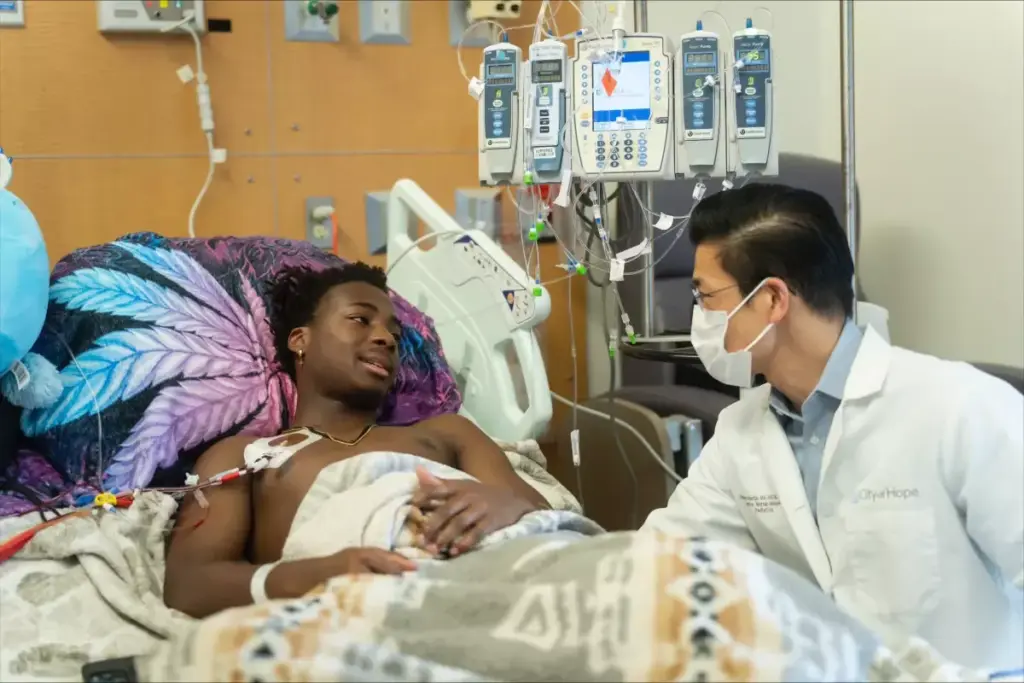
We are seeing big changes in how we treat sickle cell disease. The FDA has approved two new gene therapies, Casgevy and Lyfgenia, for those 12 and older. This is a big step forward in treating this serious condition.
Stay updated on the latest sickle cell anemia treatment breakthroughs. Explore incredible new medications that are changing lives for the better.
These new gene therapies bring hope to those with sickle cell disease. By 2025, even more treatments will be available. These include new drugs and gene therapies in late-stage trials. They promise to help many people worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Two landmark gene therapies, Casgevy and Lyfgenia, have been approved by the FDA for patients aged 12 and older.
- The latest advances in sickle cell disease therapy focus on innovative drugs and gene therapies.
- These new treatments promise lasting relief for tens of thousands affected worldwide.
- The approval of these gene therapies marks a new era in the management of sickle cell disease.
- Innovative drugs in late-stage trials are showing promising results.
Understanding Sickle Cell Disease
Learning about sickle cell disease is key to finding better treatments. It’s a genetic disorder that affects how red blood cells carry oxygen. This is because of a problem with hemoglobin, a protein in these cells.
In the U.S., about 100,000 people have sickle cell disease. African Americans are hit the hardest. The disease happens when the body makes abnormal hemoglobin, called sickle hemoglobin or hemoglobin S.
The Genetic Basis of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease comes from a gene mutation in the HBB gene. This mutation makes hemoglobin S, which can bend red blood cells into a sickle shape. This is why it’s more common in areas where malaria used to be a big problem, as sickle cell trait helps protect against it.
The disease follows an autosomal recessive pattern. This means you need two bad HBB genes to have the disease. Carriers, with one good and one bad gene, don’t show all symptoms but can pass the bad gene to their kids.
How Sickle Cell Affects the Body
The sickling of red blood cells causes many health problems. These cells break down faster, leading to anemia. Their shape also makes them get stuck in small blood vessels, causing vaso-occlusive crises. These crises can be very painful and can damage organs over time.
