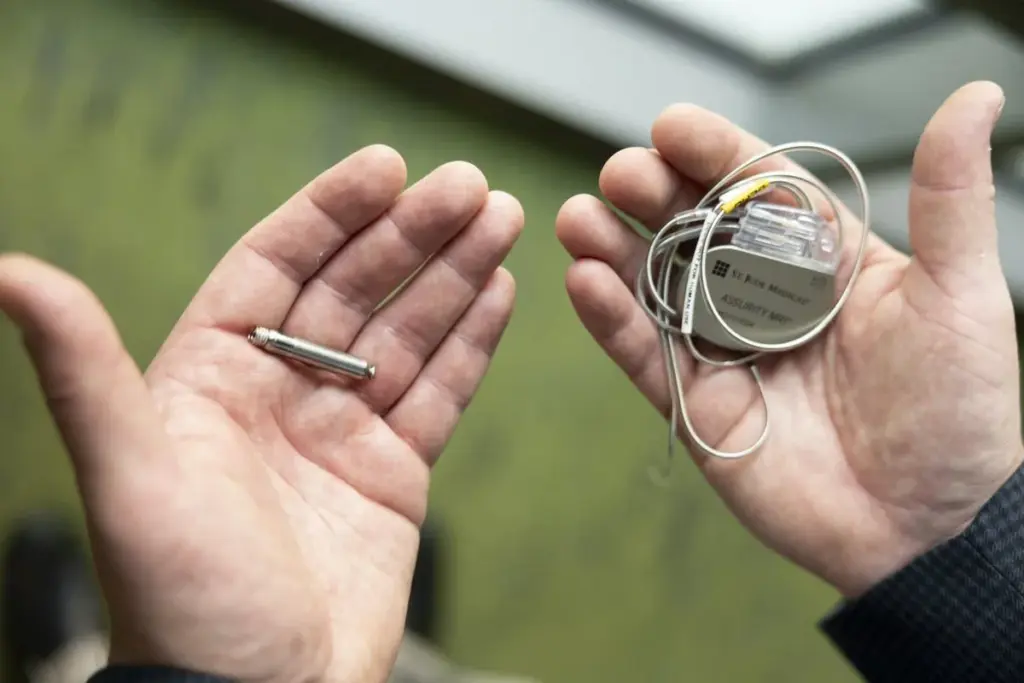

Did you know most people getting pacemakers are over 65? Pacemaker surgery for seniors is common because older adults often have heart rhythm issues.
As we get older, the chance of needing a pacemaker goes up. Older adults and pacemakers are often linked. This is because aging can harm the heart’s electrical system. It’s important to understand age considerations for pacemaker placement for both patients and doctors.
Choosing to get a pacemaker can be scary, but it’s becoming safer for seniors. Thanks to new medical technology and care, getting a pacemaker at 70 or older is now more common and safe.
Key Takeaways
- Most pacemaker recipients are over 65 years old.
- Pacemaker surgery is common among seniors due to heart rhythm disorders.
- Aging can lead to the deterioration of the heart’s electrical system.
- Understanding age considerations is key for pacemaker placement.
- Pacemaker implantation is becoming safer for older adults.
