At LivHospital, we know how complex aplastic anemia is. It’s a rare and serious blood disorder. The bone marrow fails to make blood cells.
This condition, also known as marrow aplasia, greatly reduces the production of red and white blood cells and platelets.
We know aplastic anemia can be caused by many things. This includes autoimmune disorders, toxins, and some medicines. The symptoms are tough to deal with, like feeling very tired, getting sick easily, and bleeding a lot.
To find out if you have it, doctors do blood tests and a bone marrow biopsy.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes of aplastic anemia is key to managing it well.
- Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious blood disorder.
- Symptoms include fatigue, infections, and bleeding due to low blood cell counts.
- Diagnosis involves blood tests and bone marrow biopsy.
- Treatment options include immunosuppressive therapy and stem cell transplantation.
What is Aplastic Anaemia?

Aplastic anaemia is a rare and serious condition. It happens when the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. This results in fewer red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood.
Definition and Basic Pathophysiology
Aplastic anaemia is when the bone marrow fails to make blood cells. The bone marrow is key for making all blood cells. But in aplastic anaemia, it can’t do this job well.
This failure is due to the immune system attacking the bone marrow. This attack stops it from making new blood cells.
Difference Between Aplastic Anaemia and Other Anemias
Aplastic anaemia is different from other anemias. It affects all blood cell types, not just one. For example, iron deficiency anemia mainly affects red blood cells.
In contrast, aplastic anaemia reduces all blood cells. This makes its symptoms and treatment unique compared to other anemias.
People with aplastic anaemia often feel tired, weak, and bruise easily. They also get sick more often. These symptoms show why it’s important to know about this condition and get help early.
Fact 1: Aplastic Anaemia Affects All Blood Cell Types
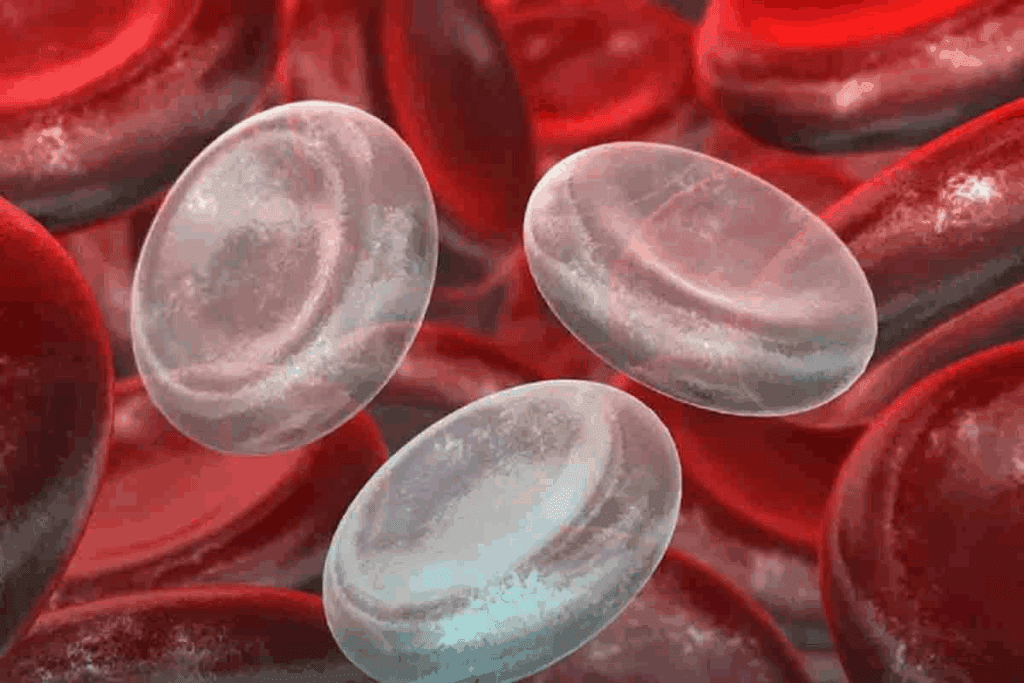

Aplastic anaemia is a condition where the bone marrow doesn’t make enough blood cells. This affects red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Impact on Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells carry oxygen to our bodies. With aplastic anaemia, not enough red blood cells are made. This leads to anaemia, causing fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. We’ll see how this affects health.
