Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
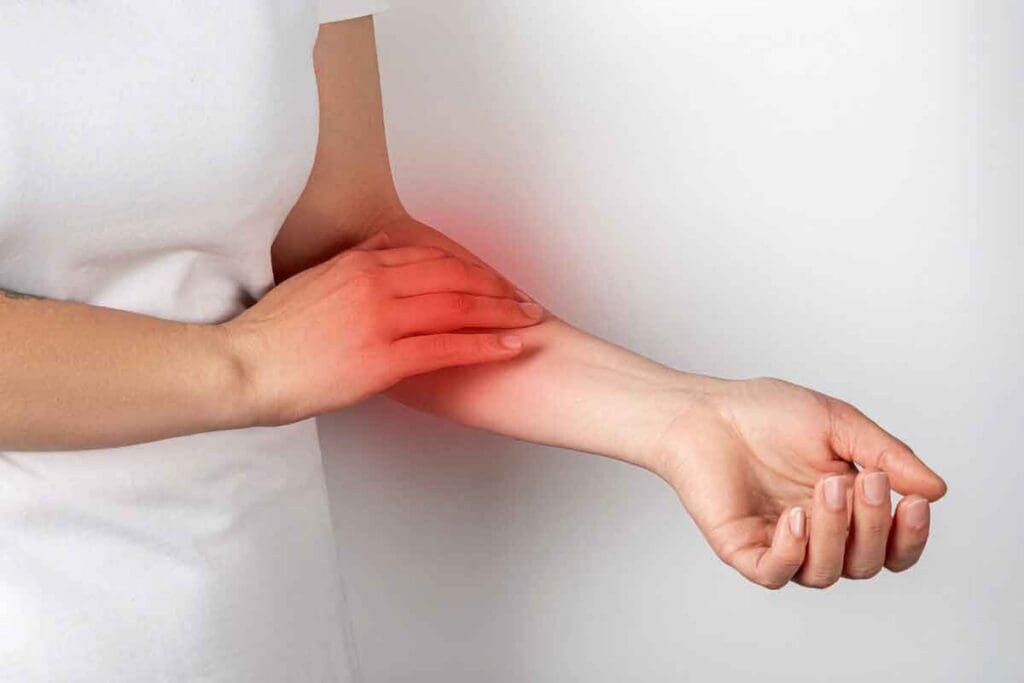
Spotting blood clots in the arm can be tricky. They often look like bruises. Knowing how to tell them apart is key to getting help fast.
Liv Hospital’s doctors say blood clots look reddish, swollen, and warm. They feel rope-like. Bruises, on the other hand, start purple and turn yellow. They stay flat. Knowing these signs helps you get the right treatment.
It’s important to know what causes blood clots and bruises in the arm. These are two different issues that can happen in the arm. Each has its own reasons and signs.
Blood clots in the arm can come from many things. These include being stuck in one place for too long, some medicines, smoking, or health problems. Is when a blood clot forms in deep veins, often in the arms or legs.
Bruises happen when small blood vessels near the skin get damaged. This lets blood spill into the tissues around it. This can happen from hitting the arm, falling, or even small injuries.
As a bruise heals, it goes through color changes. It starts as red or purple, then turns blue or black, green or yellow, and ends as yellow or brown before it fades away.
Being able to spot blood clots and bruises is key. Bruises are usually not serious and heal by themselves. But blood clots can be very dangerous if they move to the lungs or brain.
Knowing how to tell the difference between a blood clot and a bruise is important. This helps people know when to get medical help. The main differences are in color, swelling, and texture, which we’ll look at next.

Blood clots have unique visual signs that set them apart from bruises. Knowing these signs is key to early detection and treatment.
Blood clots show up as reddish or purplish spots on the skin, often with swelling. The color stays the same, unlike bruises that change color as they heal. The affected area may feel warm to the touch because of inflammation.
The skin over the clot might look normal or slightly off. Look for swelling or tenderness as well.
A blood clot can make the area feel firm or rope-like. This texture is due to the clot itself, which can be felt in some cases. The area may also be tender.
The texture can change based on the clot’s location and size. For example, a clot near the skin’s surface is easier to feel than one deeper.
Blood clots don’t change color much over time. But, he area around it may swell or get more inflamed. Watching these changes is key to understanding how serious the condition is.
In some cases, the clot may hurt more as it gets worse. If symptoms get worse or new ones appear, seek medical help.
It’s important to know how to tell blood clots and bruises apart. Both can hurt and change how your arm looks. But they look different in many ways.
Bruises change color as they heal. They start red, then turn purple, green, and yellow before fading. Blood clots usually stay red or dark.
Key Observation: If an area changes color over days, it’s likely a bruise. If it stays red or dark, it might be a blood clot.
Blood clots often cause swelling, which can spread. Bruises might swell a bit, but not as much as blood clots.
Notable: Big swelling, warmth, and pain point to a blood clot.
The skin’s feel can tell you a lot. Blood clots make the skin warm or hot. Bruises usually don’t.
Blood clots make the skin warmer because of inflammation. Bruises don’t usually change the skin’s temperature.
The next 8 differences will help you tell blood clots from bruises. They show how each looks different.
By looking at these 12 differences, you can tell if you have a blood clot or a bruise. This helps you know what to do next and when to see a doctor.
Blood clots in the arm can show up in different ways, depending on where they are. They can be in the upper arm, forearm, or hand. Knowing these differences is key to the right diagnosis and treatment.
Blood clots in the upper arm can cause a lot of swelling and pain. The skin might look red or have a different color. It can also feel warm to the touch.
