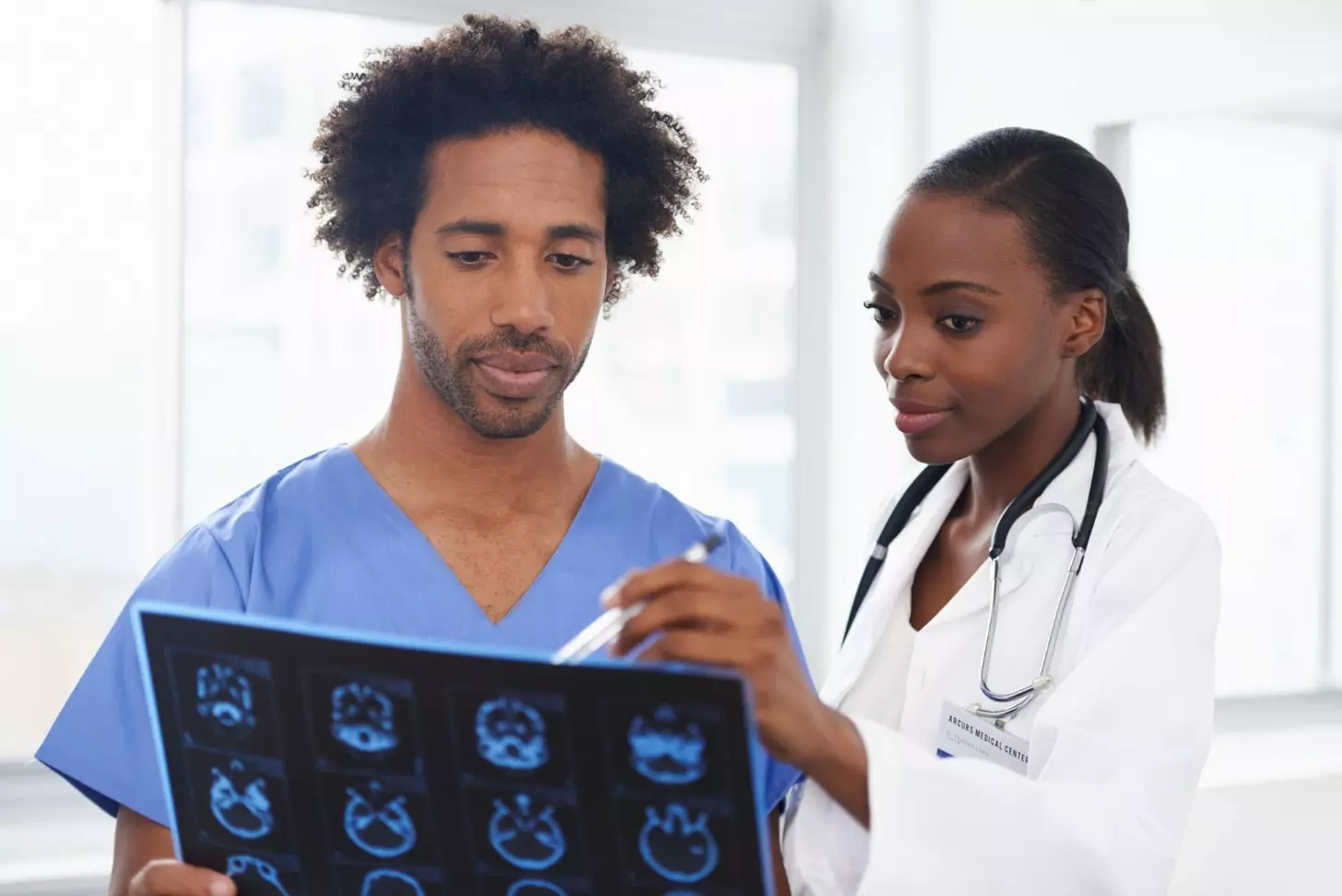
Understanding the brain biopsy procedure can give patients peace of mind. A brain biopsy is a surgery where a small brain tissue sample is taken. It helps diagnose issues like tumors, infections, or diseases.
Liv Hospital focuses on patient care with the latest in brain biopsy techniques. The process includes several steps. These include preparing the patient, making an incision on the scalp, and creating a hole in the skull. Then, a biopsy needle is used to get tissue samples.
Key Takeaways
- Knowing about the brain biopsy procedure can ease patient worries.
- A brain biopsy is key for finding out what’s wrong in the brain.
