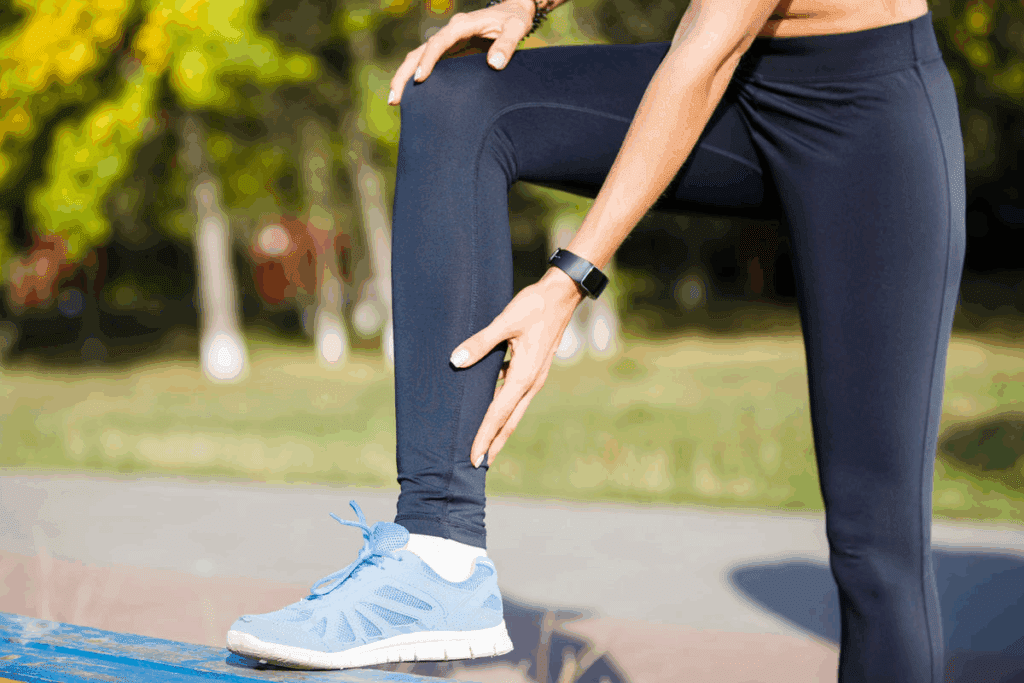
Tendon injuries are common in sports, with over 50% of all sports injuries involving tendons. Tim Patrick’s torn Achilles tendon is a good example. It shows how important it is to know the difference between a torn and strained tendon. Ultimate guide to torn tendon vs strained tendon. Know the Crucial difference for accurate and fast treatment.
It’s key to tell the difference between a torn and strained tendon for the right treatment. A strained tendon might heal with simple care, but a torn tendon often needs surgery. Knowing the symptoms and severity of tendon injuries helps people get the right medical help.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the difference between torn and strained tendons is key for proper treatment.
- Tendon injuries are common in sports, affecting many athletes.
- Tim Patrick’s torn Achilles tendon is a severe example of a tendon injury.
- Conservative treatment works for strained tendons, but torn tendons often need surgery.
- Knowing the symptoms of tendon injuries is vital for getting the right medical care.
Understanding Tendons and Their Function
Tendons are key in our body’s movement system. They link muscles to bones, making it possible for us to move. These strong, yet flexible, cords help us do everything from walking to complex sports moves.
What Are Tendons?
Tendons are made of dense tissue rich in collagen fibers. They handle tension well, helping muscles move bones. Unlike muscles, tendons don’t contract. Their main job is to connect and support.
How Tendons Connect to Muscles and Bones
Tendons link muscles to bones, forming a strong connection for movement. At the muscle end, tendons blend with muscle fibers. At the bone end, they merge with the bone matrix. This ensures a solid bond.
Common Locations of Tendon Injuries
Tendon injuries can happen anywhere, but some spots are more likely. The Achilles tendon, rotator cuff, patellar tendon, and elbow and wrist tendons are common injury sites. Knowing these areas can help prevent and diagnose injuries early.
Doctors say tendon injuries are common, mainly in athletes and those who do repetitive activities. Taking care of tendons can lower injury risks.
Causes of Tendon Injuries
It’s important to know why tendon injuries happen. This knowledge helps prevent and treat them. Tendon injuries, like tears and strains, come from many sources.
Acute Trauma and Sudden Injuries
Direct blows or falls can hurt tendons. Sudden injuries often happen in sports or activities that require quick movements. For example, Tim Patrick’s torn Achilles tendon happened during a game.
