A hidden pain or swelling in the groin can signal a serious health risk. Liv Hospital, known for its advanced and patient-focused care, sheds light on the top symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the groin. This condition can be lifesaving if promptly addressed.
DVT is a condition where a blood clot forms inside a vein, typically deep within the leg. Recognizing the warning signs is key to prevent serious complications. Symptoms include swelling, redness, and tenderness in the affected area.
Understanding these symptoms is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment. If left untreated, DVT can lead to severe health issues.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize the warning signs of DVT in the groin.
- Understand the risks associated with DVT.
- Know the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Be aware of the symptoms, including swelling and redness.
- Seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis in the Groin Area
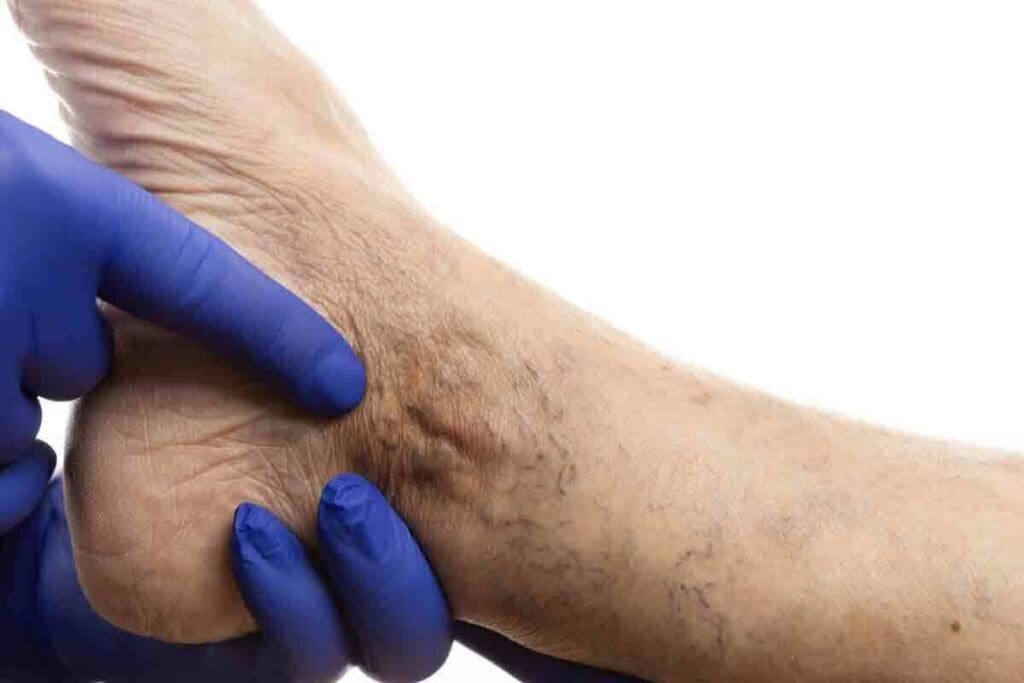
It’s important to know about Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in the groin. DVT is when a blood clot forms in a deep vein. This can lead to serious health problems if not treated quickly.
What is a Groin Blood Clot?
A blood clot in the groin is linked to DVT. It happens when a clot forms in the deep veins of the groin. This can cause serious issues, like a pulmonary embolism.
Clots in the groin can be caused by immobility, trauma, or genetic predispositions. These factors affect how blood clots.
Can You Get a Blood Clot in Your Groin?
Yes, you can get a blood clot in your groin. The groin has many veins, making it a high-risk area for DVT.
Things like long surgeries, cancer, or hormonal changes can raise your risk of getting a clot in the groin.
Prevalence and Impact of DVT in the Groin
DVT can happen in any deep vein, including the groin. While it’s more common in the legs, the groin is not safe. DVT in the groin is less common but very risky.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on DVT Risk |
| Immobility | Prolonged periods of inactivity | High |
| Trauma | Injury to the groin or surrounding areas | Moderate to High |
| Genetic Predisposition | Family history of clotting disorders | High |
DVT in the groin can lead to serious problems like pulmonary embolism or post-thrombotic syndrome. Knowing these risks helps prevent and treat DVT early.
Early Stage Blood Clot in Groin Symptoms: The 7 Warning Signs

Knowing the signs of a groin blood clot is key to avoiding serious problems. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in the groin can show itself in different ways. Spotting these signs early can greatly improve treatment results and patient outcomes.
Pain and Tenderness in the Groin Area
Pain or tenderness in the groin is a main sign of a blood clot. This discomfort can feel like a mild ache or a sharp, throbbing pain. It’s important to remember that this pain can get worse if not treated.
Swelling in the Affected Leg
Swelling in the leg is another common symptom of DVT in the groin. The leg may look bigger because of fluid buildup. It can also feel heavy or tight.
Redness Over the Vein
Redness or discoloration over the vein is a clear sign of DVT. The skin might look red or purplish and feel warm. This is because of the inflammation from the clot.
