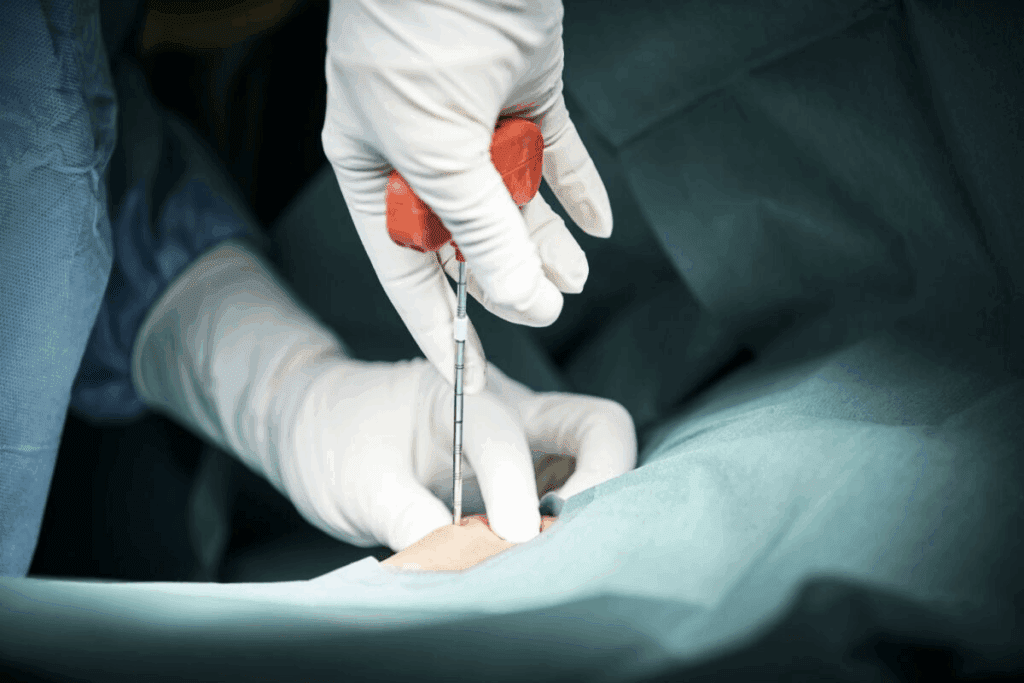
If your doctor can’t find the cause of anemia, they might suggest bone marrow analysis through a biopsy. This test helps get a clear diagnosis and the right treatment. At Liv Hospital, we know the importance of bone marrow analysis for checking blood cell production and uncovering underlying causes like blood disorders, cancers, or infections. This procedure provides vital information that routine blood tests cannot, guiding targeted and effective anemia management to improve patient outcomes.
A bone marrow test for anemia is often suggested when usual blood tests don’t show enough. It’s also used when bone marrow diseases are thought to be present. By looking at the bone marrow, doctors can learn more about anemia and other blood problems.
Key Takeaways
- A bone marrow biopsy is a key tool for diagnosing anemia.
- Liv Hospital’s expertise and focus on patients help you every step of the way.
- A bone marrow test gives important information on blood cell production.
- Doctors might suggest a bone marrow biopsy if standard blood tests don’t work.
- Getting an accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment and care.
Understanding Bone Marrow and Its Role in Blood Production
Bone marrow is essential for making blood cells and fighting anemia. It’s the soft tissue inside big bones like hips and breastbone. This tissue is vital for our blood production system.
The Structure and Function of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow has blood vessels and special cells that make blood cells. It turns stem cells into red and white blood cells and platelets. This process is key for oxygen delivery, fighting infections, and stopping bleeding.
“The bone marrow is a highly active organ that produces over 500 billion blood cells daily,” showing its importance for health. It has red marrow for blood cell making and yellow marrow for fat.
