Childhood soft tissue sarcomas are rare and often misunderstood cancers. They can look like harmless lumps. This makes it very important to spot them early for the best treatment. Discover childhood soft tissue sarcoma pictures and how to recognize early signs.
At Liv Hospital, we know how critical it is to give accurate diagnoses and caring support. We help families dealing with these tough conditions.
These cancers make up about 7 percent of tumors in kids around the world. Childhood soft tissue sarcomas need expert evaluation. We aim to offer top-notch healthcare and support for families from abroad.
We are here to help families understand their child’s health better. Our team uses advanced diagnostic imaging and focuses on patient care. This way, families can make informed choices about their child’s health.
Key Takeaways
- Childhood soft tissue sarcomas are rare and often resemble harmless lumps.
- Early recognition is key for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced diagnostic imaging and patient-centered care.
- Our team is dedicated to delivering world-class healthcare for international patients.
- We provide full support for families facing complex conditions.
What Are Childhood Soft Tissue Sarcomas?
Childhood soft tissue sarcomas are a type of cancer that affects children. They come from the soft tissues in the body. These cancers are complex and can start in different parts of the body.
Definition and Prevalence
These cancers start from cells that turn into muscles, fat, and blood vessels. They are a big concern in treating children with cancer. About 7% of all childhood cancers are soft tissue sarcomas.
Studies show that about 11 cases of soft tissue sarcomas happen every year for every million kids under 20. This shows how important it is to catch these cancers early.
Common Types and Classifications
There are many types of soft tissue sarcomas in children. The most common ones are:
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Synovial sarcoma
- Fibrosarcoma
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
Each type looks different under a microscope and grows at different rates. Knowing the type helps doctors choose the best treatment.
| Type of Sarcoma | Common Locations | Typical Age Group |
| Rhabdomyosarcoma | Head and neck, genitourinary tract | 0-14 years |
| Synovial Sarcoma | Extremities | 15-19 years |
| Fibrosarcoma | Extremities, trunk | 0-4 years |
Risk Factors and Causes
Many things can increase a child’s chance of getting soft tissue sarcoma. These include genes, radiation, and viruses.
Genetic predispositions are a big factor. Kids with certain conditions like Li-Fraumeni syndrome or neurofibromatosis type 1 are at higher risk.
Exposure to radiation is also a risk. This can be from past cancer treatments or environmental sources.
Knowing about these risks helps us find and treat these cancers early. Early detection can greatly improve a child’s chances of beating the disease.
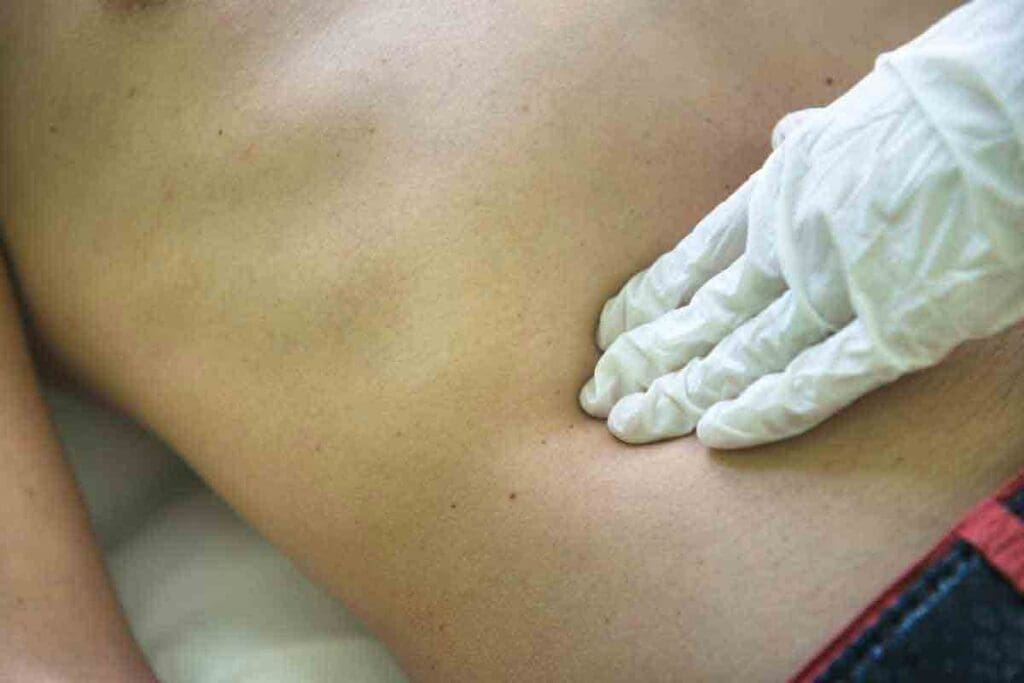
Recognizing the Warning Signs of Childhood Sarcomas
Spotting the early signs of childhood sarcomas can greatly improve treatment chances. These cancers often show up as a painless lump or swelling. It’s easy to miss them, but knowing the signs can help catch them early.