In some cases, you might see a lump or a cord-like structure under the skin.
Forearm blood clots have similar symptoms to those in the upper arm. These include swelling, pain, and redness. But because the forearm is smaller, these symptoms can seem more intense.
Blood clots on the top of the hand are easy to spot because of the thin skin there. They look like a visible lump or swelling. The skin might also be red or purple.
It’s important to tell these clots apart from other conditions that might look similar.
| Location | Common Symptoms | Visual Characteristics |
| Upper Arm | Swelling, pain, warmth | Redness, visible lump |
| Forearm | Pain, swelling, redness | Swollen area, red or discolored skin |
| Hand | Visible lump, swelling, pain | Red or purple discoloration, swelling |
It’s important to know how blood clots look in different parts of the arm. This helps with early detection and treatment. If you think you have a blood clot, get medical help right away.
It’s important to know about the different blood clots that can happen in the arms. This knowledge helps in spotting and treating them early. Blood clots in the arms come in various forms, each with its own risks and symptoms.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) forms in the deep veins of the arm. It’s less common than in the legs, but it s serious. DVT in the arm can cause swelling, pain, and discoloration. The risk factors include:
Superficial thrombophlebitis is a blood clot in a vein near the skin. It can cause pain, redness, and swelling along the vein. Though less severe than DVT, it can be uncomfortable and may lead to complications.
Blood clots in the arm can lead to embolism. If a clot breaks off, it can travel and block another part of the body, like the lungs. This is a serious risk that needs quick medical attention if you think you have a blood clot.
The main types of blood clots in the arms and their characteristics are:
| Type of Clot | Location | Common Symptoms |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Deep veins | Swelling, pain, discoloration |
| Superficial Thrombophlebitis | Superficial veins | Pain, redness, swelling along the vein |
Many things can make blood clots more likely in the arms. This includes health conditions and lifestyle choices. Knowing these risks helps find who’s at higher risk and how to prevent it.
Some health issues can raise the chance of blood clots in the arms. These include:
| Medical Condition | Risk Level for Arm Blood Clots | Common Symptoms |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis | High | Swelling, pain, and warmth in the affected arm |
| Cancer | Moderate to High | Varies, but can include swelling or pain in the arm |
| Heart Disease | Moderate | May not directly cause arm symptoms, but can lead to clot formation |
Our lifestyle choices also affect blood clot risk in the arms. These include:
Recent medical procedures can also raise blood clot risk in the arms. This includes:
Knowing these risk factors helps us and healthcare providers prevent blood clots in the arms. For those at higher risk, watching for clot signs and getting medical help quickly is key.
If you think you have a blood clot in your arm, it’s important to know the signs that mean you need to see a doctor right away. A blood clot in the arm can be serious and may cause big health problems if not treated quickly.
There are several symptoms that mean you should get medical help fast. These include:
Some blood clots may not show symptoms. It’s key to watch for changes in your body and get medical help if you’re worried.
Not treating blood clots can lead to serious problems, including:
Seeing a doctor quickly can lower the risk of these problems.
When you go to the doctor with suspected arm blood clots, you’ll get a detailed check-up. This might include:
Your doctor will then create a treatment plan just for you. This might include medicines, compression stockings, or other treatments.
Healthcare professionals use different tests to find out if there’s a blood clot in the arm. These tests help tell if it’s a clot or something else, like a bruise. They also guide the treatment needed.
Imaging tests are key in finding arm blood clots. The main ones are:
Blood tests also help find clotting disorders that might cause blood clots. The main tests are:
It’s important to tell clots from bruises to get the right treatment. Doctors use:
By using these methods, doctors can accurately find arm blood clots. Then, they can plan the best treatment.
Early detection and treatment of blood clots in the arm are key to avoiding serious problems. Knowing the difference between blood clots and bruises is vital for quick action.
Understanding blood clot pictures in the arm helps people spot clots early. This knowledge lets them get medical help fast. Blood clot pictures offer important clues for timely treatment.
Knowing the risk factors and warning signs of blood clots is important. If symptoms don’t go away or get worse, seeing a doctor is essential. Doctors can give the right diagnosis and treatment, helping patients get better.
Being aware of arm health can prevent and manage blood clots. Early detection and treatment are critical. They help protect health and prevent long-term damage.
Symptoms include swelling, pain, and tenderness. The area may also feel warm or red. Sometimes, you might not notice any symptoms at all.
Blood clots are firm and localized. Bruises are softer and spread out. They also change color over time.
Blood clots can be dangerous. They might travel to the lungs, causing serious problems. Other risks include post-thrombotic syndrome and more clots forming.
No, you need medical help for blood clots. Treatment often includes medicine. Sometimes, more serious procedures are needed.
Tests include ultrasound and venography. Blood tests also check for clotting disorders. A doctor will choose the best test for you.
Yes, staying healthy helps. Keep a good weight, drink water, and exercise. Avoid sitting too long.
Yes, conditions like cancer and heart disease raise the risk. So do clotting disorders.
Look out for sudden pain, swelling, or trouble moving. Chest pain or shortness of breath are also signs.
Superficial thrombophlebitis has inflammation and pain in a surface vein. Deep vein thrombosis causes more swelling and pain.
Yes, trauma, surgery, immobility, cancer, and genetic disorders are risks.
A doctor will examine you, take your medical history, and might order tests. They’ll figure out if you have a clot and what to do next.
Yes, clots can come back if risks aren’t managed. You might need ongoing care to prevent this.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!