How Bone Marrow Relates to Anemia Development
Anemia happens when bone marrow can’t make enough red blood cells or has production problems. This can be due to many reasons, like nutritional issues, bone marrow disorders, or chronic diseases. Understanding bone marrow’s role in anemia is key to diagnosis and treatment.
A bone marrow biopsy is often needed for blood cell count issues or severe anemia. It involves taking a bone marrow sample with a needle. This helps doctors find anemia’s cause and plan treatment.
Types of Anemia That May Warrant Further Investigation

When anemia doesn’t get better with usual treatments, more tests might be needed. Anemia means not enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen. There are many types, and some need more detailed checks.
Iron-Deficiency Anemia vs. Other Types
Iron-deficiency anemia is common, mainly in women. It happens when the body lacks iron for hemoglobin in red blood cells. Iron supplements often help, but other anemias need different treatments.
Key differences between types of anemia include:
- Cause: Whether it’s due to a lack of iron, a vitamin deficiency, chronic disease, or bone marrow issues.
- Symptoms: While common symptoms include fatigue and weakness, some types may present with additional or more severe symptoms.
- Response to treatment: How well the anemia responds to initial treatments can indicate whether further investigation is needed.
When Standard Blood Tests Are Inconclusive
Standard blood tests might not show the cause of anemia. A bone marrow biopsy can help. It lets doctors see how blood cells are made and find problems.
“A bone marrow biopsy is a critical diagnostic tool when the cause of anemia remains unclear after initial testing.”
Expert Opinion
Refractory Anemia Conditions
Refractory anemia doesn’t get better with treatment. This can be hard and might mean a serious problem. Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of disorders that can cause this anemia. They affect blood cell production and can lead to infections and bleeding.
Here’s a table that shows the main points about different anemias and when more tests are needed:
| Type of Anemia | Causes | Response to Standard Treatment | Need for Bone Marrow Biopsy |
| Iron-Deficiency Anemia | Lack of iron | Often responds well | Rarely needed |
| Vitamin Deficiency Anemia | Deficiency in vitamins like B12 or folate | Responds to vitamin supplements | Generally not needed |
| Anemia of Chronic Disease | Chronic diseases like cancer or rheumatoid arthritis | May not respond until underlying disease is treated | May be considered if underlying disease is unclear |
| Refractory Anemia | Various, including bone marrow disorders | Does not respond | Often necessary |
In conclusion, while many anemias can be treated with standard tests, some need more checks. Knowing the different types and their signs is key to knowing when more tests are needed.
Common Reasons for a Bone Marrow Biopsy
Doctors might suggest a bone marrow biopsy for several reasons, mainly for complex blood disorders. This test is key to figuring out the causes of blood-related issues.
Unexplained or Severe Anemia
One main reason for a bone marrow biopsy is to check on unexplained or severe anemia. Anemia happens when there aren’t enough red blood cells or when the red blood cells lack hemoglobin. This test helps find out if the bone marrow is making enough red blood cells.
Doctors say, “A bone marrow biopsy is the best way to find the cause of anemia that other tests can’t explain.” It lets doctors see the bone marrow up close. This gives them clues about blood cell production.
Abnormal Blood Cell Counts
Another reason for a bone marrow biopsy is to look into abnormal blood cell counts. This includes having too few or too many white blood cells or platelets. Doctors can spot problems with these cells by looking at the bone marrow. This can point to different blood disorders.
For more details on blood cell counts and related issues, check out MedlinePlus. It’s a trusted source for medical information.
Suspected Bone Marrow Disorders
A bone marrow biopsy is also key when there’s a suspicion of bone marrow disorders, like leukemia, lymphoma, or myeloma. These conditions mess with the bone marrow’s ability to make healthy blood cells. Doctors can diagnose these and plan treatment by looking at the bone marrow.
The results from a bone marrow biopsy are essential for diagnosing and tracking blood and marrow diseases. They give a clear view of the bone marrow’s health. This helps doctors make better decisions for patient care.
