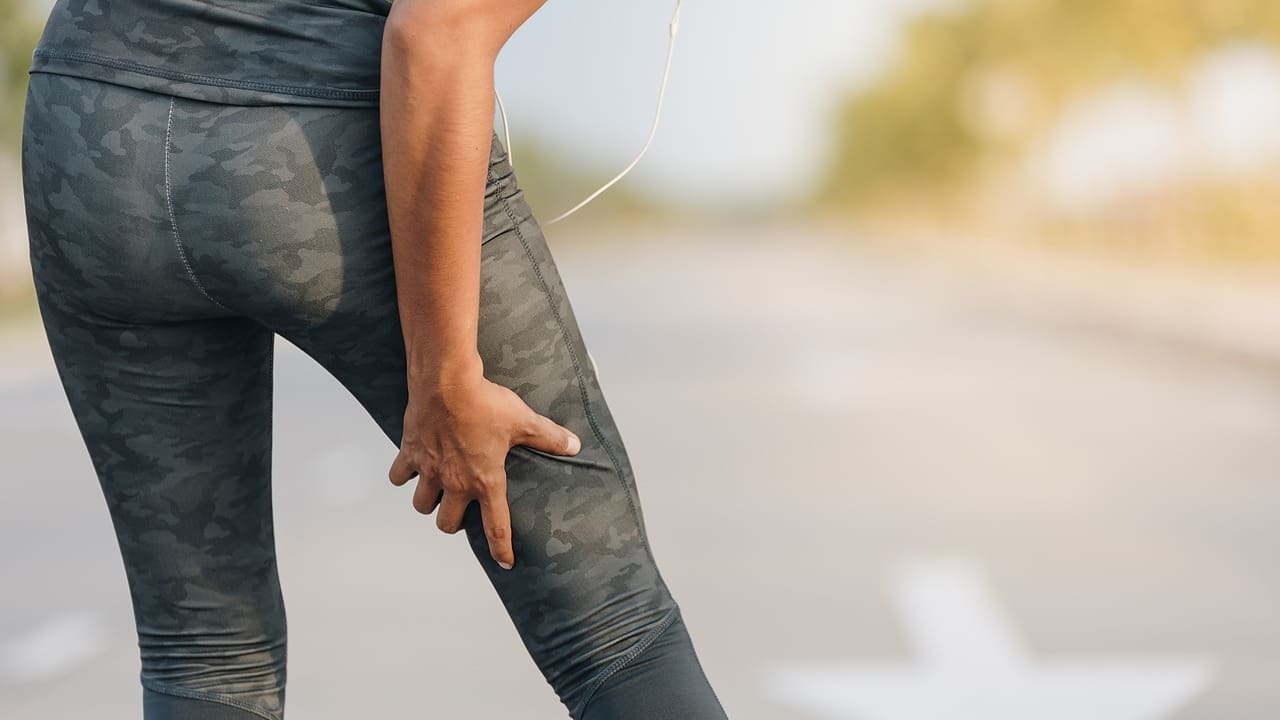
Muscle aches in the lower legs can really hurt, affecting up to 30 percent of people who stand or walk a lot. At Liv Hospital, we understand the impact of back leg muscle pain on daily life. We’re committed to providing top-notch, multidisciplinary care.
Persistent discomfort in the back of the legs is a big worry for athletes and older adults. We’ll look into the common causes and share quick ways to feel better.
Knowing what causes muscle pain is key to treating it well. We’ll talk about the main reasons for back leg muscle pain. Then, we’ll share simple tips to ease the pain.
Key Takeaways
- Muscle aches in lower legs are common among people who stand or walk for long periods.
- Back leg muscle pain can affect daily activity and overall well-being.
- Understanding the causes is key for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers multidisciplinary care for international patients.
- Effective relief tips will be discussed to alleviate discomfort.
