Neurology diagnoses and treats disorders of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, as well as thought and memory.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Symptoms that lead to endovascular surgical evaluation arise from impaired blood flow, vessel wall instability, or abnormal vascular connections. Because blood vessels supply every organ system, symptom presentation depends on the vascular territory involved and the speed at which pathology develops. From a neurological and systemic perspective, symptoms often reflect tissue ischemia, pressure effects, or risk of rupture, and they may progress silently until a critical threshold is reached. Recognizing symptom patterns and underlying risk factors is essential for timely intervention.

Vascular disease suitable for endovascular treatment may produce gradual, intermittent, or sudden symptoms.
Common general features include
• Symptoms related to reduced blood flow
• Worsening with physical or metabolic demand
• Sudden onset when vessel occlusion or rupture occurs
• Fluctuation based on collateral circulation
• Disproportionate severity compared to external findings
Symptoms may be subtle until advanced disease develops.
When vessels supplying the brain are affected, neurological symptoms often predominate.
Possible neurological manifestations include
• Sudden weakness or numbness affecting one side of the body
• Difficulty speaking or understanding language
• Visual disturbances or loss of vision
• Sudden severe headache
• Altered level of consciousness
These symptoms reflect compromised cerebral perfusion or vessel instability.
Gradual vessel narrowing often produces progressive symptoms.
Common features include
• Activity related discomfort or weakness
• Reduced endurance in affected regions
• Symptoms that improve with rest
• Gradual functional decline over time
Progressive narrowing may remain unnoticed until advanced stages.

Sudden vascular compromise produces abrupt and severe symptoms.
Acute presentations may include
• Rapid onset neurological deficits
• Severe pain in the affected area
• Sudden loss of function
• Signs of tissue ischemia
These situations often require urgent evaluation.
Structural vessel weakness can remain silent until complications develop.
Possible warning signs include
• Headache or pressure sensations
• Localized pain near affected vessels
• Neurological symptoms caused by compression
• Sudden symptom escalation if rupture occurs
Early detection is critical due to potential severity.
Vascular disease may also produce generalized symptoms.
These may include
• Fatigue related to poor perfusion
• Dizziness or lightheadedness
• Reduced exercise tolerance
• Coldness or color changes in extremities
Systemic symptoms often coexist with localized findings.
Risk factors reflect cumulative effects on vessel health and integrity.
Conditions affecting blood vessels increase procedural relevance.
Key factors include
• Long standing vascular disease
• Metabolic imbalance affecting vessel walls
• Chronic inflammation
• Altered blood flow dynamics
These factors contribute to vessel narrowing or weakening.
Aging alters vascular structure and function.
Age related influences include
• Reduced vessel elasticity
• Accumulated microvascular damage
• Increased susceptibility to narrowing or dilatation
Age modifies both risk and symptom presentation.
Certain factors specifically increase neurovascular vulnerability.
These include
• Previous cerebrovascular events
• Structural vessel abnormalities
• Impaired cerebral blood flow regulation
Such factors heighten the importance of early detection.
Long term lifestyle patterns influence vascular integrity.
Contributing factors include
• Physical inactivity
• Prolonged physiological stress
• Dietary influences on vascular health
Lifestyle factors interact with biological risk.
Some individuals have inherent vascular vulnerability.
Predisposing factors may include
• Inherited vessel wall characteristics
• Congenital vascular variations
• Family history of vascular disease
These factors can influence disease onset and severity.
Many vascular conditions suitable for endovascular treatment progress silently until complications occur. Awareness of subtle neurological changes, activity related symptoms, or sudden unexplained deficits supports early evaluation and intervention. Early recognition reduces the risk of irreversible tissue injury.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
They may be sudden or gradually progressive depending on blood flow changes.
Yes, subtle changes can precede significant events.
Yes, aging alters vessel structure and resilience.
No, risk varies depending on vessel location and function.

