Pulmonology focuses on diagnosing and treating lung and airway conditions such as asthma, COPD, and pneumonia, as well as overall respiratory health.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Diagnosing emphysema requires a synthesis of clinical history, physical examination, and advanced physiological and imaging assessments. It is not enough to identify airflow obstruction; the clinician must define the extent of parenchymal destruction, the degree of hyperinflation, and the impact on gas exchange. At Liv Hospital, we utilize a multimodal approach not only to confirm the presence of the disease but also to quantify the extent of the destruction and its impact on the patient’s functional capacity. Because emphysema involves structural destruction, imaging plays a more central role in its specific diagnosis compared to chronic bronchitis. Early and accurate evaluation is paramount to implementing strategies that can slow disease progression and optimize symptom management.
The physical exam provides the first clues to the presence of emphysema. Clinicians look for specific signs of hyperinflation and airflow obstruction.
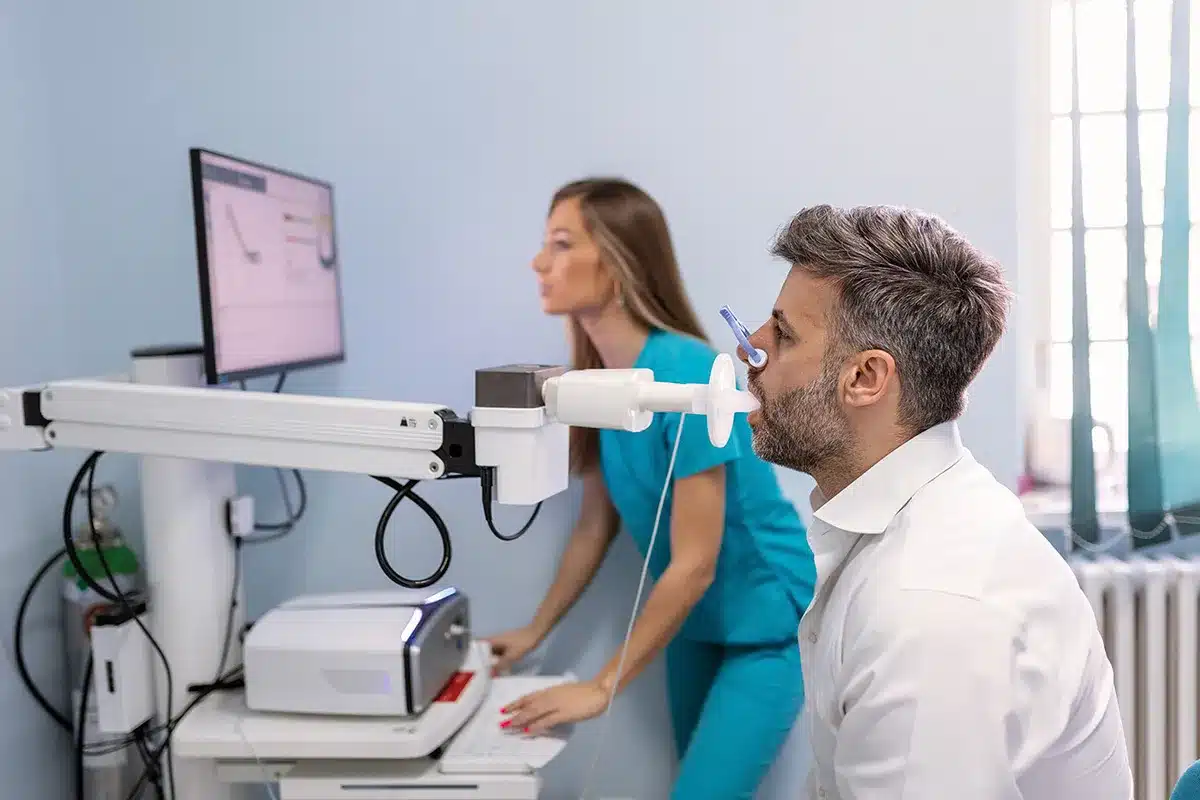
Spirometry is the gold standard for diagnosing airflow limitation. It measures the volume and speed of air a patient can exhale.
While spirometry measures airflow, body plethysmography (body box) measures the volume of air in the lungs. This is crucial for quantifying hyperinflation, a hallmark of emphysema.
The DLCO test is the single most crucial physiological test to distinguish emphysema from chronic bronchitis and asthma. It measures the lungs’ ability to transfer gas from the alveoli into red blood cells.
CT imaging has revolutionized the evaluation of emphysema. Unlike a standard chest X ray, which is insensitive to early disease, a CT scan provides detailed visualization of the lung parenchyma.
Given the genetic implications, the World Health Organization recommends that all patients with a diagnosis of COPD or emphysema be screened once for Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency.
In advanced disease, ABG analysis is performed to assess gas exchange efficiency.
Functional capacity is evaluated using the 6 minute walk test. This measures the distance a patient can walk in six minutes and monitors oxygen saturation during the activity.
Because emphysema damages the blood vessels in the lungs (by destroying the capillary bed), it can strain the heart. An echocardiogram is used to screen for pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lung arteries) and cor pulmonale (enlargement of the right side of the heart). Assessing proper ventricular function is critical for overall prognosis and management.


Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
CT scans use X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images and are excellent for visualizing kidney stones, detecting tumors, and evaluating traumatic injuries. They are fast and widely available. MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues, making it superior for staging prostate cancer, evaluating bladder wall invasion, and assessing pelvic floor disorders without ionizing radiation.
Contrast dye, usually iodine-based, is injected into a vein to highlight the blood vessels and urinary tract organs. As the kidneys filter the dye from the blood, it opacifies the urine. This allows the radiologist to see the internal structure of the kidneys, the ureters, and the bladder clearly, revealing blockages, tumors, or structural abnormalities that would be invisible on a non-contrast scan.
Multiparametric MRI is an advanced imaging technique that combines standard anatomical sequences with functional sequences like Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced imaging. This provides a comprehensive assessment of the prostate, allowing doctors to distinguish between benign conditions like BPH and significant prostate cancer, and to guide targeted biopsies.
CT scans do involve exposure to ionizing radiation, which carries a small theoretical risk of cellular damage over time. However, modern CT scanners use dose-modulation technology to minimize this exposure to the lowest level necessary for a diagnostic image. The benefit of an accurate and timely diagnosis for serious urological conditions typically far outweighs the minimal risk of radiation.
Many modern orthopedic implants are MRI-safe, although they may cause some image distortion. However, older pacemakers, defibrillators, and certain metal clips may be unsafe in the strong magnetic field. It is critical to inform the imaging team of any metallic implants so they can verify their safety compatibility or recommend an alternative test like a CT scan.




It’s important to know the difference between anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock. Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction. It affects many parts of the body



Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)