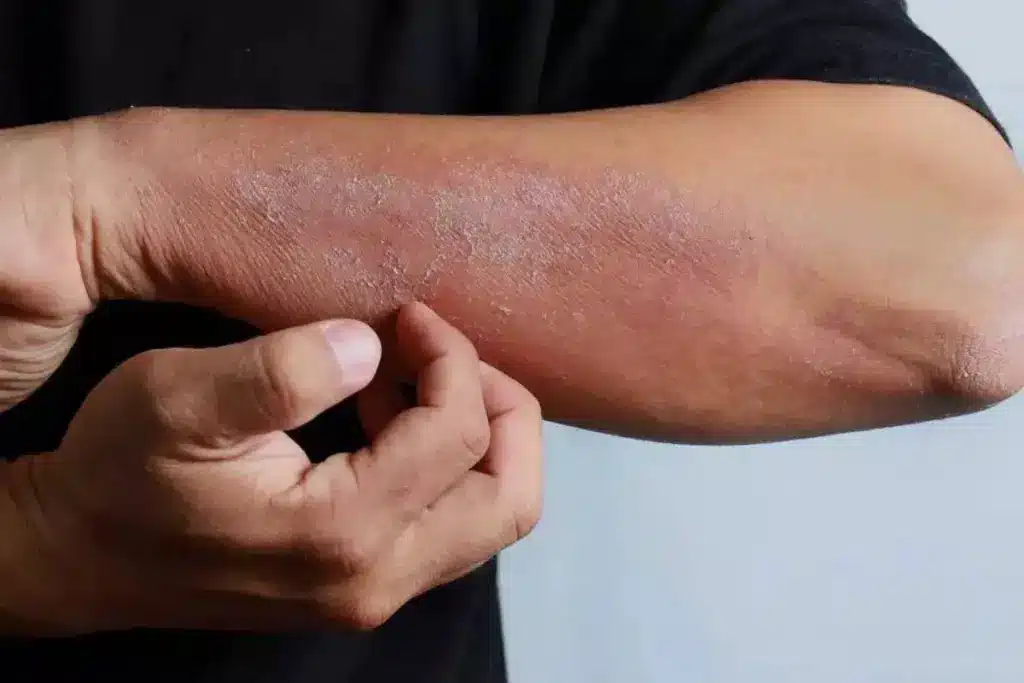
Up to 1% of people worldwide will get chronic hives at some time. This makes it a big skin problem that touches millions of lives.
Dealing with itchy, raised welts is tough. Chronic hives, or chronic urticaria, means these welts keep coming back. They can stick around for more than six weeks.
This condition can be either acute or chronic. The chronic kind lasts longer and needs more care. There are treatments, like antihistamines for hives, to help ease symptoms and make life better.
Getting the right diagnosis and hives treatment is key to handling it well. We’ll dive into chronic hives, its causes, symptoms, and treatments. This will help you understand this complex issue better.
Key Takeaways
- Chronic hives affect up to 1% of the global population.
- The condition is characterized by itchy, raised welts that last more than six weeks.
- Chronic urticaria requires thorough management.
- Antihistamines are a common treatment for hives.
- Proper diagnosis is vital for effective treatment.
What Are Chronic Hives?
