When you see bleeding under the skin, it’s important to know why and what to do. At Liv Hospital, we focus on your health and safety. We make sure to spot subdermal bleeding early.
Subdermal bleeding, or subcutaneous hemorrhage, happens when blood leaks under the skin. It can be due to injury, blood issues, or side effects from medicines. We’ll look at the usual reasons and signs, so you can get help fast.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes of subdermal bleeding is key to quick medical help.
- It can come from injury, blood problems, or medication side effects.
- Knowing the signs of subdermal bleeding helps you get the right care.
- Liv Hospital is all about top-notch care for subdermal bleeding patients.
- Knowing when to get medical help can save your life.
What Is Subdermal Bleeding? Understanding Blood Under the Skin
Subdermal bleeding happens when blood leaks into the tissues under the skin. It can come from many causes. This bleeding can cause visible signs like bruising.
“Seeing blood under the skin can be scary. But knowing what it is and why it happens can help you get the right care,” says a top dermatologist.
Medical Terminology: Subcutaneous and Intradermal Hemorrhage
Doctors call subdermal bleeding subcutaneous hemorrhage or intradermal hemorrhage. It depends on where the bleeding is. Subcutaneous hemorrhage occurs when blood gets into the fat layer under the skin. Intradermal hemorrhage is when it happens in the skin layer just under the outermost layer.
Knowing these terms helps doctors diagnose and treat the problem correctly. Intradermal hemorrhage shows up as small red or purple spots on the skin, called petechiae or purpura.
Different Types of Subdermal Bleeding
Subdermal bleeding can show up in different ways:
- Bruises: These happen when blood vessels get damaged, letting blood leak into the tissue.
- Petechiae: These are tiny spots on the skin from small hemorrhages from broken blood vessels.
- Purpura: These are bigger purple spots on the skin, showing more serious bleeding under the skin.
Each type of bleeding has its own reasons and health effects. Knowing the differences helps figure out the cause and what to do next.
Physical Trauma: The Primary Cause of Bleeding Under the Skin
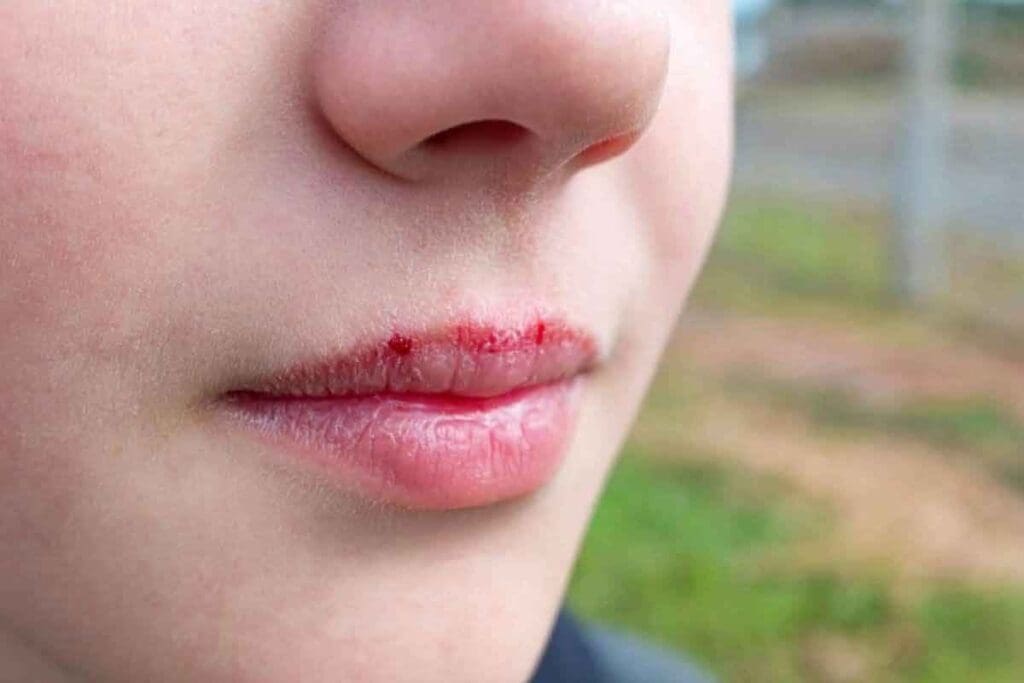

Physical trauma is a main reason for bleeding under the skin. This can happen from accidents, injuries, or surgeries.
