Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
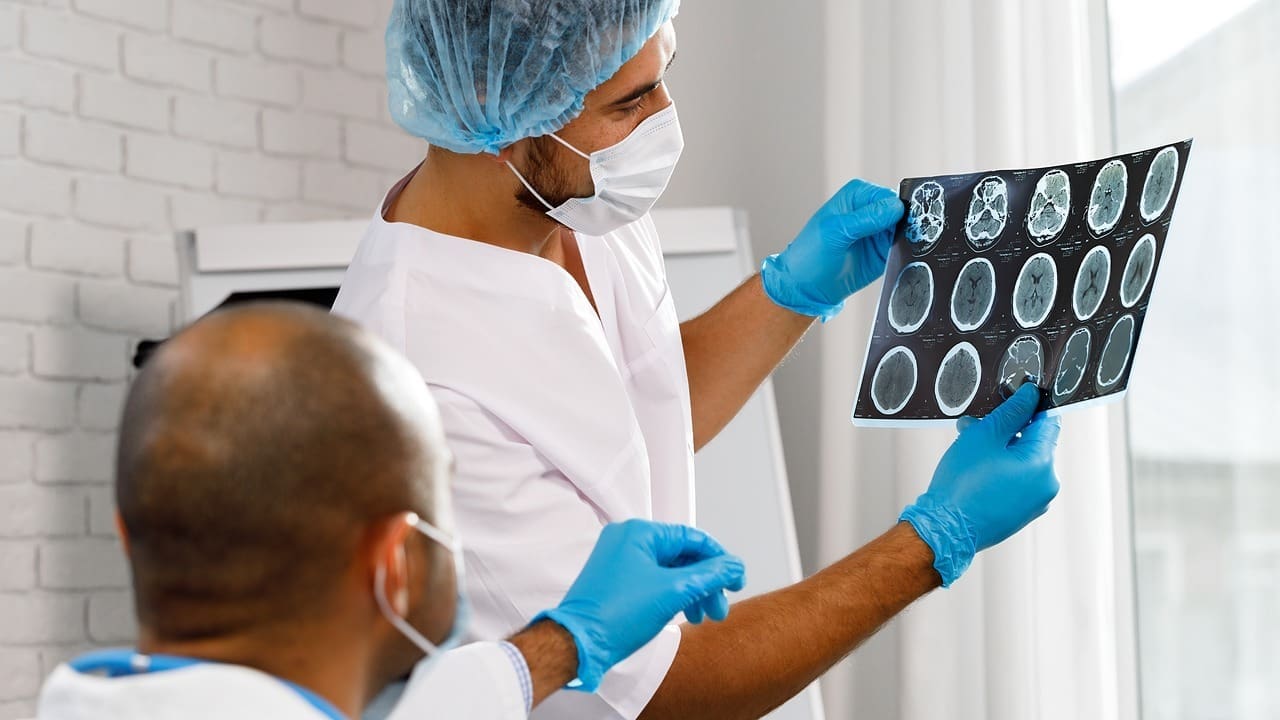
Having brain surgery is scary, and dealing with cerebral edema later is a big challenge for patients and their families.
At Liv Hospital, we put your care and safety first. We give you clear, evidence-based info and top-notch treatment. This way, you can focus on getting better with confidence. Cerebral edema is a common issue after brain surgery. It happens when fluid builds up in brain tissue.
Knowing how long cerebral edema lasts and how to treat it is key for a smooth recovery. Our team is dedicated to giving you the best care and support every step of the way.
Neurosurgery can cause cerebral edema, a serious brain condition. It leads to brain swelling and high pressure. This can greatly affect how well a patient recovers.
Cerebral edema is when the brain swells due to too much fluid. This swelling puts pressure on the brain, which can harm it. Cerebral edema is a serious issue that can happen after brain surgery.
The body’s response to injury after surgery can cause inflammation. This leads to fluid buildup in the brain. Understanding this process is key to treating cerebral edema well.
Cerebral edema can slow down recovery. High pressure in the brain can cause headaches, nausea, and problems with thinking. The table below shows how cerebral edema can affect recovery.
| Symptom | Impact on Recovery |
|---|---|
| Headaches | Increased discomfort and pain |
| Nausea and Vomiting | Nutritional deficiencies and dehydration |
| Cognitive Disturbances | Delayed cognitive recovery and rehabilitation |
Knowing about cerebral edema helps doctors create better treatment plans. This can improve patient outcomes.
It’s important to know why brain swelling happens after surgery. This swelling, or cerebral edema, is a possible side effect. We’ll look at what causes it.
Surgery can hurt the brain and cause swelling. The body reacts to this injury by releasing chemicals. These chemicals can make the brain swell.