Warmth in the Affected Area
The area with DVT often feels warmer than the rest. This is because of the inflammation from the blood clot. Patients might notice their affected leg is hotter than the other.
- Pain that gets worse when standing or walking
- A feeling of tightness or heaviness in the leg
- Visible veins
It’s important to know these symptoms and seek medical help if they happen. Early treatment can greatly reduce the risk of DVT complications.
| Symptom | Description |
| Pain and Tenderness | Persistent pain or tenderness in the groin area, ranging from mild to severe. |
| Swelling | Swelling in the affected leg due to fluid accumulation. |
| Redness | Redness or discoloration over the vein where the clot is forming. |
| Warmth | Increased temperature in the affected area due to inflammation. |
Medical experts stress the importance of recognizing these symptoms early. “Prompt medical attention is essential for effective management of DVT and prevention of potentially life-threatening complications,” says a leading vascular specialist.
How Symptoms May Differ: Blood Clot in Groin Female Symptoms
Women need to know how hormonal changes and pregnancy affect DVT symptoms. They are at a higher risk of DVT during pregnancy. Spotting symptoms early is key for managing the condition effectively.
Gender-Specific Presentation of DVT
Studies show DVT symptoms can differ between men and women. Women might feel pain and swelling more than men. Knowing these differences helps doctors diagnose and treat DVT better.
Hormonal Influences on Blood Clot Formation
Hormonal shifts, like those in pregnancy or with hormone therapy, affect blood clotting. Estrogen levels can increase clotting factors, making women more prone to DVT. For more on groin blood clot signs.
Pregnancy-Related Groin Blood Clots
Pregnancy raises DVT risk due to leg pressure and hormonal changes. The risk grows after childbirth, more so after cesarean sections. It’s vital to recognize DVT symptoms in pregnancy to avoid serious complications.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on DVT Risk |
| Hormonal Changes | Increased estrogen levels | Higher risk of blood clot formation |
| Pregnancy | Increased venous pressure and hormonal changes | Significantly increased risk of DVT |
| Postpartum Period | Especially after cesarean delivery | Further increased risk of DVT |
Grasping these factors aids in spotting and managing DVT in women, mainly during pregnancy and after childbirth.
Risk Factors for Developing DVT in the Groin
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in the groin is a serious condition. It can be triggered by various risk factors. Knowing these risk factors is key for prevention and early detection.
The risk of developing DVT in the groin is influenced by lifestyle, medical, and situational factors.
Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors
Lifestyle choices and habits play a big role in DVT risk. Obesity puts extra strain on veins in the groin. Smoking damages blood vessel linings and raises blood pressure.
A sedentary lifestyle also increases DVT risk. Prolonged immobility can lead to blood clots. Regular exercise can help reduce this risk.
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Certain medical conditions raise DVT risk in the groin. For example, cancer and its treatment can affect blood clotting. Heart disease and varicose veins also increase risk.
Conditions that affect blood clotting, like thrombophilia, make DVT more likely.
Situational Risk Factors
Situational factors also play a role in DVT development. Recent surgery or trauma can raise risk due to immobility and blood vessel damage.
Long-distance travel involving sitting for long periods also increases risk. Pregnancy and the postpartum period are high-risk times due to blood clotting and venous pressure changes.
It’s important to recognize these risk factors for DVT in the groin. By understanding and addressing these factors, individuals can take steps to lower their risk.
Is a Blood Clot in the Groin Dangerous? Understanding Complications
A blood clot in the groin is a serious issue that can be deadly if not treated fast. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in this area can cause a lot of harm. It’s important to know the dangers and take action quickly.
Pulmonary Embolism: A Life-Threatening Complication
Pulmonary embolism is a severe complication of DVT. It happens when the blood clot moves to the lungs and blocks blood flow. This can be fatal if not treated right away. Symptoms include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
Post-thrombotic syndrome is another complication of DVT. It causes chronic pain, swelling, and skin discoloration in the affected leg. This happens because of damage to the veins and valves from the blood clot. It can greatly affect a person’s quality of life.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Care
If you have severe pain, swelling, or trouble breathing, seek emergency care. Prompt medical attention can greatly improve your chances and prevent long-term damage. If you think you have a blood clot in your groin, go to the emergency room right away.
Mortality and Morbidity Statistics
DVT and its complications lead to a lot of illness and death worldwide. Pulmonary embolism is a major cause of death in DVT patients. Knowing these risks shows how critical early diagnosis and treatment are.
In conclusion, a blood clot in the groin is a dangerous condition that needs immediate medical care. Recognizing the complications and getting timely treatment can save lives and prevent long-term health problems.
Advanced Diagnostic Approaches for Blood Clots in Groin Area
Diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the groin area is a detailed process. It combines clinical checks and advanced diagnostic tools. Getting the diagnosis right is key to managing the condition and avoiding serious issues.
