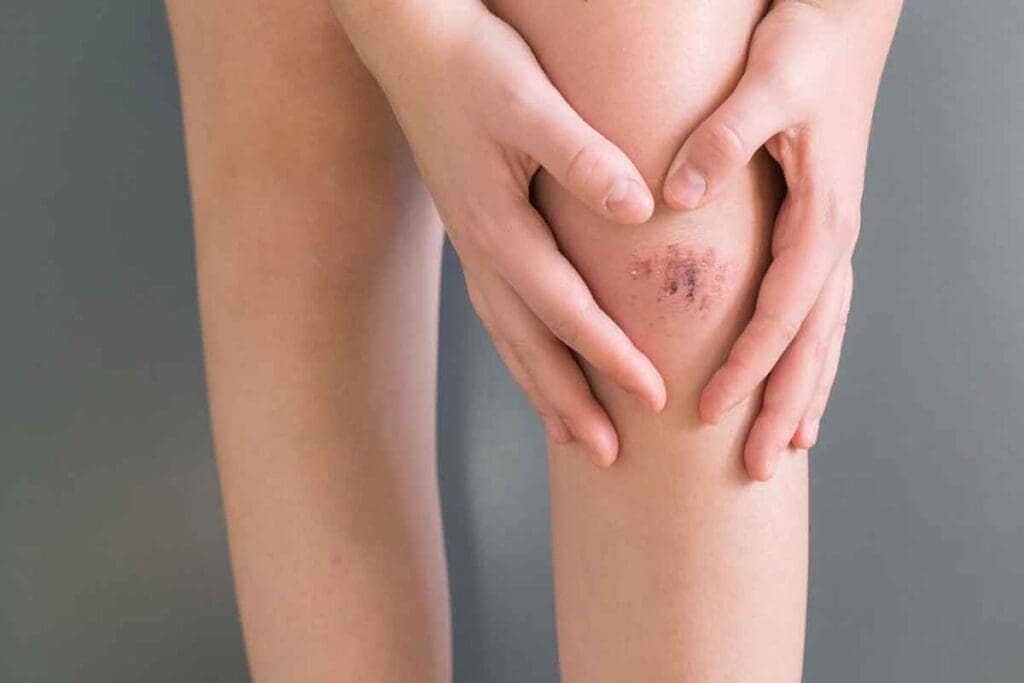
Not every bruise or ache in your leg is harmless. It’s important to know the difference between bruises and blood clots. Liv Hospital’s expert team is here to guide you through these differences.
Bruises are collections of blood under the skin, caused by trauma that breaks small blood vessels. Blood clots, like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the leg or calf, may not be visible. They can cause swelling, persistent pain, and skin warmth.
Telling bruises apart from blood clots is key because of the risks of blood clots.does a blood clot look like a bruiseWhat Causes Blood to Thin? Understanding the Dangers of Thin Blood While bruises are usually harmless, blood clots can be deadly if not treated.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the differences between bruises and blood clots is vital for your health.
- Bruises are typically caused by trauma and are superficial.
- Blood clots, like DVT, can cause swelling, pain, and skin warmth.
- Distinguishing between the two conditions is vital due to the risks associated with blood clots.
- Liv Hospital’s expert team provides world-class, patient-centered care.
Understanding Bruises and Blood Clots
Bruises and blood clots may look similar at first, but they have different causes and health impacts. Both are related to blood, but they show different health problems.
What Is a Bruise?
A bruise, or contusion, happens when blood vessels are damaged. This causes blood to spill into the tissue around it. This blood leakage is what makes bruises look discolored.
The color of a bruise can change based on how bad the injury was and the person’s skin color.
Key characteristics of bruises include:
- Discoloration that changes color over time (typically progressing from red to purple, then to green or yellow before fading)
- Pain or tenderness at the site of injury
- Swelling in some cases
What Is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot is a thick, gel-like mass made of blood cells and proteins. It forms in veins or arteries as a natural response to injury. This helps stop too much bleeding. But, if clots form where they shouldn’t or don’t dissolve, they can cause serious problems like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism.
- Formation can be triggered by injury, immobility, or genetic factors
- It can be life-threatening if they obstruct blood flow to critical areas
- May not always present with obvious symptoms
Why Distinguishing Between Them Matters
Telling bruises apart from blood clots is important because their treatments and risks are different. Bruises are usually just on the surface and get better by themselves. But blood clots can be deadly and need quick medical help.
The main differences are in their causes, symptoms, and possible dangers. Knowing these differences helps people get the right medical care when they need it.
