An aneurysm in the carotid artery is a rare but serious issue. It involves a bulging or swollen artery in the neck. Knowing about this condition is key to keeping your brain healthy.
Recent studies show that cerebral aneurysms affect millions globally. If not treated, they can cause severe problems.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on trusted, patient-centered care for carotid artery aneurysms. Our team works hard to offer full support and the latest treatments. We aim for the best results for our patients.
Key Takeaways
- Carotid artery aneurysms are rare but potentially dangerous.
- Understanding the causes and symptoms is key for early detection.
- Liv Hospital provides complete care for carotid artery aneurysms.
- Advanced treatment options are available to manage the condition.
- Patient-centered care is our top priority at Liv Hospital.
Understanding Carotid Artery Aneurysms
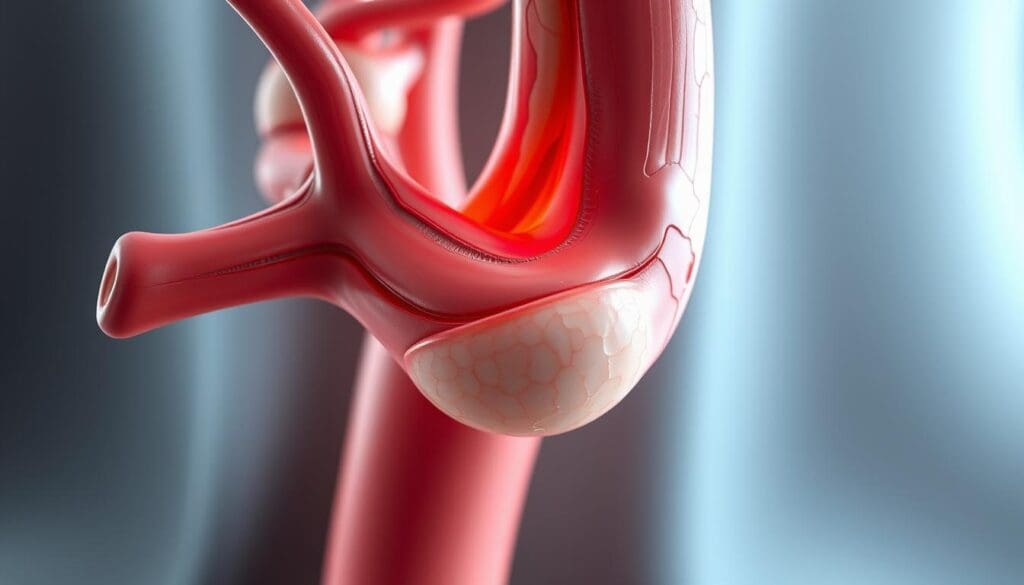
The carotid artery is key for blood flow to the brain. Any issues here can be serious. We’ll look at the artery’s structure and what an aneurysm is.
What Is a Carotid Artery?
The carotid arteries are big blood vessels in the neck. They carry blood to the brain, neck, and face. There are two, one on each side, splitting into internal and external parts.
The internal carotid artery goes to the brain. The external one goes to the neck and face.
Definition and Characteristics of Aneurysms
An aneurysm is when a blood vessel bulges or gets too big. It can happen in any artery, like the carotid. Aneurysms might not show symptoms or could cause neck pain and trouble swallowing.
Research shows many things can cause carotid artery aneurysms. These include atherosclerosis, trauma, and infections.
| Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Carotid artery aneurysms can occur at any point along the carotid artery |
| Symptoms | Neck pain, difficulty swallowing, visible bulging or pulsation in the neck |
| Causes | Atherosclerosis, trauma, infections, connective tissue disorders |
Knowing about carotid artery aneurysms is key for finding and treating them. We’ll dive deeper into types and causes next.
The Anatomy of Carotid Arteries
It’s key to know how carotid arteries work to understand aneurysms’ effects on brain blood flow. These arteries are vital, bringing blood to the brain.
Location and Function
The carotid arteries sit on both sides of the neck. They carry oxygen-rich blood to the brain. Starting from the aortic arch, they go up the neck and split into two branches.
Blood Supply to the Brain
The internal carotid artery mainly feeds the brain. The external carotid artery goes to the face and neck. These arteries are essential for brain health.
Normal Structure vs. Aneurysmal Changes
Aneurysms happen when the artery wall weakens, causing it to bulge. This can mess up blood flow and lead to serious problems.
| Characteristics | Normal Carotid Artery | Aneurysmal Carotid Artery |
|---|---|---|
| Wall Structure | Intact, without dilation | Weakened, with bulging |
| Blood Flow | Normal laminar flow | Turbulent flow |
Types of Aneurysm in Neck Artery
It’s important to know about the different aneurysms in the carotid artery. This knowledge helps in choosing the right treatment. Aneurysms vary in type and location, which guides treatment.
True Aneurysms
True aneurysms affect all layers of the artery. They cause the artery to dilate uniformly.
