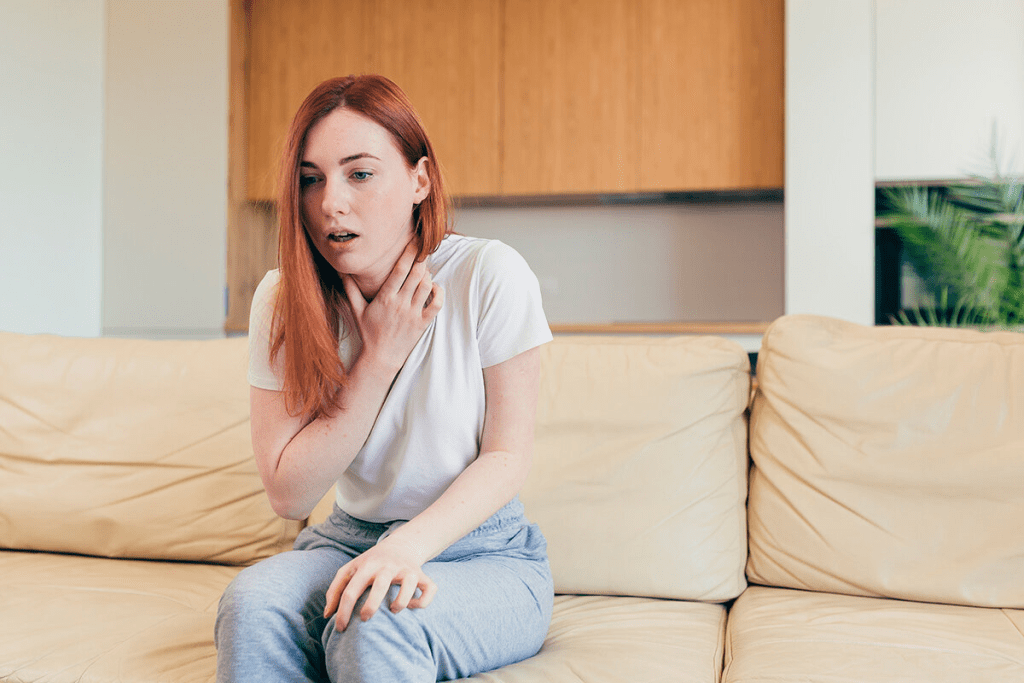

About 1 in 4 people worldwide have anemia. This is when the body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. These cells are key for carrying oxygen to our body’s tissues. Anemia can cause serious problems, like shortness of breath.
Without enough red blood cells or hemoglobin, our body can’t get enough oxygen. This can make us feel tired, weak, and have trouble breathing. It’s important to know how low hemoglobin levels can affect our breathing.
Key Takeaways
- Anemia is a global health issue affecting a significant portion of the population.
- The condition impairs the body’s ability to transport oxygen, leading to various symptoms.
- Shortness of breath is a significant concern for individuals with anemia.
- Low hemoglobin levels are directly related to the severity of anemia symptoms.
- Understanding anemia’s impact on the body can help in managing its symptoms.
Understanding Anemia and Its Impact on Breathing
Anemia is a condition in which there are not enough red blood cells. These cells are key for carrying oxygen around the body. This can cause breathing problems among other health issues.
What Defines Anemia as a Medical Condition
Anemia means you have too few red blood cells or ones that don’t work right. These cells carry hemoglobin, a protein that brings oxygen from the lungs to the body. Without enough healthy red blood cells, your body can’t get enough oxygen. This can make you feel tired and short of breath.
The Critical Role of Hemoglobin in Oxygen Transport
Hemoglobin is vital for moving oxygen. It’s the protein in red blood cells that picks up oxygen in the lungs and carries it to the body’s tissues. If you have anemia, you might not have enough hemoglobin. This makes it hard for your body to get the oxygen it needs, leading to shortness of breath.
Knowing how hemoglobin works is key to understanding anemia. It helps us see why anemia affects breathing. By understanding this, people can better grasp their symptoms and why they need to see a doctor if they have anemia.
The Science Behind Anemia Symptoms and Breathing Difficulties

To understand how anemia causes shortness of breath, we need to look at oxygen delivery. This process involves the lungs, heart, and blood vessels. They work together to give the body’s tissues the oxygen they need.