Does a Blood Clot Look Like a Bruise? Visual Differences Explained
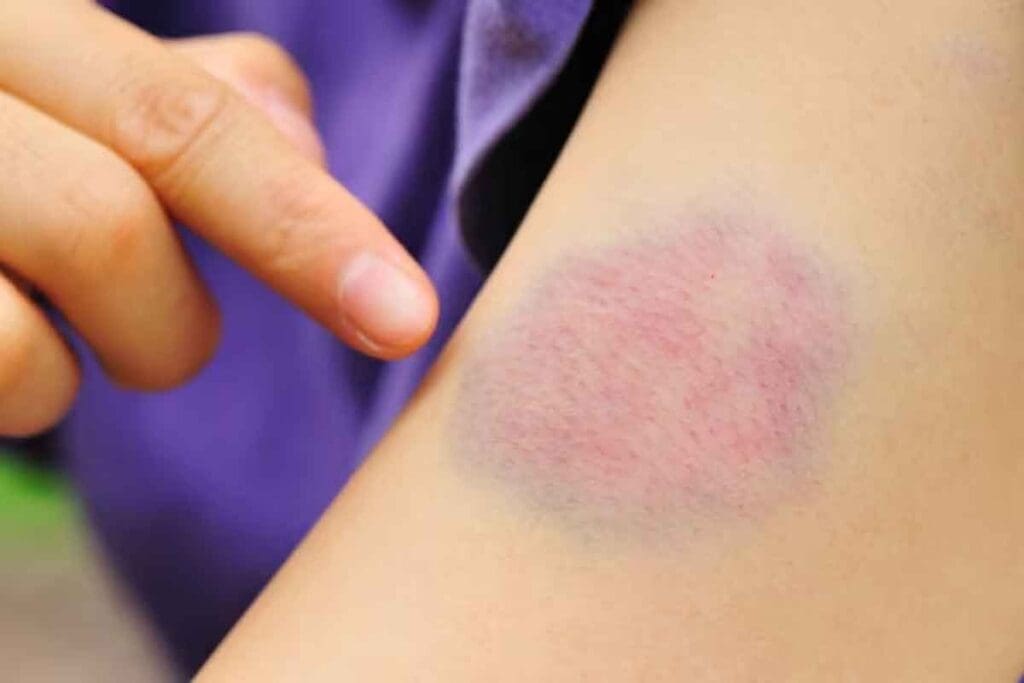
Bruises and blood clots might look similar at first, but they are different. Knowing how to tell them apart is key to spotting health problems.
Bruise Appearance and Color Changes
A bruise shows up as a skin discoloration because of blood leaking from damaged vessels. It starts ofd or purple and then changes color as it heals. It goes through blue, green, and yellow before fading away.
The color change happens as the body breaks down and absorbs the blood. This color shift is a clear sign of a bruise.
Blood Clot Visual Characteristics
A blood clot causes swelling, redness, or discoloration that doesn’t change color like a bruise does. It might feel warm and hurt when touched.
Blood clots can be either close to the skin’s surface or deep inside tissues. Surface clots might show visible skin changes, but deep clots are harder to spot.
What Does a Blood Clot Under the Skin Look Like?
A blood clot under the skin feels tender and swollen, and might be red or discolored. The skin could be warm and soft to the touch. Sometimes, you can’t see the clot but can feel it as a firm lump under the skin.
Watch out for signs of trouble like more pain, swelling, or trouble moving the affected area.
How Bruises and Blood Clots Feel Different
Knowing the difference between a bruise and a blood clot isn’t just about looking at them. You also need to feel the difference. Both can happen from injury, but they feel different.
Does a Blood Clot Feel Like a Bruise?
A bruise feels sore when you touch it. But a blood clot hurts more and gets worse when you move. This is because a bruise is blood outside the vessels, and a clot is a thick mass inside a vessel.
Pain Patterns: Soreness vs. Persistent Pain
Bruise pain is usually not too bad and gets better as it heals. But blood clot pain is strong and lasts longer. It might also make the area swell, feel warm, or turn red.
- Bruise Pain: Typically mild to moderate, decreasing over time.
- Blood Clot Pain: Can be severe, persistent, and may worsen with activity.
When Pain Indicates a Medical Emergency
Pain from a blood clot can be a sign of a serious problem, like deep vein thrombosis (DVT). If you have sudden, bad pain or trouble breathing, chest pain, or a lot of swelling, get help right away.
- Recognize the symptoms: Severe pain, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Act quickly: Seek medical help without delay.
Knowing how bruises and blood clots feel can help you know when to get help. If you’re not sure, always talk to a doctor.
Causes and Risk Factors
Bruises and blood clots can happen for many reasons. These include injuries, genetics, and some health issues. Knowing why they happen helps us figure out what to do next.
How Bruises Form
Bruises come from injuries that hurt blood vessels and cause bleeding. This can happen from falls, blows, or even tight clothes. How bad the bruise is depends on the injury and the person’s health.
