pigmentation
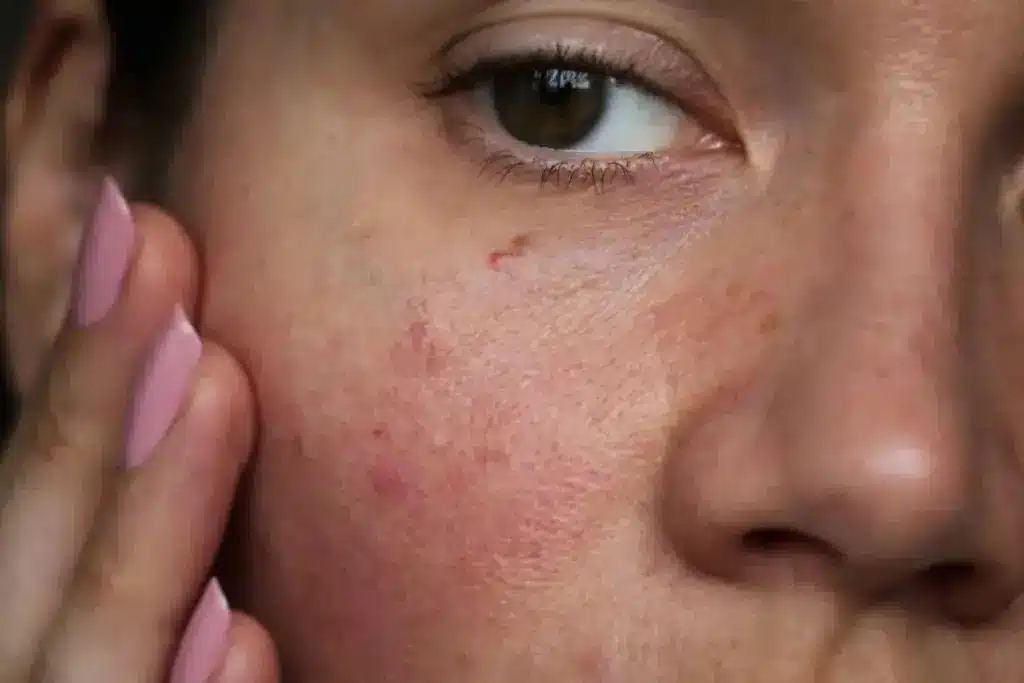
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that affects millions. It causes more than just itchy skin. It can also change the skin’s color, making it lighter or darker.
TCA peels are used to treat skin discolorations. This shows how important it is to deal with pigmentation issues. Eczema’s effect on skin color can be upsetting. It’s key to know why it happens.
Key Takeaways
- Eczema can cause significant changes in skin pigmentation.
- Skin lightening or darkening are common effects of eczema.
- Understanding pigmentation changes is key for effective treatment.
- TCA peels are used to treat skin discolorations caused by eczema.
- Managing eczema means addressing its impact on skin color.
Understanding Eczema and Its Effects on Skin
eczema on black skin
Eczema affects the skin in many ways, changing its structure and color. It’s not just about skin irritation. It’s a complex condition that can greatly affect a person’s life.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, makes the skin inflamed, itchy, and sometimes blistered. It’s caused by genetics, environment, and the immune system. Stress, allergens, and irritants often play a role.
Common Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema. Atopic dermatitis is the most common, often seen in those with allergies. Contact dermatitis happens when the skin reacts to something. Seborrheic dermatitis affects oily areas, like the scalp.
How Eczema Affects Skin Structure
[PLACE THE IMAGE HERE]
Eczema changes the skin’s structure, making it lose more water and become dry. It also makes the skin more prone to infections. The inflammation can cause changes in skin color, leading to light or dark patches.
|
Type of Eczema |
Common Characteristics |
Typical Locations |
|---|---|---|
|
Atopic Dermatitis |
Itchy, inflamed skin |
Elbows, knees, face |
|
Contact Dermatitis |
Reaction to irritants/allergens |
Area of contact |
|
Seborrheic Dermatitis |
Oily, scaly patches |
Scalp, face, torso |
Eczema affects people with different skin tones in different ways. For example, eczema on black skin or eczema on black people skin can cause more noticeable dark patches on skin. It’s important to understand these differences for proper treatment.
