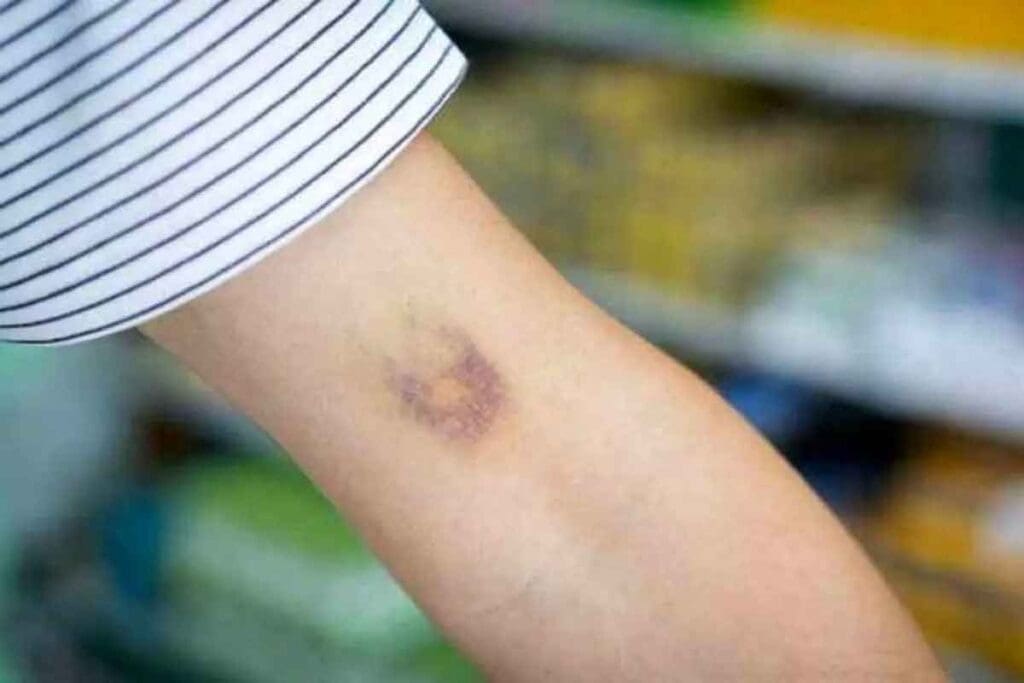
Bruising is a common concern for those on blood thinners. These meds help prevent stroke by making blood less likely to clot. But they also mean even small injuries can cause more bruising. See why blood thinners and bruising pictures occur and their stages explained.
Knowing why bruising happens and how bruises heal can help manage this side effect. At Liv Hospital, experts focus on patient safety and clear communication. They make sure patients get the latest care.
Key Takeaways
- Blood thinners can cause more frequent and noticeable bruising due to their effect on blood clotting.
- Minor injuries can lead to larger, darker, or longer-lasting bruises when taking these medications.
- Understanding the stages of bruise healing can help in managing the condition.
- Patient safety and clear communication are prioritized in healthcare practices like Liv Hospital.
- Recognizing the signs and stages of bruising can aid in responding to this common side effect with confidence.
Understanding Blood Thinners and Their Effects
To understand how blood thinners affect bruising, we first need to know what they are. Blood thinners are medicines that stop blood clots from forming. These clots can be dangerous if they block blood flow to important parts of the body.
Types of Blood Thinners and How They Work
There are mainly two kinds of blood thinners: anticoagulants and antiplatelets. Anticoagulants, like warfarin, stop the liver from making clotting factors. This makes blood less able to form clots. Antiplatelets, such as aspirin, stop platelets from sticking together, which is key in clot formation.
These medicines work by messing with the body’s clotting process. Knowing how they work helps patients understand their risks and benefits.
The Relationship Between Blood Thinners and Clotting
Blood thinners change how the body forms clots. They help prevent dangerous clots but can also lead to more bruising and bleeding. This is because the body can’t stop bleeding as well.
On blood thinners, injuries take longer to heal. The body might not stop bleeding right away, causing bigger bruises. Knowing this helps manage the risks of taking blood thinners.