Repetitive Motion and Overuse
Doing the same thing over and over can hurt tendons. Running or cycling can cause inflammation and strain. Athletes who suddenly start training harder often get overuse injuries.
Age-Related Degeneration
As we get older, our tendons weaken. This makes them more likely to tear or strain. Years of repetitive stress can speed up this weakening.
Sports and Activities with High Risk
Some sports and activities are riskier for tendon injuries. Jumping, quick turns, or direct contact can be dangerous. Basketball, soccer, and tennis are examples of high-risk activities.
Doctors say prevention is key for tendon injuries. Knowing the causes and taking steps to prevent them can lower the risk. This shows how important it is to be aware and take care of our tendons.
Torn Tendon vs Strained Tendon: Understanding the Difference
Many people confuse torn tendons with strained ones, leading to wrong treatment. It’s key to know the difference for the right diagnosis and care.
Defining Tendon Tears
A torn tendon, or rupture, happens when the tendon fibers are damaged. This injury can come from sudden trauma or long-term wear. Tendon tears cause a lot of pain and can make it hard to move.
Defining Tendon Strains
A strained tendon means the fibers are stretched too far. Strains are mild, moderate, or severe, based on the damage. Unlike tears, strains might not stop the tendon from working completely.
Severity Grades of Tendon Injuries

Tendon injuries, whether tears or strains, have different levels of severity. These levels help decide the best treatment. Here’s a table showing the common grading system:
| Grade | Description | Symptoms |
| 1 | Mild strain or micro-tears | Mild pain, minimal loss of function |
| 2 | Moderate strain or partial tear | Moderate pain, some loss of function |
| 3 | Severe strain or complete tear | Severe pain, significant or complete loss of function |
Impact on Daily Activities
Tendon injuries affect daily life differently, based on their severity and where they are. For example, a torn Achilles tendon makes simple tasks like walking hard. But a mild strain might just cause some discomfort.
Knowing if a tendon is torn or strained is key for managing treatment. Accurate diagnosis leads to a better recovery plan, tailored to the injury’s needs.
Common Symptoms of Tendon Injuries
Knowing the signs of tendon injuries is key to getting the right treatment. Tendon injuries, like strains or tears, show different symptoms. These symptoms can be mild or severe.
Pain Characteristics and Patterns
Pain is a clear sign of a tendon injury. The pain characteristics depend on the injury’s severity and where it is. For example, a torn tendon might cause sharp, intense pain right away. A strained tendon might start with a dull ache.
The pain might stay in the tendon area or spread to nearby parts.
Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling and inflammation often happen with tendon injuries. Swelling is the body’s way of reacting to injury, bringing more blood to the area. This swelling can make the area tender and warm.
In severe cases, like torn tendons, swelling is more noticeable and quick.
Bruising and Discoloration
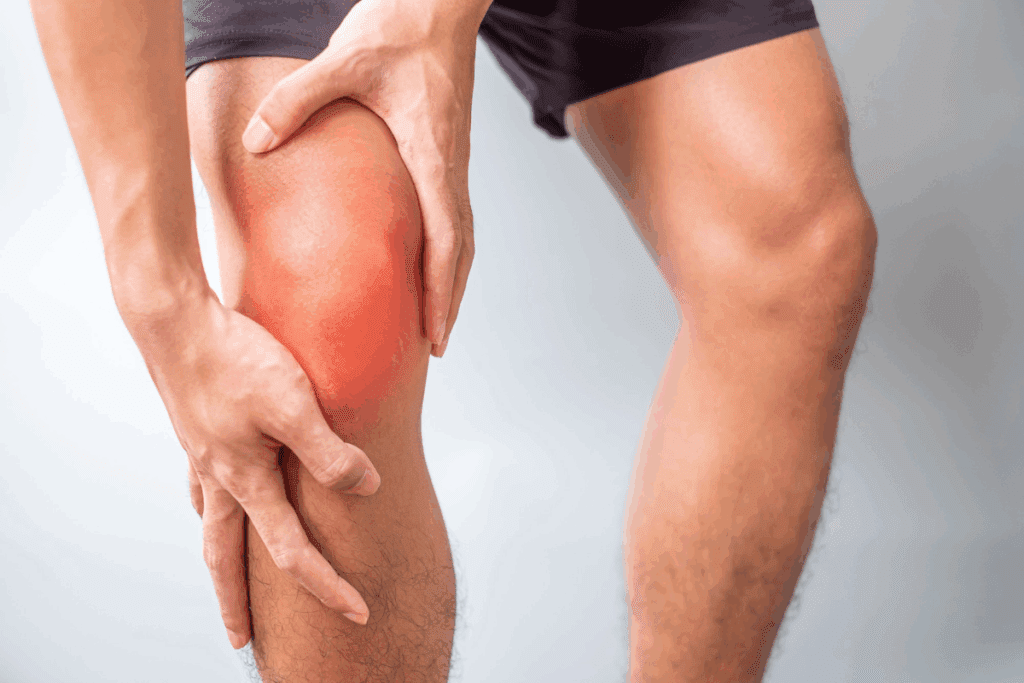
Bruising and discoloration can show up in severe injuries, like tendon tears. Bruising happens when blood vessels are damaged, causing blood to leak into tissues. This can make the area look red, purple, or yellow as it heals.