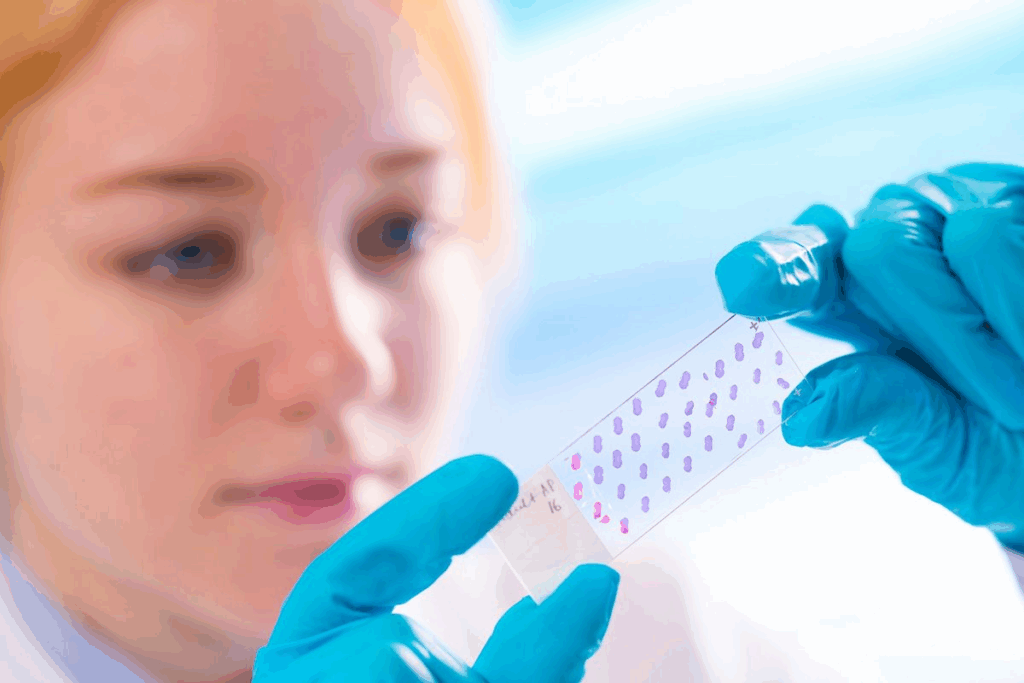
Bone Marrow Analysis: What Information It Provides
Bone marrow analysis is a key tool for checking the health of the bone marrow. It helps understand how it makes blood cells. Doctors look at bone marrow samples to find problems and understand anemia and blood disorders better.
Cell Morphology Evaluation
One main goal of bone marrow analysis is to check cell shapes and sizes. Doctors look at red, white blood cells, and platelets. This helps spot issues like anemia or bone marrow problems.
For example, odd red blood cells might show iron or nutrient issues. White blood cell oddities could point to infections or cancers.
Assessment of Marrow Function
Doctors also check how well the marrow works. They look at blood cell production and any problems in making new cells. This helps see if the marrow is working right and if cells are maturing properly.
Low red blood cell production might mean aplastic anemia. Too many cells could suggest cancer.
Detection of Malignancy or Infiltration
Another key part is finding cancer or abnormal cells in the marrow. Doctors look for cancer cells or other odd cells. This helps diagnose leukemia, lymphoma, or cancer spread.
Finding cancer is vital for knowing the disease’s stage and treatment options. It helps decide if chemo, radiation, or other treatments are needed.
In summary, bone marrow analysis is very important. It gives insights into the marrow’s health and blood cell production. Doctors use it to spot problems and plan treatments for blood disorders.
When Your Doctor Might Recommend a Bone Marrow Test for Anemia
A bone marrow test for anemia is used in certain situations. It helps doctors find the cause of anemia and plan treatment.
Doctors might suggest a bone marrow biopsy for anemia in specific cases. Knowing these reasons can help patients get ready for the test.
Persistent Cytopenias Despite Treatment
One key reason for a bone marrow biopsy is when blood cell counts stay low despite treatment. This includes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. A bone marrow test can uncover issues not seen in blood tests.