Understanding Back of Leg Muscle Pain

Pain in the back of the leg can be scary. Knowing the symptoms is the first step to feeling better. Muscle pain in this area can really affect your daily life and how you feel overall.
Common Symptoms and Sensations
The symptoms of back of leg muscle pain can be different for everyone. You might feel sharp or dull pain, numbness, tingling, or muscle cramps. Some people also feel pain on the side of the lower leg or weakness in their leg.
Peripheral nerve entrapment can lead to pain and other feelings in the legs. It’s important to find out why you’re feeling this way.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Most back of leg muscle pain can be handled on your own. But, there are times when you need to see a doctor. If you have sudden, severe pain, swelling, or redness, or if walking is hard, get help right away.
Also, if your leg feels cold or pale, or if you’ve had deep vein thrombosis before, see a doctor fast.
It’s key to watch your symptoms and get help when you need it. This way, you can get the right diagnosis and treatment.
Anatomy of the Back of the Leg
To understand back of leg muscle pain, we need to look at its parts. The back of the leg, or posterior leg, has several important structures. These work together to help us move and support our body’s weight.
Major Muscle Groups
The main muscles in this area are the hamstrings. They include the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus muscles. These muscles help us bend our knee and straighten our hip. Strains or tears in these muscles are common causes of pain in the back of the leg.
Nerves and Blood Vessels
The nerves in the back of the leg come from the sciatic nerve. This nerve runs down the back of the thigh. The sciatic nerve can cause pain if it’s compressed or irritated. The femoral and popliteal arteries bring oxygenated blood to the muscles in this area.
Side and Lower Leg Anatomy
The side and lower leg anatomy also affects pain in this area. The peroneal muscles on the lateral side of the leg help with foot eversion. Issues here can cause pain on the side of the leg. Knowing these details helps us figure out where the pain comes from, whether it’s on the left, right, or elsewhere in the leg.
Cause #1: Hamstring Strains and Tears
Hamstring strains and tears are common causes of pain at the back of the leg. They affect athletes and non-athletes. These injuries happen when the hamstring muscles stretch too far or tear. The hamstring muscles are key for running, jumping, and climbing.
How Hamstring Injuries Occur
Hamstring injuries often happen during quick movements or sudden stops. Sports like soccer, basketball, and track and field are common causes. But, they can also happen during everyday activities if the muscle is stressed too much.
Things like not warming up enough, muscle imbalances, and past injuries can raise the risk of hamstring injuries.
Symptoms and Severity Levels
The symptoms of a hamstring strain or tear vary with the injury’s severity. Mild strains might cause a slight ache or tightness in the back of the leg. Severe tears can lead to sharp pain, swelling, and bruising.
In severe cases, there might be a pop or snap at injury time, followed by a lot of pain and trouble walking. If you have ongoing pain or severe symptoms, getting medical help is key to check for a complete hamstring tear.
Initial Treatment Approaches
First steps in treating hamstring strains and tears include reducing pain and swelling, helping the muscle heal, and getting back to normal. The RICE principle (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is often recommended first. Resting the leg, using ice, compression bandages, and elevating the leg can help.
Cause #2: Muscle Cramps and Spasms
The back of your legs can hurt a lot because of muscle cramps and spasms. These sudden muscle contractions are very painful. They worry many people.
Triggers for Leg Muscle Cramps
Many things can cause leg muscle cramps. Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances are common reasons. They mess with how muscles work.
- Dehydration
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Certain medications
- Overuse or strain
Nighttime Cramping
Nighttime cramping can really mess up your sleep. For tips on how to stop it, check out this page.
Immediate Relief Strategies
To ease muscle cramps, stretch the muscle, use heat or cold, and drink plenty of water. Stretching can help relax the muscle and stop the cramping.
Cause #3: Sciatica and Nerve Compression
Sciatica is a condition where nerves get compressed, causing pain in the back of the leg. It often needs medical help. We’ll look at how it affects the leg and what treatments are out there.