Changes in Range of Motion
Tendon injuries can affect how well you move. You might feel stiff, less mobile, or weak. In bad cases, like a complete tear, you might not be able to move the limb at all.
Spotting these symptoms early can help you get the right medical help. This can lower the chance of more damage and improve your recovery.
Specific Signs of a Torn Tendon
A torn tendon can be very painful and limit your movement. It shows up suddenly and severely. Knowing the signs can help you get the right treatment fast.
Sudden Pain and Popping Sensation
One clear sign is sudden pain and a popping sound. This happens when the tendon tears. Tim Patrick’s injury is a good example of how severe this can be.
Severe Swelling and Bruising
After a tear, the area swells and bruises a lot. This is your body’s way of reacting to the injury. It can make moving very hard.
Significant Loss of Function
A torn tendon can make it hard to use the affected area. You might feel weak or unable to move as you should. How much you’re affected depends on the tear’s size and where it is.
Visible Deformity in Some Cases
In some cases, you can see that something is wrong. The tendon or muscle might look like it’s in the wrong place. This is more common with certain injuries, like to the Achilles tendon or rotator cuff.
| Signs | Description |
| Sudden Pain | Often accompanied by a popping sensation |
| Severe Swelling and Bruising | Inflammation and discomfort |
| Significant Loss of Function | Weakness or inability to perform certain movements |
| Visible Deformity | Tendon or muscle appears out of place |
Spotting these signs early is key. It helps you get the right help and start treatment quickly. A torn tendon needs fast attention to heal right.
Identifying a Strained Tendon
To know if you have a strained tendon, you need to recognize its symptoms. Strains usually come from overuse, not sudden injuries. They are different from torn tendons.
Gradual Onset of Pain
Pain that starts slowly is a sign of a strained tendon. This pain grows as the tendon faces repeated stress. Pain that gets worse with activity is a big clue.
Mild to Moderate Swelling
Swelling is another sign, but it’s usually not too bad. How much swelling depends on the strain’s severity. Using ice and compression can help in the early stages.
Limited but Not Complete Loss of Function
A strained tendon limits your function but doesn’t stop you completely. You might feel pain or discomfort while doing things. This is different from a tear, where you can’t do much at all.
Pain that Worsens with Activity
Pain that gets worse with activity is a key sign of a strain. Using the tendon more makes the pain worse. Resting helps, which is not true for other injuries.
Knowing these signs is key for tendon strain recovery. Spotting the strain early and acting fast can prevent more harm and help it heal.
Tendon Tear vs Sprain: Differentiating Similar Injuries
Understanding the difference between a tendon tear and a sprain is key. Both are injuries to the musculoskeletal system. But they affect different tissues and have different treatment needs.
Ligament vs Tendon Injuries
Tendons and ligaments are both connective tissues. But they have different jobs. Tendons connect muscles to bones, helping us move. Ligaments connect bones to each other, keeping joints stable.
An injury to these tissues has different effects. A tendon tear or strain can hurt movement. A ligament sprain can affect how stable a joint is.
Key Differences in Symptoms
Symptoms of tendon tears and sprains can be similar. But there are key differences. Tendon tears often cause sudden, severe pain and might sound like a pop. They can also make it hard to move.
Sprains can also hurt and swell. But they usually don’t stop you from moving as much as tendon tears do.
Location-Based Differentiation
Where the injury happens can also tell you what it is. Tendon injuries often happen in places with a lot of stress, like the Achilles tendon or the rotator cuff. Sprains happen in joints, like the ankle or knee, where ligaments get stretched or torn.
