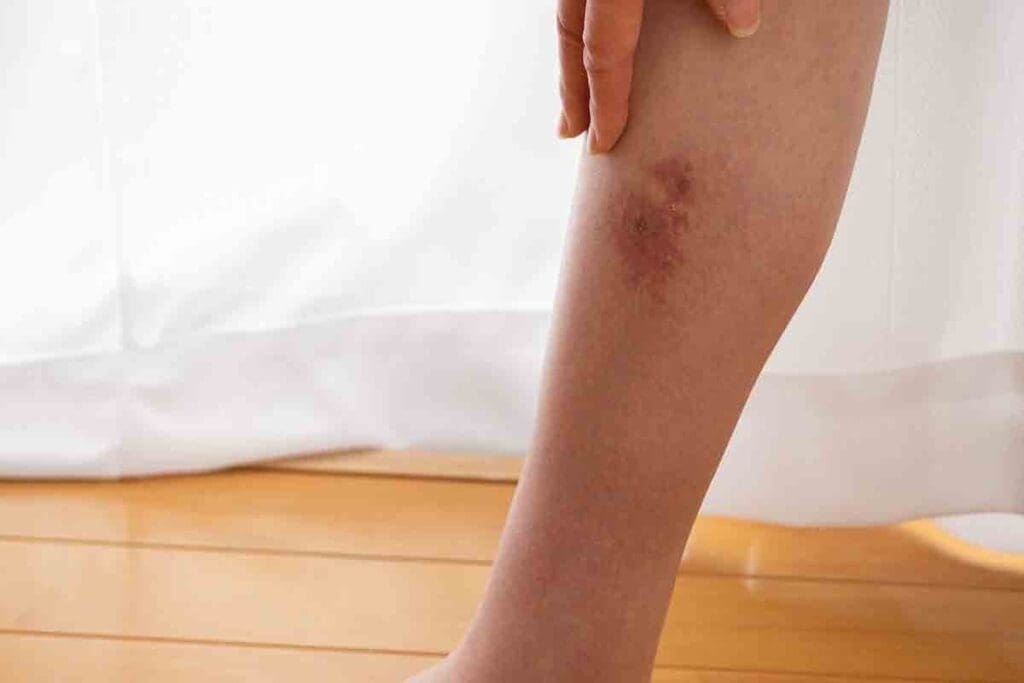
Discovering a blood clot can be frightening, and many people ask, “do blood clots resolve on their own?” The answer depends on your body’s healing process and current medical science.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), up to 900,000 Americans develop venous thromboembolism (VTE) each year, leading to around 100,000 deaths from pulmonary embolism (PE). In some cases, the body can clear smaller clots on its own through fibrinolysis and immune cell activity — but not all clots resolve naturally.
At Liv Hospital, we provide safe, patient-focused care. Our experts follow international standards to manage blood clot risks and guide you with clarity, ensuring peace of mind and better health outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT), can sometimes resolve on their own.
- The body’s natural processes, such as fibrinolysis, play a key role in clearing clots.
- Venous thromboembolism (VTE) affects up to 900,000 Americans annually.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious complication of untreated blood clots.
- Patient-centered care is vital for managing blood clot risks.