- Liv Hospital uses a patient-focused approach for brain biopsies.
- The surgery involves many precise steps.
- Getting an accurate diagnosis through a brain biopsy is essential for treatment.
Understanding Brain Biopsies: Definition and Purpose
A brain biopsy is a medical procedure used to diagnose and manage conditions affecting the brain. It involves removing a small sample of brain tissue for examination under a microscope.
What Is a Brain Biopsy?
A brain biopsy, also known as a cerebral biopsy, is a procedure where a neurosurgeon takes a sample of brain tissue. This tissue is then studied by a neuropathologist to find various brain disorders. These include tumors, infections, and inflammatory conditions.
Medical Conditions Requiring Brain Biopsies
Brain biopsies are key for diagnosing many neurological conditions. Some of the main medical conditions that may need a brain biopsy include:
- Brain tumors: Both benign and malignant tumors can be diagnosed through biopsy.
- Inflammatory diseases: Conditions like encephalitis or vasculitis can be identified.
- Infections: Biopsies can help diagnose infections affecting the brain.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Certain conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease, can be supported by biopsy findings.
Diagnostic Value in Neurological Care
The diagnostic value of brain biopsies is in their ability to provide a definitive diagnosis for many neurological conditions. By examining the brain tissue, healthcare professionals can:
- Identify the exact nature of a brain lesion or tumor.
- Guide treatment decisions, including the need for surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
- Monitor disease progression and response to treatment.
This diagnostic precision is vital for developing effective treatment plans and improving patient outcomes in neurological care.
When Is a Brain Biopsy Necessary?

Deciding on a brain biopsy involves many factors. It’s considered when other tests don’t give enough information. This helps doctors make a clear diagnosis.
Diagnostic Criteria for Brain Biopsies
Several things lead to the choice of a brain biopsy. For example, if a brain tumor can’t be seen just by looking at scans. Doctors also look at the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
Here are the main reasons for a brain biopsy:
- When other tests don’t show what’s wrong
- If a brain tumor or lesion is suspected
- When symptoms can’t be explained by other conditions
Alternative Diagnostic Methods
Before a brain biopsy, doctors try other ways to find answers. They use imaging techniques like functional MRI or PET scans. These scans show how the brain works and if there are any problems.
Other options include:
- Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to check cerebrospinal fluid
- Blood tests for infections or inflammation
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) to look at brain electrical activity
The Decision-Making Process
Choosing to do a brain biopsy is a team effort. Neurosurgeons, neurologists, and radiologists work together. They look at the patient’s tests, medical history, and symptoms.
This process involves:
- Looking at imaging studies and other tests
- Thinking about the risks and benefits of the biopsy
- Talking about the patient’s wishes and worries
By carefully weighing these points, doctors can decide if a brain biopsy is right. This helps in diagnosing and treating the patient.
Types of Brain Biopsy Procedures
There are different ways to do a brain biopsy, each with its own benefits. The choice depends on the size, location, and type of the lesion. It also depends on the patient’s health.
Stereotactic Brain Biopsy
A stereotactic brain biopsy is a small procedure. It uses a 3D system to find the exact spot in the brain to take a sample. This method is great for hard-to-reach areas.
Key Features of Stereotactic Brain Biopsy:
- Uses 3D imaging for precise location
- Is minimally invasive, so recovery is faster
- Best for deep brain lesions
Open Brain Biopsy
An open brain biopsy requires opening the skull. It’s used for big lesions or when a lot of tissue is needed.
Advantages of Open Brain Biopsy:
- Allows direct view of the brain tissue
- Can get bigger tissue samples
- Can also be used to remove tumors
Endoscopic Brain Biopsy
Endoscopic brain biopsy is a less invasive option. It uses an endoscope to see the brain tissue. It’s good for reaching certain areas with little damage.
Benefits of Endoscopic Brain Biopsy:
- Less invasive than open biopsy
- Reduces damage to surrounding tissue
- Works well with other tests
| Biopsy Type | Invasiveness | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Stereotactic | Minimally invasive | Deep-seated lesions |
| Open | Invasive | Large lesions or extensive sampling |
| Endoscopic | Less invasive | Specific areas with minimal damage |
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before a brain biopsy, it’s key to prepare well. This step is vital for safety and accurate results. It includes several important actions.
Medical Evaluation and Testing
A detailed medical check is needed to see the patient’s health. This includes looking at their medical history and doing tests. Tests like blood work and MRI scans are part of this.
