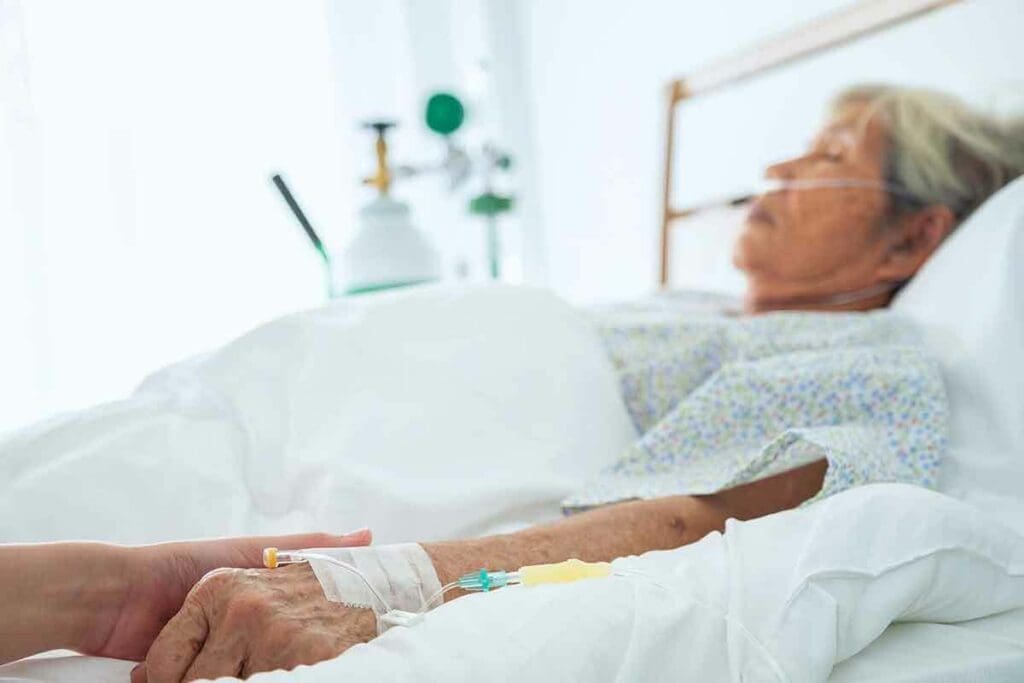
Anemia is when your body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. These cells carry oxygen to all parts of your body. It can be short-term or long-lasting, and while it’s often mild, it can be deadly.
Recent numbers show over 1.9 billion people worldwide have anemia. Sadly, thousands die from it every year.
At Liv Hospital, we take anemia seriously. We use the latest technology and focus on our patients to help those with anemia. Knowing the dangers of anemia is key, even more so in severe or untreated cases.
Key Takeaways
- Anemia can be a life-threatening condition if left untreated or severe.
- The global prevalence of anemia affects over 1.9 billion people worldwide.
- Thousands of deaths are reported yearly due to anemia-related complications.
- Anemia can be temporary or chronic, requiring different treatment approaches.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in managing anemia effectively.
The Global Impact of Anemia: Understanding the Scope

Anemia affects nearly a third of the world’s population. It’s a condition where the body doesn’t have enough red blood cells. These cells are key to carrying oxygen to our tissues. Knowing how widespread anemia is helps us tackle its effects.
What Defines Anemia and Its Various Types
Anemia isn’t just one disease; it’s a condition with many causes. These include iron and vitamin deficiencies, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders. The most common is iron deficiency anemia, where the body lacks enough iron for hemoglobin.
Other types are vitamin deficiency anemia, anemia of chronic disease, and hemolytic anemia. Each has its own causes and effects.
Worldwide Prevalence: 1.9 Billion People Affected
About 1.9 billion people worldwide have anemia. This huge number shows how common the condition is. It highlights the need for big efforts to stop and treat anemia.
The number of people with anemia varies by region and group. It depends on things like money, food, and healthcare access.
Demographic Distribution of Anemia Cases
Anemia hits different groups in different ways. Women, and those who are pregnant, lose a lot of iron. This makes them more likely to have anemia.
Children and teens are also at risk. Anemia can slow their growth and development. Older adults face it too, due to age and chronic diseases. Knowing who is most at risk helps us focus our efforts.
Can Anemia Be Fatal? Examining the Evidence
Anemia’s link to death is complex, involving different types and health issues. We look at how anemia leads to death, including yearly death rates and life-threatening cases. This will show how serious anemia is for global health.
