Embryonic Stem Cells: Basics, Ethics, and Medical Potential
Learning about embryonic stem cells is key for medical progress and new treatments. At Liv Hospital, we focus on keeping patients safe. We follow the best global standards in stem cell research.
Embryonic stem cells come from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, 4–7 days after fertilization. These embryos are usually extra from IVF treatments. This shows the need for careful ethics in our research.
We use the newest research methods to make our work both new and ethical. Our goal is to offer top-notch healthcare. We do this by using the latest research and caring deeply for our patients.
Key Takeaways
- Embryonic stem cells are obtained from the inner cell mass of blastocysts.
- Most embryos used for research are excess from IVF treatments.
- Liv Hospital prioritizes patient safety and ethical research practices.
- Our research aims to advance medical treatments and patient care.
- We adhere to international best practices in stem cell research.
The Remarkable Potential of Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells can turn into any cell type. This makes them key to big changes in healthcare. We’ll look at what makes these cells special and how they could help in medical research and treatments.
Definition and Characteristics
These cells come from embryos and can become any cell in the body. This ability is very important for studying how we develop and for new treatments. Recent studies show they could be used in many medical ways.
Embryonic vs. Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells can’t become as many types of cells as embryonic stem cells. This is why embryonic stem cells are more useful for fixing damaged tissues. Here’s a table that shows the main differences between them.
| Characteristics | Embryonic Stem Cells | Adult Stem Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Differentiation Potential | Pluripotent, can become any cell type | Limited, typically lineage-specific |
| Source | Derived from embryos | Found in adult tissues |
| Proliferation Capacity | High proliferation capacity | Lower proliferation capacity compared to embryonic stem cells |
We’ve talked about what embryonic stem cells are, their special traits, and how they differ from adult stem cells. Their unique abilities make them a big focus for future medical breakthroughs.
Embryonic Development: From Fertilization to Blastocyst
Embryonic development starts with fertilization and goes through many stages. It ends with the formation of a blastocyst. This process is key to understanding how embryonic stem cells are obtained.
The First Days After Fertilization
Right after fertilization, the zygote divides into a cluster of cells called a morula. This stage is critical as it precedes the formation of a blastocyst. The morula then splits into two groups of cells: the trophoblast and the inner cell mass. We will see why these cell groups are important later.
Formation of the Blastocyst
The morula turns into a blastocyst, a structure with a fluid-filled cavity and an inner cell mass. The blastocyst stage is key for getting embryonic stem cells because it has the inner cell mass. This process involves detailed cell divisions and changes.
The Critical Inner Cell Mass
The inner cell mass in the blastocyst is where embryonic stem cells come from. These cells can turn into any cell type in the body. The inner cell mass is vital for getting these stem cells for research and possible treatments. We will talk about how to get and grow these cells later.
Knowing the stages of embryonic development, like the blastocyst formation and the inner cell mass’s role, is key. It helps us understand how embryonic stem cells are taken and used in medical research.
Where Do Embryonic Stem Cells Come From: Primary Sources
Embryonic stem cells come from several main sources. Each source has its own ethical and scientific issues. Knowing these sources helps us understand the complex world of embryonic stem cell research.
Surplus Embryos from IVF Treatments
Most embryonic stem cells come from extra embryos made during In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). IVF is when eggs and sperm are mixed outside the body. Then, the embryos are put into the uterus. Sometimes, more embryos are made than needed for a pregnancy.
These extra embryos can be used for research with the donors’ consent. This way, they can help scientists learn about human development and diseases. It’s also a way to not throw away these embryos, which many donors find ethical.
Purpose-Created Research Embryos
Some stem cells come from embryos made just for research. These embryos are made in a lab for study. Scientists can then look into human development and diseases in a controlled way.
But, making embryos just for research raises big ethical questions. Ethical guidelines and laws differ around the world. They affect how and when these embryos can be used.
Terminated Pregnancies as Occasional Sources
Embryonic stem cells can also come from embryos after a pregnancy is ended. But, this is rare because of the ethical issues and other sources like IVF embryos.
Using embryos from ended pregnancies for research needs careful review and strict rules. It’s important to handle this topic with care and respect.