Understanding Pacemakers and Their Function
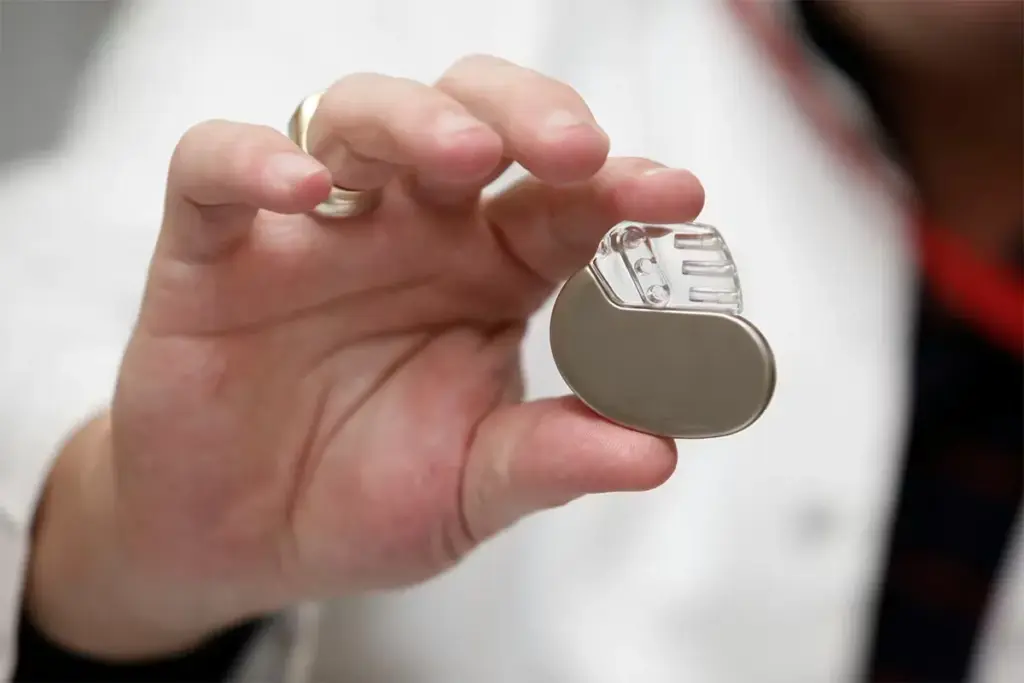

Pacemakers are key for those with heart issues. They’re small devices that keep the heartbeat steady. We’ll explore what pacemakers do and the various types out there.
What is a Pacemaker?
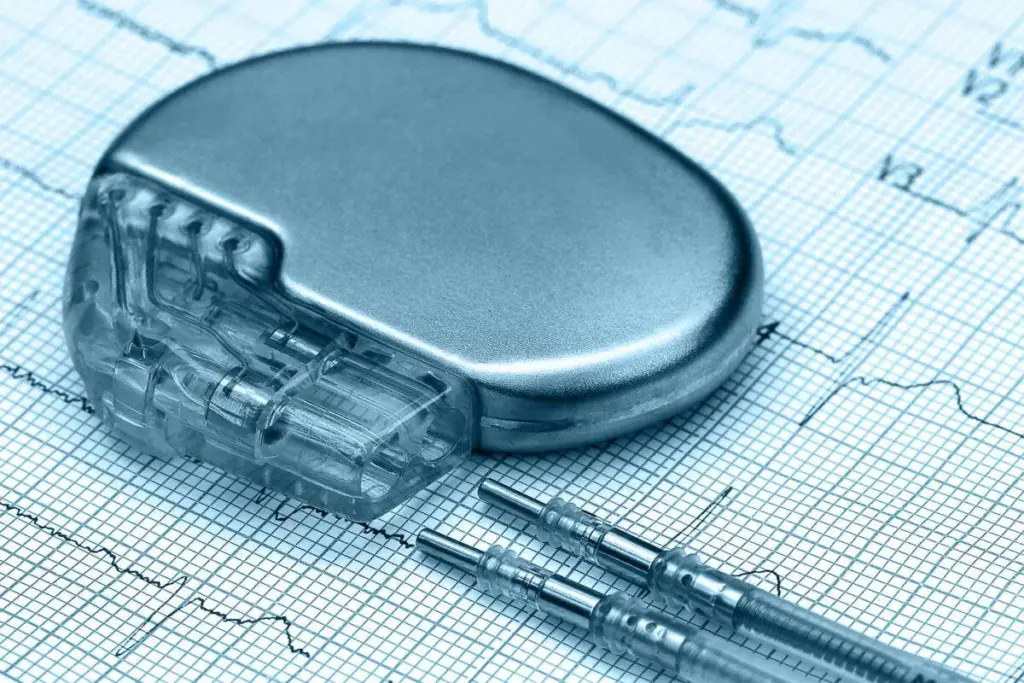
A pacemaker plays a crucial role in maintaining a normal heartbeat. It sends electrical signals to make the heart muscle contract. It’s mainly for people with slow heartbeats.
