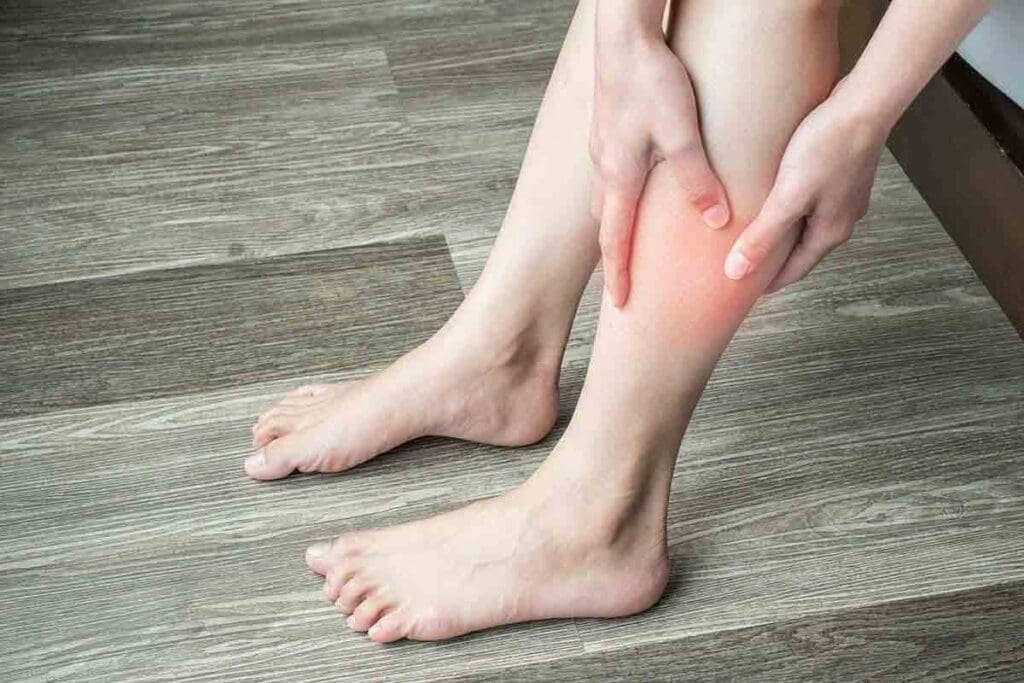
Recognizing the signs of a blood clot on top of the foot is crucial for prompt treatment. Symptoms include sudden swelling, pain, warmth, redness, or discoloration of the affected area. The skin may appear bluish or darker in color. Feelings of tenderness, tightness, or heaviness in the area are common. Some visual references of blood clot on top of foot pictures can help identify these signs, but it is essential to see a healthcare provider immediately if you suspect a clot. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent complications such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.
At LivHospital, we stress the need for quick medical care for serious issues like blood clots. If a clot moves to the lungs, it can be deadly. Our team is dedicated to providing top-notch care for such conditions.
Key Takeaways
- A blood clot on top of the foot can cause sudden swelling, pain, and discoloration.
- Prompt medical attention is key if symptoms show up.
- LivHospital offers advanced vascular treatment with a focus on patients.
- Blood clots can be dangerous if they break loose and travel to the lungs.
- Spotting the signs of a blood clot is vital for timely medical care.
Understanding Blood Clots
It’s important to know about blood clots, as they can be serious, even in the foot. If not treated quickly, they can cause big problems.
What is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot is a thick, jelly-like mass that forms when blood clots. It happens when platelets and proteins in the blood stick together. This stops bleeding, but it can also happen when it shouldn’t.
Blood clots can be dangerous because they can block blood flow. This can cause swelling, pain, and even life-threatening issues. In the foot, it can make walking hard and hurt a lot.
How Blood Clots Form in the Foot
Blood clots in the foot can happen for many reasons. These include staying in one place for too long, getting hurt, or having a family history of them. When we don’t move for a long time, like on a long flight, blood can pool in our legs. This increases the chance of a clot forming.
The clotting process starts with blood factors turning on. Then, platelets and fibrin come together to form a clot. If this clot gets too big, it can block blood flow, leading to deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This is a serious condition that needs quick medical help.