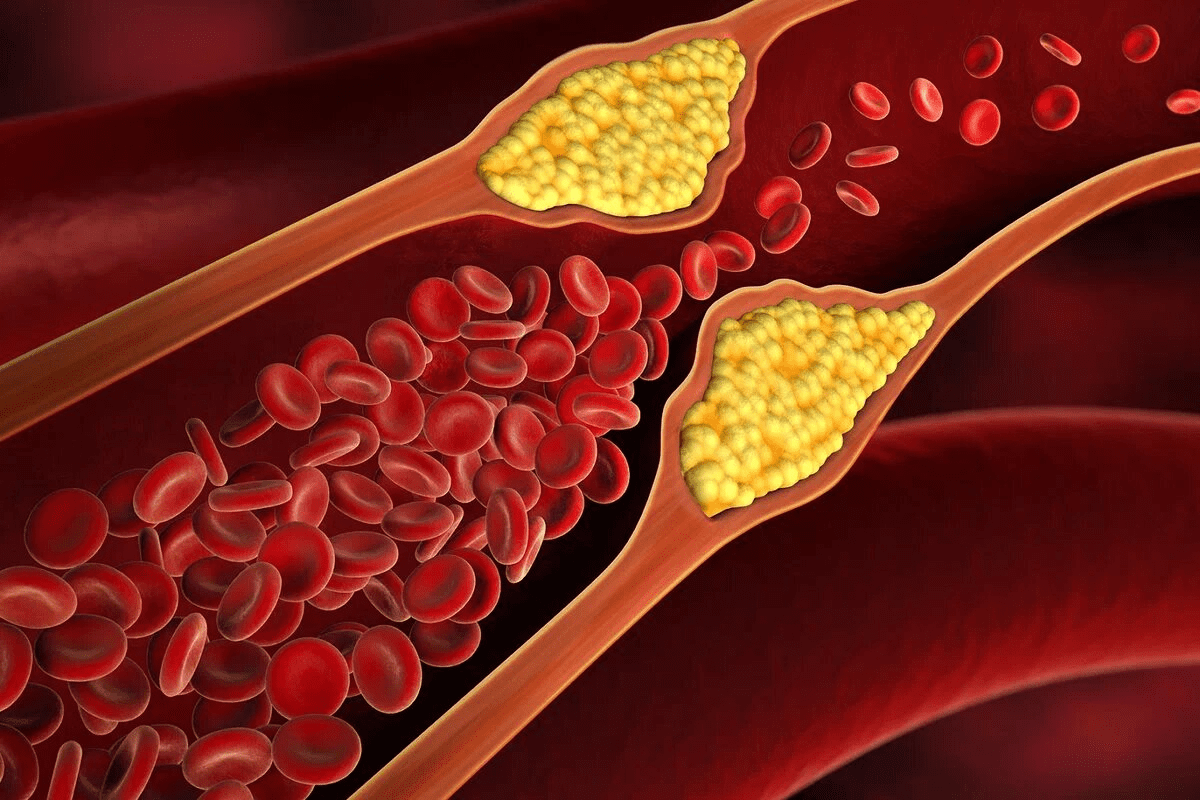
Carotid artery disease affects millions of Americans. Over 800,000 carotid endarterectomy procedures are done worldwide each year. This surgery is key to prevent strokes in

Choosing to have a carotid endarterectomy is a big decision. It’s important to know what to expect during recovery. Did you know that almost 100,000
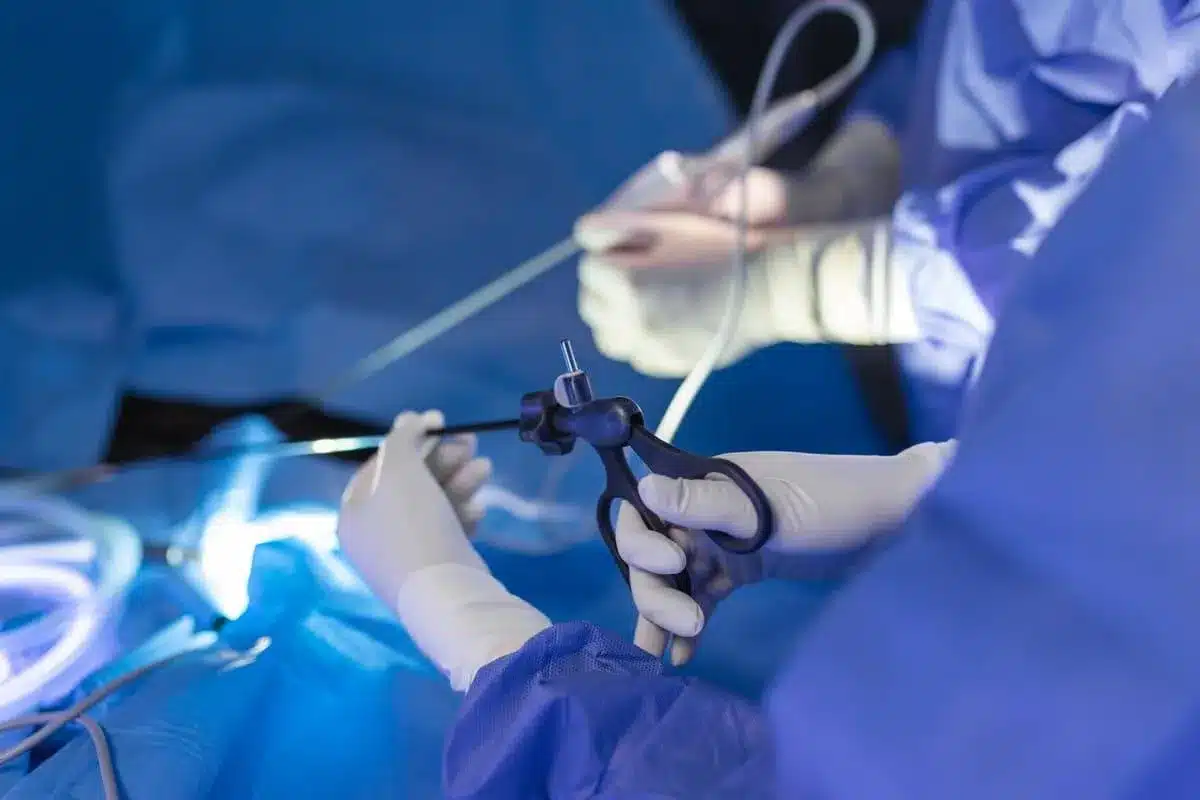
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) is a severe stroke type. It has high morbidity and mortality rates. Recent studies show early aneurysm treatment has improved outcomes.


Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)