Impact Injuries and Contusions
Impact injuries happen when we get hit hard. They can cause bruises or contusions. These injuries can break blood vessels, leading to bleeding under the skin.
For example, falling or getting hurt in sports can cause big bruises. This is more likely in areas with loose skin or where the hit is direct.
Common areas affected by impact injuries include:
- Limbs, such as arms and legs
- Face, especially around the eyes and cheekbones
- Torso, including the abdomen and chest
Crush Injuries
Crush injuries are very serious. They happen when something presses hard on a body part, damaging tissues and blood vessels. This can cause a lot of bleeding under the skin and needs quick medical help.
Crush injuries can come from:
- Industrial accidents with heavy machinery
- Car crashes
- Natural disasters like earthquakes or building collapses
Surgical Procedures and Post-Operative Bleeding
Surgeries can also cause bleeding under the skin. This bleeding can happen for many reasons, like the surgery’s complexity or the patient’s health.
“Surgical bleeding can be a significant concern, especially in patients with pre-existing bleeding disorders or those on anticoagulant therapy.”
Doctors and healthcare teams work hard to prevent bleeding after surgery. They choose patients carefully, use precise techniques, and watch them closely after surgery.
Blood and Clotting Disorders That Lead to Subdermal Bleeding
Blood and clotting disorders can cause subdermal bleeding, showing up as bruises or purpura. These issues make it hard for the body to stop bleeding, leading to blood under the skin. We’ll look at several disorders that cause this problem.
Hemophilia and Von Willebrand Disease
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that makes it hard for blood to clot, causing prolonged bleeding. Von Willebrand disease affects blood clotting due to a lack or mutation of the Von Willebrand factor. This protein is key to clotting. Both can lead to bleeding under the skin.
Key characteristics of these disorders include:
| Disease | Primary Effect | Common Symptoms |
| Hemophilia | Impaired clotting due to a lack of clotting factors | Prolonged bleeding, joint pain, muscle weakness |
| Von Willebrand Disease | Deficiency or mutation in Von Willebrand factor | Easy bruising, heavy menstrual periods, nosebleeds |
Thrombocytopenia and Platelet Dysfunction
Thrombocytopenia is when you have too few platelets, caused by many things like bone marrow issues or autoimmune diseases. Platelet dysfunction happens when platelets don’t work right, even if there’s enough of them. Both can make clotting hard and lead to bleeding under the skin.
Leukemia and Other Blood Cancers
Leukemia is a blood cancer that messes with the bone marrow, making abnormal white blood cells. This can cause low platelet counts and other clotting problems, raising the risk of bleeding under the skin. Other blood cancers, like lymphoma, can also mess with clotting.
In conclusion, many blood and clotting disorders can cause bleeding under the skin. Knowing about these conditions is key to diagnosing and treating patients with this issue.
Medication-Related Causes of Bleeding Through Skin
Certain medications can increase the risk of bleeding under the skin. It’s important to know how they affect the body. We’ll look at how different medications can cause bleeding, focusing on their effects and side effects.
Blood Thinners and Anticoagulants
Blood thinners and anticoagulants prevent blood clots. They are key in preventing strokes and other clot-related issues. But, they can also raise the risk of bleeding, including under the skin.
Examples include warfarin, heparin, and newer drugs like dabigatran and rivaroxaban. The risk of bleeding is higher when these drugs are taken with other medications or with certain health conditions.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are used for pain and inflammation. But they can also make it harder for blood to clot. This increases the risk of bleeding.
Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin. While safe when used correctly, long-term or high-dose use can raise the risk of stomach bleeding and subdermal bleeding.
Corticosteroids and Chemotherapy Agents
Corticosteroids reduce inflammation but can make the skin more prone to bruising and bleeding. Long-term use can cause skin thinning, making blood vessels more fragile.
Chemotherapy agents can lower platelet counts, leading to thrombocytopenia. This condition significantly increases the risk of bleeding.
It’s vital to understand the side effects of these medications to manage bleeding risks. Patients should be closely watched by their healthcare providers. Any unusual bleeding should be reported right away.
Vascular Conditions Causing Lines of Blood Under Skin
We look into how certain vascular conditions lead to bleeding under the skin. These conditions affect our blood vessels’ health. They can cause bleeding just beneath the skin.
Vasculitis and Blood Vessel Inflammation
Vasculitis is when blood vessels get inflamed. This can damage the walls of the vessels, causing bleeding under the skin. It can happen due to infections, autoimmune disorders, or allergies.
When vasculitis strikes, it weakens blood vessels. This can lead to subdermal hemorrhages. Vasculitis symptoms include skin lesions and purpura. Doctors use clinical exams, lab tests, and biopsies to diagnose it.
Venous Insufficiency and Varicose Veins
Venous insufficiency happens when veins can’t return blood to the heart properly. This is often due to faulty valves. It causes veins to become varicose, or twisted and enlarged.
Varicose veins can lead to subdermal bleeding because of the increased pressure. Symptoms include visible veins, swelling, and skin discoloration.
Capillary Fragility and Leakage
Capillary fragility means capillaries are more likely to break, causing small hemorrhages under the skin. It can be caused by vitamin deficiencies, aging, or certain medications. Fragile capillaries are more likely to leak, leading to subdermal bleeding.
The impact of capillary fragility shows up as petechiae. These are small, pinpoint spots on the skin from minor hemorrhages. To manage capillary fragility, you need to address the cause and strengthen the capillaries.
Infections and Inflammatory Disorders Leading to Bleeding Lesions
We look at how infections and inflammatory conditions cause bleeding lesions. These conditions include bacterial infections like sepsis and meningococcemia. They also include viral hemorrhagic fevers and autoimmune diseases like lupus.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are a major cause of subdermal bleeding. Sepsis is a severe condition that can damage the body’s tissues. It leads to bleeding under the skin because it uses up clotting factors and platelets.
Meningococcemia, caused by Neisseria meningitidis, is another serious infection. It can cause bleeding lesions. The rash from this infection can turn into purpura and ecchymosis.
- Sepsis can cause DIC, leading to widespread bleeding.
- Meningococcemia can result in purpura fulminans, a condition with severe bleeding under the skin.
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are diseases caused by viruses. These viruses, like Ebola, Marburg, and Lassa fever, damage blood vessels. This leads to increased vascular permeability and bleeding.
VHFs are known for:
- Hemorrhage from various sites, including the skin.
- High mortality rates in severe cases.
Autoimmune Conditions Like Lupus
Autoimmune diseases, such as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), can cause subdermal bleeding. SLE is caused by autoantibodies that target various tissues, including the skin and blood vessels.
Key features of lupus-related bleeding include:
- Vasculitis leading to purpura and other bleeding manifestations.
- Thrombocytopenia which can contribute to bleeding tendencies.
In conclusion, infections and inflammatory disorders are key causes of subdermal bleeding. Understanding these conditions is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Age-Related and Genetic Factors in Skin Internal Bleeding
Genetic and age-related factors play a big role in skin internal bleeding. As we get older, our skin changes, making it more likely to bruise and bleed. Genetic disorders can also weaken blood vessels and skin.