When Injuries Occur Together
Sometimes, tendon and ligament injuries happen at the same time. This makes it harder to figure out what’s wrong. For example, a bad ankle sprain might also hurt a tendon.
It’s important to think about this possibility. This way, doctors can give the right treatment and help you get better faster.
Achilles Tendon Tear vs Strain: Special Considerations
It’s important to know the difference between an Achilles tendon tear and strain. The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It can get injured, from mild strains to complete tears.
The Thompson Test for Achilles Rupture
The Thompson test checks if the Achilles tendon is okay. During the test, the patient lies on their stomach with their feet hanging off the table. The examiner then squeezes the calf muscles.
If the tendon is fine, the foot will flex downward. But if it’s torn, the foot won’t move. This shows a positive test result.
Differentiating Achilles Tendinitis from Tears
Achilles tendinitis is inflammation of the tendon. It can lead to more serious injuries like tears. Key differences include the pain’s severity and if there’s a gap in the tendon.
Tendinitis starts with gradual pain and swelling. A tear causes sudden, severe pain and might feel like a pop.
Risk Factors for Achilles Injuries
Several things can make you more likely to hurt your Achilles tendon. These include:
- Age: Tendon strength goes down with age.
- Sudden changes in exercise intensity or frequency.
- Not warming up or stretching enough before activities.
- Wearing the wrong shoes or using bad equipment.
Common Misdiagnoses
Achilles tendon injuries are often mistaken for ankle sprains or calf strains. Healthcare providers need to do detailed exams to tell them apart. The Thompson test and imaging like ultrasound or MRI help confirm the diagnosis.
For example, Tim Patrick, a pro football player, had a torn Achilles tendon. This shows how serious these injuries can be for athletes. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment is key for recovery and avoiding more problems.
Other Common Tendon Injuries and Their Signs
Tendon injuries can happen anywhere in the body. It’s important to know the signs and symptoms. These injuries can really affect how well you can do everyday things.
Rotator Cuff Injuries (Shoulder)
The rotator cuff is around the shoulder joint. It keeps the upper arm bone in place. Athletes often get hurt here because of the way they move their arms.
Symptoms of rotator cuff injuries include:
- Pain when reaching overhead or lifting
- Weakness in the arm or shoulder
- Cracking or clicking sensations in the shoulder
- Reduced range of motion
Patellar Tendon Injuries (Knee)
The patellar tendon links the kneecap to the shinbone. It’s key for knee movement. Jumping sports, like basketball, can lead to injuries here.
Signs of patellar tendon injuries include:
- Pain and tenderness below the kneecap
- Swelling or bruising
- Pain when jumping or landing
Tennis and Golfer’s Elbow
Tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow are tendon inflammation issues. They happen on the outside or inside of the elbow. These are usually from overusing the forearm muscles and tendons.
Symptoms include:
- Pain or burning on the outside (tennis elbow) or inside (golfer’s elbow) of the elbow
- Weak grip strength
- Pain when shaking hands or turning a door handle
Wrist and Hand Tendon Injuries
Wrist and hand tendon injuries can come from too much motion or a direct hit. De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is one such condition, affecting the thumb side of the wrist.
Common symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness in the wrist or hand
- Swelling or redness
- Difficulty moving the wrist or hand
| Tendon Injury | Common Symptoms | Common Causes |
| Rotator Cuff | Pain when reaching overhead, weakness, cracking sensations | Repetitive arm movements, sports injuries |
| Patellar Tendon | Pain below kneecap, swelling, pain when jumping | Jumping sports, repetitive strain |
| Tennis/Golfer’s Elbow | Pain on outside/inside of elbow, weak grip | Repetitive forearm strain, gripping activities |
| Wrist/Hand Tendons | Pain, swelling, difficulty moving wrist/hand | Repetitive motions, direct trauma |
Knowing the signs of tendon injuries is key to getting the right treatment. Early action can help a lot and make recovery faster.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important to know when to get medical help for tendon injuries. Tendon injuries can be serious if not treated right. Knowing when to seek help can greatly improve your recovery.
Red Flags That Require Immediate Care
Certain symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Sudden, severe pain that doesn’t get better with rest or medicine.
- A popping or snapping sensation when you get hurt.
- Significant swelling or bruising around the hurt area.
- Inability to move the hurt limb or joint.
- Visible deformity or a gap in the tendon you can feel.
Symptoms That Can Wait for Regular Appointment
For mild to moderate tendon injuries, you might not need to rush to the doctor. But, it’s good to see a healthcare provider. Symptoms that can wait include:
- Mild pain that gets better with rest.