Diagnostic tests help in:
- Checking the patient’s health
- Finding any health issues that might affect the procedure
- Choosing the best way to do the biopsy
Medication Management
Managing medications is a big part of getting ready. Patients must tell their doctor about all medicines they take. This includes drugs that prevent blood clotting.
| Medication Type | Action Required | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Thinners (e.g., Warfarin) | Temporarily discontinue | Reduce risk of bleeding |
| Antiplatelet Drugs (e.g., Aspirin) | Adjust dosage or stop | Minimize bleeding risk |
| Herbal Supplements | Discontinue use | Potential interaction with anesthesia or increased bleeding risk |
Patient Instructions Before Surgery
Patients get clear instructions before the surgery. These help keep them safe and comfortable. They might include fasting and what to wear.
- Fast for a set time before the procedure
- Shower or bathe as told to lower infection risk
- Wear loose, comfy clothes
Mental Preparation and Expectations
Mental prep is as important as physical. Patients should talk to their doctor about their worries. Knowing what to expect can make them feel better.
It’s essential for patients to:
- Ask about the procedure and recovery
- Know the risks and benefits
- Follow instructions carefully
How Is a Brain Biopsy Performed: The Procedure
Getting a brain biopsy involves many important steps. These steps are key to keeping the patient safe and getting the right diagnosis. It’s a complex task that needs a very skilled neurosurgeon.
Anesthesia Administration
The first thing done is giving anesthesia. General anesthesia is used to keep the patient calm and steady. The anesthesiologist picks the right amount based on the patient’s health and past medical history.
Patient Positioning and Head Fixation
Once the anesthesia kicks in, the patient is placed on the operating table. The head is secured with a stereotactic frame or something similar. This is very important for the biopsy to be accurate.
Surgical Site Preparation
The area for the biopsy is then cleaned and disinfected. A local antiseptic is used to lower the chance of infection.
Burr Hole Creation
A small hole, called a burr hole, is made in the skull. This lets the surgeon get to the brain tissue. The hole’s spot is picked based on MRI or CT scans.
As one neurosurgeon said,
“The precision in creating the burr hole is key to the biopsy’s success and the patient’s safety.”
The brain biopsy shows how far neurosurgery has come. It helps doctors make accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Advanced Imaging and Navigation Techniques
Advanced imaging and navigation are key in making brain biopsies more accurate and safe. These technologies have changed neurosurgery by giving surgeons real-time data and precise guidance. This is very important for complex operations.
MRI and CT Guidance Systems
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) are essential in brain biopsies. MRI guidance gives clear images of soft tissues, helping find the target area. CT guidance shows bony structures and calcifications well, which is helpful in some cases.
Using MRI and CT together helps surgeons plan the best path to the biopsy site. This reduces the risk of harming nearby brain areas. It makes the procedure safer and more effective.
Intraoperative Imaging
Intraoperative imaging, like intraoperative MRI or CT, lets surgeons see how the biopsy is going in real-time. This is very useful for checking if the needle is in the right place and making changes if needed.
Intraoperative imaging also helps spot any problems early, so they can be fixed right away. Combining this with navigation systems makes brain biopsies even more precise.
Computer-Assisted Navigation
Computer-assisted navigation uses preoperative images to guide surgeons during the biopsy. It shows a 3D view of the brain, helping plan and do the biopsy accurately.
Computer-assisted navigation makes it easier to place the needle correctly, lowering the chance of harming nearby important areas. This is very helpful when the target is in a hard-to-reach or sensitive part of the brain.
Precision and Safety Enhancements
Using advanced imaging and navigation in brain biopsies has greatly improved both precision and safety. These technologies give surgeons all the information they need during the procedure.
They help make the biopsy needle placement more accurate and lower the risk of complications. This leads to better results for patients. As these technologies get better, neurosurgery will continue to evolve.
Tissue Sample Processing and Analysis
The tissue samples from the brain biopsy are quickly sent for neuropathological examination. A neuropathologist does a detailed analysis to make a first guess at the diagnosis.
Immediate Neuropathological Examination
The tissue samples are closely looked at for any oddities during the immediate neuropathological examination. This includes:
- Gross examination of the tissue samples
- Preparation of tissue sections for microscopic examination
- Staining techniques to highlight cellular details
The neuropathologist looks at the samples under a microscope. They search for any unusual cell structures or other signs that might help diagnose.