Senile Purpura in Older Adults
Senile purpura is common in older adults. It shows up as purple spots on the skin from minor injuries. This happens because aging skin loses its fatty layer, making blood vessels more fragile. Older adults are more likely to get senile purpura because their skin lacks collagen and elastin, which are important for skin strength and elasticity.
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and Connective Tissue Disorders
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a group of genetic disorders that affect connective tissue. It makes skin extremely flexible and fragile. People with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are more likely to experience subdermal bleeding because their blood vessels and skin are weakened.
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is a genetic disorder that causes abnormal blood vessels. This can lead to bleeding under the skin. HHT can also cause telangiectasias, small, dilated blood vessels near the skin’s surface or mucous membranes, which are prone to bleeding.
Scurvy and Nutritional Deficiencies
Scurvy is caused by a lack of vitamin C and can lead to bleeding gums, joint pain, and subdermal bleeding. Vitamin C is key to collagen synthesis. Without enough vitamin C, blood vessels and skin can weaken, making them more likely to be damaged.
| Condition | Description | Impact on Skin and Blood Vessels |
| Senile Purpura | Purple spots on the skin due to minor trauma in older adults. | Loss of fatty layer, making blood vessels more visible and fragile. |
| Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome | A genetic disorder affecting connective tissue. | Extremely flexible and fragile skin, weakened blood vessels. |
| Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia | A genetic disorder causing abnormal blood vessel formation. | Formation of telangiectasias prone to bleeding. |
| Scurvy | Nutritional deficiency due to a lack of vitamin C. | Weakened blood vessels and skin due to impaired collagen synthesis. |
Recognizing Key Symptoms of Bleeding Under the Skin
Spotting signs of subdermal bleeding is key to fixing the problem and avoiding worse issues. We’ll show you the main symptoms to watch for. This will help you tell normal from abnormal bruising.
Normal vs. Abnormal Patterns of Bruising with Dots
Bruising is common when there’s bleeding under the skin. But not all bruises are a worry. Normal bruises happen after an injury and go away in a few weeks. Yet, odd bruises might pop up without reason, be bigger, or more common. They might also come with petechiae (small dots) or purpura (larger patches).
Let’s look at the differences between normal and odd bruising:
| Characteristics | Normal Bruising | Abnormal Bruising |
| Cause | Typically follows a known injury | May appear without an apparent cause |
| Size and Frequency | Usually small and occasional | May be larger or more frequent |
| Associated Symptoms | Rarely accompanied by other symptoms | May be accompanied by petechiae or purpura |
| Resolution | Resolves on its own within a few weeks | May persist or worsen over time |
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Some bleeding under the skin is minor, but some signs mean you need to see a doctor fast. These include:
- Severe or unexplained bruising
- Bleeding that doesn’t stop after applying pressure
- Petechiae or purpura without an apparent cause
- Bleeding under the skin accompanied by fever, fatigue, or other systemic symptoms
- Bruising or bleeding in individuals taking anticoagulant medications
If you or someone you know has these symptoms, get medical help right away.
Bleeding Under Skin in Specific Body Areas
Bleeding under the skin can happen anywhere, like the hands, face, or other spots. The importance of these signs can change based on where they are and other details. For example, bleeding on the hands or face is more noticeable and might be more serious because of how visible these areas are.
Knowing the unique traits and possible reasons for bleeding in different spots can help find the cause and the right treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Subdermal Hemorrhage
To diagnose subdermal hemorrhage, a detailed approach is needed. This includes medical checks and lab tests. We’ll cover how to diagnose and treat subdermal bleeding, from the first steps to medical treatments.
Medical Assessment and Laboratory Tests
Getting a thorough medical check is key for diagnosing subdermal hemorrhage. This means a physical exam, looking at your medical history, and lab tests to find the cause of the bleeding.