Understanding Blood Clots: Types and Formation
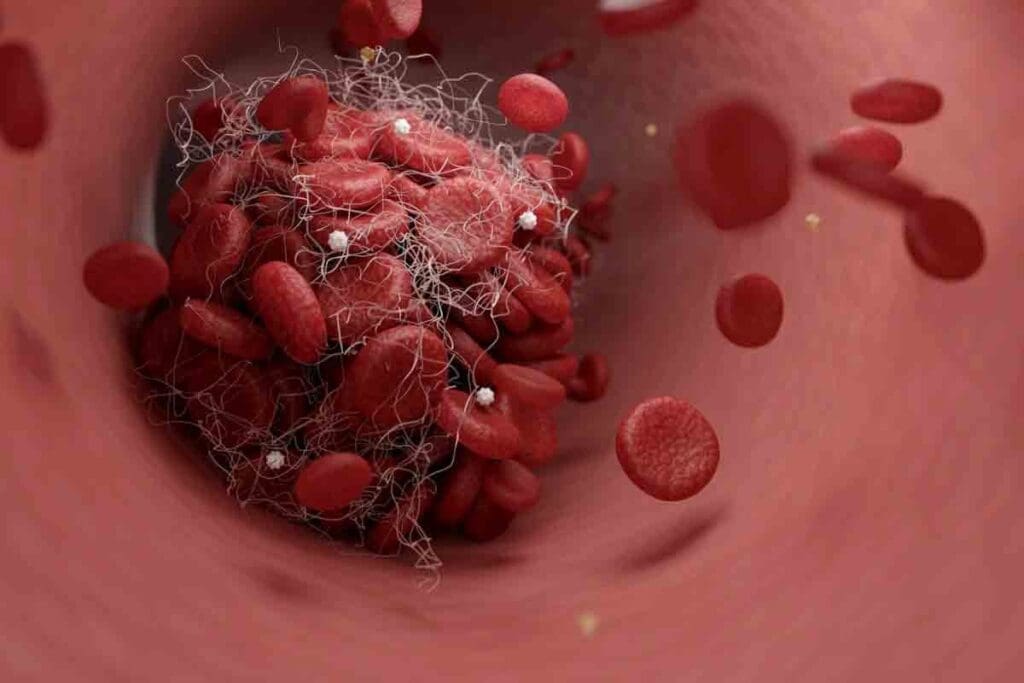
It’s important to know about blood clots to understand their risks. Blood clots are like gel-like clumps of blood that form when we bleed. They help stop too much blood loss. But, if they don’t dissolve, they can cause serious health problems.
What Is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot is when blood turns from liquid to a gel-like or solid state. This happens naturally to stop bleeding when a blood vessel is hurt. But, clots can also form inside blood vessels without injury, leading to serious health issues.
Blood clots can be found in different parts of the body. Arterial clots in arteries can cause heart attacks and strokes. Venous clots in veins can lead to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism if they travel to the lungs.
Common Types of Blood Clots
There are many types of blood clots, each with its own risks. Thrombi form inside blood vessels, while emboli are clots that travel through the bloodstream. Knowing the difference is key to the right treatment.
- Thrombi: Clots that form within a blood vessel.
- Emboli: Clots that break loose and travel through the bloodstream.
The Clotting Process Explained
The clotting process involves many steps. It starts with platelets and the coagulation cascade, leading to fibrin, a protein that makes the clot stronger. The body has natural ways to dissolve clots, like fibrinolysis and collagenolysis, thanks to immune cells.
The immune system is key in breaking down clots. Cells like neutrophils and macrophages help clear away clot debris. Knowing how clots form and dissolve is important for understanding their risks and how they can resolve on their own.
Do Blood Clots Resolve on Their Own?
Blood clots can dissolve on their own, but it depends on several things. These include how big the clot is and where it is. The body has natural ways to break down clots, but it’s a delicate process.
Natural Resolution Mechanisms
The body can dissolve blood clots through a process called fibrinolysis. This process uses an enzyme called plasmin to break down fibrin, a key clot component. Fibrinolysis is a critical natural mechanism that helps restore normal blood flow.
“The fibrinolytic system is a highly regulated process that ensures the removal of blood clots once they have served their purpose.”
Factors Affecting Spontaneous Resolution
Many things can affect how well a clot dissolves on its own. These include:
- Clot size: Larger clots are harder for the body to dissolve.
- Clot location: Clots in deep veins can be harder to dissolve naturally.
- Individual health factors: Your overall health, any other health issues, and age can also play a role.
Success Rates of Natural Resolution
About 20% of calf deep vein thrombosis (DVT) cases might dissolve on their own within days to weeks. But, how well a clot dissolves naturally can vary a lot. This depends on the factors mentioned earlier.
| Clot Location | Spontaneous Resolution Rate |
| Calf DVT | 20% |
| Proximal DVT | 5-10% |
| Pulmonary Embolism | Rare |
Knowing these factors and success rates is key to figuring out the best treatment for blood clots.
The Biology of Clot Dissolution
Clot dissolution is a complex process the body uses to fix blood flow and tissue health. It involves several key steps to break down blood clots.