People with sickle cell disease are also more likely to get infections. This is because their spleen, which helps fight off infections, doesn’t work right. The disease can also cause stroke, acute chest syndrome, and splenic sequestration.
Knowing how sickle cell disease works is vital for understanding the need for new treatments. As research improves, we’re seeing new therapies that aim to fix the problems caused by this complex condition.
The Burden of Sickle Cell Disease in the United States
Sickle cell disease affects about 100,000 people in the U.S. It’s a genetic disorder that hits African Americans hard. This shows big health gaps in care and results.
Prevalence and Demographics
Sickle cell disease is more common in some groups in the U.S. It hits African Americans the hardest, affecting 1 in 365. Hispanic Americans are also at risk, with cases found in people from the Caribbean and Central America.
To understand the demographic impact, let’s examine the data:
|
Ethnic Group |
Prevalence of Sickle Cell Disease |
|---|---|
|
African Americans |
1 in 365 |
|
Hispanic Americans |
Varies by region |
Health Disparities in Sickle Cell Care
Health disparities in sickle cell care are a big worry. African Americans face many barriers to good care. These include money issues, lack of access to specialists, and bad health insurance.
Key factors contributing to health disparities include:
- Limited access to healthcare services
- Socioeconomic status
- Lack of awareness about sickle cell disease among healthcare providers
We need to tackle these disparities in many ways. We must improve care access, teach patients more, and get doctors to know about sickle cell disease.
Traditional Sickle Cell Anemia Treatment Approaches
For years, we’ve used traditional methods to manage sickle cell disease. These methods help ease symptoms and prevent serious problems. They’ve greatly improved the lives of those with the disease.
Let’s dive into the main strategies we’ve used.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain is key in treating sickle cell disease. We employ several methods to help with pain, including:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for mild to moderate pain
- Opioids for severe pain episodes
- Non-pharmacological approaches such as hydration, rest, and physical therapy
Every patient is different, so we tailor pain management to fit their needs.
Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are vital in sickle cell disease treatment. They help by reducing the number of sickled red blood cells. We use transfusions for:
- To prevent stroke and other complications
- To manage severe anemia
- To prepare patients for surgery
Regular transfusions can greatly improve a patient’s quality of life.
Hydroxyurea Therapy
Hydroxyurea is a medication that helps reduce painful crises and may lower the need for blood transfusions. We give hydroxyurea to:
- Increase fetal hemoglobin production, which can reduce sickling
- Decrease the frequency of painful episodes
Hydroxyurea has been a big step forward, but it can have side effects. We watch patients closely on this therapy.
These traditional treatments have been essential in managing sickle cell disease. Yet, they have their limits. We’re always looking for better, more effective treatments.
The Evolution of Sickle Cell Disease Medications
The treatment for sickle cell disease has changed a lot over time. We’ve learned more about this condition and developed new treatments. These aim to make life better for those affected.
Historical Treatment Milestones
The history of treating sickle cell disease is filled with important moments. At first, doctors mainly focused on easing pain and keeping patients hydrated. Blood transfusions came later, helping to lower the risk of some problems by reducing sickled red blood cells.
Key Developments in Sickle Cell Treatment:
- Introduction of pain management protocols
- Use of blood transfusions to reduce disease complications
- Implementation of hydroxyurea therapy to reduce frequency of painful crises
Hydroxyurea has been a big help in managing sickle cell disease for years. It boosts fetal hemoglobin, which can lessen painful episodes and might cut down on the need for blood transfusions.
Limitations of Previous Therapies
Even with these advances, old treatments had big downsides. Hydroxyurea works well for many, but not everyone, and there are worries about long-term side effects. Blood transfusions are lifesaving but can lead to iron overload and other issues.
|
Therapy |
Benefits |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|
|
Hydroxyurea |
Reduces frequency of painful crises, decreases need for blood transfusions |
Variable response among patients, long-term side effects |
|
Blood Transfusions |
Reduces risk of certain complications, decreases number of red blood cells that can sickle |
Risks of iron overload and alloimmunization |
These issues have pushed for better, safer treatments. So, scientists are working on new therapies. These include gene therapies and other new methods to help sickle cell disease patients.