The device has two parts: the pulse generator and the leads. The pulse generator is a metal box with the battery and circuitry. The leads are wires that connect to the heart.
How Pacemakers Regulate Heart Rhythm
Pacemakers keep the heart rhythm steady by sending electrical impulses. This ensures the heart beats at the right rate. The device can adjust its settings for each patient.
This adjustment is key for good blood flow and preventing symptoms like dizziness.
Types of Pacemakers Available Today
There are many pacemaker types for different heart issues. Here are the main ones:
|
Type of Pacemaker |
Description |
Key Features |
|---|---|---|
|
Single-Chamber Pacemaker |
Uses one lead to connect to either the atrium or ventricle. |
Simple design, suitable for certain conditions. |
|
Dual-Chamber Pacemaker |
Employs two leads, one for the atrium and one for the ventricle, to maintain a natural heartbeat. |
More physiological pacing, can help maintain normal heart rhythm. |
|
Biventricular Pacemaker |
Used in cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), it helps synchronize the contractions of the ventricles. |
Beneficial for heart failure patients with certain electrical conduction issues. |
Each pacemaker type tackles different heart rhythm problems. The right one depends on the patient’s condition and lifestyle.
The Heart’s Electrical System and Cardiac Electrophysiology
Understanding the heart’s electrical system is key to diagnosing and treating heart rhythm disorders. The heart beats in sync thanks to its complex electrical system.
Normal Electrical Conduction in the Heart
The heart’s electrical system is a complex network that controls our heartbeat rhythm. It starts with the sinoatrial (SA) node, our heart’s natural pacemaker. This node sends out electrical impulses.
These impulses travel through the atrioventricular (AV) node and down the bundle of His. This causes the heart muscle to contract and pump blood.
Normal electrical conduction is vital for a regular heartbeat. Any issues in this pathway can cause arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats.
What is Cardiac Electrophysiology (EP)?
Cardiac electrophysiology (EP) studies the heart’s electrical properties. It deals with diagnosing and treating heart rhythm disorders. Techniques like electrophysiology studies (EPS) are used.
An electrophysiology lab is where these tests are done. It has advanced technology to record the heart’s electrical activity. It also performs procedures like catheter ablation to treat arrhythmias.
The Role of EP Studies in Diagnosing Heart Rhythm Problems
EP studies are vital in diagnosing complex heart rhythm problems. Doctors use catheters to record the heart’s electrical activity. This helps find the cause of arrhythmias and plan treatment.
The insights gained from EP studies are very important. They help create personalized treatment plans. This can greatly improve a patient’s quality of life.
Common Heart Conditions Requiring Pacemaker Implantation
Pacemakers help treat heart conditions that cause abnormal rhythms. They improve the patient’s health and well-being. These conditions affect the heart’s electrical system, leading to irregular heart rates and rhythms.
Bradycardia and Heart Blocks
Bradycardia is a slow heart rate, a common reason for pacemaker use. It can cause the heart to not pump enough blood. Heart blocks, which block the electrical pathway between chambers, can also cause bradycardia.
Symptoms include fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, it can lead to fainting or heart failure. A pacemaker helps by ensuring a consistent heart rate.
Sick Sinus Syndrome
Sick sinus syndrome happens when the heart’s natural pacemaker doesn’t work right. It leads to irregular heart rhythms. Symptoms include bradycardia, tachycardia, dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Pacemaker therapy can manage this by providing a steady heartbeat. It prevents the heart from beating too slowly or too quickly.
Atrial Fibrillation with Slow Heart Rate
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and often rapid heart rate. In older adults, it can be slow. This can be due to the disease’s progression or medications.
In such cases, a pacemaker may be needed. It ensures the heart beats at an adequate rate, improving symptoms and quality of life.
