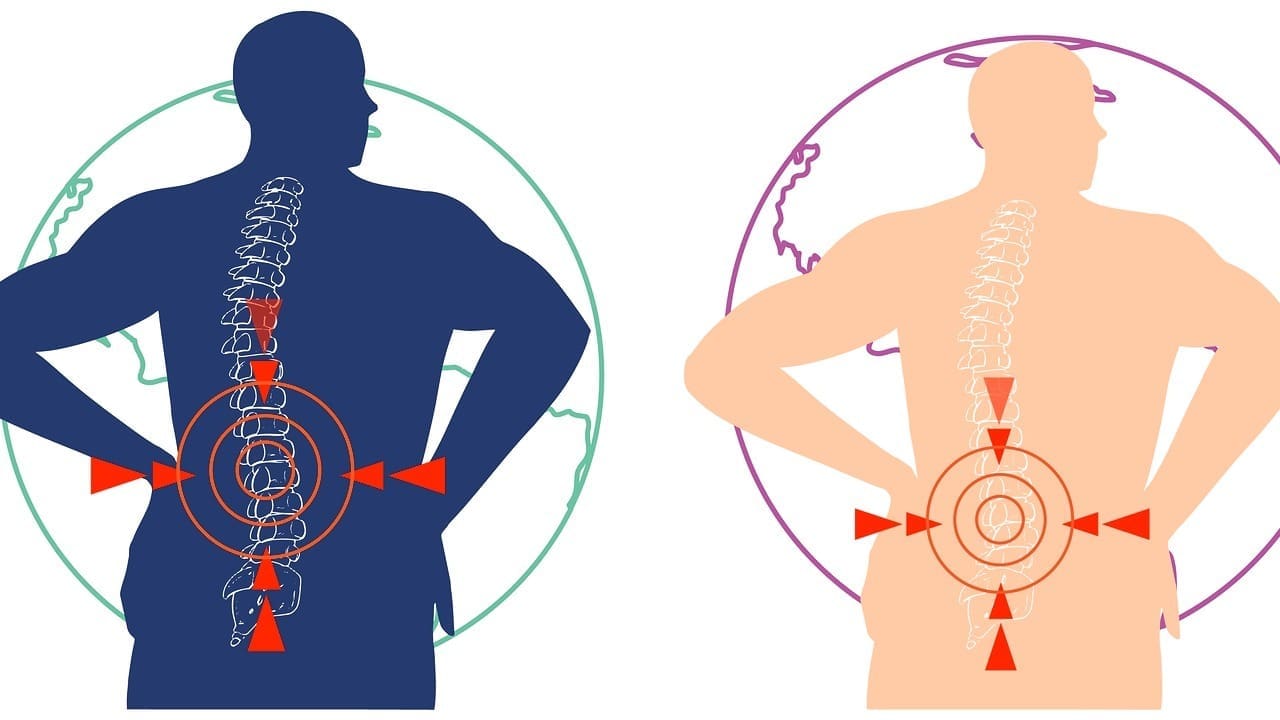
Knowing the difference between a bulging disc and a protruding disc is key for the right treatment. It’s important to get care that fits your specific needs.
A bulging disc pushes out a wide area of the disc, but the outer wall stays strong. On the other hand, a protruding disc only affects a small area. Studies show many adults have disc issues, making clear care even more important.
At Liv Hospital, we aim to give top-notch healthcare to all patients. Our team works hard to meet each patient’s unique needs with care.
Key Takeaways
- Distinguishing between bulging and protruding discs is essential for accurate diagnosis.
- A bulging disc involves a broader disc circumference, while a protruding disc is more localized.
- Understanding these differences is key for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital provides personalized care for international patients with spinal conditions.
- Advanced protocols ensure precise diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Spinal Disc Anatomy

The intervertebral disc is key for our spine’s function and movement. It has a soft center called the nucleus pulposus, surrounded by the annulus fibrosus. A thin layer of cartilage also plays a role, connecting the nucleus to the vertebrae.
Nucleus Pulposus and Annulus Fibrosus
The nucleus pulposus is like a gel that helps absorb shocks. The annulus fibrosus is a strong ring that keeps the disc stable. Together, they help our spine move and absorb impacts.
