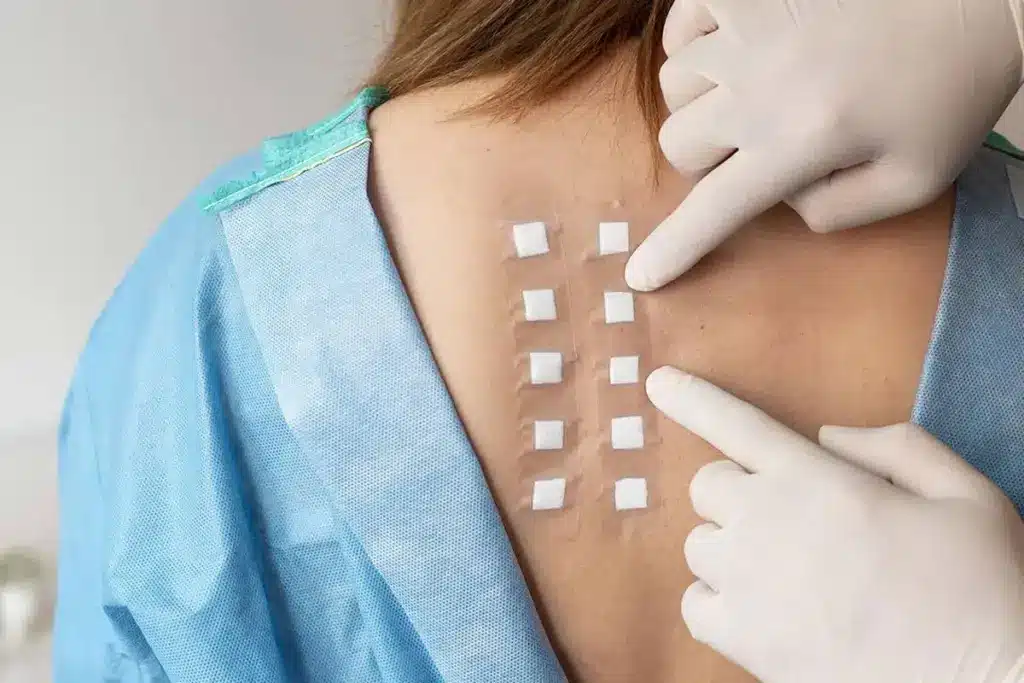
Did you know that nearly 15 million Americans suffer from skin allergies? Some of these reactions can be very severe. Finding out what causes these reactions is key.Detailing how long does a patch test usually take (three visits over 72-96 hours) from application to final reading of results.
An allergy patch test helps figure out if a certain substance causes allergic inflammation. It works by applying small amounts of possible allergens to the skin, usually on the back. Then, the body’s reaction is observed.
Knowing how long a patch test for allergies takes can ease worries. It prepares people for what they’ll experience during the test.
Key Takeaways
- A patch test is used to diagnose skin allergies.
- The test involves applying small amounts of possible allergens to the skin.
- It’s a key step in finding out what causes allergic reactions.
- The test usually lasts a few days.
- Understanding the process can help reduce anxiety for those undergoing the test.