Fibrinolysis: Breaking Down the Clot
Fibrinolysis is the main way the body breaks down blood clots. It turns plasminogen into plasmin, an enzyme that breaks down fibrin in clots. Fibrinolysis is key to restoring normal blood flow and preventing tissue damage. For more on how blood clots dissolve, check out this resource.
Collagenolysis and Tissue Remodeling
Collagenolysis is also important in clot dissolution. It breaks down collagen, a protein that supports tissues. As collagen is broken down, tissues are remodeled, restoring normal function. This process is vital for tissue health and preventing chronic issues.
Timeline for Natural Resolution
The time it takes for blood clots to dissolve naturally varies. It depends on the clot’s size, location, and individual health. Smaller clots dissolve faster than larger ones. Knowing what affects clot resolution helps manage the condition better and when to see a doctor.
While some blood clots can dissolve naturally, others need medical help. The chance of a blood clot dissolving naturally depends on health conditions. In some cases, blood clots can disappear on their own without harm. But, it’s important to watch symptoms and get medical help if they get worse or don’t go away.
Immune System’s Role in Clot Resolution
The immune system is key in breaking down blood clots. This is important for keeping our blood vessels healthy. When a clot forms, the immune system springs into action. It uses different cells to dissolve the clot and get blood flowing again.
Neutrophils: First Responders to Clots
Neutrophils are the first immune cells to tackle a blood clot. They are vital in starting the process of breaking down the clot. Neutrophils release enzymes that help dissolve the clot, which is a critical step.
Macrophages and Debris Clearance
After neutrophils start, macrophages join the fight. Macrophages clean up the mess left by the clot. They eat and digest dead cells and other debris. This is important for fixing damaged tissue.
Research shows macrophages also help break down clots. They make factors that aid in dissolving the clot.
“Immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, are not just passive bystanders in the process of clot resolution; they actively contribute to the breakdown and clearance of clots.”
A study mentioned in the article here shows how important immune cells are. They can switch from being enemies to helpers in dissolving blood clots.
Cellular Interactions During Clot Breakdown
Breaking down a blood clot is a complex task. It involves many immune cells working together. Neutrophils and macrophages team up to dissolve the clot and clear away debris. This teamwork is essential for effective clot resolution, ensuring debris doesn’t build up and tissue can heal.
In summary, the immune system is vital in dissolving blood clots. Neutrophils, macrophages, and other cells work together. Understanding this can help us see how clots can dissolve naturally, answering the question of whether blood clots can go away on their own.
Risks of Leaving Blood Clots Untreated
Ignoring blood clots can lead to serious and life-threatening conditions. Blood clots, if not treated, can cause many problems. These problems can affect a person’s quality of life and health.
Potential Complications
Untreated blood clots can cause several complications. One is pulmonary embolism (PE), where the clot travels to the lungs. Another is post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), causing chronic pain, swelling, and skin discoloration.
The risk of these complications depends on the clot’s location and size. For example, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in the deep veins, usually in the legs. If not treated, DVT can lead to PE, a serious condition.
Life-Threatening Consequences
Leaving blood clots untreated can lead to life-threatening consequences. Pulmonary embolism is a critical condition that needs immediate medical attention. The severity of PE can range from mild to severe, with severe being potentially fatal.
| Condition | Description | Risks if Untreated |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | A blood clot in the deep veins, usually in the legs. | Pulmonary Embolism, Post-Thrombotic Syndrome |
| Pulmonary Embolism (PE) | A blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries. | Respiratory failure, Cardiac arrest, Death |
Long-Term Health Effects
Untreated blood clots can also have long-term health effects. Post-thrombotic syndrome is a common complication of DVT. It causes chronic symptoms that can greatly affect a person’s quality of life.
Understanding the risks of untreated blood clots is key for early diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing these risks helps individuals seek medical attention early. This can reduce the risk of long-term health effects.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Special Considerations
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that needs immediate medical help. It happens when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, usually in the legs. If not treated, DVT can cause severe problems, like pulmonary embolism.
Resolution Without Treatment
Whether DVT can go away on its own is a complex question. Small clots might dissolve naturally, but big ones are risky and need medical help. About 50% of DVT cases don’t show symptoms, making it important to know the risk factors.
Can DVT resolve without treatment? Sometimes, yes, but it’s not always the case. The chance of spontaneous resolution depends on the clot’s size, location, and your health.