How Oxygen Delivery Works in Healthy Individuals
In healthy people, oxygen delivery is very efficient. Here’s how it happens:
- The lungs take oxygen from the air and put it into the bloodstream.
- The heart pumps this oxygen-rich blood to different parts of the body.
- Hemoglobin in red blood cells carries oxygen to tissues.
- The body’s tissues use oxygen for their metabolic needs.
This complex process makes sure tissues get the oxygen they need. Good oxygen delivery is key for energy and health.
Physiological Changes During Anemia That Affect Breathing
Anemia messes with this balance by lowering hemoglobin or red blood cells. This means tissues don’t get enough oxygen. Symptoms like shortness of breath can result.
The changes in anemia include:
- Less oxygen in the blood.
- The body tries to compensate with a faster heart rate and breathing.
- In some cases, the body tries to make more red blood cells, but it’s limited by the anemia’s cause.
Knowing these changes helps us see why anemia causes breathing problems. It also shows how treating anemia can help with these symptoms.
Common Anemia Symptoms: Beyond Shortness of Breath
Anemia affects the body in many ways, causing symptoms beyond just shortness of breath. It’s important to know these symptoms to diagnose and treat anemia well.
Respiratory Symptoms of Anemia
Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, is a key sign. But anemia can also lead to other breathing problems. You might feel like you’re not getting enough air, even when you’re sitting or doing light activities. Some people might breathe fast or feel out of breath without any obvious reason.
Non-Respiratory Anemia Symptoms
Anemia also shows up in other health issues. Here are some common ones:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Feeling very tired or weak is common. It can make everyday tasks hard.
- Pale Skin: Not having enough red blood cells can make your skin look pale. This is often seen in your face, lips, and nail beds.
- Dizziness and Lightheadedness: Anemia can make you feel dizzy or lightheaded. This is because your brain isn’t getting enough oxygen.
- Cold Hands and Feet: Anemia can cause poor blood flow. This might make your hands and feet feel cold.
- Headaches: Some people get headaches because their brain isn’t getting enough oxygen.
It’s key to recognize these symptoms to fully understand how anemia affects the body. Spotting them early and getting the right treatment can greatly improve life for those with anemia.
Iron Deficiency Anemia: The Most Common Cause of Anemia-Related Breathing Problems
Iron deficiency anemia is a common problem that makes it hard for the body to carry oxygen. This leads to symptoms like shortness of breath. It happens when the body doesn’t have enough iron to make hemoglobin, a key protein in red blood cells.
How Iron Deficiency Develops
Iron deficiency can come from not eating enough iron, losing blood too much, or needing more iron. People who don’t eat meat or animal products often don’t get enough iron. This is because plant-based iron is harder for the body to absorb.
Chronic blood loss is another big reason. It can be from ulcers, cancer, or heavy periods in women. Also, some medical conditions or pregnancy can make you need more iron.
Risk Factors for Iron Deficiency
There are several things that make you more likely to get iron deficiency anemia. These include:
- Poor diet: Not eating enough foods rich in iron.
- Chronic diseases: Conditions like celiac disease or Crohn’s disease that mess with nutrient absorption.
- Blood loss: Losing blood too much, like from regular donations or heavy periods.
- Pregnancy: Needing more iron to support the baby and the mother’s blood volume.
Characteristic Symptoms Including Dyspnea
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia can vary. But common ones are feeling very tired, weak, and pale. Dyspnea or shortness of breath is also common. This happens because the body’s tissues aren’t getting enough oxygen. It makes the heart work harder and breathe faster.
| Symptom | Description |
| Fatigue | Feeling extremely tired or weak |
| Dyspnea | Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing |
| Pale Skin | Reduced hemoglobin gives the skin a pale appearance |
Vitamin Deficiency Anemia and Respiratory Symptoms
Vitamins B12 and folate are key for making red blood cells. Without enough, you can get anemia and breathing problems. Knowing why and how these issues happen helps manage them.
B12 Deficiency: Causes and Breathing Impacts
A lack of Vitamin B12 causes megaloblastic anemia. This is when red blood cells are too big and don’t work right. It makes it hard for oxygen to reach your body’s tissues, leading to shortness of breath.
There are many reasons for B12 deficiency:
- Not getting enough B12 from food, often in vegans
- Having trouble absorbing B12 because of diseases like celiac or Crohn’s
- Some medicines can stop B12 from being absorbed
To fix B12 deficiency, you might need supplements. These can be pills or shots to help your body make more red blood cells.