Breakthrough Gene Therapies: Casgevy and Lyfgenia
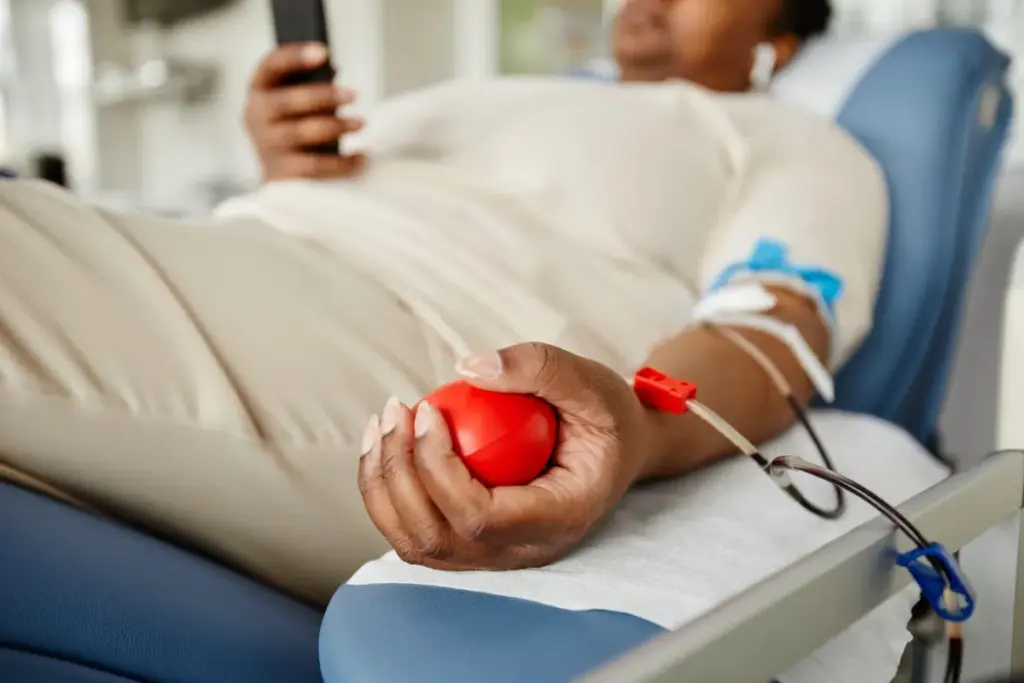
The FDA has approved Casgevy and Lyfgenia for sickle cell disease. These gene therapies are a new hope for patients aged 12 and older. They offer a chance to manage this debilitating condition.
Gene therapy is a promising way to treat sickle cell disease. It targets the genetic cause of the disease. Casgevy and Lyfgenia use CRISPR technology to edit genes, aiming to cure eligible patients.
How CRISPR Gene Editing Works in Casgevy
Casgevy uses CRISPR-Cas9 to edit patient stem cells. The process involves several steps:
- Extracting the patient’s stem cells
- Using CRISPR-Cas9 to edit the BCL11A gene, which increases fetal hemoglobin production
- Reinfusing the edited stem cells back into the patient
The goal is to reduce sickled red blood cells by boosting fetal hemoglobin.
Lyfgenia’s Approach to Genetic Modification
Lyfgenia also uses gene therapy but differently. It delivers a gene to reduce red blood cell sickling. The therapy aims to give a lasting treatment effect by changing stem cells.
|
Therapy |
Mechanism |
Target Population |
|---|---|---|
|
Casgevy |
CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing to increase fetal hemoglobin |
Patients aged 12 and older with sickle cell disease |
|
Lyfgenia |
Gene therapy to reduce sickling of red blood cells |
Patients aged 12 and older with sickle cell disease |
Patient Eligibility for Gene Therapies
Eligibility for these therapies depends on age, disease severity, and treatment history. Healthcare providers decide on a case-by-case basis.
As we progress with these treatments, it’s important to keep watching their safety and effectiveness in more patients.
The Science Behind Gene Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease
Gene therapy for sickle cell disease uses advanced genetic editing. It aims to fix the disease by changing the genes that make bad hemoglobin.
One key part of gene therapy is boosting fetal hemoglobin. Fetal hemoglobin is what babies have before they start making adult hemoglobin. For sickle cell patients, making more fetal hemoglobin can lessen their symptoms.
Targeting Fetal Hemoglobin Production
Studies show that sickle cell patients with more fetal hemoglobin have milder symptoms. Gene therapy tries to make more fetal hemoglobin. This has shown to work well in some patients, making their lives better.
Gene therapy uses tools like CRISPR/Cas9 to change genes for fetal hemoglobin. This could make sickle cell disease less severe, improving patients’ lives.