Prevalence and Statistics
Blood clots are more common than you might think. Every year, thousands of people get DVT. Risk factors include age, family history, being overweight, and certain health conditions.
| Risk Factor | Description | Prevalence |
| Age | Risk increases with age, specially after 40 | Higher in older populations |
| Family History | Having a family history of blood clots | Significant in those with genetic predispositions |
| Obesity | Being overweight or obese | Common in populations with higher BMI |
A medical expert says, “Knowing the risk factors and symptoms of blood clots is key. Quick medical action can greatly lower the risk of serious problems.”
“The key to managing blood clots is awareness and prevention. Understanding the risks and taking proactive steps can save lives.”
Vascular Surgeon
Visual Identification: Blood Clot on Top of Foot Pictures
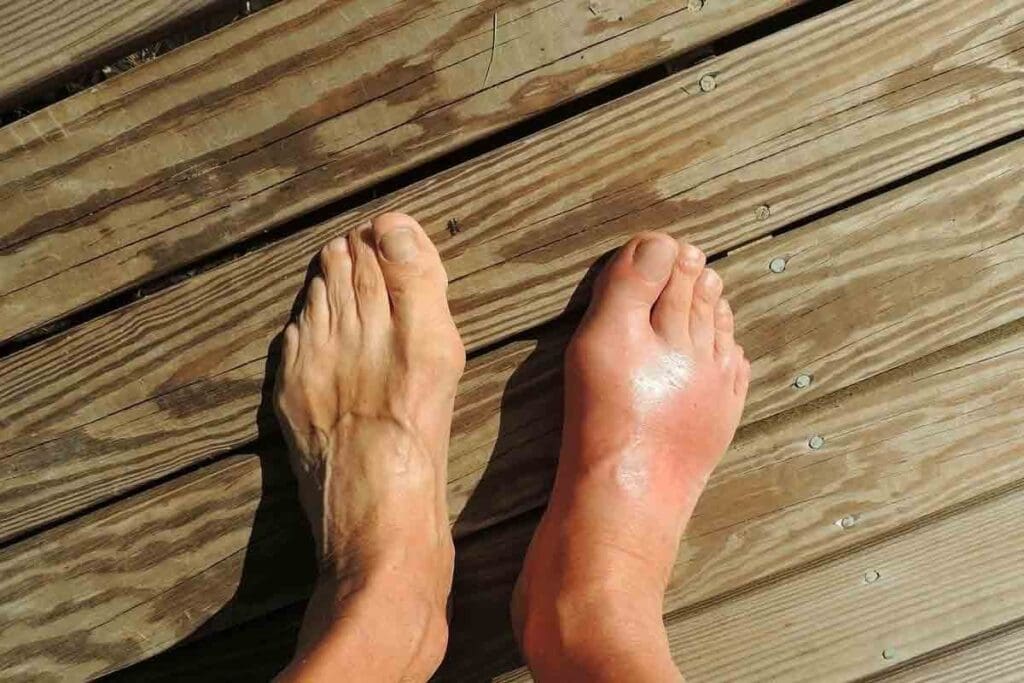
Spotting a blood clot on your foot involves looking for signs like redness and swelling. A blood clot can change how your foot looks and feels. We’ll show you what to look for to spot a blood clot.
Redness and Discoloration Patterns
A blood clot can make your foot skin turn red or change color. This happens because of inflammation and bleeding under the skin. The redness might stay close to the clot or spread out.
Key Observations:
- Redness or a reddish hue on the skin
- Possible blue or purple discoloration due to venous clots
- Localized or widespread redness
Swelling Characteristics
Swelling is a common sign of a blood clot on your foot. It happens because of fluid buildup and inflammation. Watching how much and how fast the swelling grows is important.
Notable Signs:
- Visible swelling on top of the foot
- Pitting edema (indentation upon pressing)
- Swelling that may or may not be painful
Skin Texture Changes
The skin over a blood clot can feel warm, tender, and look different. Sometimes, the skin might feel tight or shiny because of swelling and inflammation.
| Visual Cue | Description |
| Redness | Inflammation causing red or pink coloration |
| Swelling | Fluid accumulation causing the foot to appear swollen |
| Skin Texture | Changes in skin texture, such as warmth, tenderness, or shininess |
Spotting these signs early is key to treating blood clots. If you see any of these, get medical help right away.
