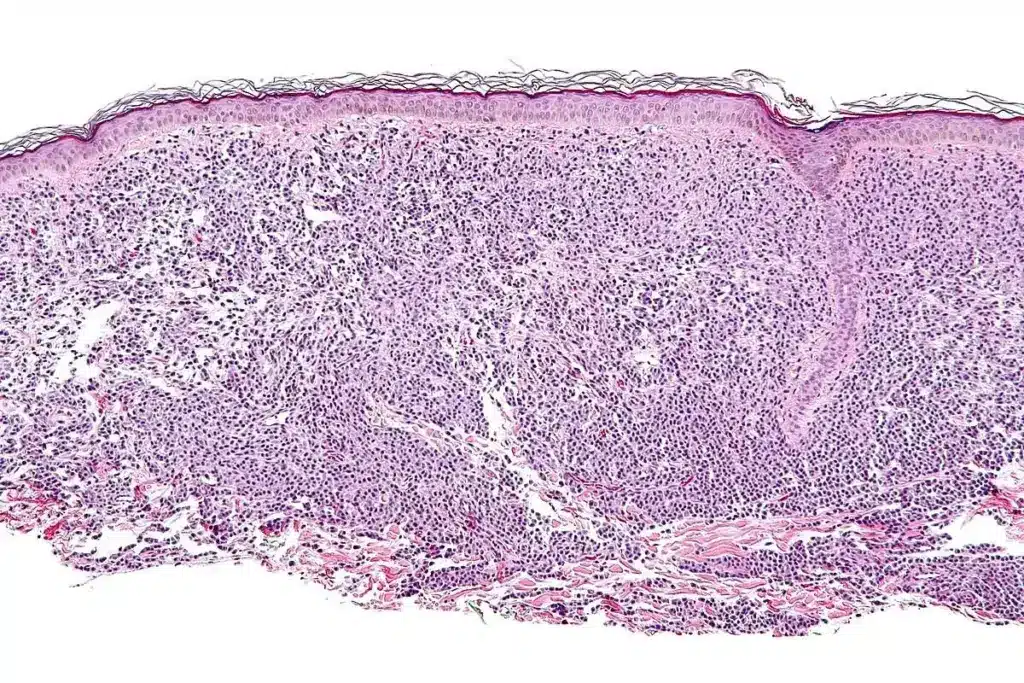
A skin biopsy is a common test used to find out what’s wrong with your skin. It helps doctors figure out if you have skin cancer or just a rash. Over 1 million skin biopsies are done every year in the United States. This makes it a key tool for skin doctors.
So, what is a skin biopsy? The Medical organization says it’s a way to take cells or skin samples from your body. These samples are then tested in a lab. The depth of the biopsy changes based on the type of test done.
Explaining how deep does a skin biopsy go depending on the type of bypsee (epidermis, dermis, or subcutaneous fat).
Key Takeaways
- A skin biopsy is used to diagnose various skin conditions.
- The procedure involves removing skin samples for lab testing.
- The depth of the biopsy varies based on the type of biopsy.
- Skin biopsies are a common diagnostic tool in dermatology.
- Over 1 million skin biopsies are performed annually in the US.
Understanding Skin Biopsies
A skin biopsy is a medical procedure that removes a small skin sample for detailed examination. It’s a key tool in dermatology for understanding skin conditions.
What is a Skin Biopsy?
A skin biopsy takes a skin tissue sample for microscopic study. It’s a simple procedure done in a dermatologist’s office. Doctors can diagnose or rule out certain skin conditions like skin cancer and actinic keratosis by examining the sample.
Why Are Skin Biopsies Performed?
Skin biopsies help diagnose or rule out skin conditions and diseases. The Medical organization says they’re vital for identifying skin cancer. Here are the main reasons for a skin biopsy:
|
Condition |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Skin Cancer |
Diagnose or rule out various forms of skin cancer, including melanoma. |
|
Actinic Keratosis |
Examine suspicious lesions that could be precancerous. |
|
Blistering Skin Disorders |
Investigate the cause of blistering conditions like pemphigus. |
The Anatomy of Skin and Biopsy Depth
[PLACE THE IMAGE HERE]
To understand how deep a skin biopsy goes, we need to know about the skin’s layers. The skin is the body’s largest organ and protects us from the outside world.
Layers of the Skin
The skin has three main layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat. The epidermis is the outer layer, acting as a shield against harm. Underneath, the dermis has blood vessels, nerve endings, and hair follicles.
The deepest layer, subcutaneous fat, is made of fatty tissue. It connects the dermis to muscles and bones below.
How Depth Relates to Diagnostic Goals
The depth of a skin biopsy depends on what the doctor wants to find. For surface issues, a biopsy might just look at the epidermis. But for deeper problems, like some inflammatory or cancerous conditions, the biopsy needs to go deeper.
Knowing the diagnostic goals helps decide how deep the biopsy should be. This makes sure the tissue taken is right for the test.