How Sciatica Affects the Back of the Leg
Sciatica happens when the sciatic nerve gets compressed or irritated. This can cause pain in the back of the leg. You might also feel numbness, tingling, or weakness.
Pain Running Down the Side of the Leg
Sciatica can also cause pain on the side of the leg. This is called radicular pain. The pain can be on either side, depending on the nerve root.
Knowing where the pain is helps doctors figure out what’s wrong.
Differentiating Nerve Pain from Muscle Pain
Telling nerve pain from muscle pain is key to treating it right. Nerve pain feels like shooting or burning. Muscle pain is more localized and aching.
We’ll work with doctors to find out what’s causing your pain.
Treatment Options for Nerve-Related Pain
Treating sciatica and nerve compression needs a few steps. This includes:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the back and improve flexibility.
- Pain Management: Medications to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Changes in daily activities to reduce strain on the back.
In some cases, treatments like steroid injections or surgery might be needed. They help relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve.
Cause #4: Overuse Injuries and Muscle Fatigue
Overuse injuries and muscle fatigue often cause back of leg pain. This is true for people who do a lot of physical activities. When we do too much exercise without resting, our muscles and tendons get strained. This leads to pain and discomfort.
Common Overuse Patterns
Running, cycling, and sports that involve a lot of kicking or jumping are common causes. These activities stress the muscles in the back of the legs, like the hamstrings and calf muscles.
Exercise-Related Muscle Soreness
Exercise can cause muscle soreness, known as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS). This soreness happens after doing something new or very hard. It usually affects the muscles used during the activity, like the hamstrings and calf muscles.
Why the Back of Legs Get Sore After Activity
The back of the legs get sore after activity because of muscle fiber tears and inflammation. Exercise causes small injuries to the muscles, leading to inflammation. This results in pain and stiffness.
Recovery Techniques
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) help with overuse injuries. Gentle stretching and foam rolling can also ease muscle soreness. Adding strength training and changing exercise routines can prevent future injuries.
| Recovery Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Rest | Avoid activities that aggravate the pain | Allows muscle repair |
| Ice | Apply ice packs to the affected area | Reduces inflammation and pain |
| Compression | Use compression bandages or sleeves | Helps reduce swelling |
| Elevation | Elevate the affected leg above heart level | Reduces swelling and promotes blood flow |
Cause #5: Vascular Conditions Affecting Leg Muscles
Vascular health plays a big role in leg muscle pain. It’s important to understand its impact. Vascular conditions can cause a lot of discomfort and pain in the back of our legs.
These conditions affect the blood vessels and circulation. They are key for muscle health.
Poor Circulation and Muscle Pain
Poor circulation is a common vascular condition. It can cause muscle pain in the legs. When muscles don’t get enough oxygen and nutrients, it leads to pain and discomfort.
Symptoms include aching, cramping, and fatigue. These symptoms are often felt after physical activity.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Warning Signs
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition. It causes a blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the legs. Warning signs include swelling, warmth, and redness in the affected leg.
Other signs are pain or tenderness. If you have these symptoms, seek medical help right away.
Left Side Leg Pain and Vascular Concerns
Pain on one side of the leg, like the left, can be due to vascular issues. While pain can happen on either side, some conditions may affect one leg more. It’s important to watch for any changes in pain and tell a healthcare professional.
Treatment for Vascular-Related Pain
Treatment for vascular-related leg pain varies by condition. For poor circulation, changes like exercise and quitting smoking can help. For DVT, anticoagulant medications are often used.
In some cases, more serious procedures may be needed. “Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in managing vascular conditions effectively,” says a healthcare expert. If you have persistent or severe leg pain, seek medical care.
Cause #6: Referred Pain from Lower Back Issues
Lower back problems can send pain to the legs, causing discomfort. This is called referred pain. It happens when lower back issues irritate nerves that go to the legs.
How Back Problems Cause Leg Pain
When the lower back is hurt, like by herniated discs or spinal stenosis, it can press on nerves. These nerves go to the legs and can cause pain, numbness, or tingling.