Mortality Statistics and Annual Death Rates
Anemia is a big killer worldwide, with studies showing many deaths each year. Data shows anemia is behind a large number of deaths globally. This makes it a major health problem. The death rates from anemia change, but they all show we need better ways to treat it.
Studies say anemia often leads to death, mainly in people with other health problems. For example, a study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website shows how anemia and other health issues can increase death risk.
46,000+ Deaths from Hemolytic Anemia in the US
Hemolytic anemia, where red blood cells break down too early, is very serious. In the US, it causes over 46,000 deaths each year. This shows how deadly some anemia types can be and why we need to act fast.
The high death rate from hemolytic anemia in the US shows how important early treatment is. Doctors must watch for at-risk patients and start the right treatment quickly.
Conditions Where Anemia Becomes Life-Threatening
Some health problems can make anemia deadly. Chronic diseases, for example, can make anemia worse, raising death risk. Cancer and kidney disease also make managing anemia harder, increasing death risk.
It’s key for doctors to know how these conditions affect anemia. By understanding these links, we can create better treatment plans and save more lives.
In summary, anemia can be deadly, especially when linked to certain health issues or not treated well. By looking at death rates and understanding risk factors, we can tackle this serious health problem better.
Fact 1: The Physiological Pathway from Anemia to Death
Anemia’s journey to fatal outcomes is complex. It starts with oxygen deprivation. When anemia worsens, the body’s tissues and organs don’t get enough oxygen. This is key for their proper functioning.
How Oxygen Deprivation Affects Vital Organs
Oxygen deprivation, or hypoxia, impacts vital organs differently. The heart, for example, works harder due to oxygen lack. This can lead to heart failure over time.
The brain, very sensitive to oxygen, can experience dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness in severe cases.
Tissue Hypoxia and Cellular Damage
Prolonged oxygen deprivation causes tissue hypoxia. This means cells can’t do their normal jobs. It leads to cellular damage and, if it continues, cell death.
The damage is most severe in organs that need a lot of energy, like the heart and brain.
The Cascade of Organ System Failures
As anemia gets worse and oxygen delivery stays low, initial organ dysfunction can start a chain of failures. For instance, kidney function might be affected, causing toxin buildup. This can harm other organs.
This chain can end in multi-organ failure, a condition with a very high death rate.
Fact 2: Iron Deficiency Anemia and Its Fatal Potentia
It’s important to know how serious iron deficiency anemia can be. This condition happens when your body doesn’t have enough iron. This leads to less hemoglobin in your red blood cells. Hemoglobin is key to carrying oxygen.
Can You Die From Low Iron Anemia?
Yes, iron deficiency anemia can be deadly if not treated. It causes severe tiredness, weakness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can greatly lower your quality of life and even be life-threatening.
Critical Iron Levels and Survival
Keeping iron levels right is vital for staying alive. Without enough iron, your heart has to work too hard. This can lead to heart failure in extreme cases.
High-Risk Populations for Iron Deficiency Mortality
Some groups face a higher risk of dying from iron deficiency anemia. These include pregnant women, older adults, and people with chronic diseases. They need close monitoring to avoid fatal outcomes.
| Iron Level Category | Hemoglobin Level (g/dL) | Associated Risks |
| Mild Iron Deficiency | 10-12 | Fatigue, Weakness |
| Moderate Iron Deficiency | 7-9 | Shortness of Breath, Dizziness |
| Severe Iron Deficiency | <7 | Heart Failure, Organ Damage |
Early detection and treatment are key to stopping iron deficiency anemia from getting worse. Knowing the risks and acting early can greatly lower your chance of serious harm from iron deficiency anemia.
Fact 3: Hemoglobin Levels and Mortality Risk
Hemoglobin levels are key in understanding anemia’s risk of death. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Low levels mean tissues and organs don’t get enough oxygen, leading to serious health issues.
Can Low Hemoglobin Cause Death?
Yes, low hemoglobin levels can increase the risk of death. When hemoglobin is too low, the body can’t transport enough oxygen to vital organs. This can cause damage and failure if not treated.
Dangerous Hemoglobin Thresholds
Studies show specific hemoglobin levels where mortality risk jumps up. For example, levels below 8-10 g/dL are critical and need urgent medical care. The exact level can depend on health, age, and other factors.
| Hemoglobin Level (g/dL) | Mortality Risk | Clinical Implication |
| Above 12 | Low | Normal or mildly anemic |
| 8-12 | Moderate | Requires monitoring and possible treatment |
| Below 8 | High | Critical; immediate medical intervention needed |
The Body’s Compensatory Mechanisms and Their Limits
The body tries to compensate for low hemoglobin by increasing heart rate and output. But, these efforts have limits. Severe or long-lasting anemia can exceed these limits, causing serious harm.