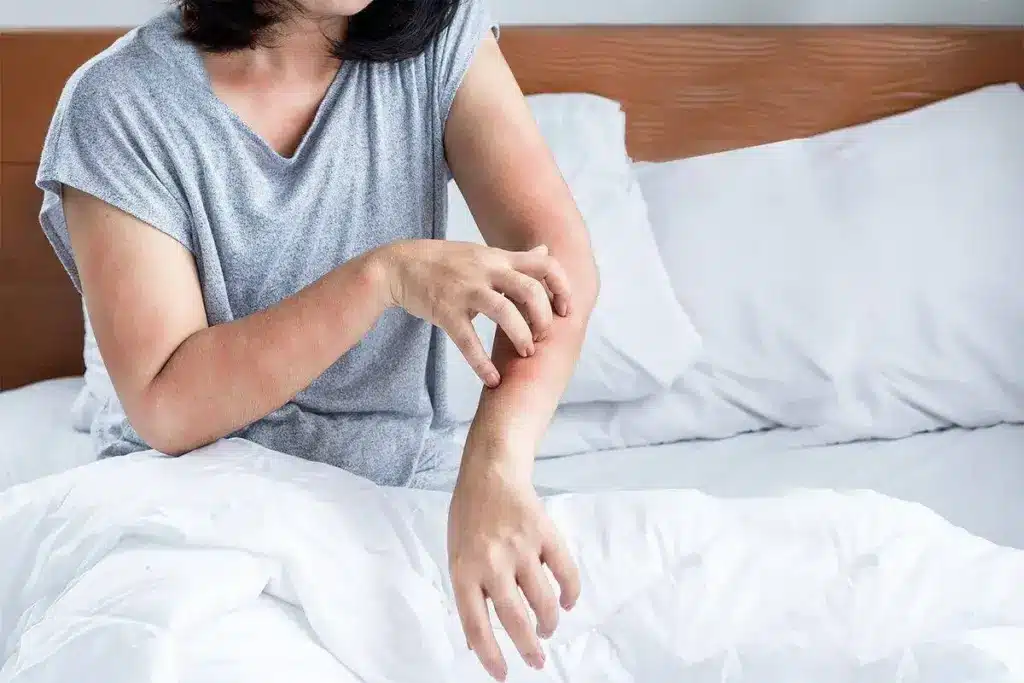

Chronic hives, or chronic urticaria, is a condition that affects many people worldwide. It causes discomfort and impacts quality of life. Understanding chronic hives involves looking at their definition, symptoms, and what keeps them going.
Definition and Symptoms
Chronic hives are marked by recurring wheals (hives) or swelling that lasts over six weeks. Symptoms vary, from mild to severe. The wheals associated with chronic hives are itchy, red, and can pop up anywhere on the body.
The condition affects not just the body but also mental health and daily life. Identifying symptoms accurately is key to managing it well.
Causes of Chronic Hives
Chronic hives have many causes, including autoimmune disorders, infections, and certain medications. Stress, temperature extremes, and some foods can also trigger it. Medications like doxycycline can cause hives in some people.
Knowing the cause is important for managing the condition. We’ll look at different triggers and how to handle them.
Duration and Persistence
Chronic hives can last months or even years. The length of time they last varies a lot. Factors like the cause, treatment, and how well someone responds to it play a role.
So, how long does urticaria last? It depends on the cause and treatment. Some cases may get better on their own, while others need ongoing care.
The Role of Medications in Chronic Hives
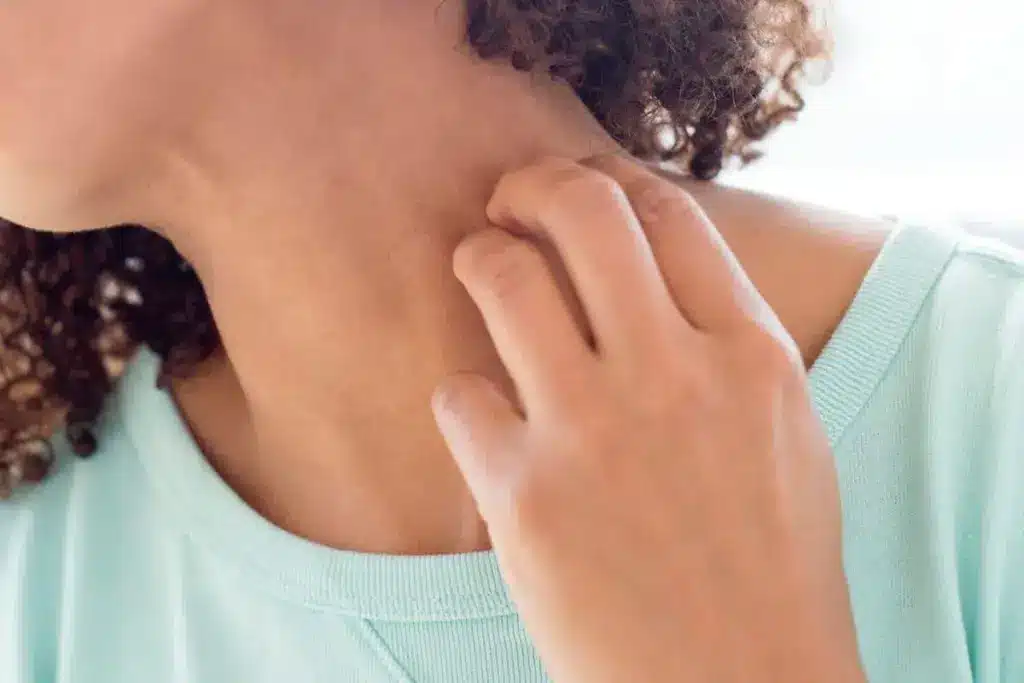
Medications are key in both causing and treating chronic hives. Some drugs can make hives worse, while others help manage them. It’s important to understand this to manage the condition well.