“The bone marrow biopsy is vital when blood cell counts don’t improve with treatment,” says a top hematologist. “It lets us see how the bone marrow works and makes cells.”
Suspected Hematologic Malignancies
Another reason for a bone marrow biopsy for anemia is when cancer is suspected. This includes cancers of the blood, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. The test can spot leukemia or lymphoma by looking at marrow cells.
- Detection of abnormal cell growth
- Identification of cancerous cells
- Assessment of the extent of disease spread
Unexplained Fevers with Blood Abnormalities
Patients with unexplained fevers and blood issues might need a bone marrow biopsy. These signs can point to a condition that needs more study. The test can find infections, inflammation, or diseases affecting the marrow.
The choice to do a bone marrow test for anemia comes when other tests don’t give answers. It’s also when a patient’s health needs more checking. Knowing why you might need this test helps you understand what to expect.
The Procedure for Bone Marrow Biopsy Explained
It’s important for patients to know about the bone marrow biopsy procedure. This test takes a sample of bone marrow for doctors to check. It’s usually done by a specialist in blood disorders or cancer.
Preparation Before the Procedure
Before the biopsy, patients get some advice. “Tell your doctor about any medications you’re taking, like blood thinners,” as they can change the procedure. You might also be told not to eat or drink for a few hours beforehand. It’s a good idea to have someone drive you home after.
Aspiration vs. Core Biopsy Techniques
There are two main ways to do a bone marrow biopsy: aspiration and core biopsy. Aspiration takes out the liquid part of the bone marrow. A core biopsy removes a small piece of bone with marrow. Both are often done together for a full check-up.
Common Biopsy Sites
The most common place for a bone marrow biopsy is the hip bone (pelvis), at the posterior superior iliac spine. This spot is chosen because it’s safe and easy to get to. Sometimes, the sternum (breastbone) is used, but this is rarer because of the risks.
“The choice of biopsy site depends on various factors, including the patient’s condition and the doctor’s preference.”
says a hematologist. The whole process usually takes 10 to 20 minutes. Afterward, patients can usually go home.
What to Expect During Your Bone Marrow Biopsy for Anemia
We’re here to guide you through the bone marrow biopsy process. We’ll explain what happens during the procedure and how to prepare. A bone marrow biopsy is a test that removes a small sample of bone marrow for examination. It’s key in finding the cause of your anemia and figuring out the best treatment.
Step-by-Step Process
The bone marrow biopsy procedure involves several steps:
- Preparation: You’ll be positioned on your stomach or side, depending on the biopsy site.
- Cleaning and numbing: The skin over the biopsy site is cleaned and numbed with a local anesthetic.
- Biopsy needle insertion: A special needle is inserted into the bone to collect a marrow sample.
- Sample collection: The needle is used to aspirate a small amount of bone marrow, which is then sent for analysis.
For more detailed information on the bone marrow biopsy procedure, you can visit Cedars-Sinai’s health library.
Pain Management and Comfort Measures
Pain management is key during the bone marrow biopsy. The procedure can be uncomfortable, but several steps are taken to reduce pain:
- Local anesthesia is used to numb the biopsy site.
- Conscious sedation may be offered to help you relax during the procedure.
- Your healthcare team will be present to monitor your comfort and adjust as needed.
Duration and Immediate Recovery
The bone marrow biopsy procedure usually takes 10 to 20 minutes. But you’ll need more time for preparation and post-procedure care. After the biopsy, you’ll be watched for a short time to check for any immediate issues. You might feel some soreness or bruising at the biopsy site, but this usually goes away in a few days.
Knowing what to expect from the bone marrow biopsy can make you feel more ready and less worried. If you have any concerns or questions, talk to your healthcare provider.
Side Effects from Bone Marrow Biopsy
Bone marrow biopsies are key in diagnosing blood-related disorders. It’s important to know the possible side effects. This helps patients understand the risks and what to expect.
