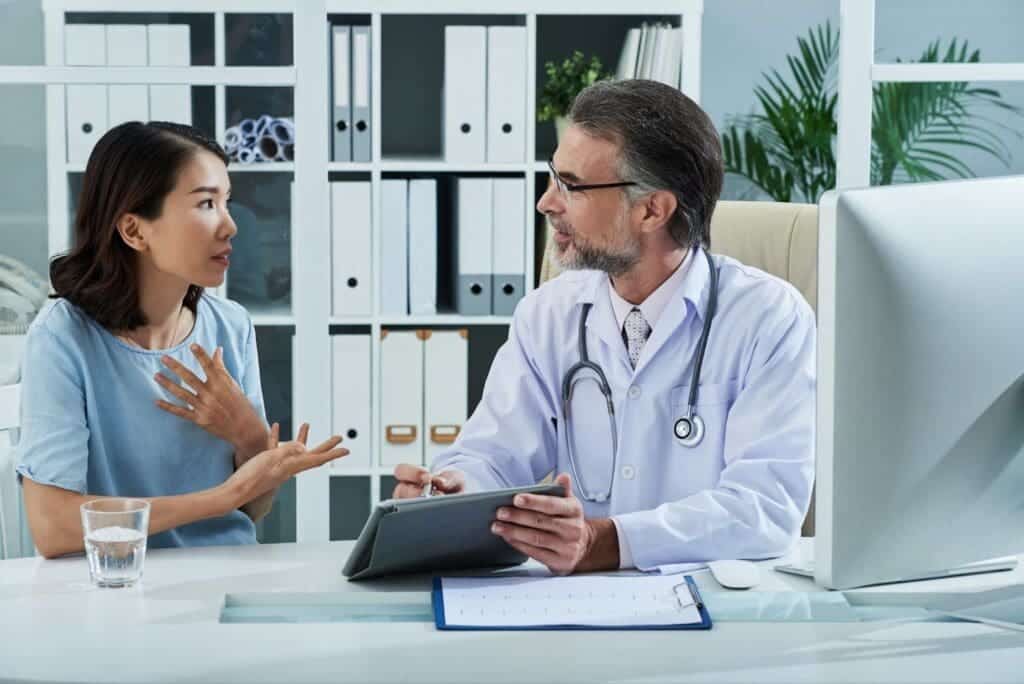
Getting a tumor diagnosis in the frontal lobe can be scary. But, thanks to modern medicine, there’s hope for a good treatment and recovery. Liv Hospital offers top-notch care and medical standards for meningioma treatment.
Surgery is a main treatment for tumors in the frontal lobe. Knowing the key facts about this procedure can make your treatment journey easier. With the right care and support, you can get the best results.
Liv Hospital is dedicated to trusted, patient-focused care. By choosing experienced doctors and modern facilities, you get the best treatment for your condition.
Understanding Frontal Meningiomas: Location and Symptoms
Frontal meningiomas are usually benign tumors. They can cause different symptoms based on their size and location. These tumors grow from the meninges, which protect your brain and spinal cord. When they grow in the frontal lobe, they can impact your brain’s functions.
What Are Frontal Meningiomas?
Frontal meningiomas develop in the frontal lobe of the brain. This area is key for making decisions, controlling movements, and more. These tumors grow slowly and are not cancerous. But, their location can affect your brain and health.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Having a frontal meningioma can lead to various symptoms. You might notice changes in your personality, motor skills, or vision. If the tumor is behind your eye, it can cause double vision or loss of side vision.
Other symptoms include headaches, seizures, or weakness in your limbs.
How Tumors Behind the Eye Affect Vision
Tumors behind the eye, a common spot for frontal meningiomas, can harm your vision. As they grow, they can put pressure on the optic nerve. This can lead to blurred vision, double vision, or even vision loss in one eye.
It’s important to know about these vision problems for early detection and treatment.
The Benign Nature of Most Meningiomas
Learning that most meningiomas are benign tumors can ease your worries. These tumors don’t spread like cancer. This fact greatly affects how they are treated and the outlook for recovery. Knowing this can help ease fears when you hear you have a tumor.
Classification and Grading of Meningiomas
Meningiomas are sorted and graded based on their traits and actions. The World Health Organization (WHO) grading system is often used. It divides meningiomas into three grades. Grade I tumors are usually benign, while Grades II and III are atypical and malignant, respectively.
- Grade I: Benign meningiomas, which are usually slow-growing and less likely to recur.
- Grade II: Atypical meningiomas, which have a higher risk of recurrence and may require more aggressive treatment.
- Grade III: Malignant meningiomas, which are rare and have a poor prognosis.
Growth Patterns and Progression Rates
The way a meningioma grows is key in planning treatment. Benign meningiomas grow slowly or not at all. Whether to treat or watch a meningioma depends on its size, location, and symptoms.
Differentiating from Malignant Brain Tumors
Unlike malignant brain tumors, benign meningiomas have clear boundaries and don’t invade brain tissue. This is important for treatment and outlook. Benign meningiomas are usually easier to treat and have better outcomes than malignant tumors.