Key Symptoms of a Blood Clot on the Foot
Knowing the signs of a blood clot on the foot is key. It helps people get medical help fast. A blood clot can show up in different ways, so it’s important to know the signs to avoid serious problems.
Pain and Discomfort Sensations
Pain from a blood clot in the foot can feel different. Some people might feel a dull ache, while others might have sharp pains. The pain might stay the same or get worse when you move your foot.
Common pain characteristics include:
- Cramp-like pain
- Pain that worsens when standing or walking
- Achiness that doesn’t improve with rest
Warmth and Temperature Changes
A blood clot can make the affected area feel warmer. This is because of the inflammation caused by the clot.
Notable signs include:
- The affected area feeling warm to the touch
- Redness or discoloration
- Swelling that may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness
Tenderness and Sensitivity
The area with a blood clot can be tender. Even light pressure can cause pain or discomfort.
| Symptom | Description |
| Pain | Can be sharp, dull, or cramp-like, often worsening with movement |
| Warmth | Affected area feels warmer than surrounding skin |
| Tenderness | The area is sensitive to touch, causing discomfort or pain |
Spotting these symptoms early is vital. If you notice any, see a doctor right away.
How Blood Clots Feel Compared to Other Foot Conditions
It’s important to know how a blood clot feels compared to other foot issues. Blood clots have specific symptoms and severity. We’ll look at the differences to help you know when to see a doctor.
Distinguishing from Sprains and Strains
Sprains and strains can cause pain and swelling, like blood clots. But, the pain and symptoms are different. Blood clot pain doesn’t get better with rest, unlike sprains and strains.
Swelling is another clue. Blood clots cause firm, local swelling. Sprains and strains have more spread-out swelling.
Differences from Infections and Cellulitis
Infections and cellulitis can look like a blood clot with redness, warmth, and swelling. But, they also bring fever, pus, or open wounds. Cellulitis spreads redness and tenderness more than a blood clot.
Fevers are a sign of infection. Blood clots usually cause pain and swelling in one spot without fever.
Comparison with Gout and Arthritis
Gout and arthritis can also hurt your foot. Gout causes sudden, severe pain and swelling. Arthritis leads to chronic pain and stiffness, worse in the morning.
Blood clots can hurt anywhere in the foot, not just joints. Their pain is constant and gets worse with movement.
| Condition | Pain Characteristics | Swelling | Additional Symptoms |
| Blood Clot | Persistent, localized pain | Localized, firm swelling | Warmth, tenderness |
| Sprain/Strain | Pain improves with rest | Diffuse swelling | Bruising, limited mobility |
| Infection/Cellulitis | Redness, warmth, swelling | Widespread redness and tenderness | Fever, pus, open wound |
| Gout/Arthritis | Sudden, severe pain (gout); chronic pain and stiffness (arthritis) | Joint-specific swelling | Redness around the joint (gout); morning stiffness (arthritis) |
Foot pain from blood clots needs quick attention. If you think you have a blood clot, see a doctor right away.
Risk Factors for Developing Foot Blood Clots
Blood clots in the foot often come from many factors. They don’t usually happen from just one thing. It’s usually a mix of several risks.
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Some medical conditions raise the risk of foot blood clots. These include:
- Inherited disorders that affect blood clotting
- Cancer, which can increase clotting factors in the blood
- Heart disease, including conditions like atrial fibrillation
- Obesity, which can put additional pressure on veins in the legs and feet
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle and environment also play big roles in foot blood clots. These include:
- Prolonged inactivity, such as during long flights or bed rest
- Smoking, which damages the lining of blood vessels
- Hormone-related factors, including pregnancy and the use of birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy
Recent Surgeries or Injuries
Recent surgeries or injuries, like those in the leg or foot, raise the risk of blood clots. This is because:
- Surgery can cause trauma to blood vessels, leading to clot formation
- Injury to the leg or foot can directly damage veins and lead to clotting
Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing and catching blood clots early. By understanding these, people can lower their risk.
Types of Blood Clots That Affect the Foot
It’s important to know about the different blood clots that can happen in the foot. These clots can form in various parts of the foot and leg. Their location and type affect their risk and how they are treated.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis, or DVT, is when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. This usually happens in the legs or feet. It’s serious because it can cause a life-threatening condition if the clot moves to the lungs.