Primary Physical Symptoms
The most common sign is a painless mass or swelling. This can happen anywhere in the body, like the arms, legs, or head. The lump might feel firm or soft and grow fast.
- A painless lump or swelling
- Swelling or pain in the affected limb
- Limping if the sarcoma is located in the leg
Some sarcomas can cause pain or discomfort. This happens if they press on nerves or organs nearby.
Systemic Manifestations
Some kids with sarcomas might also have systemic symptoms. These include:
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
These signs can mean the cancer has spread or is affecting the body’s health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If a child has a persistent or growing lump, swelling, or pain, get medical help right away. Early treatment can make a big difference.
| Symptom | Action |
| Persistent or growing lump | Consult a pediatrician or oncologist |
| Unexplained pain or swelling | Schedule a medical evaluation |
| Systemic symptoms like fever or weight loss | Seek immediate medical attention |
Knowing the warning signs and acting fast is key. Parents and caregivers can help ensure early detection and effective treatment of childhood sarcomas.
Diagnostic Process for Soft Tissue Sarcomas in Children
Identifying soft tissue sarcomas in kids is a detailed process. It’s complex and can be tough for families.
Initial Medical Assessment
The first step is a thorough medical check-up. A doctor will ask about the child’s health history and do a physical exam. This helps spot any issues that need more looking into.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Imaging is key in finding soft tissue sarcomas. We use MRI with contrast and ultrasound to see the tumor and the area around it. These tools help tell if the tumor is cancerous or not.
Biopsy and Pathological Examination
To get a tumor sample, a biopsy is done. Then, the tissue is checked under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells. This step is important to confirm if it’s a soft tissue sarcoma.
| Diagnostic Step | Purpose | Key Findings |
| Initial Medical Assessment | Gather medical history and perform physical examination | Identify abnormalities |
| Advanced Imaging Techniques | Visualize tumor and surrounding tissues | Distinguish malignant from benign lesions |
| Biopsy and Pathological Examination | Examine tissue sample for cancer cells | Confirm diagnosis of soft tissue sarcoma |
By using these steps, we can accurately find and treat childhood soft tissue sarcomas. Our goal is to give families the best care and support during this time.
Differentiating Sarcomas from Benign Conditions
Benign masses are common in kids, making it key to spot soft tissue sarcomas right. It’s hard to tell these benign conditions from the bad ones.
Common Benign Masses in Children
Kids often have benign masses that worry parents and doctors. These include lipomas, hemangiomas, and swollen lymph nodes. These grow slowly and don’t cause other symptoms.
Lipomas are fatty tumors that feel soft and move easily. Hemangiomas look like red or purple spots on the skin. Swollen lymph nodes can happen for many reasons, not just cancer.
Key Distinguishing Features
Doctors look for certain signs to tell sarcomas from benign conditions. Sarcomas grow fast and can’t move as much. They also might make you feel sick, tired, or lose weight.
Ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans help a lot in checking these masses. Sarcomas look different on scans because of dead or bleeding areas.
