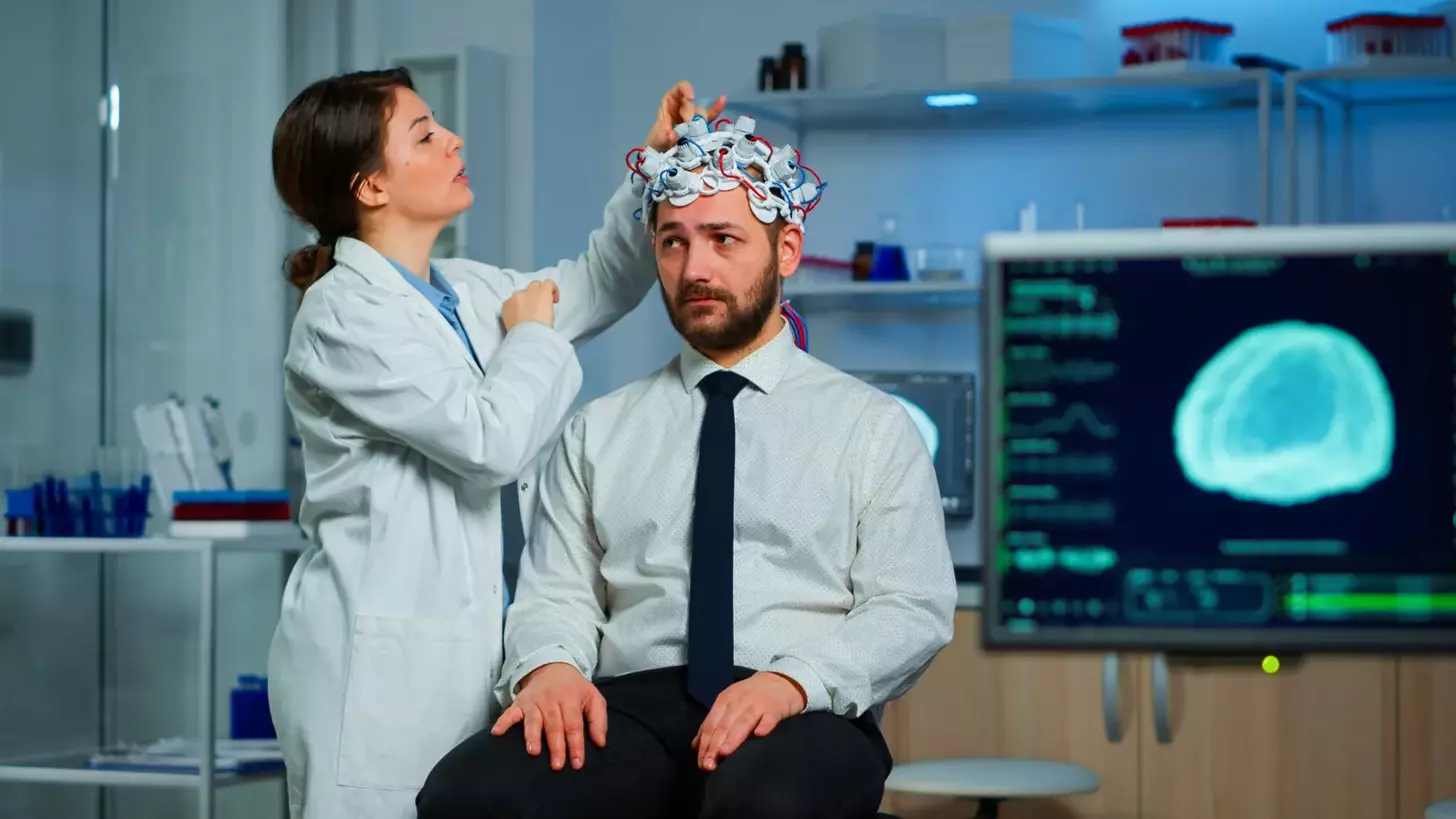
Treating brain tumors requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating various medical specialties to provide the best possible outcomes. At Liv Hospital, we utilize cutting-edge technology and a patient-centered approach to deliver advanced care for brain cancer.