Getting embryonic stem cells from different sources shows how complex this field is. As research grows, knowing where these cells come from is key. It helps us move forward in medicine while dealing with ethical questions.
The Ethical Framework of Embryo Donation
The process of embryo donation is guided by a strict ethical framework. This framework is designed to protect everyone involved. It tackles the complex issues of embryo donation for stem cell research.
At the core of this framework is informed consent. Donors must fully understand the implications of their donation. They need to know the possible uses of the embryos and the ethical debates around stem cell research.
Informed Consent Requirements
Informed consent is more than a formality. It’s a key protection that ensures donors know the purpose, risks, and benefits of donating embryos for research.
“Informed consent is a process, not just a form. It involves educating the donor about the research, its outcomes, and any risks.”
This approach respects donors’ autonomy. It makes sure their decision is informed and voluntary.
Donor Rights and Protections
Donor rights and protections are vital in the ethical framework of embryo donation. Donors have the right to privacy, confidentiality, and the assurance that their embryos will be used responsibly. We must ensure donors are not pressured or influenced unfairly. They should also know they can change their mind at any time.
Regulatory Oversight
Effective regulatory oversight is key to ensure embryo donation for stem cell research is done ethically and legally. Regulatory bodies set standards, monitor compliance, and address ethical issues. For more on stem cell sources, visit our related article.
In conclusion, the ethical framework of embryo donation is complex. It involves informed consent, donor rights, and regulatory oversight. By following these principles, we can ensure embryo donation for stem cell research is done with respect for donors and ethical standards.
How Are Embryonic Stem Cells Obtained: Laboratory Techniques
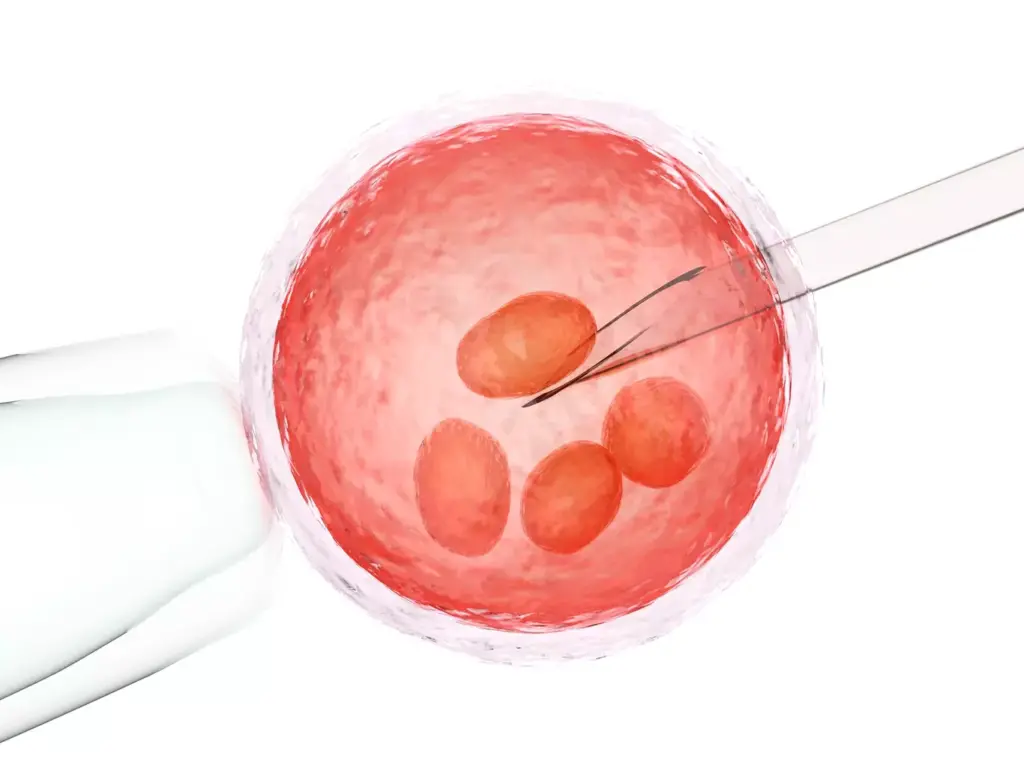
To get embryonic stem cells, scientists use several lab steps. They start by isolating the inner cell mass. This is key for getting good stem cells for research and treatments.