Folate Deficiency and Its Respiratory Effects
Folate, or vitamin B9, is also vital for making red blood cells. Not having enough folate can cause megaloblastic anemia too. This can make breathing hard, just like B12 deficiency.
Folate deficiency can come from:
- Eating too little folate, like not enough leafy greens or legumes
- Being pregnant, when your body needs more folate
- Medical conditions or medicines that mess with folate levels
To fix folate deficiency, you might need to eat more folate-rich foods. Sometimes, supplements are also needed to keep your red blood cells healthy.
In short, not having enough B12 or folate can cause serious health problems, including breathing issues. Getting the right treatment is key to feeling better.
Hemolytic Anemia: When Red Blood Cells Are Destroyed
When red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be made, hemolytic anemia occurs. This can cause breathing difficulties and other symptoms. It’s a complex condition where red blood cells are destroyed early, leading to health issues.
Mechanisms of Premature Red Blood Cell Destruction
Red blood cells can be destroyed in different ways in hemolytic anemia. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia happens when the immune system attacks the body’s own red blood cells. Another cause is inherited conditions like sickle cell disease, where red blood cells are shaped abnormally and destroyed more easily.
Other reasons include infections, certain medications, and mechanical damage. For example, mechanical heart valves can damage red blood cells as they pass through.
Breathing Difficulties in Hemolytic Anemia
Breathing difficulties or dyspnea are common symptoms of hemolytic anemia. This is because fewer red blood cells can carry oxygen to tissues and organs, including the lungs. People may find it hard to breathe even when they’re not doing much.
| Cause | Effect on Red Blood Cells | Impact on Breathing |
| Autoimmune hemolytic anemia | Immune system destroys red blood cells | Reduced oxygen delivery, potentially causing dyspnea |
| Inherited conditions (e.g., sickle cell disease) | Abnormally shaped red blood cells are destroyed | Chronic anemia leading to breathing difficulties |
| Mechanical damage (e.g., mechanical heart valves) | Red blood cells are mechanically damaged and destroyed | Potential for anemia and associated breathing issues |
It’s important to understand hemolytic anemia to manage its symptoms, like breathing problems. Treatment aims to fix the underlying cause. This might include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
Chronic Disease Anemia and Breathing Complications
Chronic disease anemia and breathing problems are linked. This is because of the body’s inflammatory response and how it affects red blood cell production. Diseases like chronic kidney disease and rheumatoid arthritis can cause anemia. This happens because of chronic inflammation.
How Chronic Inflammation Affects Red Blood Cell Production
Many chronic diseases cause chronic inflammation. This inflammation greatly affects the body’s ability to make red blood cells. Inflammatory cytokines can slow down the production of red blood cells, leading to anemia.
This anemia is often called anemia of chronic disease (ACD) or anemia of inflammation. The reasons for ACD are complex. Inflammatory cytokines can stop the production of erythropoietin, a hormone needed for red blood cells. Also, inflammation can mess with iron metabolism, making anemia worse.
Common Conditions Associated with Anemia of Chronic Disease
Several chronic conditions are linked to anemia of chronic disease. These include:
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): CKD is a major cause of anemia because the kidneys can’t make enough erythropoietin.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA’s chronic inflammation can stop erythropoiesis, leading to anemia.
- Cancer: Some cancers and their treatments can cause anemia. This is due to inflammation and bone marrow suppression.
- Chronic Infections: Long-term infections, like HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis, can also cause anemia of chronic disease.
It’s important to understand how chronic disease anemia and breathing problems are connected. By treating the root causes of anemia, healthcare providers can help patients. This can reduce symptoms like breathing difficulties and improve health outcomes.
Aplastic Anemia and Respiratory Function
Aplastic anemia is a rare and serious condition. It affects the bone marrow’s ability to make blood cells. This can lead to respiratory problems.
The bone marrow is key for oxygen transport and immune function. When it fails, as in aplastic anemia, the effects are severe. Bone marrow failure means fewer red blood cells. These cells carry oxygen to tissues and organs.
Consequences of Bone Marrow Failure
Bone marrow failure means fewer blood cells. This leads to anemia, infections, and bleeding disorders. The lack of red blood cells causes fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Patients with aplastic anemia face various respiratory symptoms. These symptoms are due to less oxygen delivery. It’s important to manage these symptoms to improve quality of life.