Some health issues can make swelling more likely after surgery. These include high blood pressure, diabetes, and past brain injuries. We watch these patients closely to lower the risk of swelling.
The type and size of surgery also matter. More complex surgeries or those in bigger areas of the brain carry a higher risk. We carefully plan surgeries to weigh the benefits against the risks.
Knowing these factors helps us manage and reduce the risk of swelling. This way, we can give our patients the best care possible.
It’s important to know the signs of brain swelling after surgery. This knowledge helps get the right treatment quickly. Look out for physical, mental, and brain signs that might show swelling.
Physical signs often show first. Headaches can range from mild to severe. They might be with nausea and vomiting, which can lead to dehydration and imbalance of salts.
Watch how often and how bad these symptoms are. If headaches get worse or if you keep vomiting, get help right away.
Brain swelling can also show in how you think and move. You might feel confused, disoriented, or have trouble focusing. Speech difficulties, like slurred words or trouble speaking, can happen too.
These signs are serious because they might mean your brain is under too much pressure. Keep an eye on them and tell your doctor if they change.
Changes in vision, like blurry or double vision, can be a sign. You might also feel numbness, tingling, or weakness in your body.
Telling normal recovery symptoms from serious ones can be hard. The main thing is to watch how symptoms get worse or better.
| Symptom | Normal Recovery | Concerning Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Headaches | Mild, manageable with medication | Severe, worsening over time |
| Nausea/Vomiting | Occasional, resolves with medication | Persistent, leading to dehydration |
| Confusion | Mild, improves with rest | Severe, worsening over time |
Knowing the difference and talking to your doctor can help you recover safely and smoothly.
Brain swelling after brain surgery can last differently for everyone. It depends on many things. Knowing how long swelling usually lasts and what affects it can help with recovery.
In the first days after surgery, some swelling is normal. This time is very important because the body reacts to the surgery. Patients are watched closely in the ICU to handle any problems.
When patients move from the ICU to a regular room, they start to feel better. In the early recovery phase, swelling usually starts to go down. But, how fast it goes down depends on health and the surgery.
For many, recovery takes longer than two weeks. The longer recovery, lasting 2 to 8 weeks, sees symptoms slowly get better. Age, health, and surgery complexity affect how long this takes.
Many things can change how long swelling lasts after surgery. Knowing these can help make recovery plans better for each person.
Older people or those with health problems might take longer to recover. Younger or healthier people usually get better faster.
The type and where the surgery is done also matter. More complex or critical surgeries can mean longer swelling and recovery.
| Recovery Phase | Typical Duration | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Post-Operative | 1-3 Days | Expected swelling, close monitoring in ICU |
| Early Recovery | 4-14 Days | Swelling begins to subside, symptom management |
| Extended Recovery | 2-8 Weeks | Gradual improvement, influenced by age, health, and surgical complexity |
Knowing the usual recovery time and what affects it helps patients and caregivers. It’s key to follow doctor’s advice and report any worries to ensure the best recovery.
Managing cerebral edema after brain surgery is key for a good recovery. We use many treatments to lessen swelling, ease symptoms, and help the body heal.
Corticosteroids help reduce brain inflammation and swelling. Medications like dexamethasone are very effective. “Corticosteroids have been a cornerstone in the management of cerebral edema, providing significant relief to patients,” say doctors.
Diuretics and osmotic agents, like mannitol, help remove brain fluid. They increase urine production to lessen brain fluid and swelling. We watch patients closely to make sure these treatments work well and adjust them as needed.
Managing pain is vital for brain surgery recovery. We use different methods, including medicines and other treatments, to reduce pain. This helps patients feel better and can also lessen swelling.
It’s important to check how well treatments work for cerebral edema. We watch patients’ symptoms, imaging, and other factors to see if treatments are effective. This helps us adjust treatments for better results.
By using these treatments and watching how they work, we can manage cerebral edema well. This helps patients recover better from brain surgery.
Surgical treatments are key for severe brain swelling that doesn’t get better with other treatments. When brain swelling is life-threatening, surgery is considered. It helps relieve pressure on the brain and prevent damage.
A decompressive craniectomy removes part of the skull. It lets the brain expand and relieve swelling pressure. This surgery can be lifesaving in severe cases. We decide if it’s needed based on each case.
Ventricular drainage uses a catheter in the brain’s ventricles to drain fluid. It reduces pressure and lets us monitor it closely. This helps us adjust treatments as needed.
Surgery is needed when brain swelling puts too much pressure on the brain. This can cause serious problems or even be life-threatening. We watch patients closely for signs that surgery is needed.