Common Medications That May Trigger Hives
Many medications can trigger chronic hives. Antibiotics like doxycycline are common culprits. Other drugs that may cause hives include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Certain pain relievers
- Some antidepressants
People with chronic hives should know these triggers. They should talk to their doctor about their medications.
Over-the-Counter vs. Prescription Drugs
OTC and prescription drugs have different roles in managing chronic hives. OTC antihistamines can help some, but others may react to them. Prescription drugs are often stronger and can be customized for each person.
We suggest talking to your doctor before changing any medication. This ensures your treatment plan is right for you.
Drugs to Avoid with Urticaria
For those with urticaria, it’s key to know which medicines to avoid. Urticaria, or hives, can get worse with certain drugs. This makes managing medications a big part of controlling symptoms.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs help with pain and swelling. But, for some with urticaria, they can make symptoms worse. Aspirin and ibuprofen are examples. Always talk to a doctor before taking NSAIDs.
|
NSAID |
Common Use |
Potential Impact on Urticaria |
|---|---|---|
|
Aspirin |
Pain relief, anti-inflammatory |
May trigger or worsen symptoms |
|
Ibuprofen |
Pain relief, anti-inflammatory |
Can exacerbate symptoms in some individuals |
|
Naproxen |
Pain relief, anti-inflammatory |
Potential to trigger or worsen urticaria |
Antibiotics and Antihistamines
Antihistamines help treat urticaria, but some antibiotics can cause allergic reactions. Penicillin and sulfonamide antibiotics are common culprits. Watch for any allergic reactions closely.
- Penicillin antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin)
- Sulfonamide antibiotics (e.g., sulfamethoxazole)
Antihistamines like diphenhydramine and loratadine are good for urticaria. But, always follow your doctor’s advice on using them.
Opioids and Other Pain Relievers
Opioids, like codeine and morphine, can make urticaria symptoms worse. Talk to your doctor about other pain relief options.
Understanding which medicines can affect urticaria is key. Knowing the triggers and working with your doctor can help manage symptoms. This improves life quality for those with urticaria.
Other Triggers Beyond Medication
Many things can cause or make chronic hives worse, not just medicine. Knowing what these are is key to handling them well.
Food Allergens
Some foods can set off or make hives worse in people who are sensitive. Shellfish, nuts, and dairy are often to blame. Staying away from these can help a lot.
Environmental Factors
Things around us can also trigger hives. This includes very hot or cold weather, sunlight, and stress. Figuring out how these affect us can help us manage our symptoms better.
|
Trigger Category |
Common Triggers |
|---|---|
|
Food Allergens |
Shellfish, Nuts, Dairy Products |
|
Environmental Factors |
Temperature Extremes, Sunlight, Stress |
By tackling these triggers, people can keep their chronic hives under control.