Impact on White Blood Cells
White blood cells fight infections. Aplastic anaemia makes it hard for the body to fight off infections. We’ll look at how this makes managing the condition harder.
Impact on Platelets
Platelets help our blood clot. With aplastic anaemia, there are fewer platelets. This can cause bleeding and bruising. We’ll talk about how to manage these symptoms.
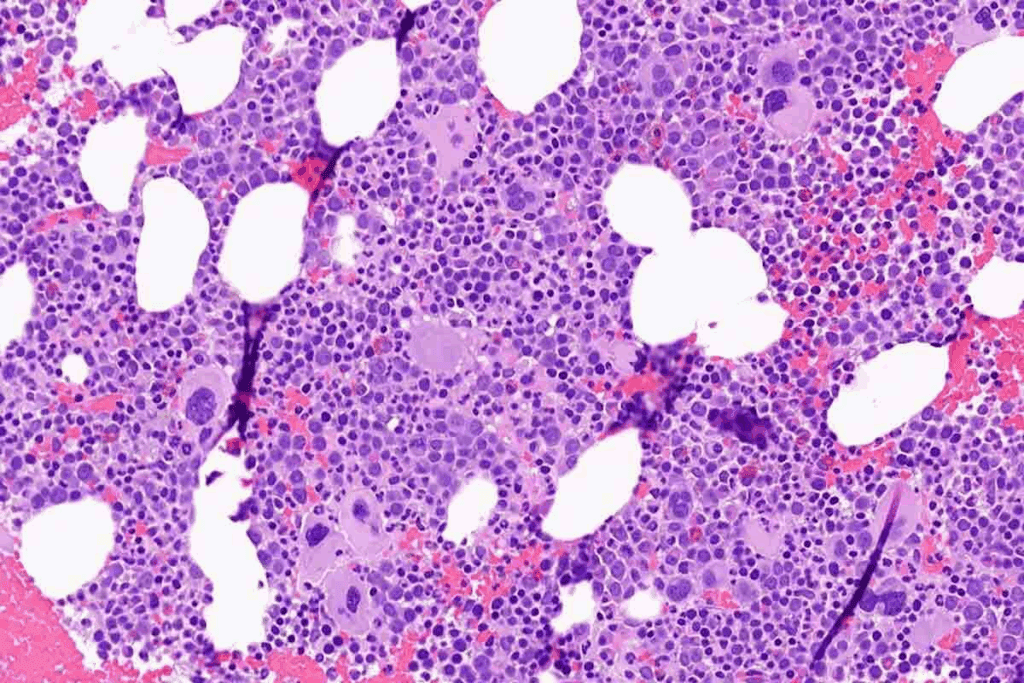
Understanding Hypocellular Bone Marrow
A key sign of aplastic anaemia is hypocellular bone marrow. This means the bone marrow has fewer cells. Doctors use blood counts and bone marrow biopsies to diagnose it. We’ll dive into what this diagnosis means for patients.
Fact 2: Multiple Causes Can Trigger Aplastic Anaemia
Aplastic anaemia is a complex condition with many causes. It happens when a mix of genetic and environmental factors harm the bone marrow.
Autoimmune Mechanisms
Autoimmune disorders are a big cause of aplastic anaemia. In these disorders, the immune system attacks the bone marrow by mistake. This attack can destroy bone marrow cells, causing aplastic anaemia.
Inherited Conditions Including Fanconi Anemia
Inherited conditions, like Fanconi anemia, also contribute to aplastic anaemia. Fanconi anemia is a rare genetic disorder. It causes bone marrow failure and raises the risk of cancer.
Environmental Toxins and Chemical Exposure
Exposure to environmental toxins and chemicals can harm the bone marrow. This can lead to aplastic anaemia. Chemicals like benzene and pesticides are linked to this condition.
Medication-Induced Bone Marrow Suppression
Some medications can weaken the bone marrow, causing aplastic anaemia. Drugs like antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and NSAIDs have been linked to this condition.
| Cause | Description | Examples |
| Autoimmune Mechanisms | Immune system attacks bone marrow | Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| Inherited Conditions | Genetic disorders affecting bone marrow | Fanconi Anemia, Dyskeratosis Congenita |
| Environmental Toxins | Chemical exposure leading to bone marrow suppression | Benzene, Pesticides |
| Medications | Drugs that induce bone marrow suppression | Antibiotics, Anticonvulsants, NSAIDs |
Fact 3: Viral Infections Are Common Triggers
Viral infections often start aplastic anemia. They harm the bone marrow and stop it from making blood cells. This is a known risk factor for the condition.