Symptoms include swelling, pain, and discoloration in the affected limb. If these symptoms don’t go away or get worse, you should see a doctor.
Superficial Thrombophlebitis
Superficial thrombophlebitis is when a blood clot forms in the veins near the skin’s surface. This type of clot is less dangerous than DVT but can be very uncomfortable and cause inflammation.
Symptoms include redness, warmth, and tenderness along the vein. While it’s not usually life-threatening, it can be a sign of something more serious that needs to be checked by a doctor.
Arterial Clots vs. Venous Clots
Blood clots can be either arterial or venous, depending on where they form. Arterial clots are in the arteries, which carry oxygen-rich blood. Venous clots are in the veins, which carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
Arterial clots can cause severe lack of blood flow and tissue death if not treated quickly. Venous clots, like DVT, can cause swelling and pain. But they are more likely to cause serious problems if they break loose.
Knowing the difference between these clots is key to the right treatment. We work with doctors to diagnose and treat blood clots. This ensures the best care for our patients.
Potential Complications of Untreated Foot Blood Clots
Untreated blood clots in the foot can cause serious problems. It’s important to know the risks to understand why quick medical help is needed. Blood clots in the foot are not just a local issue. They can affect your whole body if not treated right.
Pulmonary Embolism: A Life-Threatening Risk
Pulmonary embolism is a serious risk of untreated foot blood clots. It happens when a clot breaks off and goes to the lungs, blocking blood flow. This can be deadly and needs immediate medical care.
Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include sudden breathlessness, chest pain, and coughing up blood. If you see these signs, get to the hospital fast. Quick action can save lives.
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
Post-thrombotic syndrome is another risk. It causes chronic pain, swelling, and skin color changes in the affected limb. This can make everyday tasks hard.
This condition happens because the blood clot damages veins and valves. This leads to poor blood flow. Treatment often includes compression therapy, exercise, and sometimes surgery to help symptoms.
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency is another risk. It’s when veins can’t return blood to the heart because of valve damage from a blood clot. This can cause swelling, pain, and skin changes in the leg.
Treating this condition usually means making lifestyle changes like exercise and elevating the leg. Compression stockings are also used. Sometimes, medical procedures are needed to fix the underlying problems.
Diagnosis Process for Blood Clots in the Foot
Diagnosing blood clots in the foot requires a mix of physical checks and advanced imaging. We know how important it is to get the diagnosis right for the best treatment.
Initial Assessment and Physical Examination
When someone shows signs of a blood clot, we start with a detailed medical history and physical check. We look for swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area.
We check for tenderness and if the pain spreads. We also look at the patient’s overall health and any risk factors for blood clots.
Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT, and MRI
To confirm a blood clot, we use imaging tests. Ultrasound is often the first choice because it’s non-invasive and works well for detecting clots in veins.
| Imaging Test | Advantages | Limitations |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, quick, and effective for detecting DVT | Operator-dependent, may not detect small clots |
| CT Scan | Provides detailed images, useful for detecting clots in larger veins | Involves radiation, contrast dye may be required |
| MRI | High sensitivity for detecting clots, no radiation | Expensive, not as readily available as ultrasound or CT |
A medical expert says, “Imaging tests are key for diagnosing blood clots. Ultrasound is often the first choice because it’s safe and works well.”
“The use of ultrasound has revolutionized the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis, allowing for rapid and accurate detection.”
Vascular Specialist
Laboratory Blood Tests
Laboratory blood tests also play a big role in diagnosing blood clots. The D-dimer test is used to find clot fragments in the blood. A negative result can help rule out thrombosis, while a positive result may mean more tests are needed.
We stress the importance of a thorough diagnostic approach for accurate blood clot identification in the foot. By combining physical checks, imaging tests, and blood tests, we ensure patients get the right treatment.
Treatment Options for Foot Blood Clots
Treating foot blood clots involves understanding different treatments. This includes medicines and surgery. The main goal is to stop the clot from getting bigger and breaking loose. This can cause serious problems.
Anticoagulant Medications
Anticoagulant medicines are key in treating foot blood clots. They stop the clot from growing and prevent new ones. Heparin and warfarin are common, but newer medicines like rivaroxaban and apixaban are also used. They are easier to take and don’t need as much monitoring.
The right medicine depends on the patient’s health and the clot’s details. It’s important to stick to the treatment plan to work well and avoid bleeding.