Managing Breathing Difficulties
Managing breathing issues in aplastic anemia requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes oxygen therapy and blood transfusions to boost red blood cell count. Medications are also used to stimulate bone marrow or suppress the immune system.
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing aplastic anemia’s respiratory and other complications.
Patients can also benefit from lifestyle changes. Avoiding strenuous activities and eating a healthy diet rich in iron and nutrients is helpful.
Understanding the link between aplastic anemia and respiratory function helps healthcare providers. They can then develop effective treatment plans to manage symptoms and improve patient outcomes.
Sickle Cell Anemia and Acute Chest Syndrome
Sickle cell anemia and respiratory problems like acute chest syndrome are closely linked. This genetic disorder causes abnormal hemoglobin and deformed red blood cells. These cells can block small blood vessels, leading to serious health issues, including breathing problems.
Unique Breathing Challenges in Sickle Cell Disease
People with sickle cell disease have special breathing challenges. Acute chest syndrome is a major cause of illness and death. It involves a new lung issue, fever, breathing problems, or chest pain. This can cause severe breathing trouble, needing quick and effective treatment.
Key factors contributing to breathing challenges in sickle cell disease include:
- Acute chest syndrome
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Chronic anemia leading to decreased oxygen delivery to tissues
Recognizing and Responding to Respiratory Crises
It’s important to spot respiratory crises in sickle cell disease patients early. Look for severe chest pain, trouble breathing, and fever. Quick medical help is key to avoid complications and manage the condition well.
| Symptom | Description | Action |
| Severe Chest Pain | A sudden onset of sharp chest pain | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Difficulty Breathing | Shortness of breath or labored breathing | Administer oxygen if available and seek medical help |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature | Monitor temperature and seek medical evaluation |
Managing sickle cell anemia and its breathing issues, like acute chest syndrome, needs a full plan. This includes teaching patients, regular checks, and quick medical action.
Diagnosing Anemia When Shortness of Breath is the Primary Complaint
Figuring out if anemia is causing shortness of breath needs a detailed check-up. This step is key to finding the right treatment and easing symptoms.
Clinical Evaluation and Physical Examination
The first step is a full check-up and physical exam. Doctors look at the patient’s health history. They check for things like chronic diseases, nutritional issues, or family anemia history.
They also look for signs like pale skin, tiredness, and fast heart rate. If someone has bad shortness of breath, it’s a big clue to look deeper.
Complete Blood Count and Other Laboratory Tests
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a key test for anemia. It checks blood components like hemoglobin and red blood cells. These help figure out if someone has anemia and what kind.
More tests might be needed based on the CBC and how the patient feels. These could include iron tests, vitamin B12 and folate levels, and more.
Differential Diagnosis: Ruling Out Other Causes
When looking at anemia and shortness of breath, other reasons for breathing trouble must be checked. Things like COPD, heart failure, and blood clots need to be ruled out with tests.
Doing a thorough check helps find the real cause of breathing issues. This way, patients get the right treatment.
Treatment Approaches for Anemia-Related Breathing Problems
Dealing with anemia-related breathing issues means fixing the root cause. A mix of treatments helps ease symptoms and boost life quality.
Iron Supplementation Strategies
Iron supplements are key for iron deficiency anemia, a big cause of breathing trouble. Doctors usually give oral iron, adjusting the dose and time based on the deficiency level.
Key considerations for iron supplementation include:
- Dosage: The amount of iron prescribed varies based on the severity of the deficiency.
- Duration: Treatment may last several months to replenish iron stores.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues, which can be mitigated by taking supplements with food.
Vitamin Therapy for Nutritional Anemias
Vitamin therapy is vital for nutritional anemias due to B12 and folate deficiencies. It helps make red blood cells right, easing breathing problems.
| Vitamin | Food Sources | Supplement Form |
| Vitamin B12 | Meat, Fish, Dairy Products | Oral Tablets, Injections |
| Folate | Leafy Greens, Legumes, Citrus Fruits | Oral Tablets |
Medical Interventions for Severe Anemia
For severe anemia, doctors might use quick fixes to boost red blood cells. This includes blood transfusions and agents that help make more red blood cells.