Heart Failure and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Heart failure means the heart can’t pump enough blood. Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) can treat it. It uses a pacemaker to coordinate the heart’s chambers.
CRT can improve symptoms, increase exercise tolerance, and enhance quality of life. It makes the heart pump more efficiently, reducing heart failure symptoms.
Understanding these heart conditions helps patients and healthcare providers make better treatment choices. This improves outcomes.
Age Demographics of Pacemaker Recipients
As the world’s population gets older, more people need pacemakers. This is most true for seniors. Knowing who gets pacemakers helps doctors give better heart care.
Statistical Overview of Pacemaker Implantation by Age
Most people getting pacemakers are older. Studies show the average age is about 75. This info helps doctors plan better care for older patients.
|
Age Group |
Percentage of Pacemaker Recipients |
|---|---|
|
65-69 |
15% |
|
70-74 |
25% |
|
75-79 |
30% |
|
80+ |
20% |
The 70-80 Age Group: The Most Common Recipients
People between 70 and 80 are most likely to get pacemakers. This is because they often have heart problems like slow heartbeats. Pacemakers help manage these issues.
“The elderly population is more susceptible to heart rhythm disorders, making pacemakers a critical component of their cardiac care.”
Why Elderly Patients Commonly Need Pacemakers
Elderly people often need pacemakers because of heart issues. Problems like slow heartbeats are common in older adults. Pacemakers help keep their heart rhythm steady.
Trends in Pacemaker Implantation Across Different Generations
More people of all ages are getting pacemakers. This is because technology has improved. It helps doctors manage heart problems better.
This trend shows a shift towards better heart care for everyone. It’s not just for the elderly anymore.
Getting a Pacemaker at 70: What to Expect
Pacemaker surgery for seniors is becoming more common. Knowing what to expect can help reduce anxiety for those at 70. We’ll guide you through the process, covering the key steps and things to consider.
Initial Evaluation and Candidacy Assessment
The first step is a thorough evaluation to see if you’re a good candidate for a pacemaker. This includes tests like electrocardiograms (ECGs), echocardiograms, and sometimes an electrophysiology study (EPS). Our medical team will look at your health, medical history, and test results to decide if a pacemaker is right for you.
It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about any concerns or questions. They can explain how a pacemaker might help and address any fears you have about the procedure.
Pre-Procedure Preparations for Seniors
After being deemed a good candidate, you’ll need to prepare for the pacemaker implantation. This might include adjusting your medications, fasting before surgery, and arranging for a ride home. It’s also wise to talk to your family or caregivers about post-procedure care plans.
Our team will give you detailed instructions on how to prepare. We’ll also discuss what to expect during recovery, helping you plan.
Special Considerations for Older Adults
Older adults may face unique challenges with pacemaker implantation. Health conditions or certain medications can affect the procedure or recovery. Our experienced medical professionals will assess these factors to tailor the treatment to your specific needs.
We also understand the importance of discussing the pros and cons of pacemakers for seniors. We’ll talk about how the benefits of pacemaker therapy can outweigh the risks for many seniors, improving their quality of life and heart health.
The Pacemaker Implantation Procedure for Seniors
Seniors thinking about getting a pacemaker need to know what to expect. We’ll explain the procedure, its benefits, and what happens during recovery. You’ll learn about the steps, anesthesia choices, and how long you’ll stay in the hospital.
Step-by-Step Overview of the Surgery
The pacemaker implantation is a minor surgery with several steps:
- Preparation: You’ll get antibiotics to prevent infection. You’ll also be connected to monitors to watch your heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia numbs the area where the pacemaker will go. Some might also get sedation to relax.
- Pacemaker Implantation: A small incision is made. The pacemaker leads are guided through a vein into the heart. Then, the pacemaker generator is placed under the skin.
- Testing: The pacemaker is tested to make sure it’s working right.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples. The area is then bandaged.