Diagnostic Challenges
Even with better imaging, finding sarcomas is hard. Some sarcomas look like benign things on scans, and some benign ones might look bad.
A biopsy is usually needed to know for sure. It lets doctors look at the tissue closely to tell if it’s cancer or not.
| Characteristics | Benign Masses | Sarcomas |
| Growth Rate | Slow | Rapid |
| Systemic Symptoms | Absent | Present (e.g., fever, weight loss) |
| Imaging Appearance | Homogeneous | Heterogeneous (necrosis, hemorrhage) |
Knowing the differences is key for right diagnosis and treatment of childhood sarcomas. Doctors use what they see, scan results, and tissue tests to help patients.
Childhood Soft Tissue Sarcoma Pictures: A Visual Guide
Medical imaging is key in diagnosing and treating childhood soft tissue sarcoma. It’s important to understand these images well. This helps doctors know how far the disease has spread and how to treat it.
Understanding Medical Imaging of Sarcomas
Techniques like MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound are used to get important info. They show the size, location, and details of soft tissue sarcomas in kids. These images help doctors plan surgeries and check if the cancer has spread.
The main imaging tools for soft tissue sarcomas are:
- MRI: Gives detailed views of soft tissues, showing tumor boundaries and nearby structures.
- CT scans: Shows tumor size and location, and if it’s touching bones.
- Ultrasound: Good for first checks and guiding biopsies.
How to Interpret Diagnostic Images
Understanding diagnostic images is important. Doctors look at tumor size, shape, and how it looks on different scans. For example, some sarcomas might look mixed on MRI because of dead tissue or bleeding.
Important things to notice in images are:
- Where the tumor is and how it’s near important parts.
- How big the tumor is and how far it’s spread.
- What it looks like on MRI or CT scans.
- If there’s dead tissue or bleeding inside the tumor.
The Role of Visual Assessment in Treatment Planning
Looking at images is vital for planning treatment. It helps decide if surgery is possible, if radiation is needed, and if chemo is required. It also helps track how well the treatment is working and if the cancer comes back.
By using info from different scans, doctors can make a treatment plan that fits each child’s needs.
Picture 1: Rhabdomyosarcoma Imaging Characteristics
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a common soft tissue sarcoma in kids. It has unique imaging features. Accurate diagnosis is key, using MRI and CT scans.
MRI and CT Appearances
Rhabdomyosarcoma looks like a heterogeneous mass on scans. MRI shows it as low to intermediate signal intensity on T1 and high signal intensity on T2. CT scans show a soft tissue mass that changes after contrast.
Common Locations and Growth Patterns
Rhabdomyosarcoma can be found in the head and neck, genitourinary tract, and extremities. It grows fast and can spread to nearby tissues. Knowing where it grows helps doctors plan treatment.
Case Examples and Visual Identifiers
Many case studies show how rhabdomyosarcoma can look different. For example, a kid with a head and neck tumor had a big, mixed mass on MRI. This helps doctors tell it apart from other tumors.
Picture 2: Synovial Sarcoma Visual Presentation
It’s key to know how synovial sarcoma looks to diagnose it. This rare cancer often shows up near joints. This makes it hard to spot because it looks like other joint problems.
Typical Imaging Features
Synovial sarcoma has unique signs on scans. MRI shows it as a clear mass with mixed signals. Contrast makes its blood flow stand out.
CT scans add more details. They show if the tumor has calcium and how it affects bones. These details help doctors plan surgery.
Anatomical Distribution Patterns
Synovial sarcoma mostly happens in the arms and legs. It’s most common near the knee, ankle, and elbow. But it can also appear in the chest and head and neck, though that’s rarer.
| Location | Frequency | Common Imaging Features |
| Lower Extremity | 40% | Heterogeneous signal on MRI, possible calcification |
| Upper Extremity | 30% | Well-defined margins, variable signal intensity |
| Trunk and Others | 30% | Cystic components, enhancement with contrast |
Distinguishing from Joint-Related Conditions
It’s important to tell synovial sarcoma apart from other joint issues or soft tissue tumors. Doctors use imaging and clinical signs to make this distinction. Things like calcification and how the tumor reacts to contrast help.