False Aneurysms (Pseudoaneurysms)
False aneurysms happen when the artery wall is damaged. This leads to blood leaking into the tissue around it. It forms a sac that connects with the artery.
Fusiform vs. Saccular Aneurysms
Fusiform aneurysms are long and spindle-shaped, affecting the whole artery. Saccular aneurysms are pouch-like and only affect part of the artery.
Extracranial vs. Intracranial Carotid Aneurysms
Extracranial aneurysms are outside the skull. Intracranial aneurysms are inside the skull. The location impacts treatment choices.
Knowing the type of aneurysm is key to choosing the right treatment. Below is a table that outlines the main characteristics of each type:
| Type of Aneurysm | Characteristics | Location |
|---|---|---|
| True Aneurysm | Involves all layers of the arterial wall | Can occur anywhere along the carotid artery |
| False Aneurysm (Pseudoaneurysm) | Disruption of the arterial wall, blood leakage | Often associated with trauma or infection |
| Fusiform Aneurysm | Spindle-shaped, involves entire circumference | Can occur in both extracranial and intracranial locations |
| Saccular Aneurysm | Pouch-like, involves part of the arterial wall | More common in intracranial locations |
We’ve looked at the different aneurysms in the neck artery. We’ve highlighted their unique features and where they occur. This knowledge is essential for doctors to create a treatment plan that meets each patient’s needs.
Common Causes of Carotid Artery Aneurysms
It’s important to know what causes carotid artery aneurysms. This knowledge helps in preventing and treating them. We’ll look at the different factors that lead to these aneurysms.
Atherosclerosis and Plaque Formation
Atherosclerosis is a big risk for carotid artery aneurysms. It happens when plaque builds up in the arteries. This buildup can weaken the artery walls.
Trauma and Physical Injury
Carotid artery aneurysms can also be caused by neck trauma. This includes injuries from accidents or surgery. Such trauma can damage the artery walls.
Infections and Inflammatory Conditions
Infections and inflammation can also cause carotid artery aneurysms. Some infections can weaken the artery walls. Chronic inflammation can also harm the blood vessels.
Connective Tissue Disorders
People with certain connective tissue disorders are at higher risk. Conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome can weaken the blood vessels.
Genetic Factors and Family History
Having a family history of aneurysms can increase your risk. Genetic factors can affect the strength of the artery walls.
In summary, carotid artery aneurysms have many causes. These include atherosclerosis, trauma, infections, connective tissue disorders, and genetics. Knowing these causes helps in finding better ways to prevent and treat them.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Swollen Carotid Artery
It’s important to know the signs of a swollen carotid artery for treatment. Carotid artery aneurysms can show different symptoms. Some are easy to spot, while others need a closer look.
Visible Bulging or Pulsation in the Neck
A visible bulge or pulsation in the neck is a common and scary symptom. This happens when the artery swells, making it noticeable. “The presence of a pulsatile mass in the neck is a classic sign of a carotid artery aneurysm.” If you see this, get medical help right away.
Pain and Discomfort
Pain or discomfort in the neck or face might mean you have a carotid artery aneurysm. This pain comes from the aneurysm pressing on nerves or structures. The pain can feel like a dull ache or a sharp stab.
Difficulty Swallowing and Hoarseness
A carotid artery aneurysm can also cause trouble swallowing (dysphagia) or hoarseness (dysphonia). This happens when the aneurysm presses on the esophagus or nerves. These symptoms can really affect your daily life and need medical attention.
Neurological Symptoms
Neurological symptoms can happen if the aneurysm affects blood flow to the brain or if it ruptures, leading to a stroke. Symptoms include dizziness, confusion, weakness on one side of the body, or trouble speaking.
“Prompt recognition of neurological symptoms is critical, as timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes.”
Asymptomatic Aneurysms
Carotid artery aneurysms can also be without symptoms, meaning you won’t notice anything. They might be found during a routine check-up or imaging study for something else. Regular health checks are key, even more so for those with risk factors.
Knowing and spotting the symptoms of carotid artery aneurysms is key for early treatment. If you’re showing any of these signs, see a doctor right away.
Potential Complications of Untreated Aneurysms
Carotid artery aneurysms can cause severe problems if not treated. It’s key to know these risks to stress the need for quick medical help.
Stroke Risk from Clot Formation
One big risk is stroke from clots. Blood in the aneurysm can clot and move to the brain. This can cause a stroke. Studies show this risk is high, making early treatment vital as highlighted in studies on carotid artery.
Rupture and Hemorrhage
Rupture of a carotid artery aneurysm is a serious issue. It can cause severe bleeding into the tissues. This is a medical emergency that needs immediate care.
Compression of Surrounding Structures
An aneurysm can press on nearby structures in the neck. This can cause swallowing problems, hoarseness, and pain. If not treated, it can lead to serious health issues.
Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
A carotid-cavernous fistula is a rare but serious problem. It’s when the carotid artery connects to the cavernous sinus abnormally. Symptoms include pulsatile exophthalmos and vision problems. Specialized treatment is often needed.
