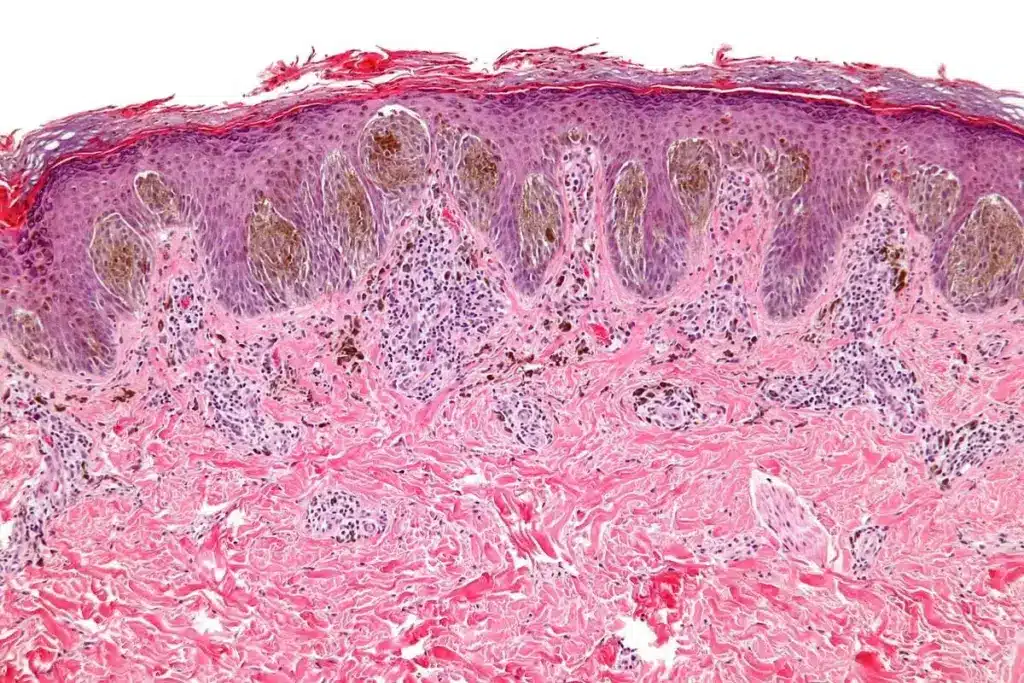
Melanoma is a dangerous form of skin cancer. If caught early, it has a very good treatment outcome. The American Academy of Dermatology says the five-year survival rate for people with localized melanoma is 99%.
This shows how important early detection is. It helps manage and treat this potentially deadly disease effectively.
Early detection greatly improves survival rates, as treatments are more effective when melanoma is found early.
This is why regular skin checks are so important. Knowing the risks of melanoma cancer is also vital.
Answering is melanoma curable if caught early (yes, nearly 100%) and emphasizing the importance of early detection.
Key Takeaways
- Melanoma is highly treatable if caught early.
- The five-year survival rate for localized melanoma is 99%.
- Early detection is key for effective treatment.
- Regular skin checks can significantly improve survival rates.
- Awareness of skin cancer risks is essential for prevention.
Understanding Melanoma: The Most Dangerous Form of Skin Cancer
It’s important to know about melanoma to catch it early and treat it well. Melanoma starts in cells called melanocytes. These cells make melanin, which gives skin its color.
Melanomas are often black or brown, but they can also be pink, red, purple, or the same color as your skin. Because they can look different, it’s key to watch for any new or changing spots on your skin.
What Is Melanoma and How Does It Develop?
Melanoma happens when melanocytes grow out of control because of genetic changes. This can cause a tumor to form. The tumor can grow deeper into the skin and even spread to other parts of the body.
We don’t know all the reasons why melanoma happens, but too much sun or tanning beds are big risks. Sun or tanning bed rays can hurt the DNA of melanocytes, leading to the changes that cause melanoma.
The Difference Between Melanoma and Other Skin Cancers
Melanoma is different from other skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It starts in melanocytes and can grow aggressively. Other skin cancers usually don’t spread as much, but melanoma can, making it very dangerous.