Managing Chronic Hives Effectively
To manage chronic hives well, it’s important to understand the condition. You should also identify what triggers them and make lifestyle changes and use medical treatments. By being proactive, you can lessen how often and how bad hives get.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Making lifestyle changes can help a lot with chronic hives. Avoiding known triggers is a big first step. This means changing your diet to avoid allergens, finding ways to relax, and staying away from extreme temperatures or sunlight.
Home remedies can also help. A cool compress on the affected area can ease itching and swelling. Oatmeal baths are also good, as oatmeal is anti-inflammatory and soothing.
“One of the most effective ways to manage chronic hives is through a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical therapy. Identifying and avoiding triggers is key.”
An Dermatologist
- Avoid tight clothing that can irritate the skin.
- Use gentle, fragrance-free soaps and cleansers.
- Keep a cool environment to reduce sweating.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
While you can manage chronic hives on your own, sometimes you need medical help. If your hives are severe, last a long time, or come with other symptoms like trouble breathing, get help right away.
|
Symptom |
Action |
|---|---|
|
Mild hives with no other symptoms |
Manage with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications |
|
Severe or persistent hives |
Consult a healthcare provider for prescription medication |
|
Hives with difficulty breathing or swallowing |
Seek emergency medical care |
Seeing a healthcare provider regularly is important. They can help keep an eye on your condition, change your treatment plan if needed, and answer any questions you have.
Treatment Options for Chronic Hives
Chronic hives treatment has grown, giving patients many choices. We’ll look at antihistamines and corticosteroids, key treatments for symptoms.
Antihistamines and Their Effectiveness
Antihistamines are a top choice for chronic hives. They help with itching and make hives less visible. The best antihistamine for hives depends on the person’s symptoms and how well they handle medicine.
Some common antihistamines for hives are:
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- Loratadine (Claritin)
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- Fexofenadine (Allegra)
These drugs block histamine, a chemical that makes blood vessels swell and causes hives. Antihistamines are usually effective but can cause side effects like drowsiness or dry mouth.
|
Antihistamine |
Common Brand Name |
Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
|
Diphenhydramine |
Benadryl |
Drowsiness, dry mouth |
|
Loratadine |
Claritin |
Headache, fatigue |
|
Cetirizine |
Zyrtec |
Drowsiness, stomach upset |
|
Fexofenadine |
Allegra |
Dizziness, nausea |
Corticosteroids for Severe Cases
For severe chronic hives, corticosteroids are used. They reduce inflammation and help symptoms. Corticosteroids are strong anti-inflammatory drugs given orally or by injection.
Though effective for severe hives, corticosteroids are used short-term due to side effects. These include weight gain, mood changes, and higher infection risk.
Healthcare providers carefully choose the treatment for chronic hives. They consider the symptoms’ severity, medical history, and individual needs.
The Importance of Keeping a Symptom Diary
Keeping a symptom diary is a powerful way to manage chronic hives. It helps you track your symptoms and find what triggers them. This way, you can make better choices for your health.
Identifying Triggers Through Detailed Tracking
Tracking your symptoms and possible triggers can reveal patterns. This is key in finding out what foods, environments, or medicines might cause your hives.
For example, a diary can show how your body reacts to certain foods or stress. It gives you clues about what might be causing your hives.
Effective Tips for Maintaining a Symptom Diary
To make the most of a symptom diary, be consistent and detailed. Here are some tips:
- Be Detailed: Write down the date, time, and how bad your symptoms are.
- Note Possible Triggers: List any foods, medicines, or environments that might cause your hives.
- Track Your Activities: Record your daily activities, including stress and any changes in your routine.
Being consistent is important. By tracking your symptoms and triggers, you can understand your condition better. This helps you make better health choices.
|
Symptom Diary Entry |
Date |
Time |
Symptom Severity |
Potential Triggers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
2023-03-01 |
08:00 |
Mild |
New medication |
|
2 |
2023-03-02 |
12:00 |
Moderate |
Consumed shellfish |
|
3 |
2023-03-03 |
18:00 |
Severe |
High stress level |
By looking at your diary, you and your doctor can create a better plan for managing your hives.