Common Back Conditions That Affect Legs
Several lower back conditions can lead to leg pain. These include:
- Herniated discs
- Spinal stenosis
- Degenerative disc disease
- Spondylolisthesis
These conditions can make pain go down one or both legs. They can also cause weakness or numbness.
Integrated Treatment Approaches
Treating leg pain from the back often means fixing the back problem first. This might include:
| Treatment Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Exercises to strengthen back and leg muscles |
| Medications | Pain relief and anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Posture correction, weight management |
By treating both the back and leg symptoms, we can offer full relief. This improves life quality greatly.
Cause #7: Compartment Syndrome and Pressure-Related Pain
Compartment syndrome happens when too much pressure builds up in the muscle compartments of the leg. This causes pain and other symptoms. It can really hurt your ability to move and your quality of life if not treated right.
Acute vs. Chronic Compartment Syndrome
There are two types of compartment syndrome: acute and chronic. Acute compartment syndrome is a serious emergency that needs quick help. It usually comes from a big injury, like a broken bone, and can cause lasting damage if not treated fast. Chronic compartment syndrome, or exertional compartment syndrome, happens when you exercise a lot and goes away when you rest.
Pain on Side of Lower Leg
Pain on the side of the lower leg is a common sign of compartment syndrome. This pain can be very strong and may also cause swelling and tightness. Sometimes, numbness or weakness can happen because of nerve pressure.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Some things can make you more likely to get compartment syndrome, like doing too much exercise, getting hurt, or having certain health issues. To prevent it, you can start exercising slowly, do warm-ups and cool-downs, and wear the right shoes.
When Surgery May Be Necessary
In very bad cases of compartment syndrome, like acute compartment syndrome, surgery might be needed. This surgery, called fasciotomy, cuts open the tight muscle compartment to let blood flow again.
Diagnosing the Source of Your Back of Leg Muscle Pain
Figuring out why your back of leg hurts involves a few steps. First, you’ll assess yourself, then get medical tests, and talk to doctors. We’ll walk you through each step to understand the process better.
Self-Assessment Techniques
Start by noticing when and how bad the pain is. See if anything makes it better or worse. Writing down your pain in a journal can help track these details.
Medical Tests and Procedures
Doctors might run tests to find out what’s causing your pain. These can include:
- MRI or CT scans to see muscle and nerve damage
- Electromyography (EMG) to check muscle function
- Blood tests to look for conditions like diabetes or artery disease
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| MRI or CT scans | Visualize muscle and nerve damage |
| Electromyography (EMG) | Assess muscle function |
| Blood tests | Check for underlying conditions |
Working with Healthcare Professionals
Getting help from doctors is key to finding out what’s wrong. Look for a specialist like an orthopedist or sports medicine doctor. They can understand your test results and give a clear diagnosis.
By doing self-assessment, getting medical tests, and talking to doctors, we can figure out why your back of leg hurts. Then, we can make a plan to fix it.
Quick Relief Tips for Back of Leg Pain
Finding quick relief from back of leg pain is key to staying active. When your legs hurt, it can really slow you down. Here, we’ll look at ways to ease this pain.
Immediate Pain Management Strategies
When your leg starts to hurt, stop what you’re doing right away. Rest and elevation can cut down on swelling. Also, try some gentle stretching to loosen up tight muscles.
- Stop activity immediately
- Elevate the affected leg
- Gentle stretching
Effective Stretches and Exercises
Some stretches and exercises can really help with back of leg pain. Hamstring stretches are great because they work on the muscles at the back of your thighs.
- Hamstring stretches
- Calf raises
- Leg press exercises
Over-the-Counter and Home Remedies
There are many remedies you can try at home or buy over the counter. These include:
Topical Treatments
Topical creams or gels with arnica or capsaicin can be applied to the skin. They help reduce pain.