The Science of Skin Pigmentation
Edit
Full screen
Delete
skin pigmentation process
The science behind skin pigmentation shows how eczema can affect it. Skin color is mainly due to melanin, a pigment made by melanocytes in the skin.
How Melanin Works
Melanin decides our skin color, with two types: eumelanin (brown/black) and pheomelanin (red/yellow). The mix of these melanins sets our natural skin color. Melanin production is influenced by genetics, sunlight, and hormones.
Factors Affecting Skin Color
Many things can change our skin color, including:
- Genetic predisposition
- Exposure to UV radiation
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Inflammatory conditions like eczema
These factors can cause skin color changes, like hyperpigmentation (darkening) or hypopigmentation (lightening).
Normal Pigmentation Processes
In healthy skin, pigmentation is well-controlled. Melanocytes make melanin in response to different triggers. This melanin then goes to keratinocytes, the main skin cells.
This process helps our skin stay the same color. But, eczema and other conditions can mess with it, causing color changes.
How Eczema Disrupts Normal Skin Pigmentation

eczema patches
Eczema can change how skin looks by causing inflammation. This affects melanocytes, leading to skin lightening or darkening. The exact change depends on the person’s skin and how bad the eczema is.
Inflammatory Response and Melanocytes
The inflammation from eczema can harm melanocytes. These cells make melanin, which colors our skin. Damage to these cells can cause hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation.
How much the skin changes can vary. Some people see big changes, while others don’t notice as much.
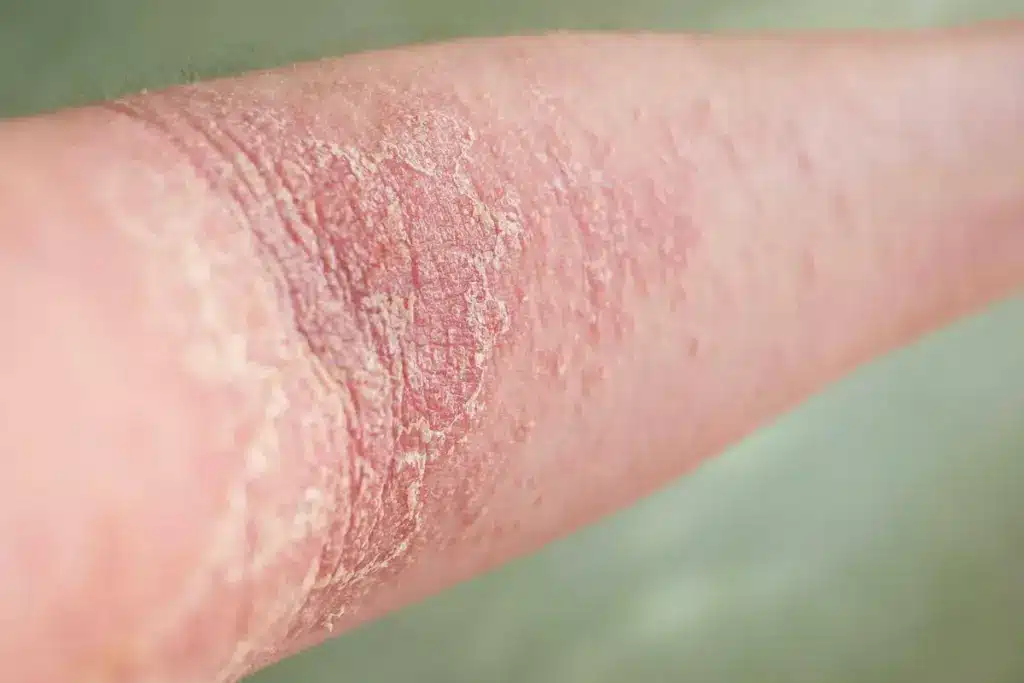
Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation
Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation happens when eczema makes skin lighter. It’s more noticeable in darker skin tones. The skin usually gets its color back, but sometimes it doesn’t.