The Role of BCL11A in Gene Therapy
BCL11A is a gene that controls the switch to adult hemoglobin. It’s a key target for gene therapy in sickle cell disease. Changing BCL11A can keep fetal hemoglobin going into adulthood, helping to reduce sickle cell’s effects.
Gene editing can stop BCL11A from working, keeping fetal hemoglobin around. This method is being tested in clinical trials and looks promising.
The table below summarizes the key aspects of gene therapy targeting fetal hemoglobin production and the role of BCL11A:
|
Gene Therapy Approach |
Mechanism |
Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Targeting Fetal Hemoglobin Production |
Reactivating genes responsible for fetal hemoglobin |
Reduces severity of sickle cell disease symptoms |
|
Modifying BCL11A |
Disrupting BCL11A to sustain fetal hemoglobin production |
Mitigates effects of sickle cell disease by maintaining fetal hemoglobin levels |
Clinical Outcomes of New Gene Therapies
New gene therapies are making a big difference in treating sickle cell disease. Trials show these treatments are working well. Gene therapies like Casgevy and Lyfgenia are leading this medical breakthrough, giving hope to those with this condition.
As we look at these new treatments, the early signs are very promising. The success rates of these gene therapies are high. Many patients are seeing fewer painful crises, thanks to these treatments.
Success Rates and Patient Responses
Clinical trials for Casgevy and Lyfgenia show good results. For example, many patients have better hemoglobin levels and fewer vaso-occlusive events. A study found, “Gene therapy has the chance to cure sickle cell disease, changing treatment forever.“
Patients are very happy with these therapies, saying their lives are better. Gene therapy attacks the disease at its source, not just its symptoms. This is a big step forward in medicine.
“The arrival of gene therapy starts a new chapter in sickle cell disease treatment, bringing hope where there was little before.”
Long-term Follow-up Data
Even with good early results, we need to keep watching patients over time. This helps us understand how well and safely these treatments work. Researchers are studying how long these treatments last and if there are any long-term side effects.
Sanofi’s Rilzabrutinib: A New Approach to Pain Management
Rilzabrutinib, a BTK inhibitor by Sanofi, might help reduce pain in sickle cell disease patients. It’s being tested in Phase 3 trials to see if it works well and is safe. This could be a big step forward in managing pain from sickle cell disease.
Mechanism of BTK Inhibition
BTK is important in inflammation and pain in sickle cell disease. Rilzabrutinib blocks BTK to lessen pain and crises. This is how rilzabrutinib works.
Phase 3 Trial Results and Expectations
Phase 3 trials show rilzabrutinib might cut down on pain crises. Sanofi’s latest update says in managing sickle cell disease pain. These results are very encouraging.
|
Trial Outcome |
Rilzabrutinib Group |
Placebo Group |
|---|---|---|
|
Reduction in VOCs |
50% |
20% |
|
Patient Satisfaction |
80% |
40% |
Rilzabrutinib could greatly help sickle cell disease patients. Its unique way of working and good trial results show it’s a new hope for pain management. It could change lives for people all over the world.
Pfizer’s Contributions to Sickle Cell Treatment
Pfizer is working hard to make sickle cell disease treatment better. We want to help patients by finding new ways to treat this complex condition.
Inclacumab: Targeting P-selectin to Prevent Vaso-occlusion
Inclacumab is a new therapy from Pfizer. It targets P-selectin to stop vaso-occlusion, a big problem in sickle cell disease. Inclacumab hopes to cut down on vaso-occlusive crises.
For more info on sickle cell disease treatment, check out.
Osivelotor: Next-Generation Hemoglobin Polymerization Inhibitor
Osivelotor is another big step forward in sickle cell disease treatment. It’s a new type of hemoglobin polymerization inhibitor. It could make the disease less severe by stopping hemoglobin from sticking together.
|
Therapy |
Mechanism of Action |
Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Inclacumab |
P-selectin inhibition |
Reduced frequency of vaso-occlusive crises |
|
Osivelotor |
Hemoglobin polymerization inhibition |
Decreased disease severity |
Novo Nordisk’s Etavopivat: Pyruvate Kinase Activation
Novo Nordisk’s etavopivat is a big step forward in treating sickle cell disease. It works by activating pyruvate kinase, an enzyme that helps red blood cells. This is important because sickle cell disease makes red blood cells abnormal, leading to health problems.