Common Minor Side Effects
Most people have minor side effects after a bone marrow biopsy. These include:
- Soreness or Pain at the biopsy site, which can be eased with over-the-counter pain meds.
- Bruising around the site, which usually goes away in a few days.
- Mild Bleeding or oozing, which can be stopped with pressure.
Rare but Serious Complications
Though rare, serious complications can happen. These include:
- Infection at the site, which might need antibiotics.
- Excessive Bleeding that doesn’t stop with pressure, needing medical help.
- Nerve Damage near the site, causing numbness, tingling, or pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to seek help after a bone marrow biopsy is key. If you notice any of these, call your doctor:
- Increasing pain or swelling at the site.
- Signs of infection, like redness, warmth, fever, or pus.
- Prolonged or heavy bleeding.
- Numbness or tingling that lasts.
Being aware of these side effects and complications helps patients prepare. It also tells them what to watch for during recovery.
Bone Marrow Biopsy Risks and Safety Considerations
Deciding to have a bone marrow biopsy means knowing the possible risks. The procedure is usually safe, but some factors can make it riskier.
Risk Factors That Increase Complications
Some things can make a bone marrow biopsy more dangerous. For example, low platelet counts can lead to bleeding. Also, a weak immune system can slow healing and raise the chance of infection.
Key risk factors to consider:
- Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
- Weakened immune system (immunocompromised)
- Bleeding disorders or taking anticoagulant medications
- History of radiation therapy or previous bone marrow biopsies
Safety Measures During the Procedure
Doctors take many steps to keep you safe during a bone marrow biopsy. They use clean tools, numb the area with local anesthesia, and watch your vital signs closely.
They also use imaging like fluoroscopy or ultrasound. This helps place the needle correctly, lowering the risk of problems.
Allergic Reactions to Anesthetics
Another risk is an allergic reaction to the anesthetic. While rare, these reactions can be mild or severe.
To avoid this, we check if you have any allergies or bad reactions to anesthetics before starting.
| Risk Factor | Potential Complication | Safety Measure |
| Low Platelet Count | Bleeding or Hematoma | Platelet Transfusion Before Procedure |
| Weakened Immune System | Infection | Prophylactic Antibiotics |
| Allergy to Anesthetics | Allergic Reaction | Careful Medical History and Alternative Anesthetics |
Knowing these risks and taking the right steps can help make the bone marrow biopsy safer and more successful.
Recovery After a Bone Marrow Biopsy
Understanding the recovery process after a bone marrow biopsy is key. It helps ensure a smooth and comfortable healing. We’ll guide you through the necessary steps for a successful recovery.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after the procedure, you’ll be asked to lie on your back for 10 to 15 minutes. This helps stop bleeding and promotes clotting. Our medical team will watch over you to make sure everything is okay.
Following our instructions carefully is very important. You’ll get specific guidance on caring for the biopsy site. This includes how to change any dressings or bandages.
Long-term Site Care
Proper care of the biopsy site is essential to prevent infection and aid healing. Keep the area clean and dry. Avoid activities that might cause discomfort or bleeding. You might need to apply a dressing or bandage and change it as directed.
Watch for signs of infection, like redness, swelling, or increased pain. If you notice these symptoms, contact our medical team right away.
Activity Restrictions and Return to Normal
After a bone marrow biopsy, avoid heavy lifting or bending for a few days. This helps the site heal and reduces complications. You can usually go back to your normal activities in a few days. But always follow our specific guidance.
Recovering from a bone marrow biopsy can be tough, but with the right care, you can manage discomfort and aid healing. If you have concerns or questions, reach out to our medical team for support.
Understanding Your Bone Marrow Biopsy Results
The results of your bone marrow biopsy are key to your treatment plan. After the test, the samples go to a lab for analysis.
Timeframe for Results
Results usually come in a few days to a week. But it depends on the test’s complexity and the lab’s workload. Your doctor will tell you when to expect them and explain them to you.