The Impact of Chronic Hives on Quality of Life
Chronic hives can really change a person’s life. It’s not just about feeling itchy and uncomfortable. It also affects your mental health and how you feel emotionally.
Mental Health and Emotional Well-being
Living with chronic hives can be really tough on your mind. The itching, discomfort, and unpredictable outbreaks can make you feel frustrated, anxious, and even depressed. These feelings can make it hard to do everyday things, sleep well, and connect with others.
The emotional burden is huge. Many people feel isolated or embarrassed about their condition. It’s important to see the mental health side of chronic hives and treat it as part of the whole plan.
Support Groups and Resources
Support groups and resources are key for dealing with chronic hives. Meeting others who face the same challenges can offer emotional support, useful advice, and a sense of belonging.
Looking into different resources is a good idea. This includes online forums, local support groups, and educational materials. They can help you understand your condition better, manage symptoms, and improve your life quality.
|
Resource Type |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Online Forums |
Platforms for individuals to share experiences and advice |
Emotional support, practical tips, community connection |
|
Local Support Groups |
In-person meetings for those affected by chronic hives |
Face-to-face support, local resources, shared understanding |
|
Educational Materials |
Information on managing chronic hives and related conditions |
Better understanding of the condition, improved symptom management |
Conclusion: Navigating Chronic Hives
Managing chronic hives needs a full plan. This includes knowing the condition, finding what triggers it, and handling symptoms well. We’ve looked at chronic hives from many angles. This includes how medicines work, other things that can cause hives, and the value of keeping a symptom diary.
Key Takeaways for Effective Management
Good management of chronic hives mixes lifestyle changes, home fixes, and doctor’s treatments. We talked about treatments like antihistamines and corticosteroids. It’s key to see a doctor to find the best treatment.
Taking the Next Steps
To handle symptoms well, being active and informed is key. Knowing what causes chronic hives and what triggers it helps make a personal plan. This plan can improve life quality.
Working closely with a doctor is important to put these plans into action. Adjustments might be needed. A proactive and informed approach can lessen the effect of chronic hives on daily life. It can also boost overall well-being.
FAQ
What are chronic hives, and how do they differ from acute hives?
Chronic hives are itchy, raised welts that last more than six weeks. They differ from acute hives, which are usually caused by an allergic reaction and go away in a few days. Chronic hives can keep coming back over time.
What causes chronic hives?
Many things can cause chronic hives, like autoimmune disorders or thyroid disease. Sometimes, we can’t find out what causes them.
How long does urticaria typically last?
Urticaria can last a different amount of time for everyone. Acute urticaria usually goes away in a few days to weeks. But chronic urticaria can last months or even years.
Can certain medications trigger or worsen hives?
Yes, some medicines like NSAIDs, antibiotics, and opioids can make hives worse. Always talk to your doctor about your medicines to find out if they might be the problem.
What is the role of antihistamines in treating chronic hives?
Antihistamines are often used to treat chronic hives. They help with itching and make welts less noticeable. But, not all antihistamines work for everyone, so your doctor might suggest other options.
Will Benadryl help with hives?
Benadryl, an over-the-counter antihistamine, can help some people with hives. But, it’s important to only take it as directed and talk to your doctor first.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage chronic hives?
Yes, making some lifestyle changes can help manage chronic hives. Avoiding known triggers, keeping a symptom diary, and finding ways to reduce stress can be helpful.
How can I identify my hives triggers?
Keeping a symptom diary can help you figure out when your hives happen and what might cause them. Working with your doctor can also help find the root cause of your hives.
What are some home remedies for urticaria rash?
Some home remedies like cool compresses, oatmeal baths, or topical creams might help with symptoms. But, always check with your doctor before trying new remedies.
When should I seek medical attention for my hives?
If your hives are very bad, don’t go away, or you have other serious symptoms like trouble breathing or a fast heartbeat, get help right away.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC12333250/