Recent advances in medical research have significantly expanded brain tumor treatment options. We now have a range of effective treatments, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and participation in clinical trials.
Our team of internationally trusted experts works together to develop personalized treatment plans, ensuring that each patient receives the most effective care for their specific condition.
Key Takeaways
- Multidisciplinary approach is crucial in treating brain tumors.
- Various treatment options are available, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
- Personalized treatment plans are developed for each patient.
- Participation in clinical trials may be an option for some patients.
- Advanced technology and patient-centered care are essential in brain tumor treatment.
Understanding Brain Tumors and Their Impact
Understanding the intricacies of brain tumors is crucial for developing a treatment plan that addresses the unique needs of each patient. Brain tumors, whether benign or malignant, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, making timely and appropriate management essential.
Types of Brain Tumors and Their Characteristics
Brain tumors are broadly classified into primary and metastatic tumors. Primary brain tumors originate in the brain, while metastatic tumors spread to the brain from other parts of the body. Primary brain tumors can be further divided into gliomas, meningiomas, and acoustic neuromas, among others. Each type has distinct characteristics that influence treatment decisions.
Gliomas, for instance, arise from the brain’s glial cells and can range from low-grade to high-grade (glioblastoma). Meningiomas, typically benign, develop in the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain. Understanding these differences is vital for effective brain tumor management.
- Gliomas: Arise from glial cells, varying in grade and aggressiveness.
- Meningiomas: Usually benign, originating in the meninges.
- Acoustic Neuromas: Benign tumors affecting the nerve connecting the inner ear to the brain.
Signs and Symptoms That Necessitate Treatment
The signs and symptoms of brain tumors vary widely depending on the tumor’s location, size, and type. Common symptoms include persistent headaches, seizures, and cognitive changes such as memory loss or difficulty concentrating. Early detection and understanding of these symptoms are critical for initiating appropriate brain cancer treatment.
Patients may also experience neurological deficits, such as weakness or numbness in parts of the body, vision changes, or difficulties with speech and language. The diversity of these symptoms underscores the importance of a comprehensive diagnostic approach to identify the underlying cause and guide treatment.
- Headaches and seizures are common initial symptoms.
- Cognitive and neurological deficits may develop as the tumor grows.
- Symptoms can vary significantly based on tumor location and type.
By understanding the different types of brain tumors and their characteristics, healthcare providers can develop targeted treatment strategies that improve patient outcomes. Effective brain tumor management involves a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating the latest advancements in medical science to provide comprehensive care.
The Diagnosis Process: First Steps Toward Treatment
Accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective brain tumor treatment, and we’re here to guide you through the process. Diagnosing a brain tumor involves a combination of advanced imaging techniques and precise biopsy procedures to determine the type and characteristics of the tumor.
Imaging Techniques Used for Brain Tumor Detection
We utilize various imaging techniques to visualize brain tumors. These include:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of the brain and is particularly useful for identifying soft tissue abnormalities.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Offers quick and precise images, especially useful in emergency situations.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography) Scan: Helps in understanding the metabolic activity of the tumor.
These imaging techniques are crucial for identifying the location, size, and characteristics of the tumor, which in turn inform the treatment plan.
Biopsy and Tumor Classification
After imaging, a biopsy is often performed to classify the tumor. This involves:
- Surgical Biopsy: A surgical procedure to obtain a tissue sample.
- Stereotactic Biopsy: A less invasive procedure using a stereotactic frame to guide the biopsy needle.
The tissue sample is then examined to determine the tumor type and grade, which are critical factors in deciding the treatment strategy.
We understand that the diagnosis process can be daunting, but with advanced imaging and precise biopsy techniques, we can develop an effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
The Multidisciplinary Approach to Brain Tumor Management
The treatment of brain tumors is most effective when a multidisciplinary team of specialists works in coordination. We believe that this collaborative approach is essential for providing comprehensive care to brain tumor patients.
A brain tumor treatment team typically consists of various medical professionals, including neurosurgeons, neuro-oncologists, radiation oncologists, neuroradiologists, and neuropathologists. Each specialist plays a crucial role in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of brain tumors.