Being patient and understanding the importance of timely results is vital for planning your next steps.
Interpreting Common Findings
When your results are ready, your doctor will explain them. They might talk about abnormal cells, bone marrow health, or signs of disease.
“The biopsy results will help us understand the underlying cause of your anemia and guide us toward the most appropriate treatment.” – This is what doctors often say about the results’ importance.
As a medical expert noted,
“Bone marrow biopsy is a critical diagnostic tool that provides direct evidence of the bone marrow’s condition, helping us tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs.”
Next Steps Based on Results
After reviewing your results, your doctor will discuss your next steps. This could mean more tests, starting a new treatment, or changing your current one.
- If the results show a specific condition, like leukemia or lymphoma, your doctor will talk about treatment options.
- If there are no major issues, your doctor might suggest more monitoring or other tests.
- If the results are unclear, more tests might be needed to make a diagnosis.
Understanding your bone marrow biopsy results is key to managing your health. By working with your healthcare team, you can make informed decisions about your care.
Conclusion: The Value of Bone Marrow Evaluation in Anemia Diagnosis
Bone marrow evaluation is key in diagnosing anemia. It gives us detailed info about your bone marrow and blood cells. This helps us understand the causes of anemia and find the right treatment.
A bone marrow test is very helpful when blood tests don’t give clear results. It helps find bone marrow problems that might cause anemia. Doctors can see how blood cells are made and find any issues.
In short, bone marrow tests are essential for treating anemia. They help doctors make better decisions for patient care. This leads to better treatment results. Knowing how bone marrow tests help diagnose anemia helps patients understand their care better.
FAQ
Why is a bone marrow biopsy recommended for anemia?
A bone marrow biopsy is suggested when blood tests don’t give clear answers. It’s also recommended when treatments don’t work. This test helps doctors find and track diseases affecting the blood and marrow.
What does a bone marrow biopsy diagnose?
A bone marrow biopsy can spot diseases like anemia, leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. It shows how well the bone marrow makes blood cells.
What is the difference between a bone marrow aspiration and a bone marrow biopsy?
Bone marrow aspiration takes a liquid sample from the marrow. A biopsy takes a tissue sample. Both are often done together.
Is a bone marrow biopsy painful?
Getting a bone marrow biopsy might hurt a bit. But doctors use pain relief to make you comfortable. They numb the area first.
What are the risks and complications of a bone marrow biopsy?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and damage to nearby tissues. Serious but rare problems can happen. If you have severe symptoms, see a doctor right away.
How long does it take to recover from a bone marrow biopsy?
Recovery from a bone marrow biopsy takes a few days to a week. You might feel some pain, bruising, or swelling. But these usually go away by themselves.
When will I receive the results of my bone marrow biopsy?
Results from a bone marrow biopsy usually take a few days to a week. Your doctor will talk to you about the findings and what to do next.
What do abnormal bone marrow biopsy results mean?
Abnormal results can mean different things, like anemia, leukemia, or lymphoma. Your doctor will explain what they mean for your health and treatment.
Can a bone marrow biopsy detect cancer?
Yes, a bone marrow biopsy can find cancer, like leukemia or lymphoma. It can also spot other bone marrow issues.
How is a bone marrow biopsy performed?
A bone marrow biopsy involves a needle in the hip or pelvis. It uses aspiration and/or biopsy, with local anesthesia for pain.
What are the common minor side effects of a bone marrow biopsy?
Minor side effects include discomfort, bruising, or swelling. These usually go away in a few days.
Are there any activity restrictions after a bone marrow biopsy?
Yes, you might need to avoid heavy lifting or bending for a few days. Your doctor will tell you when you can go back to normal activities.
References
- Cazzola, M., & Malcovati, L. (2015). Practical guide to bone marrow sampling for suspected myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica, 100(5), 606–616. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5995536/

