Benign meningiomas and malignant brain tumors differ in growth rate, tissue invasion, and recurrence risk. Understanding these differences helps in making informed treatment choices.
Frontal Meningioma Surgery: Procedure and Techniques
If you’re facing frontal meningioma surgery, understanding the process is key. This surgery removes a tumor near the frontal lobe of the brain. Knowing the steps and techniques can help you through your treatment.
Preoperative Planning and Imaging
Before surgery, detailed planning is vital. Advanced imaging like MRI and CT scans are used. They help find the tumor’s exact location and how it affects nearby brain areas. This info guides neurosurgeons on the best surgical path.
- Detailed imaging helps identify the tumor’s size and location.
- It assesses the involvement of critical brain structures.
- Surgeons use this information to plan the optimal surgical route.
Surgical Approaches to the Frontal Lobe
The surgery method depends on the tumor’s size and location. Often, a craniotomy is used, where part of the skull is temporarily removed. Choosing the right approach is key to avoid damage and ensure successful removal.
Your surgical team will pick the best method for you. They consider the tumor’s location, your health, and other factors.
Gross Total vs. Subtotal Resection Goals
The main goal is usually to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is called gross total resection. It leads to better long-term results. But, sometimes, not all of the tumor can be removed to protect brain function.
Your neurosurgeon will talk to you about your specific situation. They’ll consider the tumor’s type and your health.
Safety Profile and Risks of Meningioma Surgery
Meningioma surgery is generally safe. But, several factors can affect its safety. Knowing these factors helps you make better treatment choices.
Potential Complications During Surgery
Several complications can happen during meningioma surgery. These include:
- Bleeding or hemorrhage
- Infection
- Damage to surrounding brain tissue
- Seizures
Postoperative Risks and Management
After surgery, you might face some risks. These include:
- Cerebral edema (swelling of the brain)
- Infection
- Seizures
- Cognitive or neurological deficits
Good postoperative care is key to manage these risks. Your healthcare team will watch you closely and provide the right care.
Factors That Influence Surgical Safety
Several things can affect the safety of your surgery. These include:
- The size and location of the tumor
- Your overall health and age
- The expertise of your surgical team
Knowing these factors helps you and your healthcare provider make the best treatment plan.
Long-Term Outcomes After Frontal Lobe Meningioma Surgery
Patients often ask about their future after frontal lobe meningioma surgery. It’s key to know the long-term effects to make good treatment choices. Success in surgery is shown by controlling the tumor, preventing it from coming back, and improving life quality.
10-Year Progression-Free Survival Rates
Research shows that up to 87.6 percent of patients stay tumor-free for 10 years after surgery. This is good news, showing most patients can avoid tumor return for a long time.
The rate of staying tumor-free is a key measure of treatment success. It shows how many patients don’t see their tumor come back or grow after surgery.
Recurrence Rates and Risk Factors
Even with good results, meningioma can come back after surgery. Several things can make this more likely, such as:
- How well the tumor was removed during surgery
- The type of meningioma
- If any tumor was left behind
Knowing these risk factors helps set realistic hopes and plan for after surgery care.
Quality of Life After Surgery
The surgery’s effect on life quality is a big worry. But, many patients see big improvements in their symptoms and overall health after surgery.
Things that help improve life quality after surgery include:
- Managing any problems after surgery well
- Getting the right rehabilitation
- Keeping an eye out for any tumor return
Symptom Improvement Following Meningioma Removal
Removing a meningioma can greatly improve a patient’s life. Many see big improvements in their symptoms. Up to 80 percent of patients experience long-term neurological gains.
Neurological Recovery Timeline
Recovery times after meningioma surgery vary. Most start feeling better a few weeks to months after. The size and location of the tumor and the patient’s health play big roles.
- Immediate post-surgery recovery: Focus on managing pain and addressing acute complications.
- Short-term recovery (weeks to months): Gradual improvement in neurological functions.
- Long-term recovery (months to years): Continued enhancement in cognitive and physical abilities.
Cognitive and Personality Changes After Surgery
Frontal meningioma surgery can lead to cognitive and personality changes. Some may face temporary cognitive challenges. Yet, many see their cognitive abilities improve over time.
Personality changes can also happen. But, they are often positive, showing a return to the patient’s pre-tumor personality.
Physical and Occupational Rehabilitation
Physical and occupational rehabilitation are key after meningioma surgery. A customized program helps patients regain strength and independence. This ensures the best possible recovery.
- Physical therapy: Focuses on improving mobility and strength.
- Occupational therapy: Helps patients regain daily living skills and independence.
- Speech therapy: Addresses any communication difficulties.
Understanding symptom improvement after meningioma removal helps patients navigate their treatment. It leads to better outcomes.
Radiation Therapy for Meningiomas: When and Why
Radiation therapy is key in treating meningiomas, mainly for tumors in tricky spots. It’s used when surgery is not an option or when the tumor might come back.