The Brain Tumor Treatment Team
The brain tumor treatment team is responsible for developing a personalized treatment plan for each patient. This team works together to:
- Review diagnostic images and test results
- Discuss treatment options and recommendations
- Coordinate care across different departments
- Provide ongoing support and monitoring
Coordinated Care Planning
Coordinated care planning is a critical aspect of brain tumor management. We ensure that all aspects of a patient’s care are well-planned and executed. This includes:
- Developing a comprehensive treatment plan
- Coordinating with other healthcare providers
- Providing education and support to patients and their families
- Monitoring patient outcomes and adjusting the treatment plan as needed
Studies have shown that a multidisciplinary approach improves treatment outcomes for brain cancer patients. By working together, we can provide more effective and personalized care, leading to better patient outcomes.
How Do You Treat a Brain Tumor: Primary Treatment Options
The treatment of brain tumors involves a range of strategies, each tailored to the specific characteristics of the tumor and patient. The choice of treatment depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for many brain tumors. The goal of surgical intervention is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while preserving surrounding brain tissue. Advances in neurosurgical techniques, including intraoperative MRI and awake brain surgery, have improved the precision and safety of tumor resections.
Benefits of surgical intervention include the potential for complete tumor removal, relief of symptoms caused by tumor pressure, and obtaining tissue for pathological examination. However, surgery carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding brain areas.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is another primary treatment modality for brain tumors. It uses high-energy particles or waves to destroy or damage cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be external (external beam radiation therapy) or internal (brachytherapy).
Radiation therapy is particularly useful for tumors that are inoperable or have residual disease after surgery. It can also be used in combination with chemotherapy to enhance treatment efficacy.
- Types of radiation therapy include:
- External beam radiation therapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Proton therapy
Chemotherapy Protocols
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. For brain tumors, chemotherapy can be administered orally, intravenously, or directly into the cerebrospinal fluid. The choice of chemotherapy agents and the treatment schedule depend on the type of brain tumor and the patient’s overall health.
Chemotherapy protocols may involve a single agent or a combination of drugs. The treatment is often used in conjunction with surgery and/or radiation therapy to maximize its effectiveness.
By understanding the primary treatment options available, patients and their families can make informed decisions about their care. It’s essential to discuss the benefits and risks of each treatment modality with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Surgical Techniques for Brain Tumor Removal
Advances in surgical techniques have revolutionized the treatment of brain tumors, providing new hope for patients. Surgical intervention remains a primary treatment modality for many brain tumors, and the choice of surgical technique depends on various factors, including tumor type, location, and patient health.
Traditional Craniotomy
A traditional craniotomy involves temporarily removing a portion of the skull to access the brain tumor. This technique allows surgeons to visualize the tumor and surrounding structures directly. It is often used for larger tumors or those in more accessible locations.
While effective, traditional craniotomy carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and potential damage to brain tissue. Advances in neurosurgical techniques and postoperative care have minimized these risks.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as endoscopic surgery, have become increasingly popular for certain types of brain tumors. These procedures involve smaller incisions and less disruption of brain tissue, potentially leading to quicker recovery times and fewer complications.
Awake Brain Surgery
Awake brain surgery, also known as awake craniotomy, is a specialized technique used when tumors are located near critical brain areas, such as those controlling speech or movement. During the procedure, the patient remains awake and responsive, allowing the surgical team to monitor brain function in real-time.
“Awake craniotomy allows for the precise removal of tumors located near eloquent brain areas, potentially improving outcomes for patients with tumors in these challenging locations.”
The advantages of awake brain surgery include more precise tumor removal and reduced risk of damaging critical brain functions. However, it requires a highly skilled surgical team and a cooperative patient.
| Surgical Technique | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Craniotomy | Direct visualization, effective for large tumors | Higher risk of infection and brain damage |
| Minimally Invasive Procedures | Smaller incisions, quicker recovery | Limited applicability, requires specialized skills |
| Awake Brain Surgery | Precise removal near critical areas, preserves brain function | Requires cooperative patient, highly skilled team |
We continue to refine these surgical techniques, offering patients a range of options tailored to their specific needs. The choice of surgical technique is a critical decision made by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals.