Hepatitis Viruses and Aplastic Anaemia
Hepatitis viruses are linked to aplastic anemia. They can infect and destroy bone marrow cells. This leads to aplastic anemia. Hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia is a known condition.
“The association between hepatitis viruses and aplastic anemia is well-documented, stressing the need for monitoring patients with hepatitis for bone marrow failure signs.”
Other Viral Associations
Other viruses also cause aplastic anemia. For example, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) can lead to it by damaging bone marrow cells. Parvovirus B19 and cytomegalovirus (CMV) are also involved.
| Virus | Association with Aplastic Anemia |
| Hepatitis Viruses | Strongly associated; can directly infect bone marrow cells. |
| Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) | Occasional cases reported; damages bone marrow cells. |
| Parvovirus B19 | Implicated in some cases; affects red blood cell production. |
| Cytomegalovirus (CMV) | Implicated; can cause bone marrow suppression. |
How Viruses Damage Bone Marrow Function
Viruses harm bone marrow in several ways. They can infect and kill stem cells needed for blood. They can also trigger an immune response that harms the bone marrow. Knowing how they work helps in finding treatments.
Viral infections are key in causing aplastic anemia. Knowing the viruses involved is vital for early diagnosis and treatment.
Fact 4: Recognizing the Symptoms of Aplastic Anaemia
It’s important to know the symptoms of Aplastic Anaemia early. This helps in getting the right treatment fast. The disease happens when the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells.
Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue and weakness are common signs of Aplastic Anaemia. This is because of not enough red blood cells. It can make everyday tasks hard and lower your quality of life.
Bleeding and Bruising Tendencies
People with Aplastic Anaemia often get bleeding and bruising easily. This is because they have low platelet counts. It can show as easy bruising, nosebleeds, or bleeding that won’t stop after injuries.
Increased Susceptibility to Infections
Aplastic Anaemia also makes you more likely to get sick. This is because of not enough white blood cells. It’s harder for your body to fight off infections, which can lead to serious problems.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
It’s key to know when to seek emergency medical attention. Severe symptoms like heavy bleeding, serious infections, or extreme fatigue need quick medical help.
Knowing these symptoms helps both patients and doctors spot Aplastic Anaemia early. This can lead to better treatment results.
Fact 5: Diagnosis Requires Multiple Tests
To diagnose aplastic anemia, doctors use several tests. These tests help understand how the disease affects blood cells and bone marrow.
Complete Blood Count Findings
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is the first test for aplastic anemia. It checks the levels of red, white blood cells, and platelets. In aplastic anemia, the CBC shows pancytopenia, meaning low counts of all blood cells.
| Blood Cell Type | Normal Count Range | Aplastic Anemia Count |
| Red Blood Cells | 4.32-5.72 million cells/μL | Decreased |
| White Blood Cells | 3,500-10,500 cells/μL | Decreased |
| Platelets | 150,000-450,000 cells/μL | Decreased |
Bone Marrow Biopsy Procedure
A Bone Marrow Biopsy is key for diagnosing aplastic anemia. It takes a small bone marrow sample, usually from the hipbone. This test checks the bone marrow’s cell count and rules out other conditions.
Histological Examination and Hypocellularity
The bone marrow sample is examined under a microscope in a histological examination. In aplastic anemia, the bone marrow is hypocellular, meaning it has fewer cells than normal. This is a key sign of the disease.
Ruling Out Other Conditions
Diagnosing aplastic anemia also means checking for other diseases with similar symptoms. Doctors use the CBC, bone marrow biopsy, and other tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Fact 6: Aplastic Anaemia vs. Aplastic Crisis
It’s important to know the difference between aplastic anemia and aplastic crisis. Both involve bone marrow failure, but they affect patients differently.
Understanding the Fundamental Differences
Aplastic anemia is a long-term condition where the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. An aplastic crisis, on the other hand, is a sudden and severe failure of the bone marrow. It usually happens in people with certain blood diseases.
Aplastic anemia means the bone marrow slowly stops making blood cells. This leads to fewer red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. An aplastic crisis, by contrast, causes a quick and severe drop in the patient’s condition.