Laboratory Testing Methods
More tests are done in the lab to get more info about the samples. These tests might include:
- Molecular diagnostics to find genetic mutations
- Cultures to check for infections
- Specialized staining techniques to spot specific cell types
Timeframe for Results
How long it takes to get the brain biopsy results can vary. The first results from the neuropathological exam might be ready in a few days. But, the full lab test results could take a week or two.
Understanding Your Brain Biopsy Results
It’s key to understand your brain biopsy results. The neuropathologist or your doctor will explain what they found. This might show things like tumors, infections, or other brain issues.
It’s important to talk about what the results mean and what treatment options you have with your healthcare team. The results will help make a treatment plan just for you. This plan might include surgery, medicine, radiation, or other treatments based on your diagnosis.
Post-Procedure Hospital Care
After a brain biopsy, it’s key to keep patients safe and comfortable. They are watched closely in a recovery area.
Immediate Recovery Monitoring
Doctors track important signs like blood pressure and heart rate. They also look for any signs of brain problems or other issues.
Key Monitoring Parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Vital Signs | Blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation |
| Neurological Status | Level of consciousness, pupil response, limb strength |
| Complications | Bleeding, infection, seizure activity |
Pain Management
Managing pain is a big part of care after a procedure. Patients get the right medicine to ease their discomfort.
Pain assessment scales help doctors know how much pain a patient has. They then adjust the medicine as needed.
Neurological Assessment
Doctors do regular checks to see if there are any new brain problems. They look at thinking skills, movement, and how the body feels things.
When to Alert Medical Staff
If a patient or their family notices something odd, like a bad headache or trouble speaking, they should tell the doctors right away.
By keeping a close eye on patients and managing pain well, doctors can lower the chance of problems. This helps patients recover better.
Brain Biopsy Recovery Process
Knowing how to recover after a brain biopsy is key for patients. The journey to healing includes several important steps. These include understanding the recovery timeline, knowing physical limits, attending follow-up appointments, and caring for the wound properly.
Timeline for Recovery: What to Expect
The recovery time usually lasts several weeks. During this time, patients may face different physical and neurological symptoms. At first, they are watched closely in the hospital for any immediate issues.
Recovery Timeline:
| Timeframe | Expected Recovery Progress |
|---|---|
| 1-2 Weeks | Gradual improvement in symptoms, reduction in swelling |
| 2-4 Weeks | Increased mobility, return to light activities |
| 4-6 Weeks | Significant recovery, possible return to normal activities |
Physical Limitations During Healing
Patients should avoid heavy lifting, bending, and hard work during recovery. This helps prevent bleeding or injury at the biopsy site.
It’s vital to follow the specific instructions from healthcare professionals about physical limits and activity levels.
Follow-up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are key to the recovery process. They let healthcare providers check on healing, address concerns, and remove stitches or staples.
- Schedule follow-up appointments as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Report any unusual symptoms or concerns during these appointments.
Wound Care and Brain Biopsy Scar Management
Proper wound care is vital for healing and preventing infection. Patients should keep the wound clean and dry. They should also follow any specific wound care instructions from their healthcare team.
By understanding and following these recovery steps, patients can heal better and avoid complications after a brain biopsy.
Potential Risks and Complications
It’s important to know the risks of brain biopsies before making a decision. These tests are key for diagnosing, but they come with some risks. It’s vital to understand these risks.
Bleeding and Hematoma
Bleeding or hematoma at the biopsy site is a big risk. Careful patient selection and precise surgical technique can lower this risk. Also, using advanced imaging during the procedure helps spot bleeding early.
Infection
Infection is another possible complication. Following strict sterile techniques and proper care after the procedure can help. Patients are watched closely for infection signs, and antibiotics are given when needed.
Neurological Deficits
Damage to brain tissue can lead to neurological deficits. Using advanced navigation and imaging helps target the biopsy site accurately. Before the procedure, patients are evaluated to assess risks.
Long-term Considerations
Long-term issues like scar tissue and seizures can occur. Follow-up care is key to catch and manage these effects.
The table below outlines the risks of brain biopsies and how to reduce them:
| Complication | Risk Factors | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Bleeding/Hematoma | Poor patient selection, surgical technique | Advanced imaging, careful patient selection |
| Infection | Break in sterile technique, postoperative care | Strict sterile technique, postoperative antibiotics |
| Neurological Deficits | Damage to brain tissue during procedure | Advanced navigation and imaging techniques |
| Long-term Effects | Scar tissue formation, seizure development | Follow-up care, management of complications |
Conclusion: Advances in Brain Biopsy Techniques
Brain biopsy techniques have seen big improvements. These changes have made diagnosing diseases more accurate and treatments more effective. New imaging and navigation tools have made these procedures safer and more precise.