Radiation Therapy Approaches for Brain Cancer Treatment
We utilize radiation therapy as a key treatment modality for brain cancer, employing a range of sophisticated techniques. Radiation therapy is a critical component of brain cancer treatment, offering various approaches tailored to individual patient needs. The choice of radiation therapy technique depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location, as well as the patient’s overall health.
External Beam Radiation
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) is a common radiation technique used to treat brain tumors. It involves directing high-energy X-rays from a machine outside the body to the tumor site. This method allows for precise targeting of the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
EBRT is often delivered in multiple sessions, allowing for the treatment to be fractionated and reducing the risk of side effects. The treatment planning process for EBRT is highly sophisticated, involving advanced imaging techniques to ensure accurate delivery of radiation.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a highly precise form of radiation therapy that delivers a large dose of radiation to a specific area. Despite its name, SRS is not a surgical procedure but rather a non-invasive treatment that uses multiple beams of radiation to converge on the tumor. This technique is particularly useful for treating small, well-defined tumors.
SRS is often used for tumors that are difficult to treat with conventional surgery or for patients who are not good candidates for surgical intervention. The precision of SRS minimizes damage to surrounding brain tissue, reducing the risk of side effects.
Proton Therapy
Proton therapy is a type of radiation therapy that uses protons instead of X-rays to kill cancer cells. This approach can be particularly beneficial for treating tumors near critical structures, as protons can be controlled to release most of their energy directly into the tumor, sparing surrounding tissue.
Proton therapy is especially considered for certain types of brain tumors, particularly in pediatric patients, to minimize long-term side effects. The precision of proton therapy makes it a valuable treatment option for tumors that are close to critical brain structures.
Chemotherapy and Drug Treatments for Brain Tumors
The role of chemotherapy in managing brain tumors is multifaceted, involving different agents and delivery methods. Chemotherapy is often used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery and radiation therapy, to provide comprehensive care for patients with brain tumors.
Standard Chemotherapy Agents
Several chemotherapy drugs are used to treat brain tumors, including temozolomide, carmustine, and lomustine. These drugs work by targeting rapidly dividing cancer cells, thereby slowing tumor growth.
Temozolomide is particularly noteworthy as it is commonly used for treating certain types of brain cancer, such as glioblastoma. Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier makes it an effective option for targeting brain tumors.
Delivery Methods and Schedules
Chemotherapy can be administered through various methods, including oral capsules, intravenous infusions, and direct implantation into the tumor site during surgery. The choice of delivery method depends on the type of brain tumor, its location, and the patient’s overall health.
Delivery schedules can vary, with some chemotherapy regimens given in cycles over several weeks or months. This allows for the treatment of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells.
Blood-Brain Barrier Considerations
The blood-brain barrier poses a significant challenge for chemotherapy in brain tumor treatment. This barrier, which protects the brain from harmful substances, can also prevent chemotherapy drugs from reaching the tumor in effective concentrations.
Researchers are exploring ways to overcome this challenge, including the development of drugs that can cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively and techniques to temporarily disrupt the barrier during chemotherapy administration.
By understanding the complexities of chemotherapy and drug treatments for brain tumors, we can better appreciate the need for personalized treatment plans that take into account the unique characteristics of each patient’s tumor.
Advanced Brain Cancer Treatment Options
Advanced treatment options for brain cancer are expanding, providing new avenues for patient care. As research continues to uncover the complexities of brain tumors, innovative therapies are being developed to target these cancers more effectively.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy represents a significant advancement in brain cancer treatment. This approach involves using drugs that specifically target the genetic mutations or proteins that are involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. By focusing on these specific targets, targeted therapy can help reduce the harm to normal cells, potentially leading to fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Benefits of Targeted Therapy:
- Precision in targeting cancer cells
- Potential for reduced side effects
- Possibility of more effective treatment for specific genetic mutations
Immunotherapy Approaches
Immunotherapy is another promising area in brain cancer treatment. This approach harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer. By enhancing the body’s natural defenses, immunotherapy can help identify and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
| Immunotherapy Type | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Checkpoint Inhibitors | Drugs that release the brakes on the immune system, allowing it to attack cancer cells more effectively. | Enhanced immune response against cancer |
| Cancer Vaccines | Vaccines designed to stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. | Specific targeting of cancer cells |
| Adoptive T-cell Therapy | A treatment that involves removing T cells from the body, modifying them to recognize cancer, and then reinfusing them. | Personalized treatment approach |
Gene Therapy and Precision Medicine
Gene therapy and precision medicine are at the forefront of brain cancer research. Gene therapy involves introducing, removing, or changing genetic material within a patient’s cells to fight or prevent disease. Precision medicine tailors treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient’s cancer, often based on genetic profiling.