Distinguishing Features in Diagnosis
To diagnose aplastic anemia and aplastic crisis, doctors use a few key steps. They check the patient’s blood and do a bone marrow biopsy. These tests help figure out how much bone marrow failure there is.
| Diagnostic Feature | Aplastic Anemia | Aplastic Crisis |
| Onset | Gradual | Sudden |
| Bone Marrow Function | Chronic failure | Acute failure |
| Underlying Condition | Often idiopathic | Typically in patients with hemolytic diseases |
Different Treatment Approaches
Treatment for aplastic anemia and aplastic crisis varies. For aplastic anemia, doctors might use drugs to suppress the immune system or bone marrow transplants. For aplastic crisis, immediate care is needed, like blood transfusions, to help the bone marrow recover.
Knowing the difference between these two conditions is key. It helps doctors give the right treatment. This way, patients can get better faster.
Fact 7: Treatment Options Have Improved Survival Rates
The treatment for aplastic anemia has changed a lot, giving patients new hope. New medical treatments have made managing this condition better. This has led to higher survival rates and a better quality of life.
Immunosuppressive Therapy Approaches
Immunosuppressive therapy is key in treating aplastic anemia. It uses medicines to calm down the immune system. This is because the immune system is too active in these patients. Antithymocyte globulin (ATG) and cyclosporine are common medicines used.
These medicines help the bone marrow make blood cells better. This means patients can have better blood counts and need fewer blood transfusions. But, not everyone responds the same way to treatment.
Stem Cell Transplantation Candidacy and Process
Stem cell transplantation is another option for treating aplastic anemia. It replaces the damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor. The choice to have this transplant depends on the patient’s age, health, and if a good donor is found.
The process starts with treatments to weaken the immune system. Then, the new stem cells are given to the patient. These cells go to the bone marrow and start making new blood cells. Stem cell transplantation can cure some patients, but it also has risks like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Supportive Care and Blood Transfusions
Supportive care is very important for managing aplastic anemia. Blood transfusions help with symptoms like tiredness and shortness of breath. Platelet transfusions are also used to prevent bleeding.
Supportive care also includes antibiotics to prevent infections. Other treatments help manage symptoms and improve life quality. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are key to keep track of the patient’s health and adjust treatments as needed.
Conclusion: Living with Aplastic Anaemia
Living with aplastic anemia means having a detailed plan to improve your life. With the right treatment and care, you can handle your symptoms better. This helps lower the chance of serious problems.
Managing aplastic anemia means seeing your doctor often, following your treatment, and making lifestyle changes. Knowing about your condition and how it affects your body helps you manage your care better.
Good management of aplastic anemia includes steps to avoid infections, handle bleeding and bruising, and fight fatigue. Working closely with your healthcare team is key to creating a care plan that fits you.
Being proactive in managing aplastic anemia can greatly improve your health and quality of life. We stress the need for ongoing care and support for those living with aplastic anemia.
FAQ
What is aplastic anemia?
Aplastic anemia is a rare blood disorder. It happens when the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. This leads to fatigue, infections, and bleeding.
What causes aplastic anemia?
It can be caused by autoimmune disorders or inherited conditions like Fanconi anemia. Exposure to toxins and certain medications also play a role.
What are the symptoms of aplastic anemia?
Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and bleeding. You might also bruise easily and get infections more often.
How is aplastic anemia diagnosed?
Doctors use a complete blood count and a bone marrow biopsy. They also do a histological examination to confirm the condition.
What is the difference between aplastic anemia and aplastic crisis?
Aplastic anemia is a long-term condition. Aplastic crisis is a sudden and severe episode. They need different treatments.
What are the treatment options for aplastic anemia?
Treatment includes immunosuppressive therapy and stem cell transplantation. Supportive care, like blood transfusions, helps manage symptoms.
Can viral infections trigger aplastic anemia?
Yes, infections like hepatitis and Epstein-Barr virus can damage the bone marrow. This can trigger aplastic anemia.
How does aplastic anemia affect different blood cell types?
It affects the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This leads to anemia, infections, and bleeding.
What is hypocellular bone marrow?
Hypocellular bone marrow has fewer cells than normal. This is a key feature of aplastic anemia.
How can patients with aplastic anemia manage their condition?
Patients can improve their quality of life by following treatment plans. Regular appointments and lifestyle adjustments help manage symptoms.
Reference
- PubMed – Diagnosis and Treatment of Aplastic Anemia (Review)