Isolation of the Inner Cell Mass
The inner cell mass is taken from the blastocyst. They use immunosurgery or mechanical dissection for this. Immunosurgery uses antibodies to remove the outer layer. Mechanical dissection physically separates the inner cell mass from the rest.
Cell Culture and Propagation Methods
After isolating the inner cell mass, it’s grown in a special medium. This medium is full of nutrients to help the cells grow and multiply. The conditions are set up to keep the stem cells in a pluripotent state.
Important factors in cell culture include:
- Growth factors to promote cell division
- Nutrients to support cellular metabolism
- Optimal environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality checks are strict for embryonic stem cells. These include:
| Protocol | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Mycoplasma testing | Detection of mycoplasma contamination | Monthly |
| Cell line authentication | Verification of cell line identity | Quarterly |
| Viability assessment | Evaluation of cell viability | Weekly |
By following these quality checks, scientists make sure their stem cells are top-notch. This is important for research and treatments.
Alternative Sources: Fetal and Extra-Embryonic Stem Cells
Stem cells are not just found in embryos. Fetal and extra-embryonic tissues also hold great promise. These sources offer new paths for medical research and treatments.
Amniotic Fluid Collection Procedures
Amniotic fluid surrounds the fetus and protects it during pregnancy. It’s a rich source of stem cells. Amniocentesis, a procedure to get this fluid, is used for testing but also for stem cell research.
These stem cells can turn into different cell types. This makes them very useful for research and possible treatments.
Placental Tissue as a Valuable Source
The placenta is another key source of stem cells. It contains stem cells that can become many types of cells. After birth, these cells can be taken from the placenta.
This method not only gets stem cells but also uses tissue that would be thrown away. It’s a good and ethical way to get these cells.
Umbilical Cord Blood Banking and Processing
Umbilical cord blood is collected after a baby is born. It’s a source of stem cells important for blood production. These cells have been used to treat blood disorders and cancers.
Storing cord blood is a process that tests and freezes it for later use. It’s a safe and ethical way to get these stem cells.
In summary, amniotic fluid, placental tissue, and umbilical cord blood are rich in stem cells. They offer hope for new treatments and therapies. As we learn more about these cells, we get closer to better health.
The Role of Fertility Clinics in Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research benefits a lot from fertility clinics. These clinics connect reproductive health with regenerative medicine. They give access to embryos and know-how in reproductive tissues.
Specialized Facilities and Expertise
Fertility clinics have top-notch facilities and skilled staff. This expertise is key in stem cell research. It’s needed for working with embryos carefully.
- Advanced IVF labs for embryo care
- Experts in freezing embryos and stem cells
- High standards for quality in reproductive tissues
The Bridge Between Clinical Practice and Research
Fertility clinics link clinical work and research. They work with researchers to apply stem cell therapies. Researchers share new findings with clinicians.
This teamwork is key for making stem cell research useful. For example, clinics give researchers embryos for research. This helps in making new treatments.
Patient Education and Recruitment
Teaching patients is vital in stem cell research. Fertility clinics help by explaining the benefits and ethics of donating embryos. They guide patients well so they can decide wisely.
- Explaining the research and embryo use
- Talking about ethics and consent
- Helping with donation for research
Fertility clinics and researchers work together. They aim to understand stem cells better. We support this work and care for our patients well.
Controversies and Challenges in Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Embryonic stem cell research has great promise but faces big ethical and legal challenges. The use of human embryos for research is a hot topic. It sparks debates among scientists, ethicists, and lawmakers.
Ethical Debates and Perspectives
The ethical debates on embryonic stem cell research are complex. Some believe the benefits of this research, like finding new treatments, are worth it. Others think destroying human embryos is like taking a human life.
There are many views on this:
- Utilitarian Perspective: Focuses on the greater good and the research’s benefits.
- Deontological Perspective: Stresses the moral rules and the sanctity of human life.
- Stakeholder Perspective: Looks at the rights and interests of patients, donors, and researchers.