Understanding Patch Tests
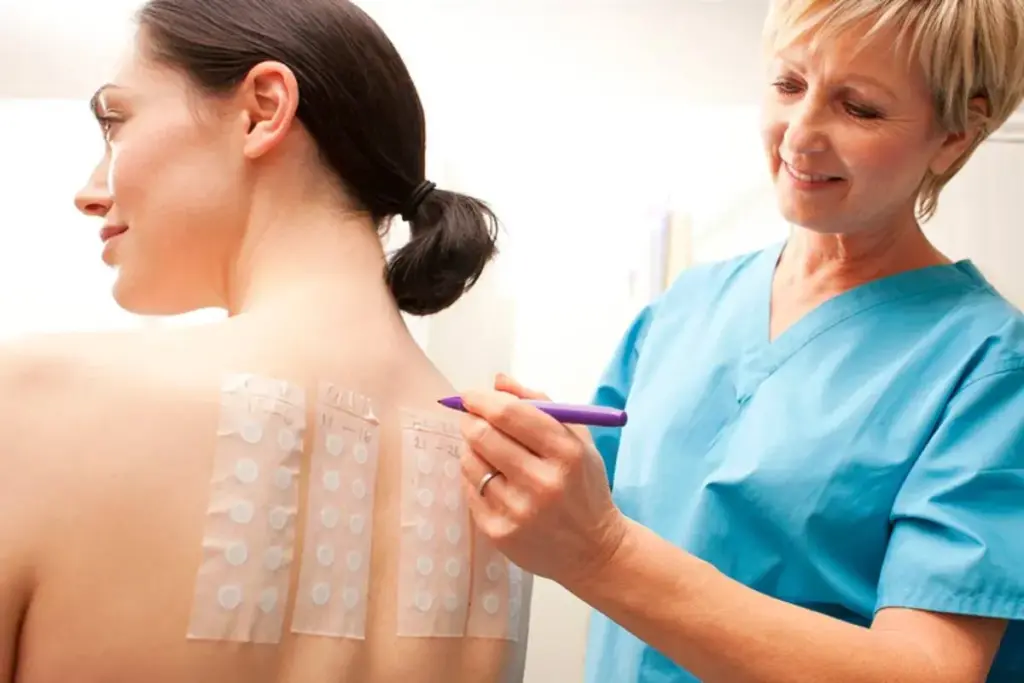
A patch test is a way to see if a substance causes skin allergies. It’s key for doctors to find out what makes skin react. This helps them give the right treatment.
What Is a Patch Test?
A patch test puts small amounts of possible allergens on the skin, usually on the back. Then, it watches for signs of an allergic reaction over a few days. The patch test procedure is easy and doesn’t hurt much, making it safe for people of all ages.
First, a doctor talks with the patient to figure out what to test. Then, the patches are put on the back for 48 hours.
Common Types of Patch Tests
There are many types of patch tests, each for different allergens. The main ones are:
- Standard patch tests, with a set list of allergens.
- Specialized patch tests, for specific substances or ingredients.
- Photopatch tests, for reactions to sunlight.
Each test is made for a specific need, making sure it fits the patient’s situation.
When Patch Tests Are Recommended
Patch tests are suggested for people with allergic contact dermatitis or other skin issues from allergies. Signs like skin rashes, itching, and redness, mainly in areas touched by certain things, might lead to a test.
Doctors also suggest them for those who’ve had skin problems from makeup, jewelry, or other items. The aim is to find the exact allergen, so the patient can avoid it and get the right treatment.
The Complete Patch Test Timeline
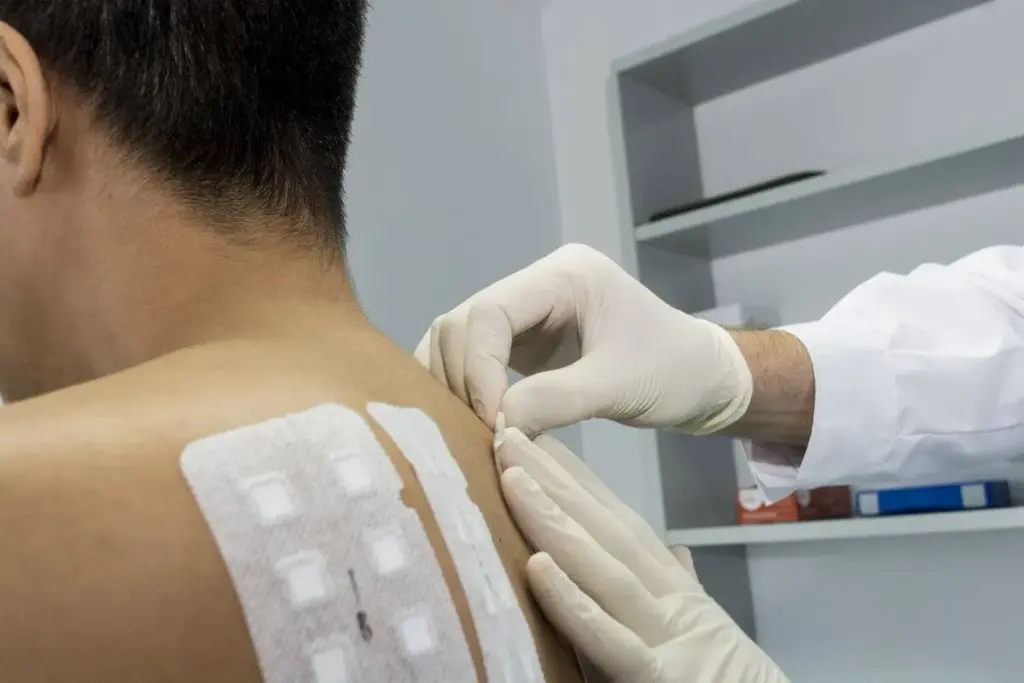
Knowing the timeline of a patch test helps manage expectations and reduces anxiety. A patch test is a multi-step process. It involves several key stages, from the initial consultation to the final reading of results.