Common causes of bruises include:
- Physical injury or trauma
- Sports injuries
- Accidental bumps or falls
- Certain medical conditions that affect blood clotting
Blood Clot Formation Mechanisms
Blood clots form through a complex process. It involves many clotting factors. This can start with an injury, but also with genetics, staying in one place too long, or health issues. Unlike bruises, blood clots can happen without any visible injury.
Key factors in blood clot formation include:
- Damage to blood vessels
- Immobility or prolonged bed rest
- Genetic conditions affecting clotting
- Certain medications or hormonal changes
Risk Factors for Developing Blood Clots
Some things can make you more likely to get blood clots. These include clotting disorders, recent surgery, or staying in one place for too long. Knowing these risks helps prevent and catch blood clots early.
Notable risk factors for blood clots:
- Family history of blood clots
- Recent surgery or hospitalization
- Prolonged immobility
- Certain cancers or treatments
Understanding bruises and blood clots can help us prevent them. While bruises are usually okay, blood clots are serious and need quick attention.
Location Matters: Common Sites and Appearances
Knowing where bruises and blood clots usually show up is key to telling them apart. Both can happen in different body parts. But their spots and looks often give away what they are.
Bruises on Legs vs. Blood Clots in Legs
Bruises on the legs are common due to injuries. They look like discolored patches, from red to purple, and heal in a couple of weeks. Blood clots in the legs. They might not show up on the skin’s surface.
Key differences in appearance:
| Characteristics | Bruises on Legs | Blood Clots in Legs |
| Visible Symptoms | Discoloration, swelling | May not be visible; swelling, pain, warmth |
| Location | Anywhere on the legs | Typically, in deep veins, often in the calf or thigh |
| Healing Process | Heals on its own within weeks | Requires medical attention; may not resolve on its own |
What Does a Blood Clot in the Calf Look Like?
A blood clot in the calf, a common site for DVT, can make the area swollen, painful, and warm. Unlike a bruise, it might not show color changes but causes discomfort and pain, mainly when walking or standing.
Blood Clot vs. Bruise on Thigh
On the thigh, both bruises and blood clots can happen. A bruise is from trauma and shows color changes over time. A blood clot in the thigh, being deeper, might not be seen right away, but it causes pain, swelling, and tenderness.
It’s vital to tell them apart, as a blood clot can be deadly if it breaks loose and goes to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
Timeline: How Bruises and Blood Clots Progress
Knowing how bruises and blood clots change over time is key. Both involve blood issues, but they heal differently.
Bruise Healing Process and Color Changes
A bruise changes color as it heals. It starts red or purple, then goes through blue, green, yellow, and brown before fading. This shows the body’s healing work.
- Initial Stage: Red or purple due to fresh blood
- Healing Stage: Blue or black as blood oxygen levels decrease
- Resolution Stage: Green or yellow as biliverdin and bilirubin are produced
- Final Stage: Brown before complete resolution
Blood Clot Development and Resolution
Blood clots form and dissolve at different rates. They can dissolve on their own or need medical help to avoid serious problems.
The body’s fibrinolytic system breaks down clots. This process depends on the clot size, health conditions, and treatment.
When Healing Doesn’t Follow the Expected Pattern
Sometimes, bruises or blood clots don’t heal as expected. Unusual changes in bruises or persistent clots need medical check-ups.
Watch for signs like increased pain, swelling, or trouble moving. Early signs mean quick medical help.
Common Confusion Points: DVT or Bruise?
Distinguishing between DVT and bruises can be tricky. Both can show up in the legs, confusing. This makes it hard for people to know what they have.
Does a Blood Clot Cause Bruising?
A blood clot, like in DVT, doesn’t directly cause bruising. But it can cause swelling and inflammation. This might look like bruising. Bruising happens when blood vessels are damaged and blood leaks into the tissue. This is different from how a blood clot forms.
Bruising on Leg vs. Blood Clot Symptoms
Bruising and blood clots in the leg might look similar at first. But they have clear differences. Bruising shows up as discoloration that changes color as it heals. Blood clots, on the other hand, cause pain, swelling, and warmth.
| Symptom | Bruising on Lethe g | Blood Clot (DVT) |
| Primary Characteristic | Discoloration | Pain, Swelling, Warmth |
| Color Change | Changes color as it heals (blue, green, yellow) | No specific color change |
| Pain | Typically tender to the touch | Pain or aching, often persistent |
When Conditions Coexist
Sometimes, bruising and blood clots can happen together, like after a leg injury. It’s important to see a doctor if symptoms don’t go away or get worse. Blood clots need quick treatment.
Knowing the difference between DVT and bruising is key to the right treatment. If you’re unsure, talk to a doctor. They can figure out what’s going on.