The Science Behind Bruising

Bruising is a common concern for people on blood thinners. But what happens under the skin? Bruises occur when blood leaks from damaged blood vessels into the tissue around them. This usually happens because of trauma or injury that breaks the blood vessel walls.
What Are Bruises Made Of?
A bruise is a collection of blood outside the blood vessels, called a hematoma. When blood vessels get injured, blood spills into the tissue around them. This causes the discoloration we see in bruises.
The color changes in bruises come from the breakdown of hemoglobin in red blood cells. As the body heals, the bruise changes color. It goes from purple or blue to green, then to yellow, and eventually to brown before fading away. This shows the stages of hemoglobin breakdown.
Normal Bruising vs. Bruising on Blood Thinners
For people not on blood thinners, bruising is usually limited and heals quickly. But for those on anticoagulant therapy, it’s different. Blood thinners make it harder for blood to clot, leading to more bleeding and bigger bruises.
Bruises on blood thinners can look different. They might be larger, spread out more, or take longer to heal. Knowing these differences helps manage and reduce bruising while on blood thinners.
Blood Thinners and Bruising Pictures: What to Expect
Blood thinners can change how bruises look and heal. It’s important to know what to expect. Bruises from blood thinners are often bigger, darker, and last longer than usual bruises. Knowing how these bruises look and why they differ is key for those on these medications.
Typical Appearance of Blood Thinner-Related Bruises
Bruises from blood thinners are usually bigger and more colorful. They can turn from red to purple, blue, and even black as they heal. The color change can be more noticeable and take longer to fade.
Why Blood Thinner Bruises Look Different
Blood thinner bruises look different because these meds stop blood from clotting. When you get hurt, more blood leaks into the tissues. This makes bruises bigger and more noticeable.
Here’s a comparison of typical bruises and those from blood thinners:
| Characteristics | Typical Bruises | Blood Thinner Bruises |
| Size | Generally smaller | Often larger |
| Color | Red, blue, or purple | More intense colors, potentially darker |
| Healing Time | Usually heals within a week or two | It can take longer to heal |
Understanding these differences helps those on blood thinners manage their condition better. It also tells them when to get medical help if needed.
The Stages of Bruise Healing: A Visual Timeline
When a bruise heals, it changes color. Knowing these changes helps us understand how it’s healing. It also tells us what to expect.
Initial Stage: Red to Purple (1-2 days)
The first sign of healing is a red or purple color. This comes from the blood in the bruise. It usually lasts for the first couple of days after getting hurt.
Middle Stages: Blue, Black, and Green (3-10 days)
As it heals, the bruise might turn blue or black. This is because the blood is breaking down. Around 5-7 days, it might look greenish because of a green pigment.
Final Stages: Yellow and Brown (10-14+ days)
In the last stages, the bruise will likely turn yellow or brown. This is because of a yellow pigment from the breakdown of the green one. As the body absorbs the blood, the bruise will fade away.
| Stage | Days | Color | Description |
| Initial | 1-2 | Red/Purple | Hemoglobin presence |
| Middle | 3-10 | Blue/Black/Green | Hemoglobin breakdown |
| Final | 10-14+ | Yellow/Brown | Bilirubin presence |
Learning about the stages of bruising pictures helps us track healing. It also helps spot any problems early on.
Factors That Influence Bruise Appearance and Healing
Several factors can affect how bruises look and heal. Taking blood thinners often leads to bruising. Knowing these factors can help manage this condition better.
Age and Skin Type
Age greatly influences bruise appearance and healing. Older people bruise more easily because their skin is thinner and has less collagen. This makes blood vessels more likely to get damaged. People with fair skin also tend to show bruises more.
A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that older adults bruise more. This is because aging reduces collagen and skin elasticity.
“The skin’s ability to withstand trauma decreases with age, making older adults more susceptible to bruising.”
Medication Interactions
Medications can also affect how bruises look and heal. Taking blood thinners means being careful about other medications. Drugs like antiplatelet agents or NSAIDs can raise the risk of bruising.
| Medication | Effect on Bruising |
| Blood Thinners | Increased risk of bruising |
| Antiplatelet Drugs | Enhanced anti-clotting effect, increasing bruising risk |
| NSAIDs | May increase bruising risk due to anti-clotting properties |
Location on the Body
The spot on the body where a bruise forms can change how it looks and heals. Bruises in fatty areas like the thighs or buttocks look different from those on bony spots like the shins or forehead.