- Little swelling or bruising.
- Some loss of function, but you can move the area a bit.
What to Tell Your Healthcare Provider
When you go to the doctor, tell them everything about your injury. Include:
- How you got hurt.
- The pain’s severity and what makes it better or worse.
- If you’ve had injuries or conditions in the same area before.
Self-Care vs Professional Treatment
For mild tendon injuries, you might be able to manage with self-care like rest and ice. But, more serious injuries need a doctor’s help. Professional evaluation helps figure out how bad the injury is and what treatment you need.
In summary, knowing when to get medical help for tendon injuries is key for good treatment and avoiding more problems. If you’re not sure about your injury, always talk to a healthcare professional.
Diagnostic Methods for Tendon Injuries
Tendon injuries are hard to diagnose. A detailed check-up is needed, including a physical exam, patient history, and imaging tests. Getting the diagnosis right is key to picking the right treatment and helping the patient recover well.
Physical Examination Techniques
A healthcare expert starts with a detailed physical check-up. They look for pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area. They also check the range of motion and strength.
They might do specific tests to stress the tendon and see if it hurts. For example, the Thompson test is used to check for Achilles tendon ruptures.
Imaging Tests (MRI, Ultrasound, X-ray)
Imaging tests are vital for confirming the diagnosis and seeing how bad the injury is. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is great at finding tendon tears and strains. It also spots other soft tissue injuries.
Ultrasound is another useful tool. It shows tendon movement and tears in real-time. X-rays aren’t as good for tendons but help rule out bone fractures.
Differential Diagnosis: Ruling Out Other Conditions
Differential diagnosis is important. It means looking at other possible causes for the symptoms. This could be ligament sprains, muscle strains, or other soft tissue injuries. Getting this right helps make sure the treatment is on target.
What to Expect During Evaluation
During the check-up, you’ll get a full assessment. This might include a physical exam, looking at your medical history, and possibly imaging tests. It’s important to share all the details about your symptoms.
A thorough history and physical examination are foundational to making an accurate diagnosis and developing an effective treatment plan.
“
Treatment Options for Torn Tendons
Treating torn tendons can be done in many ways. This includes both non-surgical and surgical methods. The right treatment depends on how bad the tear is, the patient’s health, and how active they are.
Conservative Management Approaches
For mild tendon tears, doctors might suggest non-surgical treatments. This usually includes resting, physical therapy, and pain relief medicines.
- Rest and ice to reduce pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy to maintain or improve range of motion and strength
- Use of orthotics or assistive devices to reduce stress on the tendon
Surgical Interventions
For more serious tendon tears, surgery might be needed. This is true if other treatments don’t work or if the tear really affects the patient’s life. Surgery can repair or rebuild the tendon.
Surgical Techniques:
- Open repair: A traditional surgical approach where the tendon is repaired through a single incision.
- Minimally invasive surgery: Techniques that involve smaller incisions and potentially less tissue damage.
Post-Treatment Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is key, whether you had surgery or not. Programs are made to fit the patient’s needs and the tear’s severity.
Rehabilitation includes:
- Physical therapy exercises to improve strength and flexibility
- Gradual progression of activities to avoid re-injury
- Education on proper techniques for movement and exercise
Recovery Timeline Expectations
How long it takes to recover from a torn tendon varies. It depends on the tear’s severity, the treatment, and the patient’s health and age.
| Treatment Approach | Typical Recovery Time |
| Conservative Management | 6-12 weeks |
| Surgical Repair | 3-6 months |
Following your doctor’s advice and rehabilitation plan is key. It helps in a smooth recovery and lowers the chance of complications.
Managing Strained Tendons
Dealing with strained tendons needs a full plan. This plan includes quick care and long-term healing steps. A strained tendon has tiny tears in the fibers. This can really hurt your daily life and sports skills.
The RICE Protocol
The first step for a strained tendon is the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This is key to lessen pain and swelling. Rest means avoiding things that make it worse. Ice helps with pain and swelling. Compression bandages or sleeves cut down swelling. And Elevation of the limb above heart level also reduces swelling.
Medications for Pain and Inflammation
For pain and swelling, over-the-counter NSAIDs are often used. It’s important to follow the dosage and talk to a doctor. This is true if you have other health issues or take other medicines.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is key for healing strained tendons. A physical therapist will create a plan with exercises to strengthen the tendon. They might also use ultrasound and electrical stimulation to help it heal.