Lab tests might include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check for blood disorders
- Coagulation studies to assess clotting function
- Platelet count to diagnose thrombocytopenia
- Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scans, to evaluate the extent of bleeding
| Laboratory Test | Purpose |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | To check for blood disorders |
| Coagulation studies | To assess clotting function |
| Platelet count | To diagnose thrombocytopenia |
Home Remedies for Minor Bruising
For minor subdermal bleeding, home remedies can help. These include:
- Applying ice to reduce swelling
- Elevating the affected area to reduce blood flow
- Using compression bandages to apply pressure
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers to manage pain
Medical Interventions for Serious Cases
For serious subdermal hemorrhage, medical help is needed. This can include:
- Administration of clotting factors or platelets to promote clotting
- Surgical drainage of the hematoma
- Monitoring for complications, such as infection or organ damage
It’s vital to seek medical help if symptoms don’t get better or get worse. Quick diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes for those with subdermal hemorrhage.
Conclusion: When to Seek Medical Help for Bleeding Under the Skin
Knowing when to get medical help for bleeding under the skin is key. We’ve talked about why it happens, like injuries, blood problems, and infections. Age can also play a role.
If you see a lot of bleeding under your skin, or it doesn’t stop, see a doctor. Leg bleeding that hurts, swells, or makes it hard to move is urgent. Getting medical help fast is vital, even if it’s just a little bleeding.
Getting help early can make a big difference. Watch your body for changes and don’t wait to see a doctor if you see bleeding. Knowing the signs helps you stay healthy.
FAQ
What is subdermal bleeding?
Subdermal bleeding happens when blood vessels get damaged. This lets blood leak into the tissue around it. You might see bruising, swelling, or other signs.
What are the common causes of bleeding under the skin?
Many things can cause subdermal bleeding. This includes physical injuries, blood disorders, and some medicines. Also, vascular conditions, infections, and inflammatory diseases can play a part. Age and genetics also matter.
What is the difference between subcutaneous and intradermal hemorrhage?
Subcutaneous hemorrhage is bleeding into the fat layer under the skin. Intradermal hemorrhage is bleeding in the skin itself. Both can make the skin look bruised or discolored.
What are petechiae, purpura, and bruises?
Petechiae are small spots on the skin from minor bleeding. Purpura are larger patches of purple or red from bleeding under the skin. Bruises are skin discoloration from blood leakage after injury.
Can certain medications cause bleeding under the skin?
Yes, some medicines can lead to subdermal bleeding. This includes blood thinners, anticoagulants, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and chemotherapy agents. They affect how the body clots blood.
How do blood and clotting disorders lead to subdermal bleeding?
Disorders like hemophilia and thrombocytopenia can stop blood from clotting. This leads to bleeding under the skin.
What are the symptoms of subdermal bleeding that require medical attention?
You should see a doctor for unusual bruising, bleeding that won’t stop, severe pain, swelling, or signs of infection. Also, bleeding in sensitive areas like the face or eyes needs immediate care.
How is subdermal bleeding diagnosed?
Doctors use a medical check-up, blood tests, and sometimes imaging to find the cause of bleeding.
What are the treatment options for subdermal bleeding?
Treatment varies based on the cause and severity. For minor bruising, home remedies might help. But serious cases might need medication changes or procedures.
Can age-related factors contribute to subdermal bleeding?
Yes, getting older can increase the risk of bleeding under the skin. This is because skin elasticity and blood vessel strength decrease with age.
Are there any genetic conditions that can cause bleeding under the skin?
Yes, conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can affect blood vessels. This increases the risk of subdermal bleeding.
How can I prevent bleeding under the skin?
To prevent subdermal bleeding, manage your health conditions, avoid certain medicines, and live a healthy lifestyle. Also, take steps to avoid injuries.
When should I seek medical help for bleeding under the skin?
Seek medical help for unusual bruising, severe bleeding, or signs of infection. Also, if you’re worried about your symptoms or health conditions.
References:
- Dean, L. (2005). The ABO blood group – Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens. National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2267/



