- Types of Skin Cancer:Basal Cell Carcinoma: The most common form, typically slow-growing and locally invasive.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Can grow more quickly than basal cell carcinoma and has a higher risk of spreading.
- Melanoma: The most dangerous due to its high risk of spreading and causing death.
Why Early Detection Is Critical
Finding melanoma early is very important. If caught early, it can often be treated with surgery. But if it’s not found until it has spread, treatment is harder and the outlook is worse.
To find melanoma early, know the signs and symptoms. Look for changes in the size, shape, or color of a mole, or the appearance of a new mole. Regular self-checks and doctor visits are key to catching melanoma when it’s most treatable.
Types of Melanoma and Their Characteristics

It’s important to know the different types of melanoma to catch it early. Melanoma is a serious skin cancer with various types based on its growth and look.
Superficial Spreading Melanoma
Superficial spreading melanoma is the most common, making up about 70% of cases. It starts by growing across the skin’s surface before going deeper. Early detection is key because it can be treated well if caught early.
Nodular Melanoma
Nodular melanoma grows straight into the skin from the start. It looks like a firm, dome-shaped nodule, often black but sometimes not. Because it grows fast, catching it early is very important.
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
Lentigo maligna melanoma happens more in older people on sun-damaged skin, often on the face. It starts as a flat, pigmented lesion and can turn into invasive melanoma if not treated. Spotting the signs of lentigo maligna is key to stopping it from getting worse.
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
Acral lentiginous melanoma is rare but shows up on palms, soles, or under nails. It’s not caused by UV rays and can be hard to spot. Knowing about this type is important for catching it early in unusual places.
Rare Melanoma Subtypes
There are also rare types like desmoplastic melanoma and uveal melanoma. Desmoplastic melanoma is linked to nerve damage and can be tricky to diagnose. Uveal melanoma is in the eye and has its own treatment methods.
Knowing the different melanoma types and their signs is vital for early detection and treatment. Each type has its own traits, and understanding them can greatly improve treatment results.
Recognizing Early Melanoma Symptoms: The ABCDE Rule
Spotting melanoma early is key to better treatment. The ABCDE rule helps people and doctors spot possible melanomas.
Asymmetry
Asymmetry is a big sign of melanoma. If a mole doesn’t look symmetrical, it’s a red flag. Benign moles usually are symmetrical, so any asymmetry means you should check it out.
Border Irregularity
Melanomas have irregular borders, like notches or scallops. Benign moles have smooth borders. This irregularity is a big clue to a mole’s risk.
Color Variation
Melanomas can show many colors, like brown, black, and even red, white, or blue patches. Benign moles usually have one color.
Diameter Concerns
Melanomas are often bigger than benign moles. A size over 6mm is a warning sign.
Evolution and Changes Over Time
Changes in size, shape, or color are big signs of melanoma. Watching your moles can catch these changes early.
Additional Warning Signs Beyond ABCDE
Other signs of melanoma include new or changing moles, sores that don’t heal, and unusual bumps or rashes. Paying attention to these signs can help catch melanoma early.
Risk Factors for Developing Melanoma
Many things can increase your chance of getting melanoma. These include your genes, the environment, and your lifestyle. Knowing these risks helps you prevent and catch melanoma early.
UV Exposure and Tanning Beds
UV radiation is a big risk for melanoma. It comes from the sun and tanning beds. Using tanning beds before 30 raises your melanoma risk a lot. The World Health Organization says UV-emitting tanning devices are harmful.
Skin Type and Complexion
People with fair skin and light hair are more at risk. This is because they have less melanin, which protects against UV. But, anyone can get melanoma, no matter their skin type.
Family History and Genetic Factors
A family history of melanoma raises your risk. Some genes, like CDKN2A, can also increase your risk. If you have a strong family history, you might get tested for these genes.
Previous Skin Cancer Diagnosis
Having had skin cancer before makes you more likely to get melanoma. It’s important to see a dermatologist regularly if you’ve had skin cancer before.
Number of Moles and Atypical Moles
Many moles or atypical moles raise your risk. Atypical moles are bigger and have odd shapes or colors. Watching these moles for changes is key to catching melanoma early.