It’s vital for healthcare providers to understand the link between hemoglobin levels and mortality risk. This helps identify high-risk patients and treat them effectively. Recognizing the dangers of low hemoglobin and the body’s limits helps manage anemia and prevent fatal outcomes.
Fact 4: Underlying Conditions That Increase Anemia Mortality
Certain conditions can make anemia more deadly. We’ll look at how chronic diseases, cancer-related anemia, and kidney disease raise the risk of death in anemia patients.
Chronic Diseases and Anemia Death Risk
Chronic diseases play a big role in anemia-related deaths. Heart disease, diabetes, and COPD can make treating anemia harder. When anemia and these diseases are together, the body can’t handle the lack of red blood cells well. This can lead to organ failure and death.
Cancer-Related Anemia Fatalities
Cancer and its treatment can cause anemia, which affects treatment success. Anemia in cancer patients can cause fatigue, lower quality of life, and shorter survival times. Severe anemia can also limit how intense cancer treatment can be, affecting the patient’s chances of recovery.
Kidney Disease and Fatal Anemic Complications
Kidney disease also raises the risk of anemia-related death. The kidneys make erythropoietin, a hormone that helps make red blood cells. When kidney function drops, erythropoietin production falls, causing anemia. Patients with CKD or ESRD are at higher risk of severe anemia, leading to heart problems and increased mortality.
It’s key to understand how underlying conditions and anemia interact. By managing these conditions and treating anemia quickly, doctors can lower the risk of fatal outcomes and improve patient care.
Fact 5: Age, Comorbidities, and Anemia Death Risk
The link between age, health conditions, and anemia death risk is complex. Elderly patients face special challenges that raise their risk of death.
Why Elderly Patients Face Higher Mortality
Elderly people are more at risk of anemia-related death. This is because their bodies naturally slow down with age. Health problems add to the challenge of managing anemia in this group.
Research shows older adults often have severe anemia. This can lead to more serious health issues and death. The reasons include less production of a key hormone and problems with iron.
The Compounding Effect of Multiple Health Conditions
Having many health problems makes anemia risk worse. Conditions like kidney disease, heart failure, and cancer increase the risk of death from anemia. It’s important to manage these conditions well to lower the risk of bad outcomes.
| Comorbidity | Impact on Anemia Mortality |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | Increased risk due to decreased erythropoietin production |
| Heart Failure | Higher risk of cardiovascular complications |
| Cancer | Increased risk due to chemotherapy-induced anemia |
Socioeconomic Factors in Anemia-Related Deaths
Socioeconomic factors also affect anemia-related death risk. Lack of healthcare, poor diet, and lack of social support increase the risk. We need to tackle these issues to lower anemia-related death rates.
In conclusion, the relationship between age, health conditions, and anemia death risk is complex. Understanding these factors and addressing the challenges faced by elderly patients can help reduce anemia-related death.
Fact 6: Anemic Life Expectancy and Survival Factors
Anemia’s life expectancy varies based on its cause and severity. It’s not a disease itself but a sign of many health problems. These can range from not getting enough nutrients to chronic diseases and genetic issues.
Life Expectancy With Different Types of Anemia
Each type of anemia has its own outlook. Iron deficiency anemia, the most common, usually has a good outcome with proper treatment. But anemias linked to chronic diseases or bone marrow failure have a tougher outlook.
| Type of Anemia | Typical Life Expectancy | Prognostic Factors |
| Iron Deficiency Anemia | Normal life expectancy with treatment | Response to iron supplementation, underlying cause |
| Anemia of Chronic Disease | Variable, depends on the underlying condition | Severity of underlying disease, response to treatment |
| Aplastic Anemia | Guarded, depends on bone marrow function | Response to immunosuppressive therapy or bone marrow transplant |
The table shows how anemia type affects life expectancy. Knowing the specific type and cause is key to understanding prognosis.
Prognostic Indicators for Anemia Survival
Several factors can predict anemia survival. These include hemoglobin levels, treatment response, and underlying health conditions.
“The severity of anemia at diagnosis and the patient’s response to initial treatment are strong predictors of long-term survival.”
- Senior Hematologist
Key indicators include:
- Hemoglobin levels: Lower levels often mean poorer outcomes.
- Response to treatment: A Good initial treatment response usually leads to better survival.
- Underlying health conditions: Chronic diseases or malignancies can worsen prognosis.
Quality of Life Considerations for Anemia Patients
While life expectancy matters, quality of life is just as important for anemia patients. Good anemia management can greatly improve a patient’s life quality.