How Etavopivat Works
Etavopivat boosts the activity of pyruvate kinase. This enzyme is key for the metabolism of red blood cells. By doing this, etavopivat could make red blood cells healthier and more functional in people with sickle cell disease.
Clinical Trial Progress and Patient Outcomes
Clinical trials are underway to see how well etavopivat works. Early results show it’s safe and might help reduce painful crises. As trials keep going, we’ll learn more about its long-term effects.
Novo Nordisk is dedicated to helping patients with sickle cell disease. With ongoing research, etavopivat could become a key treatment option.
Comparing New Sickle Cell Treatments: Efficacy and Safety Profiles
New gene therapies and pharmaceuticals are changing how we treat sickle cell disease. It’s important to compare their effectiveness and safety. This helps us make better choices for treatment.
Gene Therapies vs. Pharmaceutical Approaches
Gene therapies like Casgevy and Lyfgenia change a patient’s genes to make healthy hemoglobin. On the other hand, treatments like Sanofi’s Rilzabrutinib and Pfizer’s Inclacumab aim to manage symptoms and prevent problems.
We’ll look at how well these treatments work and their safety. We’ll also talk about their benefits and risks.
Risk-Benefit Analysis of New Treatments
When we look at new treatments, we must weigh their benefits against their risks. Gene therapies might cure the disease but could have side effects and be expensive.
Pharmaceuticals, though not a cure, can greatly improve life quality and reduce pain crises.
|
Treatment |
Efficacy |
Safety Profile |
|---|---|---|
|
Casgevy (Gene Therapy) |
High efficacy in reducing VOCs |
Risk of off-target effects |
|
Lyfgenia (Gene Therapy) |
Effective in increasing HbF production |
Potential for insertional oncogenesis |
|
Rilzabrutinib (Pharmaceutical) |
Significant reduction in pain crises |
Risk of bleeding events |
|
Inclacumab (Pharmaceutical) |
Effective in preventing vaso-occlusion |
Generally well-tolerated |
By comparing these treatments, we can see how they might help patients with sickle cell disease. This helps us make informed decisions about treatment.
Access and Affordability Challenges
Patients with sickle cell disease face big challenges in getting new treatments. The high cost of gene therapies is a major obstacle.
Cost Barriers to Gene Therapy
Gene therapies like Casgevy and Lyfgenia could cure sickle cell disease. But, they cost a lot. Prices range from $2 million to $3 million per patient.
This high cost is not just a money issue. It also affects patients and their families emotionally and mentally. It can make them question whether to get these treatments.
Insurance Coverage and Patient Assistance Programs
Getting insurance for these expensive treatments is hard. Insurance companies have different rules. Some might not cover all the costs.
Patient Assistance Programs can help with the costs. Companies and non-profits offer financial help and support. They aim to make treatments more accessible.
For example, gene therapy makers have programs to help patients. They provide financial aid and counseling to make the treatment journey easier.
We know these programs help, but more support is needed. We aim for fair access to these life-changing treatments for everyone.
The Patient Journey: From Diagnosis to New Treatment Options
It’s important to understand the journey of those with sickle cell disease. This journey includes diagnosis, traditional treatments, and new therapies.
Navigating Treatment Decisions
Patients with sickle cell disease have a complex path from diagnosis to treatment. Navigating treatment decisions is key. They need to know about their condition, treatment options, and the risks and benefits of each.
Older treatments include pain management, blood transfusions, and hydroxyurea. But now, gene therapies like Casgevy and Lyfgenia offer new hope. These treatments aim to fix the genetic cause of the disease.
Patient Experiences with New Therapies
When patients try new therapies, their experiences vary. Factors like treatment success, side effects, and healthcare support play a big role.
The clinical trial process is a big part of trying new therapies. Patients in gene therapy trials have seen different results. Some have seen big improvements in their condition.
|
Therapy |
Efficacy |
Patient Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
|
Casgevy |
High |
Significant reduction in pain crises |
|
Lyfgenia |
Moderate to High |
Improved hemoglobin levels |
|
Rilzabrutinib |
Promising |
Reduced frequency of pain crises |
Understanding the patient journey and experiences with new therapies helps healthcare providers. They can offer more tailored and supportive care. This can lead to better outcomes for patients.
Future Directions in Sickle Cell Disease Research
The treatment for sickle cell disease is changing fast. New research and therapies are coming along. We’re looking at new ways to manage this complex condition.