Oral Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help with inflammation and pain.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Using heat or cold packs on the area can help. Cold is good for sudden injuries, while heat is better for ongoing pain.
By using these tips, you can quickly ease back of leg pain. This can also help prevent it from happening again.
Preventing Future Episodes of Back of Leg Muscle Pain
To stop back of leg muscle pain, you need to change your lifestyle, do specific exercises, and eat right. A good plan can lower the chance of pain coming back.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle can help a lot. Keep a healthy weight, don’t stand or sit for too long, and wear the right shoes.
Exercise and Strengthening Programs
Regular exercise, like strengthening the back of your legs, can prevent pain. Focus on exercises for your hamstrings and calf muscles.
Nutrition and Hydration Tips
Good nutrition and staying hydrated are key for muscle health. Make sure you get enough potassium, magnesium, and calcium to avoid muscle cramps.
When to Use Support Garments
Support garments, like compression sleeves, can offer extra support. They’re great for people who do a lot of hard work or have jobs that involve lifting or standing a lot.
By following these tips, you can lower the risk of back of leg muscle pain. As an expert says, “Prevention is the best way to manage muscle pain. Taking action early can keep your legs healthy and pain-free.”
Conclusion
Understanding why we get back of leg muscle pain is key to feeling better. We looked at seven main reasons, like hamstring strains and sciatica. We also talked about muscle cramps and overuse injuries.
Knowing the signs and what causes these issues helps us find ways to feel better. This knowledge lets us take steps to prevent and treat muscle pain in our legs.
We stress the need for a full approach to avoid muscle pain in the future. This includes making lifestyle changes, exercising, and staying hydrated. These steps can greatly improve your life and reduce muscle pain.
Our aim is to give people the tools and knowledge to handle their muscle pain. This way, they can move freely and enjoy life more fully.
What are the common causes of back of leg muscle pain?
Back of leg muscle pain can come from many sources. This includes hamstring strains and muscle cramps. Sciatica, overuse injuries, and vascular conditions are also common causes. Referred pain from lower back issues and compartment syndrome can also play a role.
How do I know if my back of leg muscle pain is serious?
Severe pain, swelling, redness, or trouble walking are signs to see a doctor. If you’ve had deep vein thrombosis or traveled far recently, get medical help too.
What is the difference between nerve pain and muscle pain in the back of the leg?
Nerve pain goes down the leg and might feel numb or tingly. Muscle pain is usually in one spot and feels stiff or sore.
How can I relieve back of leg muscle pain?
Try stretching, foam rolling, and exercises to help. Over-the-counter pain meds and creams can also help. Heat or cold therapy, and rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can reduce pain and swelling.
Can poor circulation cause back of leg muscle pain?
Yes, poor circulation can lead to muscle pain. It causes fatigue, cramping, and pain, mainly when active.
How can I prevent future episodes of back of leg muscle pain?
Regular exercise and stretching can prevent pain. Maintaining a healthy weight and good posture also helps. Wearing proper shoes and staying hydrated are important too. Managing stress and getting enough sleep can also prevent muscle pain.
When should I seek medical attention for back of leg muscle pain?
See a doctor for severe pain, swelling, or trouble walking. If you have a history of medical conditions, get help. Symptoms like numbness, tingling, or weakness, or fever, redness, or warmth in the area also need medical attention.
Can back problems cause pain in the back of the leg?
Yes, back problems can cause pain in the legs. Issues like herniated discs or spinal stenosis can irritate nerves. This leads to pain, numbness, or tingling in the legs.
What is compartment syndrome, and how does it cause pain on the side of the lower leg?
Compartment syndrome is when pressure builds up in a muscle. This causes pain, swelling, and can be serious. Pain on the side of the lower leg might be a sign of this, along with numbness, tingling, or weakness.
How can I diagnose the source of my back of leg muscle pain?
Diagnosing pain involves self-assessment, medical history, and tests like X-rays or MRI. A healthcare professional can help find the cause of your pain.