Initial Consultation (15-30 Minutes)
The first step is the initial consultation, lasting 15 to 30 minutes. A healthcare professional will assess your skin condition and medical history. They will determine if a patch test is suitable for you.
Application Phase (30-60 Minutes)
The application phase comes after the initial consultation and takes 30 to 60 minutes. In this phase, patches with various allergens are applied to your skin, usually on the back. The healthcare provider will choose the allergens based on your history and symptoms.
Waiting Period (48-96 Hours)
After applying the patches, there’s a waiting period of 48 to 96 hours. During this time, you must keep the patches dry. Avoid activities that could affect the test results.
Final Reading and Results (15-30 Minutes)
The final stage is the final reading and results, taking 15 to 30 minutes. The healthcare provider will check your skin’s reaction to the allergens. They will interpret the results, giving a diagnosis and treatment recommendations if needed.
Understanding the patch test timeline is key for patients. It helps them prepare for the procedure and know what to expect. By following this process, patients can get accurate patch test results. These results help diagnose and manage allergies.
Preparation for Your Patch Test
Edit
Full screen
Delete
patch test preparation
Getting ready for your patch test is very important. You need to follow certain steps before and during the test.
Pre-Test Instructions
Your healthcare provider will tell you what to do before the test. You might need to stop using some skincare products or stop topical corticosteroids on the test area. Also, tell your doctor about any allergies or skin issues you’ve had.
Medications to Avoid
Some medicines can mess up your patch test results. Your doctor might ask you to stop oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs before the test. Also, don’t take antihistamines or certain anti-inflammatory medicines as they can change how your skin reacts.
Skin Preparation Guidelines
Your skin should be clean and without lotions, creams, or oils on test day. Don’t exfoliate or scrub the area where the patches will go. And, don’t shave the area as it can cause irritation and mess up the test.
By following these steps, you can make sure your patch test results are right. This helps your healthcare provider make the best treatment plan for you.
What to Expect During a Patch Test Procedure
Understanding the patch test procedure is key to being ready. It’s a way to find out what causes skin allergies. Small patches with possible allergens are put on your skin. Then, you wait to see how your skin reacts.
Step-by-Step Application Process
The patch test application is simple. First, your skin is cleaned. Then, patches with allergens are placed on your back. They are held in place with tape.
This whole process takes about 30 to 60 minutes.
The steps are:
- Cleaning the skin area
- Preparing the patches with allergens
- Applying the patches to the skin
- Securing the patches with adhesive tape
Common Application Sites
The back is the most common place for patch tests. It’s big and flat, making it easy to keep patches in place. Sometimes, the arms or other areas are used if the allergy is in a specific spot.
Number of Allergens Tested
The number of allergens tested varies. Standard kits have common ones like metals and fragrances. The True Test system has many, usually 30 to 80.
More allergens might be tested if you have a history of allergies. Your doctor will choose the right ones for you.
Duration of Wearing the Patch Test
Edit
Full screen
Delete
patch test duration
The time you wear a patch test is key to getting accurate results. Knowing how long to wear it and what might change that is important. It helps in understanding the test’s success.
Standard 48-Hour Wearing Time
A patch test is usually worn for 48 hours. This lets your skin react to the allergens. It’s important to keep the patches on to get right results.
Patients are told to keep the patches dry and avoid activities that might move them. The 48-hour mark is standard. It’s enough time for most allergic reactions to show up.
Factors That May Extend Testing Duration
But sometimes, the test needs to go longer than 48 hours. If the first reading is unclear, you might need to come back at 72 or 96 hours. Some allergens need more time to cause a reaction.
Activity Restrictions During Testing
To keep the test working, you should avoid some things. Don’t sweat too much, avoid rubbing the patch area, and be careful when showering or bathing. This helps keep the patches in place.