Knowing how the disc works is key to understanding problems like disc bulging vs protrusion. These issues differ based on how much the disc is affected and how it impacts the spine.
Causes of Disc Abnormalities
Disc problems can come from aging, wear, or injuries. As we get older, the nucleus pulposus loses its ability to absorb shocks. The annulus fibrosus can also weaken, leading to issues like shallow disc protrusion or superimposed disc protrusion.
Genetics, lifestyle, and stress can also affect the discs. Knowing these causes helps in preventing and treating problems. It’s important to understand the differences between disc bulge versus protrusion.
Defining a Bulging Disc
A bulging disc happens when a big part of the disc bulges out. But, the outer wall of the disc stays strong. This is a common problem in the spine and can happen in different places.
We will look at what makes a bulging disc, like how it shows up on MRI scans. Knowing this helps doctors figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it.
Characteristics and Appearance on MRI
A bulging disc looks like a big bulge on the disc’s edge. It covers more than a quarter of the disc’s edge. On an MRI, it looks like the disc is spreading out beyond the vertebrae, but it’s not a sharp bulge.
Seeing a bulging disc on an MRI is key for doctors to diagnose it. It lets them see how big the bulge is and how it affects nerves and the spinal canal.
Prevalence and Demographics
Research says up to 60% of adults over 40 might have a bulging disc. It gets more common with age, and people who’ve had back pain before are more likely to have one.
Most bulging discs don’t cause pain, but they can if they press on nerves or make the spine unstable. Knowing who’s at risk helps doctors plan how to prevent problems.
Key factors associated with bulging discs include:
- Age: More common in older adults
- Spinal degeneration: Wear and tear on the spine
- History of back pain: Previous episodes of back pain
Knowing these things helps doctors catch bulging discs early. This can help avoid symptoms and problems later on.
Defining a Protruding Disc
A protruding disc is a type of disc problem that affects a small area. It’s usually less than 25 percent of the disc’s circumference. When the problem is mild, it’s called a shallow disc protrusion.
Characteristics on MRI
On MRI, a protruding disc shows up as a small abnormality. The disc material goes beyond its normal space. This can press on nearby nerves.
Prevalence and Demographics
Protruding discs are found in about 20% of MRI scans in people with symptoms. They are more likely to cause nerve compression and pain than bulging discs. Getting a correct diagnosis and treatment for protruding discs is key to relieving symptoms and avoiding more problems.
It’s important to know the difference between a protruding disc and a bulging disc for effective treatment. A protruding disc can greatly affect a person’s life. So, understanding the difference between protrusion and bulge disc is vital for finding the right treatment.
What is the main difference between a bulging disc and a protruding disc?
A bulging disc has a wide base and affects more than 25% of the disc. A protruding disc is more focused and smaller.
What is a shallow disc protrusion?
A shallow disc protrusion is a mild bulge of the disc. It’s often seen in protruding discs.
How common are bulging and protruding discs in adults?
Up to 60% of adults over 40 may have a bulging disc. About 20% of MRI scans in people with symptoms show protrusions.
What is the role of the nucleus pulposus in a spinal disc?
The nucleus pulposus is a soft, gel-like part. It helps absorb shock and spread pressure evenly.
Can bulging discs cause symptoms?
Most bulging discs don’t cause pain. But, if they press on nerves or affect spinal stability, they can cause symptoms.
Are protruding discs associated with a higher risk of nerve compression?
Yes, protruding discs are more likely to press on nerves and cause pain than bulging discs.
What is the difference between disc bulge vs protrusion?
The main difference is in how much the disc bulges. Bulging discs affect a wider area, while protruding discs are more focused.
How are bulging and protruding discs diagnosed?
Doctors use MRI scans to diagnose these conditions. MRI scans show the extent of the disc’s displacement.
What is a superimposed disc protrusion?
A superimposed disc protrusion is when a disc bulges and protrudes at the same time. It’s a combination of both.
Can a disc be both bulging and protruding?
Yes, a disc can be both bulging and protruding. This is called a superimposed disc protrusion.



