Risks Associated with Untreated DVT
Not treating DVT can lead to serious problems. The biggest risk is the clot breaking loose and going to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Other risks include post-thrombotic syndrome and chronic venous insufficiency.
| Complication | Description | Risk Factors |
| Pulmonary Embolism | A blockage of an artery in the lungs | Large clot size, clot mobility |
| Post-Thrombotic Syndrome | Chronic pain, swelling, and skin discoloration | Clot size, inadequate treatment |
| Chronic Venous Insufficiency | Long-term damage to vein valves | Recurrent DVT, inadequate treatment |
Recognizing DVT Symptoms
It’s important to know the symptoms of DVT for early treatment. Common signs include swelling, pain, and discoloration in the affected limb. If you notice these symptoms, seek medical help right away.
Early detection and treatment of DVT can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Pulmonary Embolism: A Critical Complication
A blood clot that moves to the lungs can cause a pulmonary embolism. This is a serious and potentially fatal condition. It happens when a blood clot from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow.
Mechanism of Pulmonary Embolism
A blood clot in the deep veins, usually in the legs, can break free. It then travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. There, it can block blood flow in the pulmonary arteries. This can cause serious damage to the lung tissue and is life-threatening if not treated quickly.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism can vary. They often include sudden onset of:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing
- Coughing up blood
- Rapid heart rate
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
These symptoms need immediate medical attention. Timely treatment is key.
Mortality Rates and Prognosis
The prognosis for pulmonary embolism depends on several factors. These include the size of the clot, the patient’s health, and how quickly treatment is given. The mortality rate for untreated PE is much higher than for treated cases.
| Condition | Mortality Rate |
| Untreated Pulmonary Embolism | Up to 30% |
| Treated Pulmonary Embolism | Less than 10% |
Prompt medical intervention greatly improves survival chances. It’s important to understand the risks and recognize symptoms early. This helps manage pulmonary embolism effectively.
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome and Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) is a long-term issue that can happen after deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It causes chronic symptoms like pain, swelling, and skin changes in the affected limb.
Development of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
PTS affects 20-50% of DVT patients, usually within 1-2 years. It happens because the blood clot damages the vein valves and walls. This leads to venous hypertension and symptoms.
The risk of getting PTS depends on several things. These include the clot’s size and location, how well the initial treatment worked, and the patient’s age and health conditions.
Symptoms and Progression
Symptoms of PTS can be mild or severe. They include chronic pain, swelling, heaviness, and skin changes like hyperpigmentation and ulceration. These symptoms can really affect a person’s quality of life.
PTS can progress differently for everyone. Some people may have stable symptoms, while others may see them get worse over time. It’s important to catch and manage PTS early to lessen its long-term effects.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Managing PTS aims to ease symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent further problems. Treatment includes using compression stockings, exercise, and medicines to manage pain and reduce venous pressure.
In severe cases, more serious procedures like venous stenting or surgery might be needed.
- Use of compression garments to reduce swelling
- Regular exercise to improve circulation
- Pharmacological management of pain and inflammation
- Surgical options for severe cases
Healthcare providers can help improve outcomes for PTS patients by understanding the risks and using the right management strategies.
Factors That Influence Blood Clot Resolution
It’s important to know what affects how a blood clot resolves. This process is complex and involves many body mechanisms.
Clot Size and Location
The size and where a blood clot is located matter a lot. Larger clots or those in key spots often need medical help to dissolve.
A study in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis showed big clots are harder to dissolve naturally. Where the clot is, like in deep veins or lungs, also affects its outcome.
| Clot Characteristic | Impact on Resolution |
| Size | Larger clots are less likely to resolve on their own |
| Location | Clots in critical areas (e.g., lungs, deep veins) are more dangerous |
Individual Health Factors
Health conditions and lifestyle can also affect clot resolution. For instance, people with diabetes or hypertension might have poor blood flow, making it harder for clots to dissolve.
Age and Comorbidities
Age and health issues are also key factors. Older people or those with many health problems might find it harder for their body to dissolve clots naturally. This is because their body’s functions are not as strong, and they might have conditions that make clots more likely.
A study in the Journal of Gerontology found that older patients with health problems face more risks from blood clots. They also had a lower chance of the clots dissolving on their own.