Gradual Return to Activities
Going back to activities slowly is important to avoid injury again. This means slowly increasing how hard and long you do things. It’s also good to warm up and cool down to prevent more harm. For more on tendon injuries, like patellar tendon ruptures, check out trusted health sites.
| Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| RICE Protocol | Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation | Reduces pain and inflammation |
| Medications | NSAIDs for pain and inflammation | Manages pain, reduces inflammation |
| Physical Therapy | Stretching and strengthening exercises | Improves tendon health and function |
| Gradual Return to Activities | Progressive increase in activity | Prevents re-injury, promotes healing |
Preventing Tendon Injuries
To prevent tendon injuries, we need a complete plan. This includes warm-ups, stretches, strengthening exercises, and knowing the signs of tendon problems. By following this plan, we can lower our chances of tendon injuries.
Proper Warm-up and Stretching Techniques
Before any physical activity, a good warm-up is key. It gets the tendons ready by increasing blood flow and muscle temperature. This makes them more flexible and less likely to get hurt. Dynamic stretching, like leg swings and arm circles, is very helpful.
Strengthening Exercises for Tendon Health
Regular strengthening exercises are important for healthy tendons. Eccentric exercises, like calf raises, are great for the Achilles tendon. Shoulder rotations help the rotator cuff tendons. Strengthening muscles around tendons also helps prevent injuries.
Equipment and Technique Considerations
Using the right equipment and proper technique is vital. Good sports gear and learning the right moves can prevent accidents. This helps avoid putting too much strain on tendons.
Recognizing and Addressing Early Warning Signs
Spotting early signs of tendon problems is key. Pain or stiffness are warning signs. If you notice these, reduce activity, use the RICE method, or get professional help.
Conclusion
It’s important to know the difference between torn and strained tendons to treat injuries well. A torn tendon usually happens from sudden injury or long-term wear and tear. This leads to a lot of pain, swelling, and trouble moving.
A strained tendon, on the other hand, comes from doing the same thing over and over. It starts with a little pain and makes it hard to move.
Getting a proper diagnosis is key to figuring out how bad the injury is. Doctors use physical checks and imaging tests to find out. They then choose the right treatment, which can be rest, physical therapy, or surgery.
In short, knowing the signs of tendon injuries and getting help when needed is vital. Understanding the difference between torn and strained tendons helps in managing and recovering from injuries. This way, people can get back to their usual activities without worrying about more harm.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a tendon injury?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and bruising. You might also notice changes in how you move. The pain can start suddenly or slowly, depending on the injury.
How can I differentiate between a torn tendon and a strained tendon?
A torn tendon causes sudden, severe pain and swelling. You might also see a visible deformity. A strained tendon starts with gradual pain, has mild swelling, and limits your movement a bit.
What is the difference between a tendon tear and a sprain?
A tendon tear damages the tendon that connects muscle to bone. A sprain affects the ligament, which connects bone to bone. The symptoms and where the pain is can help tell them apart.
How is an Achilles tendon tear diagnosed?
Doctors use the Thompson test to diagnose an Achilles tendon tear. They squeeze the calf to see if the ankle moves. MRI or ultrasound might also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for a torn tendon?
Treatment can be conservative or surgical, depending on the tear’s severity. Conservative treatment includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Surgery might be needed for more severe tears. After treatment, rehabilitation is key for recovery.
How can I manage a strained tendon?
Managing a strained tendon involves the RICE protocol. You might also take pain and inflammation medications. Physical therapy and a slow return to activities are also important.
What can I do to prevent tendon injuries?
To prevent injuries, warm up and stretch properly. Do exercises to strengthen your tendons. Use the right equipment and watch for early signs of trouble.
When should I seek medical attention for a tendon injury?
Get immediate care for severe pain, swelling, or loss of function. For milder symptoms, schedule a doctor’s appointment.
What diagnostic methods are used to evaluate tendon injuries?
Doctors use physical exams, imaging tests like MRI and ultrasound, and differential diagnosis to diagnose tendon injuries.
How long does it take to recover from a tendon tear?
Recovery time varies based on the tear’s severity and treatment. It can take weeks to months to heal.
Can tendon injuries be treated without surgery?
Yes, some injuries, like certain tears and strains, can be treated without surgery. Methods include RICE and physical therapy.
What is the RICE protocol, and how does it help with tendon injuries?
The RICE protocol includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation. It helps reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation, aiding in tendon healing.
Reference
- MedlinePlus. (2024). Achilles tendon rupture. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000449.htm




