The future of brain cancer treatment lies in the continued advancement of these innovative therapies.
As we continue to explore and understand the genetic and molecular underpinnings of brain cancer, we are likely to see even more targeted and effective treatments emerge. The integration of gene therapy, precision medicine, and other advanced treatment options holds great promise for improving outcomes for brain cancer patients.
Supportive Care and Symptom Management
Brain tumor patients require comprehensive supportive care to alleviate symptoms and improve their overall well-being. Supportive care is a critical component of the treatment plan, addressing the physical, emotional, and social needs of patients.
Medications for Symptom Control
Effective symptom management often involves the use of medications to control symptoms such as seizures, headaches, and nausea. We use a range of medications, including anticonvulsants, corticosteroids, and anti-emetics, tailored to the individual needs of each patient. Personalized medication plans help minimize side effects and maximize symptom relief.
Rehabilitation Services
Rehabilitation services play a vital role in helping patients regain their strength and independence. Our rehabilitation team includes physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists who work together to create personalized rehabilitation plans. These plans are designed to help patients recover from surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, and to manage any lasting effects of their treatment.
Psychological Support
A diagnosis of a brain tumor can be emotionally challenging for patients and their families. We provide psychological support through counseling services, support groups, and cognitive rehabilitation. Our goal is to help patients cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of their diagnosis, improving their overall quality of life.
By integrating supportive care into the treatment plan, we can significantly enhance the patient’s quality of life. Our multidisciplinary team works together to provide comprehensive care that addresses the complex needs of brain tumor patients.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Brain Cancer Therapies
Clinical trials play a crucial role in the development of new brain cancer treatments, offering patients access to innovative therapies. These trials are essential for advancing our understanding of brain cancer and improving treatment outcomes.
How to Find and Qualify for Clinical Trials
Finding and qualifying for clinical trials can be a complex process. We recommend that patients start by discussing their options with their healthcare provider, who can help identify relevant trials based on their specific condition and medical history.
Patients can also search for clinical trials on online databases such as ClinicalTrials.gov, which provides a comprehensive list of ongoing trials worldwide. When searching for trials, it’s essential to filter results based on specific criteria, including the type of brain cancer, treatment being investigated, and trial location.
To qualify for a clinical trial, patients must meet specific inclusion criteria, which may include factors such as the stage of their cancer, previous treatments, and overall health.
Promising Research Directions
Emerging therapies for brain cancer are being explored in various clinical trials, offering new hope for patients. Some promising research directions include targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and gene therapy.
- Targeted therapy involves using drugs that specifically target cancer cells, reducing harm to healthy tissues.
- Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer, with approaches such as checkpoint inhibitors and CAR-T cell therapy showing promise.
- Gene therapy aims to correct genetic mutations that drive cancer growth, potentially offering a more personalized treatment approach.
These emerging therapies are being investigated in clinical trials, providing valuable insights into their safety and efficacy. By participating in clinical trials, patients not only gain access to innovative treatments but also contribute to the advancement of brain cancer research.
Can Brain Tumors Be Cured? Understanding Outcomes and Prognosis
The question of whether a brain tumor can be cured is complex and depends on several factors. As we navigate the intricacies of brain tumor treatment, understanding the potential for a cure and the factors influencing it is crucial.
Factors Affecting Curability
The curability of a brain tumor is influenced by its type, grade, and location, as well as the patient’s overall health and response to treatment. Tumor type and grade are significant because they determine how aggressively the tumor grows and how likely it is to respond to treatment.