Thrombolytic Therapy
Thrombolytic therapy is sometimes used for foot blood clots. It involves medicines that break down the clot. This treatment is for severe cases, like big clots or bad symptoms.
Choosing thrombolytic therapy depends on the case. It’s done in a hospital to watch for bleeding risks.
Surgical Interventions and Filters
Surgery might be needed for some foot blood clots. This includes removing the clot or using filters in the vena cava. Filters are for those who can’t take blood thinners or have clots again.
Surgery is considered when other treatments don’t work. The right surgery depends on the patient and the clot’s details.
Prevention Strategies for Blood Clots in the Feet
Simple daily habits can greatly lower the risk of blood clots in the feet. By adding a few easy practices to your daily routine, you can improve your vascular health a lot.
Movement and Exercise Recommendations
Regular movement and exercise are key to preventing blood clots. Doing simple activities like walking or stretching can boost blood flow and lower clot risk. For those with mobility issues, gentle leg exercises while seated can also help.
- Take regular breaks to stand and stretch if you have a job that involves prolonged sitting.
- Engage in physical activities that you enjoy, such as swimming or cycling, to keep your blood flowing.
- Consider incorporating exercises that strengthen your leg muscles.
Compression Stockings and Devices
Compression stockings are a great tool for preventing blood clots, mainly for those at high risk or undergoing surgery. These stockings apply graduated pressure to enhance blood flow back to the heart, lowering clot risk.
- Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if compression stockings are right for you.
- Ensure proper fitting to maximize the effectiveness of compression stockings.
- Consider using other compression devices if stockings are not suitable.
Hydration and Dietary Considerations
Keeping well-hydrated and eating a balanced diet are key to preventing blood clots. Drinking plenty of water makes your blood thinner and less likely to clot. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains also supports heart health.
- Drink at least eight glasses of water a day, adjusting according to your activity level and climate.
- Incorporate foods that are known to improve circulation and vascular health into your diet.
- Limit your intake of processed foods and those high in salt and sugar.
By following these prevention strategies, you can greatly lower your risk of blood clots in the feet. It’s about making smart choices and adding healthy habits to your daily life.
Conclusion: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
It’s key to know the signs of a blood clot on your foot to get help fast. Knowing when to get medical help for blood clots is vital. Quick treatment can make a big difference.
Look out for sudden swelling, pain, warmth, and redness in your foot. If you see these signs, get medical help right away.
At LivHospital, our vascular experts offer top-notch care for blood clots. We know the dangers of untreated blood clots, like pulmonary embolism and post-thrombotic syndrome. We aim to give you the best care with kindness and skill.
If you think you have a blood clot, don’t wait to get medical help. Our team is here to support and guide you every step of the way.
FAQ
What does a blood clot on top of the foot look like?
A blood clot on the foot can cause redness and swelling. The skin might look discolored and feel warm.
Can you get a blood clot on your foot?
Yes, blood clots can happen in the foot. It’s important to know the signs to get medical help fast.
What are the symptoms of a blood clot in the foot?
Symptoms include pain, warmth, and tenderness. The skin might turn discolored and feel sensitive.
How do you know if you have a blood clot in your foot?
Look for swelling, redness, and warmth. Pain or tenderness, mainly when walking, is a sign to see a doctor.
What are the risk factors for developing blood clots in the foot?
Medical conditions like deep vein thrombosis are risks. So are recent surgeries or injuries and being immobile for a long time.
Can a blood clot in the foot be life-threatening?
Yes, untreated blood clots in the foot can be deadly. They can cause a pulmonary embolism.
How are blood clots in the foot diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam and imaging tests like ultrasound, CT, or MRI. Blood tests are also used.
What are the treatment options for blood clots in the foot?
Treatments include anticoagulant meds, thrombolytic therapy, and surgery.
How can blood clots in the feet be prevented?
Prevention includes regular exercise, wearing compression stockings, and staying hydrated.
When should I seek medical attention for a suspected blood clot in my foot?
If you notice pain, swelling, or redness, get help right away. Quick treatment can avoid serious issues.
Reference
- MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine): Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) — Symptom overview and information on blood clots in the extremities, including the foot.https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001157.htm


