Knowing these factors helps people on blood thinners manage their condition and lessen bruising. If you’re worried about bruising or have questions, talk to your doctor.
Different Types of Bruises Explained
It’s important to know about the different bruises to understand their causes and effects. Each type of bruise looks different, and knowing how to spot them is key to proper care.
Ecchymosis: Standard Bruises
Ecchymosis is the common bruise everyone knows. It happens when blood leaks from small vessels into the skin. Ecchymosis can be any size and color, showing up as a blue or purple mark. It changes color as it heals.
Petechiae: Pinpoint Red or Brown Dots
Petechiae are tiny red or brown spots on the skin. They come from small blood vessel breaks. Unlike big bruises, petechiae are small and often appear in groups. They might show up due to health issues or intense pressure.
Purpura: Larger Patches of Discoloration
Purpura are bigger patches of color under the skin. They can be purple or red. These patches often show up in people with blood-clotting or vascular problems. If you see purpura suddenly or with other symptoms, see a doctor.
To sum up, knowing about ecchymosis, petechiae, and purpura is key. It helps you understand what’s happening and what to do next. By recognizing these bruises, you can take care of yourself better and know when to get medical help.
Bruises With White Centers: What They Mean
White-centered bruises are not common and might mean something serious. Bruises are usual, but a white center could point to a problem or extra pressure on the skin.
The Science Behind White-Centered Bruises
A bruise with a white center happens because of how blood builds up and is absorbed under the skin. Normally, bruises change color as they heal. But a white center might mean there’s an underlying issue, like a blood vessel problem or infection.
When to Be Concerned About White-Centered Bruises
Most bruises are not a big deal, but a white-centered one might be serious. It could be linked to vasculitis or another autoimmune disease. It’s key to watch these bruises and see a doctor if they don’t go away or if you have other symptoms.
| Bruise Type | Characteristics | Potential Concerns |
| Normal Bruise | Color changes from red to purple, blue, green, yellow, and brown | Generally none, unless excessive or frequent |
| White-Centered Bruise | Has a distinct white center, which may indicate an underlying condition | Could signal infection, vascular issue, or autoimmune disorder |
Knowing about bruises, including those with white centers, is key to spotting health problems early. If you’re worried about a bruise or have other symptoms, it’s wise to talk to a doctor.
Why Would a Bruise Get Bigger? Understanding Bruise Progression
Bruising is common, and knowing why bruises get bigger is key. They can grow because of ongoing bleeding or the impact of blood thinners.
It’s natural to wonder if a bruise will get bigger. The answer depends on the factors that affect bruise growth.
Normal Bruise Expansion vs. Concerning Growth
A bruise can grow as it heals, with blood leaking into the tissue. But, if it grows too fast or too big, it’s a worry. Watching the size and color of the bruise is key to seeing if it’s okay.
Things like where the bruise is, how bad the injury was, and your health can affect how it grows. Some bruises are normal, while others might be a sign of something more serious.
Blood Thinner Effects on Bruise Size
Blood thinners stop blood clots from forming. They’re important for heart health, but can make bruises bigger. Blood thinners can make bruises larger because they stop the body from clotting, leading to more bleeding.
It’s important to understand how blood thinners affect bruises. Knowing this can help manage their impact. This way, you can take steps to reduce any problems.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Bruising While on Blood Thinners
Knowing when to get medical help for bruising on blood thinners is very important. Bruising is a common side effect of these medications. But some symptoms can mean a serious problem.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Care
If you’re on blood thinners and notice these signs, get medical help right away:
- Severe pain or swelling in the affected area
- Rapid enlargement of the bruise
- Difficulty moving the affected limb or area
- Numbness or tingling around the bruise
- Signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or pus
Monitoring Bruises for Complications
It’s important to watch your bruises while on blood thinners. Look for:
- Changes in size or color
- Increased pain or tenderness
- Signs of bleeding, such as prolonged bleeding from minor cuts
- New bruises are appearing frequently without significant trauma
If you see any unusual changes or are worried about your bruises, talk to your doctor. They can check if your bruising is just a side effect or if it’s something more serious.