Types of Skin Biopsies and Their Depths
There are many types of skin biopsies, each with its own depth. The type chosen depends on the suspected condition and the skin layer involved.
Shave Biopsy – Superficial Depth
A shave biopsy removes the top skin layers with a special tool. It’s used for surface skin issues and doesn’t go deep. It’s good for diagnosing basal cell carcinoma or seborrheic keratosis.
Shave biopsies are simple and rarely need stitches. But, they’re not for deeper skin problems.
Punch Biopsy – Medium Depth
A punch biopsy takes a small, cylindrical skin sample with a circular blade. It goes deeper than a shave biopsy, into the dermal layer. It’s good for diagnosing melanoma or dermatitis.
Punch biopsies are quick and give a deeper sample than shave biopsies. This is helpful for some diagnoses.
Excisional Biopsy – Full Depth
An excisional biopsy removes the whole lesion or a big skin sample. It’s used for deep or widespread skin issues, like melanoma.
Excisional biopsies are more invasive and might need stitches. They give detailed info for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The Punch Biopsy Procedure in Detail
A punch biopsy removes a small, circular skin sample. It’s key for figuring out if skin lesions are harmless or cancerous. This simple yet powerful tool is a cornerstone in dermatology.
How Deep Does a Punch Biopsy Go?
Punch biopsies typically reach the dermis, about 1.5–4 mm deep, depending on the lesion and location.
Tools and Techniques Used
The punch biopsy uses a circular blade to take the skin sample. The tool is rotated gently into the skin until it reaches the right depth. Then, the sample is removed for analysis.
|
Biopsy Type |
Depth |
Diameter |
|---|---|---|
|
Punch Biopsy |
1.5 mm |
Less than 4 mm |
The punch biopsy is a key diagnostic tool. It strikes a balance between getting enough information and being minimally invasive. Knowing how it works helps patients see its value and simplicity.
Shave Biopsy: The Superficial Approach
Shave biopsies are a simple and effective way to diagnose skin conditions. They are great for skin issues that only affect the outer skin layers. This method works well for lesions that mainly stay in the epidermal layer, without going deep into the dermis.
Depth Limitations of Shave Biopsies
Shave biopsies can’t reach deep dermal tissue. The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) says they’re best for skin issues in the epidermal layer. Trying to get deeper tissue with this method can lead to not getting enough tissue for a proper diagnosis.
When Shave Biopsies Are Preferred
Shave biopsies are good for diagnosing superficial skin issues. They are simple, fast, and cost-effective. They work well for raised or pedunculated lesions, as they cause little scarring.
The AAFP notes that shave biopsies are quick and simple. This makes them a popular choice for both patients and doctors.
“Shave biopsies are used for lesions that are predominantly epidermal, without extension into the dermis,” says the AAFP. This shows their value in certain diagnostic situations.
Excisional Biopsy: The Deepest Option
Excisional biopsies are key in dermatology for checking skin lesions. They remove the whole lesion and some healthy skin too. This gives a detailed sample for skin analysis.
Full-Thickness Removal
Excisional biopsies take out the whole skin lesion. This means they get all skin layers, from the top to the bottom. This is important for finding out what’s wrong with the skin, like melanoma.
Indications for Deep Tissue Sampling
These biopsies are used for suspicious skin spots and need deep tissue sampling. Doctors choose this biopsy if the skin spot looks serious. It helps them find the right treatment.
In short, excisional biopsies are a sure way to diagnose skin problems. They’re great for checking deep skin issues. This makes them very useful in treating complex skin cases.
What to Expect During a Skin Biopsy Procedure
Knowing what to expect during a skin biopsy can make it less scary. A skin biopsy is when a skin sample is taken and looked at under a microscope. It’s a way to find out what’s wrong with your skin.
Preparation Steps
Before a skin biopsy, you’ll get some prep steps. You might need to stop taking certain medicines. It’s very important to follow these steps to make sure the biopsy goes well and to avoid problems.
The Biopsy Process
The biopsy process has a few main steps. First, the area is cleaned. Then, a numbing medicine is used to make it painless. Next, a skin sample is taken and sent to a lab for tests.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After the biopsy, you’ll get care instructions. You’ll need to keep the area clean and dry, use antibiotic ointment, and cover it with a bandage. Following these steps is key to help it heal and avoid infection.
By knowing about the prep, the procedure, and aftercare, you can handle your skin biopsy better.
Recovery and Healing After a Skin Biopsy
The healing time after a skin biopsy can change a lot. It depends on the type of biopsy done. Usually, the body starts healing right after the biopsy. The wound starts to close and heal in a few days.
Healing Timeline by Biopsy Type
The time it takes to heal can vary. Shave biopsies, being less deep, heal fast, in 1-2 weeks. Punch biopsies, which take a bit more tissue, heal in 2-3 weeks. Excisional biopsies, removing more tissue, take longer, sometimes up to months.
|
Biopsy Type |
Typical Healing Time |
|---|---|
|
Shave Biopsy |
1-2 weeks |
|
Punch Biopsy |
2-3 weeks |
|
Excisional Biopsy |
Several weeks to months |
Pictures of Skin Biopsy Healing Stages
shows how a wound heals over time. Everyone heals differently, but these pictures give a general idea.