How long the skin stays lighter depends on the eczema’s severity and treatment. Good skincare and treatment can help prevent this.
Differences Between Temporary and Permanent Changes
Eczema can lead to both short-term and long-term skin color changes. Temporary changes often go away once the inflammation does. But permanent changes can happen if melanocytes are badly damaged.
If you have lasting changes, see a dermatologist. They can help manage your eczema and protect your skin. This can reduce some of the color issues.
Hypopigmentation: Why Eczema Causes Skin Lightening
Edit
Full screen
Delete
hypopigmentation
Eczema can make your skin lighter. This is because of hypopigmentation, which shows up as white patches. It’s a big worry for people with eczema.
Mechanisms Behind Skin Lightening
The reasons for skin lightening in eczema are complex. Inflammation is key, as it messes with melanocytes. These cells make melanin, which colors our skin.
Eczema’s inflammation can damage or mess up melanocytes. This leads to lighter skin patches. This is called post-inflammatory hypopigmentation.
Common Patterns of Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation from eczema shows up in different ways. Here are some common ones:
- Localized patches: These are found in areas where eczema has been.
- Widespread lightening: Sometimes, the whole area can get lighter.
|
Pattern |
Description |
Common Locations |
|---|---|---|
|
Localized Patches |
Found in areas where eczema has been |
Arms, legs, torso |
|
Widespread Lightening |
Whole area gets lighter |
Face, neck, hands |
Timeline for Pigment Recovery
How long it takes for skin to get its color back varies. It depends on how bad the hypopigmentation is and the treatment’s success. Sometimes, it takes just a few months. Other times, it takes longer.
Some treatments, like TCA peels, might help with skin discolorations from eczema.
Hyperpigmentation: When Eczema Causes Skin Darkening
Edit
Full screen
Delete
hyperpigmentation
Eczema is often linked with red skin and swelling. But, some people might see dark patches on their skin. This can be upsetting for those who experience it.
Why Some Eczema Lesions Turn Dark
Eczema lesions can darken because of the inflammation. This inflammation makes the skin produce more melanin. This leads to dark patches on the skin.
Key factors contributing to hyperpigmentation in eczema include:
- Inflammation severity: Severe inflammation can cause more melanin production.
- Skin type: People with darker skin are more likely to see dark patches.
- Scratching and irritation: Scratching can make inflammation worse and darken the skin further.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation Process
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) often follows eczema. It happens when inflammation triggers melanocytes to make more melanin.
|
Stage |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Inflammation |
The initial inflammatory response triggers melanin production. |
|
Melanin Production |
Melanocytes produce excess melanin in response to inflammation. |
|
Pigmentation |
The excess melanin leads to visible hyperpigmentation. |
Risk Factors for Developing Dark Patches
Several factors can make dark patches more likely with eczema. These include:
- History of eczema: Those with long eczema histories are more at risk.
- Skin type: Darker skin is more prone to PIH.
- Poor eczema management: Not treating eczema well can lead to more inflammation and dark patches.
Knowing these factors can help prevent and treat dark patches from eczema.
Eczema Manifestations Across Different Skin Tones
Eczema looks different on everyone, no matter their skin color. It’s a long-lasting skin problem that can affect anyone. But how it shows up can change a lot.
Eczema on Dark Skin
For people with darker skin, eczema can be tricky to spot. It might cause different visual characteristics. This can make it harder to figure out what’s going on.
It can also lead to post-inflammatory hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation. This means the skin might look lighter or darker than usual. It’s more noticeable in darker skin.
Eczema on dark skin can look like small, raised bumps. This is called papular eczema. These bumps can be itchy and uncomfortable.
Eczema on Light Skin
On lighter skin, eczema is more straightforward. It shows up as redness, itching, and dryness. The inflammatory response is clear, making it easier to spot.
But, sometimes people with light skin don’t get treated right away. This is because the symptoms might not seem serious enough.
Challenges in Diagnosis Across Skin Types
Figuring out if someone has eczema can be tough, no matter their skin color. In darker skin, it might be missed or misdiagnosed. In lighter skin, it might be mistaken for something else.
Doctors need to understand these differences. They should know about post-inflammatory pigmentation changes. They also need to treat each patient differently.