Initial Clinical Assessment
The first step is a thorough clinical check. Doctors look at the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and risk for DVT. They use tools like the Wells’ score to guess the chance of DVT.
Clinical evaluation is important. It helps decide if more tests are needed. This includes imaging and lab tests.
Noninvasive Imaging Techniques
Noninvasive imaging is a big part of diagnosing DVT. Compression ultrasonography is often the first choice. It uses ultrasound to see the veins and check blood flow.
Other methods like duplex ultrasound and magnetic resonance venography (MRV) might be used too. They help confirm the diagnosis or see how big the clot is.
Laboratory Tests for DVT Confirmation
Laboratory tests are used along with imaging to confirm DVT. The D-dimer test is a key test. It checks for D-dimer, a protein made when a blood clot breaks down.
A negative D-dimer test can help rule out DVT in low-risk patients. But a positive test means more tests are needed.
Diagnosing DVT needs a mix of clinical checks, imaging, and lab tests. Knowing these methods helps doctors make the best decisions for their patients.
Multidisciplinary Approach to DVT Management at Specialized Centers
Specialized centers like Liv Hospital use a multidisciplinary approach to manage Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) effectively. This ensures patients get full care, from start to finish.
Clinical Protocols for DVT
Liv Hospital has robust clinical protocols for DVT management. These protocols are based on the latest research and guidelines. They ensure care is both effective and current.
The hospital’s protocols start with a thorough initial assessment. Then, advanced diagnostic techniques confirm DVT presence. Patients then receive medication and therapies tailored to their needs.
Integrated Care Pathways
Liv Hospital’s DVT management includes integrated care pathways. These pathways ensure patients get seamless care. Different departments and specialists work together for a cohesive treatment plan.
From vascular surgeons to radiologists and rehabilitation specialists, the team at Liv Hospital works together. This integrated approach helps minimize complications and improve outcomes.
Latest Innovations in DVT Treatment
Liv Hospital is committed to staying at the forefront of DVT treatment innovations. The hospital updates its treatment protocols regularly. It incorporates the latest medical technology and pharmaceuticals.
This commitment to innovation means patients at Liv Hospital get the most advanced treatments. This includes new anticoagulant medications and minimally invasive surgical techniques.
Patient Education and Support Systems
A key part of DVT management at Liv Hospital is patient education and support. The hospital believes informed patients can better manage their condition. They can also make lifestyle changes for recovery and prevention.
Liv Hospital provides detailed education programs for patients. These cover topics like DVT nature, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Support systems are also available to help patients with the emotional and physical challenges of DVT.
Conclusion: Recognizing and Responding to Groin Blood Clots
It’s key to spot early signs of blood clots in the groin to avoid serious problems. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in this area can be deadly if not treated. It can cause a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism.
Knowing the warning signs is important. These include pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the groin. If you notice these, get medical help right away. Knowing your risk factors helps you prevent blood clots.
Quick action is needed to manage groin blood clots. Places like Liv Hospital have special programs for this. They use detailed plans and teach patients to help treat and care for them.
In short, knowing the signs of blood clots in the groin and acting fast can save lives. Being informed and proactive can reduce the dangers of DVT in the groin area.
FAQ
What are the early stage blood clot in groin symptoms?
Early symptoms of a blood clot in the groin include pain and tenderness. You might also see swelling, redness, and warmth in the area.
Can you get a blood clot in your groin?
Yes, it’s possible to get a blood clot in the groin. This is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
What are the signs of blood clot in groin?
Signs of a blood clot in the groin include pain and swelling. You might also see redness and warmth. The area can be tender to the touch.
Is a blood clot in the groin dangerous?
Yes, a blood clot in the groin can be very dangerous. If it breaks loose and goes to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism.
What are the risk factors for developing DVT in the groin?
Several factors can increase your risk of DVT in the groin. These include lifestyle choices, medical conditions, and certain situations. Prolonged sitting, surgery, and hormonal changes are examples.
How do DVT symptoms manifest differently in women?
Women may experience different symptoms of DVT. Hormonal changes can affect blood clot formation. Pregnancy and the postpartum period also increase the risk.
What is the treatment for DVT in the groin?
Treatment for DVT in the groin includes medications and interventional procedures. Lifestyle changes and education are also important.
Can DVT be prevented?
While some risks can’t be avoided, there are steps you can take. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged sitting can help prevent DVT.
What are the complications of untreated DVT?
Untreated DVT can lead to serious complications. These include pulmonary embolism and post-thrombotic syndrome.
How is DVT diagnosed?
DVT is diagnosed through a combination of clinical assessment and imaging techniques. Laboratory tests also play a role.
What is the role of patient education in DVT management?
Patient education is key in managing DVT. It empowers patients to recognize symptoms and follow treatment plans. It also helps them make lifestyle changes to reduce complications.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2024). Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism (blood clots). CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/facts.html




































