Neurology diagnoses and treats disorders of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, as well as thought and memory.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Diagnosis in endovascular surgery focuses on accurately identifying vascular pathology, defining its anatomical extent, and determining whether a minimally invasive intravascular approach is appropriate. Because many vascular conditions progress silently or present with nonspecific symptoms, imaging plays a central role in both diagnosis and procedural planning. The diagnostic process integrates clinical assessment with detailed vascular imaging to guide safe and effective intervention.

The diagnostic approach prioritizes precision and anatomical clarity.
Core objectives include
• Confirming the presence of vascular pathology
• Defining vessel anatomy and disease extent
• Identifying areas of narrowing, blockage, or structural weakness
• Assessing blood flow dynamics
• Determining suitability for endovascular intervention
Accurate diagnosis directly influences procedural strategy and outcome.
Clinical assessment provides context for imaging findings.
Evaluation focuses on
• Nature and timing of symptoms
• Correlation between symptoms and vascular territories
• Progression or sudden onset patterns
• Functional impact on neurological or systemic systems
Clinical findings help prioritize imaging targets.
Imaging is the cornerstone of endovascular diagnosis.

Non invasive imaging is often the first diagnostic step.
It helps
• Visualize vessel structure and patency
• Identify areas of narrowing or occlusion
• Assess vessel wall integrity
• Estimate blood flow characteristics
These techniques guide further evaluation.
Cross sectional imaging provides detailed anatomical information.
It allows
• Precise measurement of vessel diameter
• Visualization of surrounding structures
• Identification of complex or tortuous anatomy
• Detection of associated tissue changes
High spatial resolution supports accurate planning.
In some cases, direct intravascular imaging is required.
This approach provides
• Real time visualization of blood flow
• Dynamic assessment of vessel behavior
• Precise localization of pathology
• Immediate transition from diagnosis to treatment
Catheter based imaging is central to endovascular practice.
Neurovascular imaging requires exceptional precision.
Imaging supports
• Mapping of cerebral arterial and venous systems
• Identification of critical branch vessels
• Assessment of collateral circulation
• Evaluation of lesion accessibility
Accurate neurovascular imaging minimizes neurological risk.
Beyond anatomy, functional flow assessment is essential.
Imaging helps evaluate
• Speed and direction of blood flow
• Pressure gradients across narrowed segments
• Effect of disease on tissue perfusion
Functional data inform treatment necessity and urgency.
Imaging guides every step of endovascular intervention.
Planning considerations include
• Selection of access route
• Choice of catheter and device size
• Anticipation of anatomical challenges
• Estimation of procedural risk
Detailed imaging reduces intra procedural uncertainty.
Imaging also helps rule out non vascular causes of symptoms.
This includes
• Structural lesions unrelated to vessels
• Degenerative or inflammatory conditions
• Non vascular causes of neurological deficits
Exclusion prevents unnecessary intervention.
Several factors complicate diagnosis.
Challenges include
• Incidental vascular findings of unclear significance
• Complex anatomy with overlapping pathology
• Age related vessel changes mimicking disease
• Motion or artifact affecting image quality
Careful interpretation is essential.
Using more than one imaging method often improves accuracy.
Multimodal imaging allows
• Cross validation of findings
• Better anatomical and functional correlation
• Improved confidence in treatment decisions
Comprehensive imaging supports safer intervention.
Imaging is not limited to initial diagnosis.
Follow up imaging supports
• Monitoring disease progression
• Assessing treatment durability
• Detecting recurrence or new pathology
• Guiding long term management
Longitudinal imaging informs future care decisions.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
In some cases, catheter based imaging allows immediate treatment.
Because symptoms depend on both anatomy and flow dynamics.
No, treatment depends on symptoms, risk, and progression.
Yes, follow up imaging is important for long term care.

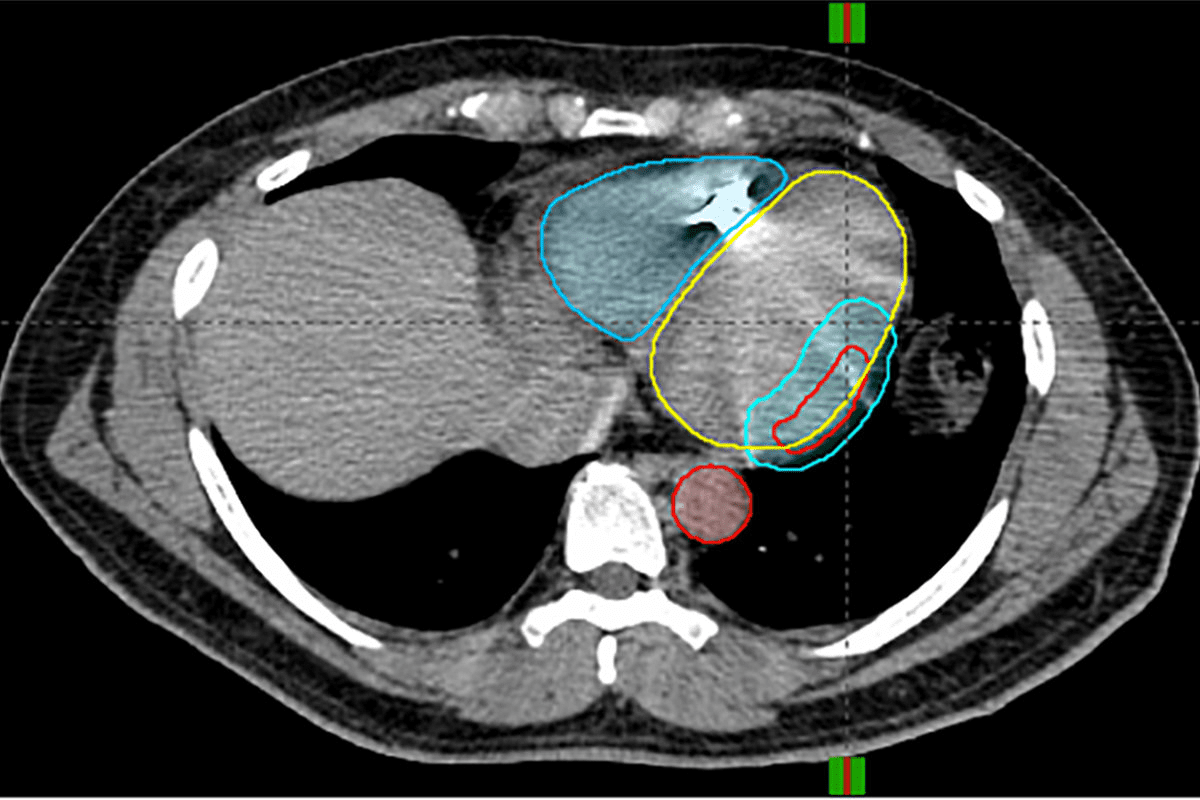
Radiosurgery is a precise way to treat cancer and other conditions with focused radiation. It’s a non-invasive method that offers a highly effective treatment. This

Endarterectomy surgery is a complex procedure that needs precision and expertise. Typically, the operation lasts between 2 to 4 hours. The actual endarterectomy procedure time
Recent studies show that nearly 80% of hospital issues, deaths, and costs come from just seven emergency surgeries. This highlights the need to know the

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)