Nutritional Management of Anemia Symptoms
Nutritional management is key to easing anemia symptoms. Eating foods rich in essential nutrients boosts the body’s ability to make healthy red blood cells. This helps lessen anemia’s impact.
Iron-Rich Foods to Improve Oxygen Transport
Adding iron-rich foods to your diet is vital for managing anemia. Iron is vital for hemoglobin, which carries oxygen. Include red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and fortified cereals in your meals. Vitamin C boosts iron absorption, so eat foods like citrus fruits or bell peppers with iron-rich foods.
For better iron absorption, try orange juice with breakfast cereal. It’s important to know there are two types of iron: heme and non-heme. Heme iron, from animal products, is easier for the body to absorb than non-heme iron from plants.
Vitamin B12 and Folate Sources
Vitamin B12 and folate are also key for preventing anemia. Vitamin B12 is mainly in animal products like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. Folate, or vitamin B9, is in leafy greens, legumes, and fortified cereals. Both are vital for making red blood cells.
“A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of foods can help ensure adequate intake of these vital nutrients.”
Dietary Combinations That Enhance Nutrient Absorption
Some foods work better together for better nutrient absorption. Vitamin C with non-heme iron sources boosts iron absorption. But, tea and coffee can lower iron absorption, so drink them between meals.
Cooking in cast-iron cookware also increases iron intake, more so with acidic foods like tomatoes. Knowing these food interactions helps those with anemia make better dietary choices.
When to Seek Emergency Care for Anemia-Related Shortness of Breath
Knowing when to seek emergency care for anemia-related breathing issues can save lives. Anemia is when you don’t have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. It can cause shortness of breath and other symptoms. While anemia itself is not usually life-threatening, severe cases or those with certain symptoms need urgent care.
Red Flag Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
Certain symptoms mean you need to get medical help right away. If you have any of these, call emergency services:
- Severe shortness of breath that comes on suddenly or is with other bad symptoms.
- Chest pain or pressure, which could mean a heart problem or something serious.
- Dizziness or fainting, as these can mean your body isn’t getting enough oxygen.
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations, which may mean your heart is working too hard because of anemia.
Distinguishing Anemia from Other Respiratory Emergencies
It’s important to tell anemia-related shortness of breath from other serious breathing problems. Issues like heart failure, pulmonary embolism, or asthma getting worse can look like severe anemia. Knowing what’s causing your symptoms is key to getting the right treatment.
If you have anemia and are short of breath, watch your symptoms closely. Any big change or getting worse means you should go to the emergency room. Doctors can check you out, do tests, and help make your symptoms better and find the cause.
Living with Chronic Anemia: Managing Daily Activities and Breathing Challenges
Living with chronic anemia means finding ways to manage your energy and activities. You need to plan your day carefully to handle the breathing issues and health problems it brings.
Chronic anemia can make simple tasks hard. But, there are ways to handle it better.
Energy Conservation Techniques
It’s important to save energy if you have chronic anemia. Simple steps can help a lot with daily tasks.
- Prioritize tasks based on importance and energy required
- Take regular breaks to rest and recover
- Use assistive devices to reduce physical strain
- Optimize living spaces to minimize unnecessary movement
These strategies help save energy and ease breathing problems.
“Pacing yourself is key when living with chronic anemia. It’s not about being lazy; it’s about being smart about how you use your energy.”
” Anemia Support Group
Safe Exercise Guidelines for Anemic Patients
Exercise is good for health, but anemic patients need to be careful.
| Exercise Type | Benefits | Precautions |
| Low-impact aerobics (e.g., walking, swimming) | Improves cardiovascular health, boosts energy | Avoid overexertion, monitor heart rate |
| Resistance training | Enhances muscle strength, supports bone health | Start with light weights, gradually increase |
| Flexibility exercises (e.g., yoga, stretching) | Improves flexibility, reduces muscle tension | Avoid deep bending or heavy stretching |
Always talk to a doctor before starting new exercises, if you have chronic anemia.
By saving energy and exercising safely, people with chronic anemia can live better. They can manage their symptoms better too.
Special Populations and Anemia-Related Breathing Difficulties
Anemia affects breathing differently in various groups, like pregnant women, the elderly, and children. Each group has its own health needs and how anemia impacts their breathing varies.
Pregnancy: Managing Anemia and Dyspnea
Pregnancy increases the body’s need for iron and nutrients. Anemia, often from iron deficiency, can cause breathing problems. Women with anemia may find it hard to breathe even when resting or doing light activities.