Types of Radiation Treatment Options
There are a few ways to use radiation for meningiomas. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (FSRT) are two common ones. SRS gives a big dose in one go, while FSRT spreads it out over time.
Choosing between SRS and FSRT depends on the tumor’s size and where it is. SRS works best for small tumors. FSRT is better for bigger ones or those near important areas.
Effectiveness as Primary vs. Adjunct Therapy
Radiation can be the main treatment for meningiomas, for those who can’t have surgery. It’s also used after partial surgery to stop the tumor from coming back.
Research shows radiation can slow tumor growth and help patients. Whether it’s the main or extra treatment depends on the tumor and what the patient wants.
Managing Side Effects of Radiation Treatment
Radiation therapy usually doesn’t cause big problems, but it can lead to fatigue, headaches, and nausea. The chance of side effects depends on the dose and type of radiation, and where the tumor is.
To deal with side effects, patients should rest, drink plenty of water, and eat well. Sometimes, doctors might give medicine to help with symptoms.
Special Considerations for Sphenoid Wing and Complex Meningiomas
Sphenoid wing meningiomas are tricky because of their location and how close they are to important parts of the body. These tumors are not cancerous but need a careful treatment plan.
Anatomical Challenges of Sphenoid Wing Tumors
The sphenoid wing area is complex, with the optic nerve and big blood vessels nearby. “Understanding the sphenoid wing’s anatomy is key,” says , a top neurosurgeon. This makes surgery planning and doing it very hard.
Multidisciplinary Treatment Approaches
Because of the sphenoid wing meningiomas’ complexity, a team effort is often needed. Neurosurgeons, radiation oncologists, and others work together to create a treatment plan. Options include surgery, radiation, or both. A says, “A team approach helps us tailor care to each patient, leading to better results.”
“The key to successful treatment of sphenoid wing meningiomas lies in a thorough understanding of the tumor’s anatomy and a collaborative approach to care.” –
Outcomes for Hard-to-Reach Meningiomas
Thanks to new surgery and radiation methods, treating sphenoid wing meningiomas is getting better. Research shows many patients can live longer and have a better life quality. For example, a study found that surgery and radiation together greatly improved survival rates for these patients.
- Careful preoperative planning is key for success.
- A team effort can lead to better patient outcomes.
- New surgery and radiation methods are expanding treatment options.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Your Meningioma Treatment
Understanding your meningioma diagnosis is key to making good treatment choices. Most meningiomas are not cancerous, and the right treatment can lead to a good outcome. It’s important to look at all treatment options to find the best one for you.
Surgery is often the main treatment for frontal meningiomas. New surgical methods have made treatment better. Your doctors will choose the best surgery for you based on the tumor’s size and your health.
In some cases, radiation therapy is used as a main or extra treatment. It can help control the tumor’s growth and lower the chance of it coming back. Knowing about meningioma treatments and their results helps you feel more in control of your care.
With the right information, you can work with your doctors to create a treatment plan that fits you. This plan aims to give you the best results possible.
What is the primary treatment for frontal lobe meningiomas?
The main treatment for frontal meningiomas is surgery. It aims to remove the tumor and control it well.
Are most meningiomas cancerous?
No, most meningiomas are not cancerous. They are usually benign and have a better prognosis than cancerous brain tumors.
What are the common symptoms of frontal meningiomas?
Symptoms include changes in personality and motor issues. Vision problems can also occur, affecting the brain’s function.
How does the location of a meningioma behind the eye affect vision?
A tumor behind the eye can cause vision issues. It can lead to double vision, loss of peripheral vision, or other problems.
What is the goal of gross total resection in meningioma surgery?
The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This helps control the tumor and lowers the chance of it coming back.
Is radiation therapy always necessary for meningioma treatment?
No, it’s not always needed. Radiation is used after partial removal or for tumors hard to reach. It helps control tumor growth.
What are the possible complications during meningioma surgery?
Complications can include infection, bleeding, or damage to brain tissue. But these risks are low, and most patients do well without major issues.
How effective is radiation therapy in treating meningiomas?
Radiation therapy is very effective. It’s often used as a second step to control tumor growth and prevent recurrence. There are different types of radiation treatment.
What is the 10-year progression-free survival rate for patients undergoing frontal lobe meningioma surgery?
The 10-year survival rate can be up to 87.6 percent. This shows a high chance of long-term control after successful surgery.
Can symptoms improve after meningioma removal?
Yes, symptoms can improve a lot. Up to 80 percent of patients see long-term neurological improvements. But, the extent of improvement varies.
What is sphenoid wing meningioma treatment focused on?
Treatment for sphenoid wing meningiomas involves a team approach. It considers the challenges of these tumors. Often, surgery and radiation are used together.
References
Zhao, L. (2020). An overview of management in meningiomas. PMC.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7473392/ PMC




