Anesthesia Options for Elderly Patients
For older patients, choosing the right anesthesia is key. Local anesthesia is often used. It lets the patient stay awake and alert during the surgery. This reduces risks from general anesthesia, which can be big for older adults.
Typical Duration and Hospital Stay
The surgery usually takes 1-2 hours. Most patients stay in the hospital for at least one night. Doctors watch the pacemaker and the patient’s health during this time.
After leaving the hospital, patients should avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard work for a few weeks. They’ll have follow-up visits to check the pacemaker and make sure they’re healing well.
Benefits of Pacemakers in Older Adults
Pacemakers have changed how we treat heart rhythm problems in older adults. They bring many benefits that make life better. As we get older, we face a higher risk of heart issues that might need a pacemaker. Luckily, new pacemaker tech is safer and works better for seniors.
Improved Quality of Life and Symptom Relief
Pacemakers greatly improve the lives of older adults. They help keep the heart beating right, easing symptoms like dizziness and shortness of breath. This makes a big difference, letting seniors stay active and enjoy their hobbies and family time.
Reduction in Hospitalizations
Pacemakers also mean fewer trips to the hospital for seniors. They keep the heart rhythm steady, avoiding serious problems that need emergency care. This is good for health and saves money on hospital bills.
Long-term Survival Benefits
Research shows pacemakers can help seniors live longer with heart issues. They keep the heart rhythm stable, avoiding dangerous arrhythmias. This can add years to a person’s life and improve their health over time.
Enhanced Independence and Activity Levels
Seniors with pacemakers feel more independent and active. This is key for both body and mind, helping prevent other health problems and boosting overall well-being.
In summary, pacemakers offer many benefits for older adults. They improve life quality, reduce hospital visits, and help seniors stay active. As technology advances, pacemakers will become even more vital for heart health in the elderly.
Potential Risks and Complications for Elderly Patients
Pacemakers save lives, but they come with risks for older adults. As we get older, our bodies change. These changes can affect how well medical procedures work, like pacemaker implants.
Procedure-Related Complications
Elderly patients face higher risks during procedures. This includes:
- Infection: Older adults might get infections more easily because their immune systems are weaker.
- Bleeding: They might bleed more during procedures, which is a concern, even if they’re on blood thinners.
- Pneumothorax: There’s a risk of a collapsed lung, which is something to think about carefully.
Device-Related Issues
There can also be problems with the device itself. These include:
- Lead Displacement: The leads that connect the pacemaker to the heart might move, needing more surgery.
- Pacemaker Malfunction: Though rare, the pacemaker can fail, so it needs to be watched closely.
- Battery Depletion: The pacemaker’s battery will eventually run out, which means it might need to be replaced.
Medication Interactions and Considerations
Older adults often take many medications. These can affect the pacemaker or its function. It’s important to:
- Monitor Medication: Keep an eye on and adjust medications to avoid problems.
- Manage Side Effects: Know how medications can affect the pacemaker or the patient’s health.
Balancing Risks and Benefits in Advanced Age
When thinking about pacemakers for older adults, weighing risks and benefits is key. Consider:
- Overall Health: Look at the patient’s health and how long they might live.
- Quality of Life: Think about how a pacemaker could improve their life.
- Patient Preferences: Respect the patient’s wishes and values in making decisions.
Healthcare providers can make better choices for elderly patients by carefully considering these factors. This helps ensure the best outcomes for pacemaker implants.
Recovery After Pacemaker Implantation for Seniors
Recovery after a pacemaker implantation is important for seniors. It involves several key steps to ensure the device works well and the senior stays healthy. We will guide you through the immediate care, activity limits, and the need for follow-up visits.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Seniors are watched closely in the hospital after the procedure. This is usually for a few hours or overnight. Our team checks if everything is okay and if the pacemaker is working right.
We also teach how to care for the wound and watch for any signs of trouble at home.