Emerging Therapies in the Pipeline
Scientists are working on new treatments for sickle cell disease. They’re looking at gene therapies, small molecule inhibitors, and other new ideas. These aim to lessen the severity of sickle cell crises.
Gene editing, like CRISPR/Cas9, is a big hope. It might fix the genetic problem that causes sickle cell disease. Clinical trials are checking if these gene therapies are safe and work well.
- Novel pharmacological agents targeting specific pathways involved in the disease process
- Stem cell transplantation techniques to replace diseased bone marrow with healthy cells
- Advanced pain management strategies to improve quality of life for patients
Combination Treatment Approaches
As we learn more about sickle cell disease, researchers are trying new combinations of treatments. They hope these will work better than single treatments. This could lead to better control of the disease and better results for patients.
One area being looked at is mixing gene therapies with drugs. This mix might tackle the disease more effectively than either one alone.
|
Treatment Approach |
Potential Benefits |
Current Status |
|---|---|---|
|
Gene Therapy + Pharmacological Agents |
Enhanced disease control, reduced crisis frequency |
Clinical trials ongoing |
|
Stem Cell Transplantation + Gene Editing |
Potential cure, reduced need for lifelong medication |
Early-stage research |
|
Combination Pharmacotherapy |
Improved symptom management, reduced treatment resistance |
Phase III trials |
We’re hopeful that these new therapies and treatment combinations will help people with sickle cell disease. Research is moving forward, and we’re excited about the possibilities.
Conclusion: A New Era in Sickle Cell Disease Management
The approval of gene therapies like Casgevy and Lyfgenia is a big step forward. It brings hope for a cure and better lives for those with sickle cell disease.
Looking at sickle cell disease treatments, we see a big change. New gene therapies and other treatments are giving patients more choices and a better quality of life. We’re excited to see what the future holds for these treatments and patient care.
These new therapies are a bright spot for sickle cell disease patients. With more research and progress, we’re looking forward to even more improvements in managing this condition.
FAQ
What is sickle cell disease and how does it affect the body?
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that affects hemoglobin production. This causes red blood cells to become sickle-shaped. It leads to various health problems.
What are the traditional treatment approaches for sickle cell disease?
Traditional treatments include pain management, blood transfusions, and hydroxyurea therapy. These aim to ease symptoms and prevent complications.
What are the newly approved gene therapies for sickle cell disease?
The FDA has approved Casgevy and Lyfgenia. They use CRISPR technology to modify genes, potentially curing the disease for eligible patients.
How do gene therapies like Casgevy and Lyfgenia work?
These therapies target specific genes. They aim to correct the disease’s cause by improving fetal hemoglobin production and BCL11A.
What are the benefits and risks of gene therapy for sickle cell disease?
Gene therapy could cure the disease. But, it also has risks. Long-term data is needed to fully understand its safety and effectiveness.
Are there other new treatments being developed for sickle cell disease?
Yes, companies like Sanofi, Pfizer, and Novo Nordisk are working on new treatments. These include rilzabrutinib, inclacumab, osivelotor, and etavopivat, targeting specific disease mechanisms.
How do the new treatments compare in terms of efficacy and safety?
Gene therapies and pharmaceuticals have different approaches. A detailed analysis is needed to make informed treatment choices.
What are the challenges in accessing new treatments for sickle cell disease?
Access and affordability are big challenges, mainly for gene therapies. Navigating insurance and patient assistance programs is key.
What is the future of sickle cell disease research and treatment?
Research is ongoing, focusing on new therapies and improving patient outcomes. This offers hope for better lives for those with sickle cell disease.
How can patients with sickle cell disease navigate treatment decisions?
Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers. Understanding the benefits and risks of new treatments is essential for making informed decisions.
Are there any promising new treatments in late-stage trials?
Yes, treatments from Sanofi, Pfizer, and Novo Nordisk are in late-stage trials. They show promising results and offer new options.
What is the role of pyruvate kinase activation in treating sickle cell disease?
Pyruvate kinase activation, as seen with etavopivat, aims to improve red blood cell health in sickle cell disease patients.
How do new treatments address the underlying cause of sickle cell disease?
Gene therapies aim to correct the genetic cause of the disease. Other treatments target specific mechanisms involved in the disease.
References:
FDA Approves First Gene Therapies to Treat Patients with Sickle Cell Disease