By knowing how eczema looks on different skin tones, doctors can help more. They can give better care and improve how patients feel.
Papular Eczema and Its Relationship to Pigmentation
Edit
Full screen
Delete
papular eczema skin pigmentation
Papular eczema shows up in different ways, like changes in skin color. It’s marked by small, raised bumps on the skin. Knowing about papular eczema helps us tackle its effects on skin color and health.
Defining Papular Eczema
Papular eczema is a form of eczema with small bumps, often with inflammation and itchiness. It can start from many things like allergens, irritants, and stress. Anyone can get it, and how bad it is can differ a lot.
Key characteristics of papular eczema include:
- Small, raised papules on the skin
- Inflammation and redness
- Itching and discomfort
- Variable severity and impact on quality of life
Impact on Skin Color
Papular eczema can really change skin color. The inflammation can make the skin lighter or darker. How much it changes depends on the skin type and how bad the eczema is.
Studies show that the inflammation in papular eczema can mess with melanocytes, leading to color changes. A dermatologist said, “The inflammation from papular eczema can really change skin color, affecting how people look and feel about themselves.”
“Managing papular eczema needs a full plan, including creams and changes in lifestyle, to lessen its effect on skin color.”
Common Locations and Appearances
Papular eczema can pop up on the arms, legs, and torso. The bumps can look different, with some being more inflamed than others.
|
Location |
Common Characteristics |
|---|---|
|
Arms |
Papules often appear on the extensor surfaces |
|
Legs |
May be accompanied by significant itching |
|
Torso |
Can present with varying degrees of inflammation |
Knowing where and how papular eczema shows up helps in diagnosing and treating it better.
Eczema on the Neck and Visible Pigmentation Changes
Eczema on the neck can cause noticeable discoloration. This is a concern for those with eczema because the neck is visible. Managing this condition is important to reduce its effects.
Why Neck Eczema Often Causes Noticeable Discoloration
Neck eczema can cause big changes in skin color. The neck’s skin is thin and sensitive. This makes it more likely to get irritated and change color.
The inflammation from eczema can mess with melanin production. This can make the skin lighter or darker. These changes are more obvious on the neck, affecting how people feel about themselves.
Special Considerations for Neck Skin
The neck’s skin needs extra care because it’s delicate. It’s also exposed to many environmental stressors. When dealing with neck eczema, it’s important to use gentle products and practices.
- Use fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers to reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
- Avoid harsh scrubbing or rubbing, which can further irritate the skin.
- Apply sunscreen daily to protect the skin from UV damage, which can exacerbate pigmentation issues.
Managing Neck Eczema to Minimize Pigmentation Issues
Managing neck eczema involves medical treatments and skincare. Topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors can reduce inflammation. Keeping the skin moisturized helps prevent irritation.
It’s important to stop the itch-scratch cycle. Scratching can make inflammation and color changes worse. Using gentle, fragrance-free products and following treatment instructions can help manage symptoms and reduce discoloration.
White Patches and Light Spots: Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to know why white patches and light spots appear. Eczema can cause these changes in skin color. This is because of the way eczema affects the skin.
Distinguishing Eczema-Related Lightening from Other Conditions
Lightening from eczema can look like other skin problems. It’s key to tell them apart for the right treatment.
Key factors to consider:
- Distribution and pattern of the light patches
- Presence of other symptoms like itching or scaling
- History of eczema or other skin conditions
Similar-Looking Conditions (Vitiligo, Tinea Versicolor, etc.)
Many conditions can look like eczema’s pigmentation changes. Vitiligo is when pigment cells are lost, causing white patches. Tinea Versicolor is a fungal infection that can also cause skin color changes.
|
Condition |
Characteristics |
Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|
|
Vitiligo |
White patches due to loss of melanocytes |
Topical corticosteroids, light therapy |
|
Tinea Versicolor |
Light or dark patches due to fungal infection |
Antifungal medications |
|
Eczema-related pigmentation changes |
Light patches due to inflammation and healing |
Topical corticosteroids, moisturizers |
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you see sudden or big changes in skin color, see a doctor. They can figure out what’s going on and suggest the right treatment.