Diagnosing Early Stage Melanoma
Melanoma diagnosis needs both self-checks and doctor visits. Finding it early is key to the right treatment.
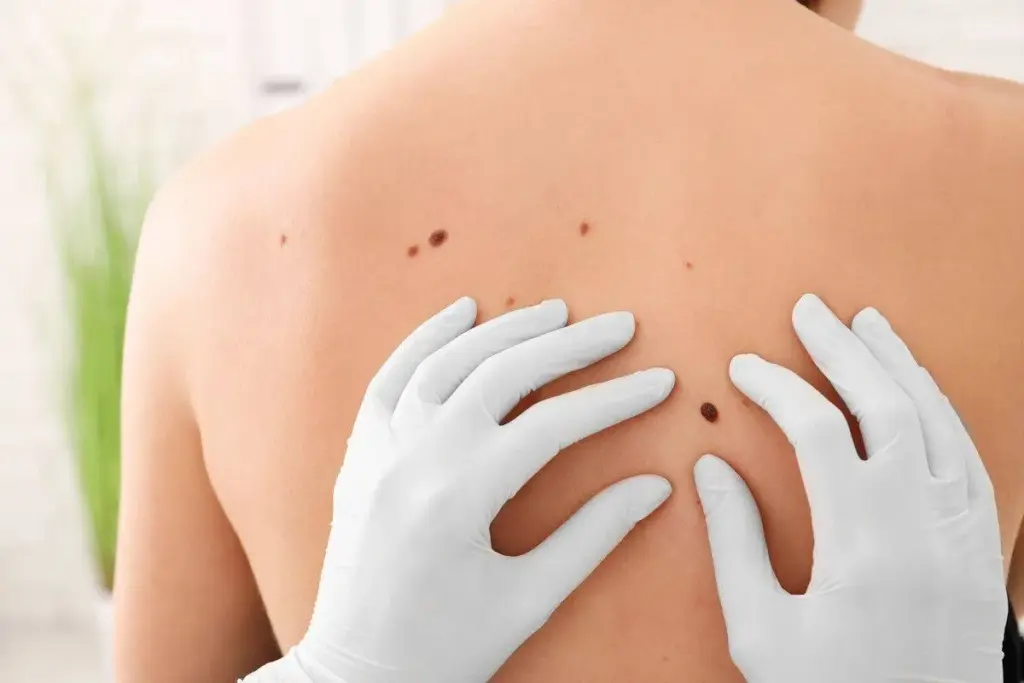
Self-Examination Techniques
Checking your skin regularly is the first step. Know your skin well and watch for any changes. The ABCDE rule helps spot possible cancer signs.
Professional Skin Examinations
While checking yourself is good, seeing a dermatologist is even better. They have the skills and tools to look closely at your skin.
Dermoscopy and Imaging Technologies
Dermoscopy lets doctors see skin lesions up close without cutting. It helps tell if a spot is safe or not. Other tools like confocal microscopy might also be used.
Biopsy Procedures and Pathology
If a doctor finds something odd, they’ll take a tissue sample. There are different ways to do this, each for its own reason.
Shave Biopsy
A shave biopsy takes off the top skin layers. It’s good for spots that stick out.
Punch Biopsy
A punch biopsy takes a deeper skin sample. It’s used for spots that aren’t easy to see.
Excisional Biopsy
An excisional biopsy removes the whole spot and some skin around it. It’s the best way to get a full sample for checking.
Knowing about these ways to find melanoma is important. Early detection leads to better treatment results.
Melanoma Staging: What Defines “Early” Melanoma
Melanoma staging looks at the tumor’s thickness and if it has spread to lymph nodes. Knowing these stages helps doctors choose the right treatment and predict how well a patient will do.
Stage 0 (In Situ): Confined to the Epidermis
Stage 0 melanoma, or melanoma in situ, is the earliest stage. The cancer cells are only in the outer skin layer, the epidermis. Early detection is key because it means the cancer can be easily treated with surgery.
Stage I: Localized, Thin Melanoma
Stage I melanoma is thin and hasn’t spread. It’s split into two parts: Stage IA and Stage IB.