The place where the biopsy is done also affects healing time. Wounds on the legs and feet heal slower than others, as the Medical organization says.
Potential Risks and Complications Based on Biopsy Depth
The depth of a skin biopsy can greatly affect the risk of complications. It’s important to know these risks. Skin biopsies are usually safe but can lead to bleeding, infection, and scarring.
Superficial Biopsy Complications
Superficial biopsies, like shave biopsies, have fewer complications because they don’t go deep. But, they’re not completely risk-free.
- Infection: Though rare, infection can happen, mainly if you don’t follow post-procedure care.
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding is common, but serious bleeding is rare.
- Scarring: Superficial biopsies might cause minor scarring, but it’s usually small.
Deep Biopsy Complications
Deeper biopsies, like punch and excisional biopsies, go deeper into the skin. This can increase the risk of complications.
- Nerve Damage: Deeper biopsies might damage nerves, causing numbness or changed sensation.
- Significant Bleeding: The chance of more serious bleeding is higher with deeper biopsies.
- Healing Issues: Deeper wounds may heal slower and could be more likely to get infected or scar badly.
Knowing these risks is key to managing expectations and ensuring proper care after a biopsy. Sources like the Medical organization and Healthdirect say being aware of these complications can help avoid them.
Understanding Biopsy Results
Getting the results of a biopsy is key for both patients and doctors. These results tell us a lot about what’s going on in the body. They help decide what treatment should come next.
How Long Do Results of Biopsy Take?
The time it takes to get biopsy results can vary. Usually, it’s a few days to a couple of weeks. This depends on the type of biopsy and how complex the analysis is.
A simple shave biopsy might give results quickly. But a more detailed excisional biopsy could take longer. It’s important for patients to ask their doctor when they can expect their results.
Interpreting Different Types of Results
Understanding biopsy results means knowing the type of biopsy and what it’s checking for. Results can show if something is benign, malignant, or if they’re not clear. Each one means different things for what happens next.
A table can help explain the different results and what they mean:
|
Result Type |
Description |
Next Steps |
|---|---|---|
|
Benign |
Non-cancerous condition |
Monitoring or minor treatment |
|
Malignant |
Cancerous condition |
Further treatment such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation |
|
Inconclusive |
Results are unclear |
Repeat biopsy or additional testing |
Conclusion
A skin biopsy is a way to check skin health by taking a sample. The depth of the biopsy varies based on the type and purpose.
There are three main types of skin biopsies: shave, punch, and excisional. Each has its own depth and use. Knowing about these helps patients make better choices for their health.
Skin biopsies are key in finding and treating skin problems. By learning about the different biopsies, patients can understand their diagnosis better. This knowledge helps in getting the right treatment.
A biopsy conclusion gives a summary of what the test found. This is important for figuring out the best treatment. It’s based on the skin sample’s examination.
FAQ
What is a skin biopsy?
A skin biopsy is a procedure where a skin sample is taken and checked under a microscope. It helps diagnose skin conditions like cancer, infections, and inflammatory diseases.
How deep does a skin biopsy go?
The depth of a skin biopsy varies. Shave biopsies are shallow. Punch biopsies can go up to 4mm deep. Excisional biopsies remove the whole skin thickness.
What are the different types of skin biopsies?
There are several types of skin biopsies. Shave, punch, and excisional biopsies each have their own use and depth. Each type is suited for different needs.
How long do results of a biopsy take?
Biopsy results usually take a few days to a week. This depends on the case’s complexity and lab processing time.
What can I expect during a skin biopsy procedure?
During a skin biopsy, the area is cleaned and numbed. A specific tool is used to take the sample. It’s then sent to a lab for examination.
How do I care for the biopsy site after the procedure?
After a biopsy, keep the site clean and apply antibiotic ointment. Cover it with a bandage. Follow specific instructions based on the biopsy type and your healthcare provider’s advice.
What are the possible risks and complications of a skin biopsy?
Risks include bleeding, infection, scarring, and allergic reactions to anesthesia. The risk level varies by biopsy type and depth.
Can I get a skin biopsy if I’m taking blood thinners?
If you’re on blood thinners, you might need to stop or adjust them before a biopsy. This is to reduce bleeding risk. Always consult your healthcare provider for advice.
How do I understand my biopsy results?
A healthcare provider interprets your biopsy results. They’ll explain the diagnosis, discuss treatment, and guide follow-up care.
What is the healing process like after a skin biopsy?
The healing time varies by biopsy type and depth. Generally, it takes days to weeks for the site to heal fully. Some scarring is possible.
Are there any pictures or resources available to show skin biopsy healing stages?
Yes, there are online resources and pictures showing skin biopsy healing stages. But, always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and care.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470457/


