“The diagnosis of synovial sarcoma relies heavily on a combination of clinical suspicion, imaging findings, and histopathological confirmation.” –
Expert Opinion
Knowing how synovial sarcoma looks and where it usually shows up helps doctors make better diagnoses. This leads to more effective treatment plans.
Picture 3: Fibrosarcoma and Dermatofibrosarcoma Imaging
Fibrosarcoma and dermatofibrosarcoma are rare in kids. They have unique features that show up on scans. This helps doctors make treatment plans.
Characteristic Appearance on Scans
These tumors look different on scans. MRI shows them as clear masses with varying signals. CT scans spot any bone or calcification issues.
It’s key to tell them apart from other tumors. For example, dermatofibrosarcoma looks like a skin issue with deep subcutaneous involvement.
Skin and Subcutaneous Manifestations
Both fibrosarcoma and dermatofibrosarcoma affect the skin and just below it. Dermatofibrosarcoma often bulges out because it spreads under the skin.
Doctors use scans and physical checks to see how deep it goes. Ultrasound is great for looking at surface issues.
Growth Pattern Visualization
Scans are important for seeing how these tumors grow. MRI is best for checking how they touch nearby tissues.
Knowing how they grow helps doctors plan treatments. Functional MRI shows how blood flows and how aggressive the tumor is.
Picture 4: Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) are aggressive growths that start from the sheath of nerves. They are known for their complex imaging and hard-to-spot diagnosis.
Neurogenic Tumor Imaging Features
MPNSTs have specific imaging signs. They grow along nerves and may make the nerve look bigger. On MRI, they show up as mixed masses with different signals on T1 and T2 images.
Key imaging features include:
- Heterogeneous signal intensity on MRI
- Fusiform enlargement of the affected nerve
- Variable enhancement pattern on contrast administration
Association with Neurofibromatosis
MPNSTs are often linked to neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). People with NF1 are more likely to get MPNSTs from their neurofibromas. “The presence of NF1 significantly increases the risk of malignant transformation,” experts say.
“Early detection of MPNSTs in NF1 patients is key for better outcomes.”
Diagnostic Imaging Challenges
It’s hard to spot MPNSTs because they look different on scans and can be mistaken for benign tumors. New imaging methods like PET/CT and diffusion-weighted MRI help tell them apart.
We suggest a detailed imaging plan to correctly diagnose and stage MPNSTs. This is vital for planning treatment.
Picture 5: Vascular Sarcomas and Hemangiopericytoma
It’s important to know how to spot vascular sarcomas and hemangiopericytoma on images. These tumors have complex blood vessels. This is key for making the right diagnosis and treatment plan.
Vascular Pattern Recognition
Vascular sarcomas and hemangiopericytoma have unique blood vessel patterns. These patterns are seen through advanced imaging. They show prominent vascularity, which helps tell them apart from other soft tissue sarcomas.
Imaging studies, like MRI and CT scans, are used to analyze these patterns. They give detailed views of the tumor’s blood vessels.
Contrast Enhancement Characteristics
Vascular sarcomas and hemangiopericytoma stand out because of how they react to contrast. They show intense enhancement on contrast-enhanced images. This is because they have a lot of blood vessels.
The way they enhance can vary. But often, they show uneven enhancement with areas of dead tissue or cysts. This helps doctors understand how aggressive the tumor is and plan treatment.
Differentiation from Benign Vascular Anomalies
Telling vascular sarcomas and hemangiopericytoma apart from benign vascular anomalies is key. While benign ones might look similar, there are important differences.
- Vascular sarcomas and hemangiopericytoma have more irregular edges and uneven enhancement.
- Benign vascular anomalies usually don’t show the aggressive signs seen in malignant tumors, like a lot of dead tissue or spreading into nearby tissues.
Getting the diagnosis right is vital. It ensures patients get the right treatment. This could be surgery for cancer or watchful waiting for benign conditions.