For instance, low-grade gliomas tend to have a better prognosis than high-grade glioblastomas. The location of the tumor is also critical, as tumors in certain areas may be more difficult to treat surgically.
Long-term Survival Rates
Long-term survival rates for brain tumor patients vary widely depending on the factors mentioned above. We have seen significant advancements in treatment options, which have improved survival rates for many patients.
For example, some types of brain tumors have a relatively high survival rate when diagnosed and treated early. It’s essential to discuss individual prognosis with a healthcare provider, as they can provide personalized insights based on specific circumstances.
Quality of Life Considerations
When considering the curability of a brain tumor, it’s also important to focus on the patient’s quality of life. Treatment plans are designed not only to cure the tumor but also to minimize side effects and maintain the patient’s functional abilities.
Rehabilitation services, including physical, occupational, and speech therapy, play a vital role in helping patients regain their strength and independence. We also emphasize the importance of psychological support to address the emotional challenges that come with a brain tumor diagnosis.
By understanding the factors that affect curability, long-term survival rates, and quality of life considerations, patients and their families can make informed decisions about their care. We are committed to providing comprehensive support throughout the treatment journey.
Conclusion: The Future of Brain Tumor Treatment
As we continue to advance in medical research, the future of brain tumor treatment is becoming increasingly promising. Emerging therapies and ongoing research offer new hope for patients and their families. We are witnessing significant progress in understanding brain tumors, their characteristics, and the most effective treatment approaches.
The development of advanced therapies, including targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and gene therapy, is revolutionizing the field of neuro-oncology. These innovative treatments are being designed to target specific tumor cells, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding healthy tissue. As a result, patient outcomes are improving, and quality of life is being enhanced.
We remain committed to providing world-class healthcare and comprehensive support to international patients seeking advanced medical treatments. By staying at the forefront of the latest research and advancements in brain tumor treatment, we can continue to offer the best possible care and hope for a better tomorrow.
What are the primary treatment options for brain tumors?
The primary treatment options for brain tumors include surgical intervention, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. We tailor the treatment plan to the individual patient’s needs, taking into account the type, size, and location of the tumor.
How is brain cancer treated?
Brain cancer treatment involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining surgical intervention, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. We also consider advanced treatment options, such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy, to provide comprehensive care.
Can brain tumors be cured?
The curability of brain tumors depends on various factors, including the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health. We discuss the factors affecting curability and long-term survival rates with our patients to provide a clear understanding of their prognosis.
What is the role of clinical trials in brain cancer treatment?
Clinical trials play a crucial role in advancing brain cancer treatment by providing access to emerging therapies and promising research directions. We help our patients find and qualify for clinical trials that may be beneficial for their specific condition.
How do you treat a brain tumor?
We treat brain tumors using a multidisciplinary approach, combining surgical intervention, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Our team of specialists works together to develop a coordinated care plan tailored to the individual patient’s needs.
What are the advanced treatment options for brain cancer?
Advanced treatment options for brain cancer include targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and gene therapy. These emerging therapies offer new hope for patients with brain cancer, and we are committed to staying at the forefront of these developments.
How do surgical techniques for brain tumor removal work?
Surgical techniques for brain tumor removal include traditional craniotomy, minimally invasive procedures, and awake brain surgery. We choose the most appropriate technique based on the tumor’s location, size, and the patient’s overall health.
What is the importance of supportive care in managing brain tumors?
Supportive care is essential in managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for brain tumor patients. We provide medications for symptom control, rehabilitation services, and psychological support to ensure comprehensive care.
Can you cure brain cancer?
While we strive to cure brain cancer, the outcome depends on various factors, including the type, size, and location of the tumor. We work closely with our patients to understand their prognosis and develop a treatment plan that addresses their unique needs.
What are the treatment options for brain cancer?
Treatment options for brain cancer include surgical intervention, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and advanced therapies such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy. We tailor the treatment plan to the individual patient’s needs, taking into account the type, size, and location of the tumor.



