Knowing how long to wear a patch test and following the rules helps. It makes sure your allergy test is done right and accurate.
Follow-Up Appointments and Readings
Edit
Full screen
Delete
patch test follow-up appointments
To find out if you have an allergy, follow-up appointments for patch test readings are key. These visits let doctors check how your skin reacts to different allergens. They then understand the results.
First Reading (48 Hours)
The first check-up is 48 hours after the test. At this time, doctors look at how your skin reacted to the allergens. This first look is important for spotting any allergic signs.
Second Reading (72-96 Hours)
Then, a second check is set for 72 to 96 hours later. This is because some reactions might not show up right away. The second check helps confirm the findings and see how strong the reaction is.
Additional Readings If Necessary
Sometimes, more tests are needed beyond the first two. This could be because reactions take longer to appear or to get clearer results. Your doctor will decide if more visits are needed based on your test results.
It’s very important to keep your follow-up appointments. This ensures you get a correct diagnosis and the right treatment plan. By sticking to these appointments, you can learn about your allergies and how to avoid them.
Managing Daily Life During Your Patch Test
When you’re doing a patch test, you need to make some changes to your daily routine. This is to get accurate results. You have to manage your daily activities carefully to keep the patches in place.
Showering and Bathing Restrictions
Keeping the patches dry is key during a patch test. Avoid showering or bathing for the first 48 hours or as your doctor tells you. If you must clean up, use a damp cloth. Be very careful around the patches.
Some tests come with a waterproof cover for showering. If you get one, follow your doctor’s instructions on how to use it.
Exercise and Physical Activity Limitations
Stay away from activities that make you sweat a lot during the test. Sweat can loosen the adhesive and mess up the test results.
- Avoid heavy lifting or bending.
- Limit your participation in sports or strenuous activities.
- Try to stay cool to minimize sweating.
Sleeping Comfortably With Patches
Sleeping with patches can be tough, but there are ways to make it easier. Try to sleep on your back if the patches are on your back. Or use a soft, breathable fabric to cover the area if the patches are on your front or arms.
If the patches start to peel off while you sleep, talk to your doctor. They can give you tips on how to keep them in place.
Interpreting Patch Test Results
Understanding patch test results is key. After the patches are taken off, the skin is checked for reactions. These can be mild redness or more serious responses.
Understanding Reaction Grades
Reaction grades show how severe the skin’s reaction is. The scale goes from 0 (no reaction) to +++ (strong reaction). A positive reaction means redness, swelling, or small blisters.
The grading is as follows:
|
Grade |
Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
No reaction |
|
+ |
Mild reaction (erythema, mild edema) |
|
++ |
Moderate reaction (erythema, edema, possible vesicles) |
|
+++ |
Strong reaction (severe erythema, edema, vesicles, or bullae) |
Positive vs. Negative Results
A positive result means you’re allergic to the tested substance. The reaction’s severity shows how sensitive you are. A negative result means you’re not allergic.
Delayed Reactions
Some reactions may not show up right away. They can appear days later. These delayed reactions are important to catch, as they affect diagnosis and treatment.
It’s vital for patients to talk to their healthcare provider about the results. They’ll discuss what steps to take next.
True Test Patch Test System
If you think you might have allergic contact dermatitis, the True Test patch test system can help. It’s designed to find out what’s causing your skin problems. This way, you can get the right treatment.
Components and Allergens
The True Test system comes with pre-prepared patches filled with common allergens. These patches are put on your skin to see how you react. It checks for things like metals, fragrances, and preservatives, which often cause skin issues.
The standard panel tests for about 35 allergens. But, this number can change with different versions of the True Test. The choice of allergens is based on lots of research and data to match what most people might be allergic to.
Advantages of the True Test System
The True Test system is known for its standardization. Using pre-made patches helps make sure results are the same everywhere. This makes it easier for doctors to use and get reliable results.
- Ease of use for healthcare providers
- Consistency in allergen concentration
- Comprehensive coverage of common allergens
Limitations of the True Test
Even though the True Test system works well, it has some limitations. It only tests for a set list of allergens. If you’re exposed to something not on that list, you might need more tests.
Also, getting the patches right and reading the results needs a doctor who knows what they’re doing. This ensures you get accurate results.