Key aspects of immediate post-operative care include:
- Resting the arm on the side of the implant to avoid putting strain on the device
- Monitoring the incision site for signs of infection or swelling
- Managing pain with prescribed medication as directed
Activity Restrictions and Gradual Return to Normal Life
After the implant, seniors need to follow some activity rules. These rules help the device settle and the wound heal. We advise avoiding heavy lifting, intense exercise, or activities that might harm the pacemaker site.
As the wound heals, seniors can start doing more things. We suggest starting with light exercises and then gradually increasing the intensity. It’s important to listen to our advice to avoid problems and make sure the pacemaker works right.
Follow-up Appointments and Monitoring
Follow-up visits are key to the recovery process. These visits let our team check the device, adjust settings if needed, and watch for any issues. We usually schedule the first visit a few weeks after the procedure, with more visits as needed.
At these visits, we might do device checks, review how the pacemaker is doing, and make any needed changes. We also answer any questions or concerns seniors have about their device or health.
By following our advice on care, activity, and attending follow-up visits, seniors can have a smooth recovery after pacemaker implantation.
Living with a Pacemaker in Later Life
Living with a pacemaker in later life means managing your health and making lifestyle changes. As we get older, our hearts change, which can impact the pacemaker and heart health.
Daily Activities and Lifestyle Adjustments
Having a pacemaker doesn’t usually limit daily activities, but some changes are needed. Avoid heavy lifting or bending for a few weeks after getting the pacemaker. Most people can go back to normal activities in a week or two.
Pay attention to how your body reacts to different activities. If you feel dizzy, tired, or have irregular heartbeats, talk to your doctor.
Device Checks and Battery Longevity
Regular checks are key to make sure your pacemaker works right. These checks can often be done remotely, so you don’t have to go to the hospital.
Pacemaker batteries last from 5 to 15 years, depending on the type and settings. Your doctor will tell you how long your battery should last and when it needs to be replaced.
|
Check-up Type |
Frequency |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
Remote Monitoring |
Regularly scheduled |
To check device function and heart rhythm |
|
In-person Visit |
At least annually |
Comprehensive check of device and overall health |
Travel Considerations with a Pacemaker
Traveling with a pacemaker needs some planning. Carry a pacemaker identification card and tell your airline or travel provider about your device. Airport security is usually safe, but let them know about your pacemaker before screening.
Research medical facilities at your destination in case of emergencies. Keep a list of emergency contacts and your doctor’s information handy.
Managing Other Health Conditions Alongside a Pacemaker
Managing other health conditions is important with a pacemaker. Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart failure need careful attention. This ensures your pacemaker works well and keeps you healthy.
Work closely with your healthcare team to manage these conditions. Regular check-ups and following your treatment plan are essential for your health and quality of life.
Advances in Pacemaker Technology Benefiting Older Adults
New pacemaker technology has changed how we treat heart rhythm problems. It helps older people a lot. These updates make pacemakers work better and improve life quality for seniors.
Older pacemakers have leads that can cause problems. But, new tech has fixed this issue.
Leadless Pacemakers
Leadless pacemakers are a big step forward. They go straight into the heart, avoiding leads. They are great for older adults because they lower infection risk and make implanting safer.
The good things about leadless pacemakers are:
- Less chance of lead problems
- Smaller, easier implant
- They are safer
MRI-Compatible Devices
Now, there are MRI-safe pacemakers. These let patients get MRI scans safely. This is key for older adults needing MRI scans for health checks.
MRI safety means patients can get needed scans without worry. It helps them get the care they need without limits.
Remote Monitoring Capabilities
Remote monitoring has changed pacemaker care. It lets doctors check devices and heart rhythms from afar. This cuts down on doctor visits.
The benefits of remote monitoring are:
- Finding problems early
- Better care through constant checks
Future Innovations in Cardiac Device Therapy
Future pacemaker tech will bring even more improvements. We’ll see better battery life, smaller devices, and more diagnostic tools. These updates will help manage heart rhythm issues in older adults even better.
As tech keeps getting better, we’re dedicated to bringing the latest in heart care to our patients. We want to make sure they get the best treatment results.