Signs that require immediate medical attention:
- Rapid progression of white patches
- Presence of other symptoms like itching, redness, or scaling
- Uncertainty about the cause of pigmentation changes
The Role of Scratching in Pigmentation Changes
Scratching can change skin color in people with eczema. It’s a natural reaction to itchiness, but it can harm the skin.
Physical Trauma and Melanocytes
Scratching causes physical harm to the skin. This harm can damage melanocytes, the cells that make melanin. Melanin is what gives skin its color.
Scratching can also mess with how melanocytes work. This can change skin color. For more info on eczema and skin color, check out https://eczema.org/information-and-advice/living-with-eczema/skin-pigmentation/.
Breaking the Itch-Scratch Cycle
Stopping the itch-scratch cycle is key to avoiding more color changes. Treatments and lifestyle changes can help. Using soft skincare and pigmentation cream can soothe the skin and lessen itchiness.
- Moisturize often to keep the skin moist.
- Stay away from harsh soaps that take away natural oils.
- Use topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors as your doctor suggests.
Long-term Effects of Chronic Scratching
Long-term scratching can cause lasting color changes. This includes skin lightening or darkening. Knowing this helps create a good pigmentation skincare plan.
|
Pigmentation Change |
Causes |
Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
|
Hypopigmentation |
Damage to melanocytes due to scratching |
Gentle skincare, moisturizing, avoiding further irritation |
|
Hyperpigmentation |
Post-inflammatory response |
Topical treatments, sun protection, pigmentation cream |
Understanding why pigmentation changes happen and using the right skincare can help manage eczema. This reduces the risk of lasting color issues.
Medical Treatments for Eczema-Related Pigmentation Issues
Pigmentation problems from eczema can be treated with various medical options. Eczema can make skin lighter or darker. It’s important to manage these changes for people with eczema.
Topical Corticosteroids and Calcineurin Inhibitors
Topical corticosteroids help reduce eczema inflammation. They can also lessen pigmentation changes. Calcineurin inhibitors, like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are good for sensitive areas or long-term use without corticosteroid side effects.
Benefits of Topical Treatments:
- Reduce inflammation
- Minimize pigmentation changes
- Manage symptoms effectively
Systemic Treatments
For severe eczema, systemic treatments are needed. These include oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, and biologics. They can control widespread eczema and pigmentation issues. But, they need careful monitoring for side effects.
|
Treatment |
Use |
Considerations |
|---|---|---|
|
Oral Corticosteroids |
Short-term relief for severe eczema |
Potential for significant side effects with long-term use |
|
Immunosuppressive Drugs |
Long-term management of severe eczema |
Requires regular monitoring of immune function |
|
Biologics |
Targeted therapy for moderate to severe eczema |
May have specific administration requirements |
Emerging Therapies for Pigmentation Management
New treatments are being researched for eczema pigmentation. These include new topical agents, laser treatments, and light-based therapies. They aim to reduce pigmentation irregularities.
These new therapies offer hope for better managing eczema pigmentation. As research continues, more treatment options will be available for those with eczema.
Skincare Approaches for Managing Pigmentation in Eczema
Effective skincare is key for managing eczema’s pigmentation changes. A good skincare routine can lessen the look of pigmentation issues. This improves the skin’s overall look.
Gentle Cleansing Practices
Gentle cleansing is vital for eczema’s pigmentation. Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers to keep the skin’s natural barrier intact. Clean with lukewarm water, not hot, to avoid losing natural oils.
- Choose cleansers for sensitive skin.
- Avoid scrubbing or harsh exfoliants.
- Pat dry the skin instead of rubbing it vigorously.
Moisturizing Strategies
Moisturizing is key in managing eczema, as it keeps the skin hydrated. Apply moisturizer right after bathing to keep moisture in. Look for moisturizers with ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or niacinamide to repair the skin’s barrier.
- Apply moisturizer at least twice a day.
- Use a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer.
- Try occlusive moisturizers at night for extra hydration.
Sun Protection and Its Importance
Sun protection is critical to prevent more pigmentation changes in eczema-affected skin. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day. Wear protective clothing and seek shade when outdoors.