Legal Restrictions Across Different Countries
Legal rules on embryonic stem cell research differ a lot around the world. This shows the wide range of cultural, ethical, and political views.
| Country | Legal Status of Embryonic Stem Cell Research |
|---|---|
| United States | Federally funded research is restricted, but some states allow it. |
| United Kingdom | Permitted under license from the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority. |
| Germany | Restricted, with specific laws governing embryonic stem cell import and research. |
Alternative Research Approaches
Researchers are looking into new ways to do stem cell research because of the ethical and legal issues. They are exploring:
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), made from adult cells.
- Stem cells from umbilical cord blood or other non-embryonic sources.
- New techniques that don’t need human embryos.
These new methods could help move stem cell research forward. They also try to solve some of the ethical problems linked to using human embryos.
Advanced Applications of Harvested Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are key in medical research. They help in regenerative medicine and drug discovery. Their special abilities make them very useful for medical science and treatments.
Regenerative Medicine Breakthroughs
Embryonic stem cells are exciting for regenerative medicine. They can turn into different cell types. This makes them great for fixing or replacing damaged tissues.
Researchers are looking at using them to create healthy heart tissue for heart disease patients. This could change how we treat heart conditions.
They are also being studied for diseases like Parkinson’s and diabetes. Scientists want to learn how to make these cells into specific types. This could lead to new ways to fix damaged tissues.
Disease Modeling and Understanding
Embryonic stem cells are also great for disease modeling. They can become specific cell types affected by diseases. This helps researchers understand how diseases work.
For example, they can model genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis or muscular dystrophy. By studying these models, scientists can learn more about the diseases. They can also find new ways to treat them.
Drug Discovery and Development
Embryonic stem cells are also used in drug discovery. They can become different cell types. This makes them a good source for testing drugs.
This method can speed up drug development and cut down on animal testing. It’s a big step forward for the pharmaceutical industry.
Conclusion: Balancing Scientific Progress with Ethical Responsibility
Exploring embryonic stem cell research shows us the need to balance science and ethics. These cells could change regenerative medicine a lot. But, we must think carefully about the ethics involved.
We’ve looked at where these stem cells come from, like IVF leftovers and research embryos made on purpose. Knowing this helps us deal with the ethics of using them.
By understanding the ethics of embryo donation and how stem cells are gotten, we can improve stem cell research. As we go on, we must keep science and ethics in check. This way, we can enjoy the benefits of stem cell research while staying ethical.
Where do embryonic stem cells come from?
Embryonic stem cells come from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. This happens 4-5 days after fertilization.
How are embryonic stem cells obtained?
To get embryonic stem cells, scientists first isolate the inner cell mass from a blastocyst. Then, they grow and multiply these cells in a lab.
What are the primary sources of embryonic stem cells?
Main sources include leftover IVF embryos, embryos made for research, and sometimes, embryos from terminated pregnancies.
What is the significance of the inner cell mass in embryonic development?
The inner cell mass is key. It grows into the fetus and is where embryonic stem cells come from. This is because it can become many different cell types.
How are embryos donated for stem cell research?
Donors give embryos for research after giving informed consent. This ensures their rights are respected and follows strict rules.
What laboratory techniques are used to isolate and culture embryonic stem cells?
Scientists use special methods to get the inner cell mass and grow the stem cells. They also follow strict rules to keep the cells healthy.
Are there alternative sources of stem cells beside embryonic stem cells?
Yes, there are other sources. These include stem cells from fetal tissues, placenta, umbilical cord, and adult stem cells. Each has its own uses.
What role do fertility clinics play in stem cell research?
Fertility clinics are important. They offer special facilities and knowledge. They also help with patient education and getting donors for stem cell research.
What are some of the controversies and challenges associated with embryonic stem cell research?
There are debates about ethics and legal issues. Some countries have laws against it. Researchers are looking for new ways to solve these problems.
What are the possible uses of harvested embryonic stem cells?
They could help in regenerative medicine and understanding diseases. They can also help in finding new drugs. This is because of their unique abilities.
How are stem cells for research obtained?
Stem cells for research come from many places. This includes leftover IVF embryos, embryos made for research, and other sources. All of this is done following strict rules and guidelines.