Specialized Patch Tests for Different Allergies
Allergy testing has grown to include special patch tests for various allergies. This helps doctors give more accurate diagnoses to patients with different allergies.
These specialized patch tests meet the needs of many patients. They help those allergic to cosmetics, metals, or certain medicines.
Cosmetic Ingredient Series
The cosmetic ingredient series is a special patch test for personal care product allergies. It checks for common allergens like fragrances, preservatives, and dyes.
- Fragrance mix
- Preservatives like parabens
- Dyes such as p-phenylenediamine
This series helps doctors find out which ingredient is causing the allergy. This way, patients can avoid it in the future.
Metal Allergy Testing
Metal allergy testing is vital. Metals like nickel, cobalt, and chromium often cause skin reactions.
“Metal allergy testing is essential for individuals who experience skin reactions to jewelry, clothing, or other metal-containing items.”
— American Academy of Dermatology
To test for metal allergy, small amounts of these metals are applied to the skin. Then, any bad reactions are observed.
Medication and Adhesive Testing
Special patch tests also check for allergies to medications and adhesives. This is key for patients needing treatments with these substances.
|
Allergen Type |
Common Allergens |
Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
Medications |
Antibiotics, NSAIDs |
Skin rash, itching |
|
Adhesives |
Acrylates, epoxy resins |
Contact dermatitis, blistering |
These tests help doctors find out which allergens are causing problems. They can then give better advice and treatment to their patients.
Potential Side Effects and Complications
It’s important to know about possible side effects and complications of patch testing. Patch testing is usually safe, but it can have risks like any medical procedure.
Common Reactions During Testing
Some people may have common reactions during the patch test. These include:
- Redness and irritation at the patch site
- Itching or burning sensations, which can vary in severity
- Swelling or blistering in rare cases
Managing Discomfort
To deal with discomfort during the test:
- Avoid scratching the patches or the area around them
- Keep the patch area dry and avoid too much sweating
- If discomfort is bad, talk to your doctor
Topical corticosteroids might be suggested to help with itching and swelling. But, it’s key to follow your doctor’s advice on using them.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Knowing when to see a doctor is important. Call your doctor if you have:
- Severe reactions that can’t be handled with usual treatments
- Symptoms that keep getting worse or don’t go away
- Any signs of an allergic reaction outside the patch test area
Being aware of these side effects and knowing how to handle them can make patch testing safer and more effective.
Special Considerations for Different Populations
It’s important to understand the special needs of different groups when it comes to patch testing. This helps in making accurate diagnoses and treatments. Healthcare providers must consider these unique needs when doing patch tests.
Patch Testing in Children
Children have sensitive skin and can react badly to patch tests. The test is similar to for adults but with some changes:
- Reduced number of allergens tested
- Lower concentration of test substances
- Careful monitoring for reactions
Key considerations include the child’s age, skin maturity, and ability to cooperate. Parents play a big role in watching for skin reactions and reporting any issues.
Patch Testing During Pregnancy
Patch testing during pregnancy is usually safe, but there are precautions. The main goal is to avoid exposing the fetus to possible allergens.
Important guidelines include:
- Avoiding patch testing during the first trimester unless absolutely necessary
- Using the minimum number of allergens required for diagnosis
- Monitoring fetal development closely
Healthcare providers must carefully consider the benefits and risks of patch testing for the fetus.
Patch Testing in Elderly Patients
Elderly patients face special challenges with patch testing. Their skin is thinner and less protective. Other things to consider include:
- Increased risk of irritation
- Potential interactions with other skin conditions
- Medications that may affect test results
A thorough medical history is key to understanding any factors that could affect the test results.
Patch Testing vs. Other Allergy Tests
Patch testing is a key tool in finding allergies. But, it’s not the only way. Knowing how it compares to skin prick and blood tests is important.
Patch Tests vs. Skin Prick Tests
Patch tests and skin prick tests help find allergies. But, they’re used for different things. Skin prick tests find quick reactions. Patch tests find reactions that take longer.
Key differences between patch tests and skin prick tests:
- Patch tests apply allergens to the skin with a patch, left on for 48-96 hours.
- Skin prick tests prick the skin with a small allergen amount and check the reaction after 15-20 minutes.