To manage anemia in pregnancy, it’s important to:
- Get regular prenatal check-ups to check hemoglobin levels
- Take iron supplements as advised by doctors
- Eat more iron-rich foods and vitamin C to help absorb iron better
Elderly Patients: Unique Challenges and Approaches
The elderly are more likely to have anemia due to less food intake, chronic diseases, and aging. Anemia can worsen heart problems, making breathing harder.
Managing anemia in the elderly involves:
- Doing a full geriatric assessment to find out why they have anemia
- Improving their diet to address deficiencies
- Managing chronic conditions that might cause anemia
Children with Anemia: Developmental Considerations
Anemia in kids can slow their growth and affect their brain and motor skills. Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type and can impact their oxygen levels and development.
To tackle anemia in children, it’s key to:
- Check for anemia during regular pediatric visits
- Teach parents about iron-rich foods for kids
- In some cases, give iron supplements under doctor’s guidance
It’s vital to understand the unique challenges of these groups to manage anemia-related breathing issues effectively. Tailoring care to the needs of pregnant women, the elderly, and children can greatly improve their health and well-being.
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing Anemia Symptoms for Better Breathing
Knowing about anemia and how it affects breathing is key for those feeling short of breath. This article has covered anemia’s definition, types, and symptoms. Recognizing anemia signs and getting medical help can lead to better breathing and health.
To tackle anemia symptoms, a full plan is needed. This includes good nutrition, medical care, and lifestyle changes. Understanding anemia’s causes and using the right treatments can help reduce symptoms like shortness of breath. This improves life quality.
In summary, it’s important to understand anemia and its symptoms to stay healthy and breathe better. Being aware and taking action can help lessen anemia’s impact. This leads to a better life overall.
FAQ
What is anemia and how does it affect the body?
Anemia is when your body doesn’t have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. This makes it hard for your body to get enough oxygen. You might feel short of breath, tired, and weak.
What are the common symptoms of anemia?
Signs of anemia include feeling short of breath, tired, and weak. You might also have pale skin, feel dizzy, and in serious cases, chest pain and heart palpitations.
How does iron deficiency anemia cause breathing difficulties?
Iron deficiency anemia means your body can’t make enough hemoglobin. This makes it hard to carry oxygen. So, you might have trouble breathing and feel short of breath.
What are the risk factors for developing iron deficiency anemia?
You might get iron deficiency anemia if you don’t eat enough iron, have chronic blood loss, are pregnant, or have certain health issues like celiac disease or ulcers.
Can vitamin deficiencies cause anemia and breathing problems?
Yes, not having enough vitamins like B12 and folate can lead to anemia. This can make you feel short of breath, tired, and weak.
How is anemia diagnosed when shortness of breath is the primary symptom?
Doctors check for anemia by doing a physical exam, blood tests, and a complete blood count (CBC). They look for the cause of your anemia.
What are the treatment approaches for anemia-related breathing problems?
To treat anemia-related breathing issues, doctors might give you iron or vitamin supplements. In severe cases, they might do a blood transfusion.
What dietary changes can help manage anemia symptoms?
Eating more iron-rich foods, vitamin B12, and folate can help. Also, eating foods that help your body absorb nutrients better can manage anemia symptoms.
When should I seek emergency care for anemia-related shortness of breath?
If you have severe shortness of breath, chest pain, or other serious symptoms, go to the emergency room. Also, if your symptoms get worse, seek help right away.
How can individuals with chronic anemia manage daily activities and breathing challenges?
People with chronic anemia can manage by conserving energy, following safe exercise plans, and making lifestyle changes. This helps with daily activities and breathing.
Are there special considerations for managing anemia-related breathing difficulties in pregnant women, elderly patients, and children?
Yes, managing anemia in pregnant women, elderly, and children needs special care. It’s important to consider their unique health needs and conditions.
What is the importance of understanding and addressing anemia symptoms?
It’s key to understand and treat anemia symptoms to improve breathing and health. Untreated anemia can lead to serious problems and lower your quality of life.
Reference
- O’Neill, L. A., & Gilroy, D. W. (2020). Inflammation and anemia of chronic disease: Mechanisms and management. Blood Reviews, 45, 100694. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32014534/