Managing and Reducing the Bruising While on Blood Thinners
Many people on blood thinners worry about bruising. But there are steps you can take to lessen it. Simple habits and home remedies can help reduce bruising.
Preventative Measures
Preventing bruises is key. Being careful and avoiding injuries can help a lot. Here are some tips:
- Be cautious in daily activities: Try not to bump into things or fall, as these can cause bruises.
- Wear protective clothing: Wear long sleeves, gloves, and padding for activities that might hurt you.
- Improve home safety: Remove things that could trip you up, use non-slip mats, and keep your home well-lit to avoid falls.
- Be gentle with your skin: Don’t rub your skin hard and use gentle products that won’t irritate it.
Home Remedies for Existing Bruises
If you get a bruise, there are ways to make it feel better. Here are some home remedies:
- Applying cold compresses: Cold can help shrink the bruise and ease the pain.
- Elevating the affected area: Keeping the bruise above your heart can also help reduce swelling.
- Using arnica gel or cream: Some research shows arnica can lessen bruising and swelling.
- Taking vitamin C: Vitamin C helps make collagen and can improve your skin’s health.
By using these tips and remedies, you can manage bruising better. This makes life easier while on blood thinners.
Conclusion
Blood thinners are important for many people. They help prevent blood clots and strokes. But they can also cause bruising.
Understanding how blood thinners and bruising are connected is key. This knowledge helps manage the condition better. It also lowers the risk of serious problems.
Bruising from blood thinners might worry some, but it’s usually normal. The look of bruises can differ. Pictures of blood thinners and bruising can show what to expect.
Things like age, skin type, and other medicines can affect how bruises look and heal. Knowing this can help.
Knowing how bruises heal and taking steps to prevent them can help. If you’re worried, seeing a doctor is important. They can check for any serious issues.
With the right knowledge and care, people on blood thinners can lessen bruising. This helps keep their health in good shape.
For more professional discussions, visit our Linkdin page.
FAQ
What are blood thinners, and how do they affect bruising?
Blood thinners stop blood clots from forming or growing. They make it harder for bruises to heal. This is because they affect how the body clots blood.
What are the different types of blood thinners?
There are many types of blood thinners. These include anticoagulants like warfarin and rivaroxaban. There are also antiplatelet agents like aspirin and clopidogrel. Each type works differently to prevent clotting.
What is a bruise made of?
A bruise is made of blood that leaks from damaged blood vessels. The body breaks down and absorbs this blood. This is why bruises change color as they heal.
Why do bruises look different on people taking blood thinners?
People on blood thinners may have different-looking bruises. This is because the medication stops the body from clotting blood. This leads to more bleeding into the tissue, making bruises larger and more noticeable.
What are the stages of bruise healing?
Bruises go through several stages. They start red or purple, then turn blue, black, and green. They eventually turn yellow and brown as they fade.
Why do bruises with white centers occur?
White centers in bruises can happen for many reasons. The injury’s severity and the body’s healing process play a part. Sometimes, a white center can signal a blood-clotting disorder.
Why would a bruise get bigger?
A bruise can grow due to ongoing bleeding into the tissue. Blood thinners can make this worse. Other factors like the bruise’s location and the person’s health also play a role.
When should I seek medical attention for bruising while on blood thinners?
Seek medical help if your bruising is severe, doesn’t heal, or comes with pain, swelling, or trouble moving. These are signs of a bigger issue.
How can I manage and reduce bruising while on blood thinners?
To reduce bruising, be gentle with your body and avoid injuries. Use protective gear. Home remedies like ice or compression can also help.
Are there different types of bruises?
Yes, there are several types of bruises. These include ecchymosis (standard bruises), petechiae (pinpoint red or brown dots), and purpura (larger patches of discoloration). Each type has its own characteristics and causes.
How do blood thinners affect the size of a bruise?
Blood thinners can make bruises larger. This is because they prevent blood from clotting. This allows more blood to leak into the tissue.
What factors influence bruise appearance and healing?
Several factors affect how bruises look and heal. These include age, skin type, medication interactions, and where the bruise is on the body.

