Patch Tests vs. Blood Tests
Blood tests check IgE antibodies in the blood for specific allergens. Unlike patch tests, blood tests don’t need skin and can be used when skin testing can’t be done.
|
Test Type |
Patch Tests |
Blood Tests |
|---|---|---|
|
Measures |
Delayed hypersensitivity reactions |
IgE antibodies in the blood |
|
Application |
Direct skin application |
Blood sample required |
When Each Test Is Most Appropriate
Choosing between patch, skin prick, and blood tests depends on the situation. Patch tests are best for contact dermatitis. Skin prick tests are for quick allergic reactions.
Choosing the right test:
- Use patch tests for suspected contact dermatitis or delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
- Use skin prick tests for immediate hypersensitivity reactions.
- Use blood tests when skin testing is not feasible or to measure IgE levels.
Cost and Insurance Coverage for Patch Testing
Many people worry about the cost of patch testing. It’s important to know how much it costs and what insurance covers. This helps patients make smart choices about their health.
Average Costs in the United States
The average cost of patch testing in the U.S. can change a lot. It depends on how many allergens are tested, where you get the test, and the doctor’s fees. Usually, it costs between $200 to $800 or more for the whole thing.
These costs include the patches, the first visit, follow-up meetings, and understanding the results.
Insurance Coverage Considerations
Insurance coverage for patch testing varies. Many plans cover it as part of dermatology services. But, how much they cover can be different.
It’s a good idea to talk to your insurance about what’s covered. Find out about any costs you might have to pay, like copays or deductibles.
Questions to Ask Your Provider
When talking to your doctor about patch testing, ask some key questions. This will help you understand the costs and what your insurance covers:
- What is the total cost of the patch testing procedure?
- How many allergens will be tested, and are there additional costs for more extensive testing?
- What portion of the costs is covered by my insurance?
- Are there any additional fees for follow-up appointments or further analysis?
Knowing about the costs and insurance can help you make better choices. It ensures you get the care you need without breaking the bank.
Conclusion
Patch testing is key in finding skin allergies and keeping skin healthy. It involves putting patches with certain allergens on the skin, usually on the back. Then, you watch for reactions over a few days.
Knowing how patch testing works is vital for getting the right diagnosis and treatment. The test starts with applying patches, then checks the skin at 48 hours and sometimes again between day 3 to 7. Some reactions might show up at 96 hours or later. This shows why it’s important to wait for all readings.
For more on when to do patch test readings, check the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and website.
Learning about patch testing helps you take care of your skin better. It’s useful whether you’re dealing with ongoing skin issues or just want to know more about your skin. Patch testing gives you important information about your skin health.
FAQ
What is a patch test, and how does it work?
A patch test helps find out if you’re allergic to something. You put a small amount of the possible allergen on your skin, usually on your back. Then, you watch how your skin reacts over a few days.
How long does a patch test usually take?
A patch test usually lasts for 48 hours. After that, you get your skin checked again at 48 and 72-96 hours.
What should I avoid doing during a patch test?
Try not to shower too much or do hard exercise during a patch test. Also, avoid sweating a lot, as it can mess up the results.
Can I continue my regular skincare routine while undergoing a patch test?
No, it’s best to skip using skincare products, lotions, or creams on the tested area. They might affect the test’s accuracy.
What are the common allergens tested in a patch test?
Tests often check for metals like nickel and cobalt, fragrances, preservatives, and some medications. It depends on what you need tested.
How do I interpret my patch test results?
Results are based on how your skin reacts to the allergen. The more severe the reaction, the higher the grade.
What is the True Test patch test system?
The True Test is a ready-made patch test system. It has a set of common allergens. It makes testing easier and more consistent.
Are there any side effects or complications associated with patch testing?
Mostly, patch testing is safe. But, you might see some redness or itching. Rarely, it can be more serious. Always talk to a doctor if you’re worried.
How much does a patch test cost, and is it covered by insurance?
Costs vary based on where you go and who you see. Many insurances cover it, but check with your provider first.
Can children and pregnant women undergo patch testing?
Yes, kids and pregnant women can get tested. But, it’s important to talk to a doctor first to make sure it’s safe.
How does patch testing compare to other forms of allergy testing?
Patch testing is for skin allergies. It’s different from skin prick tests and blood tests, which check for other types of allergies. The right test depends on your symptoms and health history.
References
The Lancet. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(10)60254-6/fulltext