Heart Health Management for Seniors with Pacemakers
Keeping the heart healthy is key for seniors with pacemakers. As we get older, our hearts change, which can affect pacemakers. So, taking care of heart health is very important.
Dietary Recommendations
Eating right is vital for heart health in seniors with pacemakers. They should eat lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins. It’s also good to cut down on sodium, sugar, and fats.
Drinking plenty of water is also important. This helps keep the body hydrated.
Some foods are great for the heart. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish like salmon and sardines are very beneficial. Adding these to your diet can help your heart stay strong.
Exercise Guidelines for Pacemaker Recipients
Exercise is key for heart health and fitness. Seniors with pacemakers should pick safe and fun exercises. Walking, swimming, and cycling are good choices because they’re easy on the body.
Always talk to a doctor before starting a new exercise routine. They can help pick the best activities and give safety tips. It’s also important to listen to your body and not push too hard.
Regular Medical Check-ups and Heart Health Monitoring
Regular doctor visits are essential for heart health in seniors with pacemakers. These visits let doctors check the pacemaker and heart health. They can also adjust treatment plans as needed.
Seniors should pay attention to their body’s signals. If they notice any changes or concerns, they should tell their doctor right away. This helps catch and manage problems early.
Emotional Well-being and Support Systems
Having a pacemaker can affect a person’s mood. It’s important to take care of emotional health. Support from loved ones and groups can help a lot.
Doing things that make you happy and using stress-reduction techniques like meditation can also help. These activities can improve emotional well-being.
Conclusion
Pacemaker implantation is a key treatment for many older adults with heart rhythm disorders. Most pacemaker users are between 70 and 80 years old. This age group can greatly benefit from this technology.
It’s important to understand what pacemakers do and how they help. They treat heart rhythm problems and improve quality of life. This knowledge is vital for both patients and doctors.
Pacemakers can make a big difference in the lives of older adults. They help manage heart health and reduce hospital stays. As technology advances, so will the care for pacemaker users.
FAQ
What does EP stand for in medical terms?
EP stands for Electrophysiology. It’s the study of the heart’s electrical system and its functions.
What is cardiac electrophysiology?
Cardiac electrophysiology studies the heart’s electrical system. It looks at both normal and abnormal heart rhythms.
What is an EP study?
An EP study, or electrophysiology study, tests for heart rhythm problems. It measures the heart’s electrical activity.
What is the typical age for pacemaker implantation?
Pacemaker implantation usually happens in people aged 70-80 years old.
What are the benefits of pacemakers in older adults?
Pacemakers can greatly improve quality of life. They also reduce hospital stays and help people live longer.
What are the possible risks and complications of pacemaker implantation in elderly patients?
Risks include complications from the procedure and issues with the device. Medication interactions are also a concern.
How do pacemakers regulate heart rhythm?
Pacemakers send electrical impulses to the heart. This ensures a consistent and proper heartbeat.
What are the different types of pacemakers available?
There are many types of pacemakers. These include single-chamber, dual-chamber, and biventricular pacemakers. There are also leadless pacemakers.
How long does pacemaker implantation surgery take?
The surgery usually takes 1-2 hours. Most patients can go home the next day.
What is the recovery process like after pacemaker implantation?
Recovery involves immediate care and activity restrictions. It also includes a gradual return to normal life. Follow-up appointments are needed for monitoring.
Can I travel with a pacemaker?
Yes, you can travel with a pacemaker. But, it’s important to take precautions and tell your healthcare provider about your plans.
How often do pacemakers need to be checked?
Pacemakers need regular checks. These can be done remotely or in-person. They ensure the device is working right and the battery lasts long.
What are the dietary recommendations for seniors with pacemakers?
Seniors with pacemakers should eat heart-healthy foods. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. They should also avoid sodium and saturated fats.
Can I exercise with a pacemaker?
Yes, you can exercise with a pacemaker. But, it’s important to follow guidelines and talk to your healthcare provider. This ensures safe and beneficial physical activity.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7838942/