It’s important to know the emergency signs that need quick medical help. These include sudden bad neurological symptoms, severe headaches, vomiting, or changes in consciousness. If you see these signs, get medical help right away.
Proper care at home is key to recovering well after a craniotomy. It’s important to know the basics of home care. This helps avoid problems and makes recovery smoother.
It’s vital to take medications as directed to manage swelling and pain. Use reminders or a pill box to stay on schedule. Knowing why you take each medicine and its side effects is also important.
Limiting activities helps prevent injury and swelling. Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard work. Also, keep your head elevated to reduce swelling. “Rest and recovery are just as important as the surgery itself,” says experts.
Drinking enough water and eating well are essential for healing. Eat foods full of fruits, veggies, and proteins. A healthy body heals faster from surgery.
Make your home recovery-friendly. Keep it clean, simple, and comfy. Having things you need close by can help you recover faster.
Knowing the signs of complications after brain surgery is key to a good recovery. It’s important to know when to get medical help. This ensures the best outcome for you.
Some symptoms after brain surgery need immediate help. These include:
If you notice any of these, call your doctor right away.
Follow-up appointments are vital for post-surgical care. To get the most from these visits, ask:
Having questions ready ensures you get the right guidance for a smooth recovery.
Keeping a record of your symptoms and any changes is very helpful. This includes:
Telling your healthcare provider about these changes during follow-ups can greatly impact your care plan.
The long-term outlook after brain surgery depends on many factors, like how bad the brain swelling is. Patients and their families want to know what to expect during recovery.
The recovery path after brain surgery changes based on the surgery’s extent, the patient’s health, and post-op care. Patients usually see slow but steady improvement over weeks to months.
Severe brain swelling can cause lasting issues. These include cognitive problems, physical disabilities, and emotional changes. How severe and lasting these effects are can vary greatly.
Rehabilitation is key to recovery. Effective rehabilitation strategies include physical, occupational, and speech therapy. These are customized to meet each patient’s needs.
Cognitive and physical therapy are essential in rehab. They help patients regain lost functions and adjust to any lasting changes.
| Therapy Type | Focus | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Motor skills and mobility | Improved strength, balance, and coordination |
| Cognitive Therapy | Cognitive functions and memory | Enhanced cognitive abilities and memory recall |
| Occupational Therapy | Daily living activities | Increased independence in daily tasks |
Recovering from brain surgery is a complex journey. Understanding brain swelling is key to a good outcome. We’ve covered the causes, symptoms, and treatments for swelling after neurosurgery.
By spotting the signs of swelling and managing it well, patients can avoid complications. This helps them recover better.
After brain surgery, sticking to your treatment plan is vital. Make sure to go to all follow-up appointments. Tell your doctor about any changes in your health.
For more details on recovering from brain surgery, check out Cancer Research UK. They offer great guidance and support.
With the right care and support, many patients regain their strength. They can even go back to their usual activities. We’re dedicated to top-notch healthcare for international patients. If you have questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare team.
Cerebral edema, or brain swelling, happens when too much fluid builds up in the brain. This causes the brain to swell. It can happen after brain surgery due to the surgery itself, inflammation, or other reasons related to the surgery.
Brain swelling after surgery can last different lengths of time. It usually starts right after surgery (1-3 days). Then, it can last a bit longer (4-14 days). Sometimes, it can even last up to 8 weeks.
Symptoms include headaches, nausea, and vomiting. You might also feel confused, have trouble speaking, see things differently, or feel numb in certain areas.
Doctors might use medicine like corticosteroids or diuretics to treat it. They might also use pain management. In serious cases, surgery like decompressive craniectomy or ventricular drainage might be needed.
Risks include the surgery itself, any health problems you had before, and how big and complex the surgery was.
At home, follow your medicine schedule and rest when needed. Stay in the best position, drink plenty of water, and eat well. Also, make your home comfortable for recovery.
Call your doctor if you have severe headaches, get more confused, have trouble speaking, see things differently, or notice other serious symptoms.
Recovery times vary, but most people get better in a few weeks to months. Severe swelling might cause lasting problems. You might need therapy to help with recovery.
Your doctor will check how well you’re doing with regular visits. They’ll watch for symptom changes and might do more tests to see if the swelling is getting better.
Cerebral edema can get worse around 48-72 hours after surgery. But, it can happen at different times based on your situation and the surgery.
Symptoms include headaches, nausea, vomiting, confusion, trouble speaking, vision changes, and feeling numb in certain areas.
Doctors might use medicine like corticosteroids or diuretics. In serious cases, surgery like decompressive craniectomy or ventricular drainage might be needed.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!