- Apply sunscreen 15-30 minutes before going outdoors.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
- Use lip balm with SPF to protect the lips.
Recent Advances in Understanding Eczema and Pigmentation
Recent studies have greatly improved our understanding of eczema’s effect on skin color. Research into eczema and skin color has revealed how it impacts melanocytes and overall skin health.
The connection between eczema and changes in skin color is becoming clearer. New research findings show that inflammation can disrupt normal pigmentation processes.
New Research Findings
Eczema can cause both lighter and darker skin patches due to its inflammatory nature. Researchers are working to understand these changes to create better treatments.
A study in a dermatology journal found that certain cytokines affect melanocyte function in eczema patients. This discovery opens up new avenues for possible treatments.
|
Research Focus |
Key Findings |
Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
Cytokines and Melanocytes |
Cytokines affect melanocyte function |
New therapeutic targets |
|
Genetic Factors |
Genetic predisposition to pigmentation changes |
Personalized treatment approaches |
|
Treatment Outcomes |
Variability in treatment response |
Improved treatment strategies |
Genetic Factors in Pigmentation Response
Genetics play a big role in how eczema affects skin color. Research is finding the genes involved in these changes. This could lead to more tailored treatments.
Knowing the genetic basis of eczema’s impact on skin color helps doctors predict treatment outcomes. They can then tailor treatments for each patient.
Future Treatment Directions
The future of treating eczema looks bright, with many new approaches being explored. Researchers are looking into new topical and systemic treatments. These could better manage eczema symptoms and skin color changes.
New treatments include biologics and small molecule inhibitors that target specific pathways. These advancements could lead to more effective treatments for eczema’s impact on skin color.
- Biologics targeting specific inflammatory pathways
- Small molecule inhibitors for precise treatment
- Personalized medicine approaches based on genetic profiling
Conclusion: Managing Eczema and Its Effects on Skin Pigmentation
Eczema can change skin color, making it lighter or darker. It’s important to understand how this happens to manage it well.
To tackle eczema, we need a full plan. This includes creams, changing our lifestyle, and sometimes pills like tranexamic acid. Research shows that different treatments can help with skin color changes from eczema.
Using gentle skincare, staying out of the sun, and getting the right medical help can help. This approach can lessen skin color changes and make skin healthier.
FAQ
What causes eczema to lighten or darken skin?
Eczema can make skin lighter or darker. This happens because of the inflammation and how it affects melanocytes. These cells produce melanin, which is what gives skin its color.
Is skin lightening or darkening caused by eczema permanent?
The skin color changes from eczema can last a short time or forever. It depends on how bad the inflammation is and your skin type.
How does eczema affect skin pigmentation on different skin tones?
Eczema can change skin color in many ways, but it looks different on everyone. For darker skin tones, the dark spots from eczema are more visible.
What is papular eczema, and how does it affect skin color?
Papular eczema is a type of eczema with small bumps. It can make skin lighter or darker, mainly where the bumps are.
Why does eczema on the neck often cause noticeable discoloration?
The neck’s thin skin makes it more likely to get darker or lighter from eczema. Clothes rubbing against it can make it worse.
How can I distinguish eczema-related lightening from other conditions?
To tell if lightening is from eczema, look at the whole picture. Check for other eczema signs, where the light spots are, and if you’ve had eczema before.
What role does scratching play in pigmentation changes caused by eczema?
Scratching can make skin color changes worse. It hurts the skin, which can mess with melanocytes and cause color changes.
What are some effective skincare approaches for managing pigmentation in eczema?
To manage eczema’s color changes, use gentle cleansers and moisturizers. Protect your skin from the sun. Choose products without fragrances or dyes to avoid irritation.
Are there any medical treatments available for eczema-related pigmentation issues?
Yes, there are treatments like creams and pills. New treatments, like biologics, might also help with eczema and color changes.
Can eczema-related pigmentation changes be prevented?
You can’t always stop eczema’s color changes, but you can try. Use treatments and skincare to manage eczema well and reduce these changes.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24784555/



