Stage IA Characteristics
Stage IA melanoma is very thin, under 1 mm thick, and doesn’t have ulcers. It’s very treatable, with a good chance of recovery.
Stage IB Characteristics
Stage IB melanoma is up to 2 mm thick or less than 1 mm with ulcers. Ulcers can change how likely the cancer is to come back, so regular check-ups are important.
Stage II: Thicker Melanoma Without Spread
Stage II melanoma has a thicker tumor but hasn’t spread. The tumor’s thickness and if it has ulcers are important for predicting how well the patient will do.
The Importance of Breslow Thickness in Prognosis
Breslow thickness is a key factor in melanoma prognosis. It measures the tumor’s depth in millimeters. A thinner Breslow thickness means a better chance of recovery. This helps doctors stage the melanoma correctly and plan the best treatment.
Treatment Options for Early Melanoma
Good news for those with early-stage melanoma: there are many treatment options. Finding it early greatly improves treatment success. The right choice depends on the melanoma’s stage and type.
Surgical Approaches
Surgery is a common first step for early melanoma. Different surgical methods offer unique benefits.
Wide Local Excision
Wide local excision removes the melanoma and some normal skin around it. This ensures all cancer cells are taken out.
Mohs Surgery
Mohs surgery removes the melanoma in thin layers. Each layer is checked under a microscope until no cancer is found.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
This procedure finds the first lymph node cancer might spread to. It helps see if cancer has started to spread.
Adjuvant Therapies for High-Risk Early Melanoma
For high-risk early melanoma, adjuvant therapies are used to lower recurrence risk.
- Interferon: A protein that boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
- Immunotherapy: Treatments that enhance the body’s natural defenses against cancer.
Immunotherapy Advances
Immunotherapy has changed melanoma treatment. Checkpoint inhibitors and adoptive T-cell therapy are used to fight melanoma.
Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies target specific cancer molecules. For melanoma, they often target the BRAF gene mutation.
Clinical Trials for Early Stage Melanoma
Clinical trials offer new treatments not yet widely available. They can be an option for some with early-stage melanoma.
It’s key for patients to talk with their healthcare provider about all treatment options. This helps find the best approach for their case.
Survival Rates and Prognosis for Early Detected Melanoma
Knowing survival rates and prognosis is key for those with early-stage melanoma. Early detection greatly improves melanoma outcomes. The American Academy of Dermatology says the 5-year survival rate for localized melanoma is 99%. This highlights the critical role of early detection.
5-Year Survival Rates by Stage
Survival rates for melanoma change a lot based on the stage at diagnosis. Here’s a table showing the 5-year survival rates for melanoma patients by stage:
|
Stage |
5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|
|
Localized (Stage I) |
99% |
|
Regional (Stage II-III) |
66% |
|
Distant (Stage IV) |
27% |
10-Year Survival Rates by Stage
Long-term survival rates give a clearer picture of melanoma prognosis. While 5-year survival rates are common, 10-year rates show long-term outcomes better.
|
Stage |
10-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|
|
Localized (Stage I) |
95% |
|
Regional (Stage II-III) |
55% |
|
Distant (Stage IV) |
15% |
Factors That Influence Prognosis Beyond Stage
While stage is key, other factors also affect prognosis. Breslow thickness, ulceration, and lymph node involvement are important. Knowing these helps fully understand prognosis.
Recurrence Risks and Long-term Monitoring
Even with successful early-stage melanoma treatment, recurrence risks exist. Regular follow-ups and skin checks are essential for monitoring and early intervention.
Those with melanoma history should watch their skin closely. Regular self-exams and doctor visits are important for any skin concerns or changes.
Prevention Strategies: Reducing Your Melanoma Risk
To protect yourself from melanoma, you need a few key steps. These include sun safety, regular skin checks, and making lifestyle changes. By following these tips, you can lower your risk of getting melanoma.
Sun Protection Best Practices
One of the best ways to prevent melanoma is to protect yourself from the sun. Use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear clothes that cover you, and stay in the shade when it’s sunny.