When Medical Intervention Is Necessary
Some blood clots can clear up on their own. But others need quick medical help to avoid serious problems. The need for medical care depends on the clot’s size, where it is, and the person’s health.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
It’s important to know the signs of a serious blood clot. Severe leg pain or swelling, chest pain, and shortness of breath are warning signs. These could mean you have a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism, both needing fast medical care.
Common warning signs include:
- Leg pain or tenderness
- Swelling in one leg
- Redness or discoloration
- Warmth to the touch
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
Diagnostic Procedures
Doctors use several ways to find out if you have a blood clot. They look at your physical exam, medical history, and do tests. Ultrasound is often used for DVT, and CT scans or ventilation-perfusion scans for pulmonary embolism.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
| Ultrasound | Detects blood clots in deep veins |
| CT Scan | Provides detailed images of internal structures |
| Ventilation-Perfusion Scan | Evaluates lung function and blood flow |
Treatment Options and Approaches
Treatment for blood clots usually includes anticoagulant medications. These stop the clot from getting bigger and lower the chance of it coming back. Sometimes, thrombolytic therapy is used to break up the clot directly.
The treatment plan depends on the clot’s size, location, and the patient’s health. For DVT, anticoagulant meds are the main treatment. Pulmonary embolism might need stronger treatments, like thrombolysis or surgery.
Conclusion: Weighing Natural Resolution Against Medical Treatment
It’s important to know if blood clots can dissolve by themselves. Some may go away naturally, but others need medical help to avoid serious problems.
The chance of a blood clot dissolving naturally depends on its size, where it is, and your health. Studies show that smaller clots might dissolve on their own. But, bigger clots usually need treatment.
So, can blood clots go away by themselves? Yes, in some cases. But, it’s key to know the dangers of not treating them. Can they go away without harm? Sometimes. But, will they? It really depends on the clot and your health.
In the end, deciding between natural resolution and medical treatment is key. It helps prevent long-term damage and gets the best results.
FAQ
Do blood clots go away on their own?
Yes, some blood clots can dissolve naturally. This happens through the body’s own healing process. But, it depends on the clot’s size and where it is in the body.
Can a blood clot resolve without treatment?
Yes, some blood clots can dissolve without medical help. The body’s healing process can break down the clot. But, not all clots can dissolve this way, and some need medical care.
What happens if you leave a blood clot untreated?
If a blood clot is not treated, it can cause serious problems. These include lung blockages, leg damage, and poor blood flow. These issues can be very serious and even life-threatening.
Can DVT resolve on its own?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) might dissolve on its own. But, it’s not always the case. The chance of it happening depends on the clot’s size and location, and your overall health.
What are the risks of leaving DVT untreated?
Untreated DVT can lead to serious issues. These include lung blockages and leg damage. These problems can be very serious and even life-threatening.
How do blood clots lead to pulmonary embolism?
Blood clots can cause pulmonary embolism when they break loose and go to the lungs. This blocks blood flow and is very dangerous. Quick medical help is needed.
What are the warning signs and symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
Signs of pulmonary embolism include shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood. These symptoms need immediate medical care.
Can blood clots disappear on their own?
Some blood clots can dissolve naturally. But, not all can, and some need medical help to avoid serious problems.
What factors influence blood clot resolution?
Several things affect if a blood clot will dissolve. These include the clot’s size and location, your health, and age. These factors can change how fast and if a clot will dissolve.
When is medical intervention necessary for blood clots?
Medical help is needed for blood clots if there are severe symptoms or a high risk of complications. Doctors use tests and treatments, like medicines, to manage the condition.
Does DVT go away on its own?
DVT might dissolve on its own, but it’s not always the case. The chance of it happening depends on the clot’s size and location, and your health.
Will a blood clot go away on its own?
Some blood clots can dissolve naturally. But, it’s not always the case. The chance of it happening depends on the clot’s size and location, and your health.
Can blood clots resolve on their own?
Yes, some blood clots can dissolve naturally. But, it depends on the clot’s size and location, and your health.
References
- Puskás, A. (2007). Spontaneous recanalization in deep venous thrombosis. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 33(3), 357-362. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17353889/



