Using MRI and CT scans with computer-assisted navigation has improved targeting brain lesions. This means fewer complications and better results from the biopsy.
Medical research keeps moving forward, and we’ll see even more improvements in brain biopsies. These advancements will help care for patients better and find new ways to treat neurological diseases.
The growth of advanced imaging and navigation is key. It makes brain biopsies safer and more accurate. This leads to better diagnosis and care for patients.
FAQ
How is a brain biopsy done?
A neurosurgeon uses MRI or CT scans to find the right spot in the brain. They make a small hole in the skull to get a tissue sample. This method is very precise.
What is a stereotactic brain biopsy?
A stereotactic brain biopsy uses a special frame or computer system. It helps find the exact spot in the brain for the biopsy. This makes the procedure less invasive.
Is a brain biopsy dangerous?
Yes, a brain biopsy has risks like bleeding and infection. But, using modern techniques and skilled surgeons can lower these risks.
How long does it take to get brain biopsy results?
Getting results can take a few days to a week. It depends on the tests and how complex the case is.
What is the recovery process like after a brain biopsy?
After a brain biopsy, you need to rest for a few days. You might have some physical limits. You’ll be watched for any problems and get instructions on wound care.
Can a brain biopsy be used to diagnose any brain condition?
A brain biopsy can help diagnose many brain issues. This includes tumors, infections, and inflammation. The decision to do a biopsy depends on your symptoms and tests.
What are the possible risks and complications of a brain biopsy?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and neurological problems. There could also be long-term effects like scarring or changes in thinking.
How is a white matter brain biopsy performed?
A white matter biopsy is done the same way as other biopsies. The neurosurgeon uses imaging and navigation to target the right area.
What is the role of computer-assisted navigation in brain biopsies?
Computer-assisted navigation is key in brain biopsies. It helps neurosurgeons find the exact spot for the biopsy, using detailed imaging.
How is the tissue sample processed and analyzed after a brain biopsy?
The tissue sample is sent for tests like histopathology and molecular diagnostics. These help make a diagnosis and plan treatment.
FAQ
How is a brain biopsy done?
A neurosurgeon uses MRI or CT scans to find the right spot in the brain. They make a small hole in the skull to get a tissue sample. This method is very precise.
What is a stereotactic brain biopsy?
A stereotactic brain biopsy uses a special frame or computer system. It helps find the exact spot in the brain for the biopsy. This makes the procedure less invasive.
Is a brain biopsy dangerous?
Yes, a brain biopsy has risks like bleeding and infection. But, using modern techniques and skilled surgeons can lower these risks.
How long does it take to get brain biopsy results?
Getting results can take a few days to a week. It depends on the tests and how complex the case is.
What is the recovery process like after a brain biopsy?
After a brain biopsy, you need to rest for a few days. You might have some physical limits. You’ll be watched for any problems and get instructions on wound care.
Can a brain biopsy be used to diagnose any brain condition?
A brain biopsy can help diagnose many brain issues. This includes tumors, infections, and inflammation. The decision to do a biopsy depends on your symptoms and tests.
What are the possible risks and complications of a brain biopsy?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and neurological problems. There could also be long-term effects like scarring or changes in thinking.
How is a white matter brain biopsy performed?
A white matter biopsy is done the same way as other biopsies. The neurosurgeon uses imaging and navigation to target the right area.
What is the role of computer-assisted navigation in brain biopsies?
Computer-assisted navigation is key in brain biopsies. It helps neurosurgeons find the exact spot for the biopsy, using detailed imaging.
How is the tissue sample processed and analyzed after a brain biopsy?
The tissue sample is sent for tests like histopathology and molecular diagnostics. These help make a diagnosis and plan treatment.
References
American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS). (n.d.). Stereotactic brain biopsy. Retrieved from https://www.aans.org/patients/conditions-treatments/stereotactic-brain-biopsy
Cancer Research UK. (n.d.). Brain tumour biopsy. Retrieved from https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/brain-tumours/treatment-surgery/biopsy



