Diagnostic Approaches: How Medical Professionals Tell the Difference
Doctors use many tools to tell if it’s a bruise or a blood clot. Bruises are usually okay, but blood clots can be deadly if not treated fast.
Clinical Assessment Techniques
First, doctors take a detailed medical history and do a physical check-up. They look for signs that show if it’s a bruise or a blood clot. They consider the area’s location, size, and color.
Key factors in clinical assessment include:
- Patient history, including recent injuries or surgeries
- Physical examination findings, such as swelling, redness, or warmth
- Presence of risk factors for blood clots, such as immobility or family history
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
Even with a good clinical check-up, tests are often needed to be sure. Tests like:
- Ultrasound: Helps find blood clots in the legs, known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- D-dimer test: A blood test that shows if a blood clot has dissolved. It helps rule out DVT or pulmonary embolism.
- Venography: An imaging test that uses dye to see blood clots in veins.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help is key. If you have severe pain, swelling, or trouble moving, see a doctor. Also, if you have sudden shortness of breath or chest pain, go to the emergency room right away.
Red flags that necessitate immediate medical evaluation include:
- Sudden onset of severe pain or swelling
- Warmth or redness in the affected limb
- Shortness of breath or chest pain
- Rapid heartbeat
Getting a diagnosis and treatment early can greatly improve outcomes for blood clot patients.
Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Managing bruises and blood clots needs different approaches. Bruises can be treated at home, but blood clots might need a doctor’s care.
Home Care for Bruises
Bruises heal with time. Using the RICE principle (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) helps. You can also take over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Medical Interventions for Blood Clots
Deep or large blood clots need a doctor’s help. Anticoagulation therapy is often used. It stops the clot from getting bigger and new ones from forming.
In some cases, thrombolytic therapy is used to break down the clot. People at risk might wear compression stockings or take anticoagulant meds.
Preventive Measures for Both Conditions
Preventing bruises and blood clots means living healthily. Exercise, eat well, and don’t sit too long. If you bruise easily, wear padding or protective clothes.
Know the signs of blood clots and see a doctor if you notice them.
Knowing your risks and acting early can help a lot. Regular health checks are also key.
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant About Vascular Health
It’s important to know the difference between bruises and blood clots for good vascular health. Both can look similar, but knowing the difference can save lives. If you think you have a blood clot, get help fast.
Bruises happen when blood leaks into tissue after injury. Blood clots form when blood thickens in a vessel. If a clot moves to the lungs or brain, it’s very dangerous.
Knowing the signs of a blood clot can prevent big problems. Regular health checks and a healthy lifestyle are key. If you’re worried about a bruise or think you have a clot, see a doctor.
Being informed about vascular health can lower the risk of serious issues. By understanding the differences and taking action, you can keep your blood vessels healthy. This protects your overall health and well-being.
FAQ
Does a blood clot feel like a bruise?
Blood clots and bruises can both be uncomfortable. But blood clots usually cause more pain and swelling. They also make the area warm.
What does a blood clot under the skin look like?
A blood clot under the skin can make the area swell, turn red, or change color. It might feel hard or sore to the touch. The skin could also be warm or sore.
Can blood clots look like bruises?
Yes, blood clots can look like bruises because they can cause similar signs, like discoloration or swelling. But, blood clots often have signs like warmth, tenderness, or pain that bruises don’t.
What is the difference between a bruise and a blood clot?
Bruises happen when blood leaks into soft tissues and are usually not serious. Blood clots form in blood vessels and can be more serious. Bruises usually heal on their own, but blood clots might need medical help.
How can I tell if I have a DVT or a bruise?
DVT can be told apart from a bruise by symptoms like constant pain, swelling, warmth, and redness in the limb. If you’re not sure, it’s best to see a doctor for a correct diagnosis.
Does a blood clot cause bruising?
Blood clots can cause some color changes, but they don’t usually bruise like injuries do. But, in some cases, a blood clot can cause bruising or skin color changes.
What are the risk factors for developing blood clots?
Blood clot risks include being immobile, having surgery, trauma, cancer, or having genetic conditions. Age, being overweight, and certain health issues can also increase the risk.
How are bruises and blood clots diagnosed?
Doctors use a mix of clinical checks, imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans, and blood tests to diagnose bruises and blood clots.
What are the treatment options for blood clots?
Blood clot treatment usually includes anticoagulant drugs, compression stockings, and sometimes thrombolytic therapy or surgery.
How can I prevent blood clots?
To prevent blood clots, stay active, keep a healthy weight, avoid sitting or standing for too long, and manage any health conditions.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023). Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Retrieved October 16, 2025, from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/facts.html




