It’s important to think about how anemia affects daily life, fatigue, and overall well-being. Treatment plans should aim to improve both physical and emotional health.
Understanding what affects anemic life expectancy and survival helps healthcare providers give better care. This not only increases survival chances but also improves life quality for those with anemia.
Fact 7: Prevention and Treatment to Avoid Fatal Outcomes
Preventing anemia is key to avoiding serious problems. Knowing the early signs is very important. We need to catch symptoms early to stop them from getting worse.
Early Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Anemia can show symptoms that are not always clear. But some signs need quick medical help. These include:
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest pain or palpitations
- Cold hands and feet
If you or someone you know has these symptoms, get medical help right away. Early treatment can make a big difference.
Effective Treatment Approaches for Different Anemia Types
Treatment for anemia depends on the cause. For iron deficiency, iron supplements are often used. Vitamin deficiency anemia is treated with B12 injections or supplements. Managing chronic disease is key for other types.
| Type of Anemia | Treatment Approach |
| Iron Deficiency Anemia | Iron supplements, dietary changes |
| Vitamin Deficiency Anemia | Vitamin B12 injections or supplements |
| Anemia of Chronic Disease | Managing the underlying chronic disease |
Good treatment not only relieves symptoms but also fixes the root cause. This lowers the risk of serious problems.
Emergency Interventions for Severe Anemia
For severe anemia, quick action is needed. Blood transfusions can quickly raise red blood cell counts. This improves oxygen delivery. Sometimes, hospital care is needed for treatments or to manage complications.
Understanding the importance of prevention and treatment of anemia is vital. Recognizing early signs and getting medical help can prevent serious issues. This approach can save lives.
Conclusion: Taking Anemia Seriously Can Save Lives
Anemia is a big health problem worldwide. It can be deadly if not treated properly. We’ve looked at what anemia is, how common it is, and how it can lead to death. Knowing the dangers of anemia is key to avoiding serious problems.
It’s important to take anemia seriously. This means noticing its signs, getting medical help when needed, and following treatment plans. This way, people can lower their chances of serious issues and death. Doctors also have a big role in managing anemia, mainly in groups at high risk.
We need to spread the word about anemia and its dangers. This can help lessen its impact globally. Good management and treatment of anemia can greatly improve health outcomes and save lives. We must treat anemia with the seriousness it deserves to protect people everywhere.
FAQ
Can anemia be fatal?
Yes, anemia can be fatal if not treated or managed well. This is true for severe cases or when there are other health issues.
Can you die from low iron anemia?
Yes, iron deficiency anemia can be deadly if it’s severe and not treated. It can cause serious health problems and damage to organs.
Can low hemoglobin cause death?
Yes, very low hemoglobin levels can be deadly. This is because the body can’t get enough oxygen to vital organs, leading to organ failure.
What are the risks associated with anemia?
Anemia can lead to heart issues, poor pregnancy outcomes, and a lower quality of life. In severe cases, it can be fatal.
How does anemia affect life expectancy?
Anemia’s impact on life expectancy depends on its type, severity, and causes. It also depends on how well it’s treated and managed.
Can anemia be life-threatening in elderly patients?
Yes, anemia is more dangerous for elderly patients. This is because they often have more health issues, and their bodies can’t handle as much stress.
What are the early warning signs of anemia that require medical attention?
Early signs include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and dizziness. If these symptoms don’t go away or get worse, you should see a doctor.
How can anemia be effectively treated?
Treatment varies based on the cause. For iron deficiency anemia, iron supplements are often used. For pernicious anemia, vitamin B12 injections are given. Treating underlying diseases is also important.
Can anemia be prevented?
While not all anemias can be prevented, there are steps to reduce the risk. Eating a balanced diet, managing chronic diseases, and getting medical help for symptoms can help.
Is anemia a significant global health concern?
Yes, anemia affects about 1.9 billion people worldwide. It’s a big health issue that needs awareness, proper management, and treatment to lessen its effects.
Can underlying conditions increase anemia mortality?
Yes, conditions like chronic diseases, cancer, and kidney disease can raise the risk of death from anemia. This is because they make managing anemia more complicated.
What is the role of socioeconomic factors in anemia-related deaths?
Socioeconomic factors, like access to healthcare and nutrition, play a big role in anemia. They can affect how common anemia is and its outcomes, mainly in poor communities.
References:
- Kebede, S. S., et al. (2024). Global prevalence of iron deficiency anemia and its determinants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scientific African, 24, e02420. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2667268524001207




