Sunscreen Selection and Application
It’s important to pick the right sunscreen. Look for one that blocks both UVA and UVB rays and has an SPF of 30 or higher. Apply it to all skin that will be exposed 15-30 minutes before going outside. Reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
Protective Clothing and Accessories
Wearing clothes that block UV rays is also key. Choose clothes with a UPF rating of 50+ to block most UV rays. Don’t forget to wear hats and sunglasses for full sun protection.
Avoiding Tanning Beds and Artificial UV Exposure
Tanning beds give off UV rays, which can lead to melanoma. It’s important to stay away from tanning beds and artificial UV sources to prevent melanoma.
Regular Skin Checks and Professional Screenings
Getting regular skin checks is vital. Do self-exams and see a dermatologist for professional screenings. This helps catch any problems early and can prevent melanoma.
Lifestyle Factors That May Reduce Risk
Some lifestyle choices might help lower your melanoma risk. Eating a diet full of fruits, veggies, and omega-3s is good. Also, staying active and keeping a healthy weight can help.
By following these prevention tips, you can lower your risk of melanoma. It’s all about making smart choices and taking care of your skin every day.
Conclusion: Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection is key for treating melanoma effectively. Knowing the warning signs and taking steps to lower risk can help prevent or catch melanoma early. Being aware of melanoma is essential for spotting it in its early stages, when it’s most treatable.
Knowing the risk factors and recognizing symptoms early can greatly reduce melanoma cases. Regular skin checks and professional screenings are important for early detection.
By raising awareness about melanoma and encouraging early detection, we can improve survival rates. Stay vigilant about your skin health. If you notice any unusual changes, seek medical help right away.
FAQ
What is melanoma and how does it develop?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. It starts in melanocytes, the cells that make pigment. These cells become abnormal and grow too much, often because of UV rays.
What are the different types of melanoma?
There are several types of melanoma. These include superficial spreading melanoma, nodular melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, and acral lentiginous melanoma. Each type looks different on the skin.
How can I identify potentially dangerous moles using the ABCDE rule?
The ABCDE rule helps spot suspicious moles. Look for Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter concerns, and Evolution or changes over time. If a mole shows any of these signs, see a doctor.
What are the risk factors for developing melanoma?
Several factors increase your risk of melanoma. These include UV exposure, fair skin, family history, previous skin cancer, and many moles. Tanning beds also raise your risk.
How is melanoma diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose melanoma. These include self-exams, professional checks, dermoscopy, and biopsies. A biopsy is the most accurate way to confirm melanoma, by examining tissue under a microscope.
What are the stages of melanoma, and what does “early” melanoma mean?
Melanoma stages range from Stage 0 to more advanced. Early melanoma is usually Stage I or II. It means the cancer is only in one place and hasn’t spread. Breslow thickness is key in determining how well you’ll do.
What are the treatment options for early melanoma?
Treatments for early melanoma include surgery and adjuvant therapies. Immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and clinical trials are also options. The right treatment depends on the cancer’s stage, thickness, and other factors.
What are the survival rates for early detected melanoma?
Survival rates vary by stage. For early melanoma, the 5-year survival rate is often over 90%. The 10-year survival rate is also high for those caught early.
How can I reduce my risk of developing melanoma?
To lower your risk, protect your skin from the sun. Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and stay in the shade. Avoid tanning beds and get regular skin checks. Knowing your risk factors is also important.
Why is early detection critical for melanoma?
Catching melanoma early is key. It greatly improves your chances of survival and better treatment results. Being aware and getting regular skin checks can help prevent and treat melanoma.
What is the importance of Breslow thickness in melanoma prognosis?
Breslow thickness is how deep the melanoma is in the skin. It’s a big factor in how well you’ll do. Thicker melanomas are more likely to spread and have worse outcomes.
Can melanoma be prevented?
While not all melanoma can be prevented, you can lower your risk. Protect your skin from UV rays, avoid tanning beds, and practice sun safety. Regular skin checks and knowing your risk factors help in early detection and prevention.



































