserves communication skills.
Vision screens also detect refractive errors like nearsightedness, ensuring children can see the board at school.
Health is shaped by where children live, learn, and play. Pediatricians screen for food insecurity, housing instability, and exposure to violence.
Addressing these “social determinants” is a form of prevention. Connecting families with food banks or legal aid can improve health outcomes more than medicine alone.
Hometown pediatrics practices often have deep roots in the community, allowing them to effectively link families with local resources.
Prevention includes mental wellness. Building resilience and coping skills helps children manage stress. Encouraging play and unstructured time is vital for development.
Screening for adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) helps identify children at risk for future health problems.
Promoting positive parenting techniques strengthens the parent child bond, which is the foundation of mental health.
Managing the digital landscape is a modern preventive challenge. Excessive screen time is linked to obesity, sleep issues, and developmental delays.
Guidelines recommend creating a “family media plan.” This involves designated screen-free zones and times.
The focus is on high-quality content and co-viewing, rather than on using screens as a digital babysitter.
Skin cancer prevention starts in childhood. A history of blistering sunburns significantly increases melanoma risk later in life.
Guidance includes using broad spectrum sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade.
Infants under 6 months should generally be kept out of direct sunlight. These habits preserve skin health for a lifetime.
Education about bodily changes removes fear and shame. Prevention involves comprehensive sexual health education to prevent STIs and unintended pregnancy.
The HPV vaccine is a cancer prevention tool administered in pre adolescence. It prevents cervical and other cancers caused by the virus.
Open conversations about consent and healthy relationships are part of the preventive health dialogue.
Prevention covers the entire alphabet of health. From a through z pediatrics, the goal is to anticipate needs before they become problems.
This comprehensive approach requires a partnership between the medical team and the family. It is proactive rather than reactive.
By addressing small issues early, the team ensures the child reaches their full genetic potential.
For prevention to work, access must be easy. Searching for pediatrics near me ensures that well visits are not missed due to travel barriers.
Local practices understand the specific risks of the community, whether it be Lyme disease in wooded areas or lead paint in historic cities.
Proximity allows for quick weight checks for newborns and convenient vaccination visits, keeping the preventive schedule on track.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Sports physicals are typically required before the start of a new competitive season to ensure the child is physically capable of participating and to screen for heart conditions or injury risks.
The HPV vaccine is most effective when given at age 11 or 12 because it produces a stronger immune response at this age and must be given before any exposure to the virus occurs.
Teenagers typically need 8 to 10 hours of sleep per night for optimal brain development, mood regulation, and academic performance, though their biological clocks often shift later.
A growth spurt is a period of rapid physical growth in height and weight; infants often experience them, and a major one occurs during puberty, often accompanied by increased appetite and sleep needs.
Newborns are born with low levels of Vitamin K, which is essential for blood clotting; a Vitamin K shot at birth prevents a rare but potentially fatal bleeding disorder called Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding.


Millions of people worldwide suffer from allergies. Over 25 million Americans experience allergic rhinitis, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). We look
Asthma affects millions worldwide, and knowing what triggers symptoms is key. Did you know that asthma triggers can vary a lot from person to person?
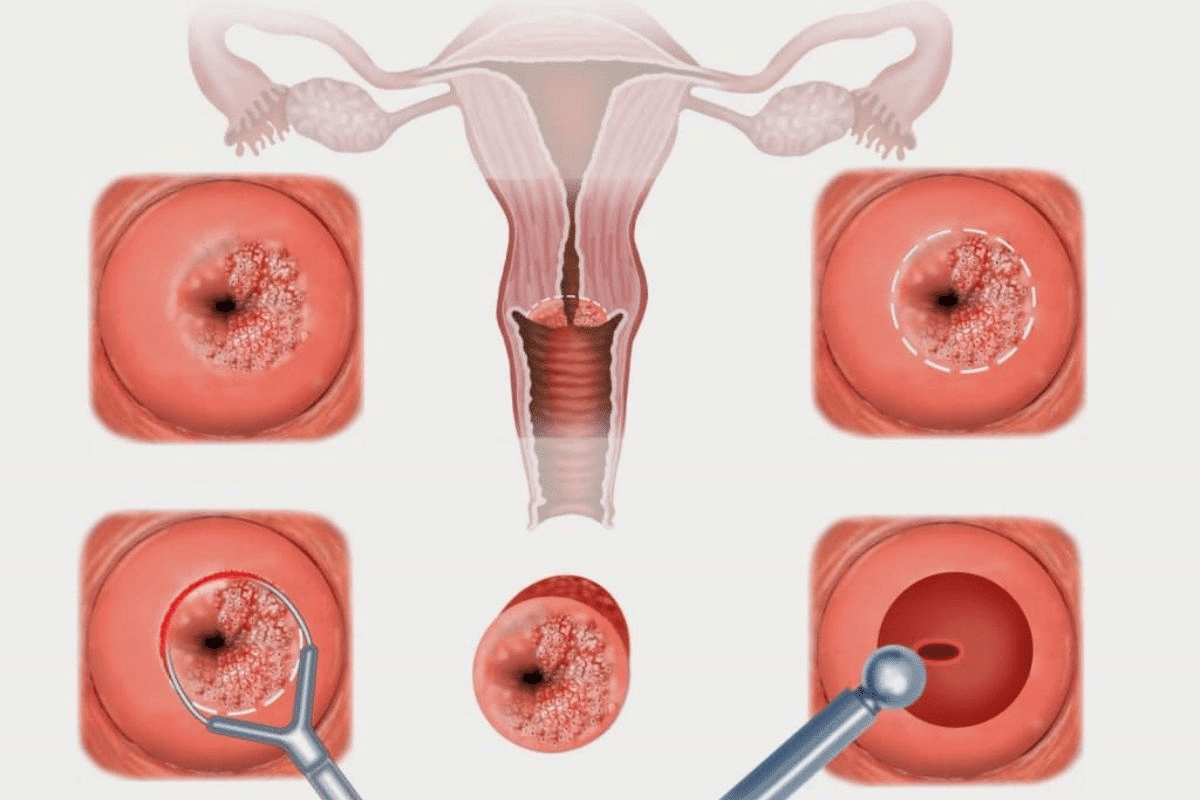
The 7 5 3 rule tonsillectomy guide defines need. specific surgery criteria. Learn the infection frequency that qualifies a child for surgery. Recurrent throat infections
Nearly 1.5 million laparoscopic procedures are done every year in the United States. Many of these involve students who must return to school after their
Nearly 1 in 100 patients who have diagnostic laparoscopy might face some complications. This shows why it’s important to know about the risks involved.The diagnostic
Did you know that advances in medical technology have made anesthesia safer? Recent studies show a big drop in anesthesia-related deaths. Now, we can better

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)