Picture 6: Undifferentiated and Rare Sarcoma Types
Childhood soft tissue sarcoma pictures, like those of undifferentiated and rare types, need expert eyes to guide treatment. These complex cases often pose challenges due to their unclear imaging features.
Imaging Features of Challenging Cases
Undifferentiated and rare sarcomas show unclear imaging signs, making them hard to tell apart from other soft tissue tumors. MRI and CT scans are key in studying these tumors.
Radiological Red Flags
Some imaging signs can hint at cancer, like fast growth, irregular edges, and mixed enhancement. Spotting these signs is key for quick further checks.
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Ambiguous Presentations
When first images are unclear, advanced methods like dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI or PET-CT can help. These methods check tumor blood flow, metabolism, and size.
| Imaging Technique | Features | Benefits |
| MRI | High soft tissue resolution, ability to assess tumor extent | Detailed anatomical information |
| CT Scan | Rapid acquisition, good for assessing calcifications and bone involvement | Quick and widely available |
| PET-CT | Assesses metabolic activity of tumors | Helps in identifying active tumor parts |
By mixing clinical data with advanced imaging, we can better diagnose and treat undifferentiated and rare childhood sarcomas.
Conclusion
It’s key to understand childhood soft tissue sarcoma pictures for early detection and treatment. We’ve looked at different types of soft tissue sarcomas and their imaging features. Visual assessment is vital for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Early detection greatly improves outcomes for kids with soft tissue sarcoma cancer. Pictures help educate healthcare teams and families about warning signs and diagnostic features. This knowledge is essential.
At Liv Hospital, we aim to provide top-notch healthcare for international patients. Our team uses advanced imaging and treatments to care for kids with soft tissue sarcomas. We’re dedicated to the best care possible.
By spotting signs and symptoms of childhood sarcomas and using imaging well, we can better diagnose and treat these young patients. Together, we can make a difference in their health.
FAQ
What are childhood soft tissue sarcomas?
Childhood soft tissue sarcomas are cancers that start in soft body tissues. These include muscles, tendons, and connective tissue. Liv Hospital offers full care for these cancers.
What are the common types of childhood soft tissue sarcomas?
Common types are rhabdomyosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, fibrosarcoma, and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Knowing the type is key for the right treatment.
What are the symptoms of childhood soft tissue sarcomas?
Symptoms include a painless lump or swelling, pain or tenderness, and systemic symptoms like fever or weight loss. Spotting these early is vital for quick medical help.
How are childhood soft tissue sarcomas diagnosed?
Diagnosis uses medical assessment, imaging like MRI and CT scans, and biopsy. Liv Hospital uses top-notch tools for accurate diagnosis.
How can sarcomas be differentiated from benign conditions?
We use diagnostic imaging and understanding key features to tell sarcomas from benign masses. Our team at Liv Hospital is skilled in making this distinction.
What is the role of imaging in diagnosing childhood soft tissue sarcomas?
Imaging is key in diagnosing and planning treatment for childhood soft tissue sarcomas. MRI and CT scans help us see the tumor’s extent and characteristics.
Can you provide examples of pictures of soft tissue sarcoma cancer?
We show detailed imaging examples, like rhabdomyosarcoma and synovial sarcoma. These help understand their visual characteristics and aid in diagnosis.
How does Liv Hospital approach the treatment of childhood soft tissue sarcomas?
Liv Hospital offers world-class healthcare with a detailed approach. This includes advanced diagnostics and personalized treatment plans for international patients.
What is the importance of early recognition of childhood sarcomas?
Early recognition is vital for effective treatment and better outcomes. We stress the need for quick medical attention if symptoms persist or get worse.
Are there any specific risk factors for childhood soft tissue sarcomas?
Certain genetic conditions and radiation exposure are risk factors. Knowing these helps in early detection and prevention.
Reference
Esnaola, N. F., Rubin, B. P., & Mayerson, J. (2022). Incidence and survival of pediatric soft tissue sarcomas. Frontiers in Oncology, 12, 890040. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4296854/



