Knowing these complications shows why it’s important to get medical help for carotid artery aneurysms. Quick diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes and lower the risk of these serious issues.
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery Bulging
Diagnosing carotid artery aneurysms involves both clinical checks and advanced imaging. It’s key to get the diagnosis right. This helps doctors figure out the best treatment.
Initial Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed physical check. Doctors might feel the neck for unusual pulsations or lumps. They also listen with a stethoscope for abnormal sounds over the carotid arteries.
While this initial check is helpful, it’s not enough to confirm the diagnosis or fully understand the aneurysm.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is often the first choice for checking carotid artery aneurysms. It’s non-invasive and gives important info about the aneurysm’s size and flow. Doppler ultrasound is great for checking blood flow and spotting stenosis or thrombosis.
CT and MRI Scans
Both CT (Computed Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans help evaluate carotid artery aneurysms. CT scans give detailed images and are good for measuring the aneurysm’s size and its position. MRI scans are excellent for soft tissue details and spotting complications.
Angiography and Other Advanced Imaging
In some cases, angiography is used to get detailed images of the carotid arteries and the aneurysm. It involves injecting contrast material into the blood vessels. This helps see the aneurysm’s shape and how it affects blood flow. Other advanced imaging, like digital subtraction angiography, might also be used.
Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to rule out other conditions that might look like carotid artery aneurysms. These include carotid body tumors or lymphadenopathy. A thorough diagnostic process ensures the right diagnosis and treatment.
By using these diagnostic methods, doctors can accurately diagnose carotid artery aneurysms. They can then create a treatment plan that meets the patient’s needs.
Treatment Options for Neck Aneurysms
Carotid artery aneurysms need a treatment plan that fits the aneurysm and the patient. This plan can be simple monitoring or more complex surgeries. It depends on the aneurysm’s size and the patient’s health.
Monitoring and Observation Approach
Small, silent aneurysms might just be watched. Doctors use imaging to check the aneurysm’s size and shape over time.
Medical Management and Medications
For some, managing risk factors is key. This includes controlling blood pressure and cholesterol. Doctors might prescribe medicines to help.
Surgical Interventions
For risky or symptomatic aneurysms, surgery is a good option. Open surgery techniques directly fix or remove the aneurysm.
Open Surgery Techniques
Open surgery might use clipping. A clip is placed around the aneurysm’s neck to stop blood flow.
Risks and Benefits of Surgery
Surgery can be very effective but comes with risks like stroke or nerve damage. Each patient’s benefits and risks are carefully considered.
Endovascular Procedures
Endovascular procedures are less invasive than open surgery. They use blood vessels to reach the aneurysm.
Stenting and Coiling
Stenting and coiling are used to block the aneurysm from blood flow. This lowers the risk of rupture.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
These methods have shorter recovery times and fewer complications than open surgery.
The right treatment depends on many factors. These include the aneurysm’s size, the patient’s health, and the doctor’s skills. A team of doctors works together to find the best treatment for each patient.
Living with a Carotid Artery Aneurysm
Getting diagnosed with a carotid artery aneurysm can change your life. It means making big changes in how you live and feel. We know it’s tough, but you can handle it by focusing on both your body and mind.
Managing Daily Activities
Living with a carotid artery aneurysm means taking care of your health every day. Even simple tasks can be tricky. Eating right, exercising lightly, and sleeping well are key.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Engage in gentle exercises like walking or yoga, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Ensure you get enough sleep to help your body recover.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The emotional side of having a carotid artery aneurysm is real. Many people feel anxious and stressed. It’s important to talk about these feelings to stay well.
Support from loved ones or groups can really help. It’s a big part of dealing with the emotional side.
Support Resources and Groups
Looking for support and joining groups can be a game-changer. These places offer connections and advice. They help you and your family deal with the challenges of carotid artery aneurysms.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Knowing when to go to the emergency room is vital. Signs like a sudden bad headache, trouble speaking, or weakness on one side need quick help.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Living a healthy lifestyle and managing health conditions can lower the risk of carotid artery aneurysms. We will look at the main ways to prevent and reduce risks.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy choices are key to avoiding carotid artery aneurysms. This means:
- Eating a balanced diet with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains
- Staying active to keep your heart healthy
- Not smoking and drinking less alcohol
- Using stress-relief methods like meditation or yoga
Managing Underlying Conditions
Some health issues can raise the risk of carotid artery aneurysms. It’s important to manage these conditions well:
- Keeping blood pressure in check with meds and lifestyle changes
- Controlling diabetes with diet, exercise, and meds
- Lowering high cholesterol with statins or other treatments
Regular checks and treatments for these conditions can lower the risk of aneurysms.
Regular Screening for High-Risk Individuals
People with a family history of aneurysms or other risk factors should get screened often. Early detection helps prevent serious problems.
| Risk Factor | Screening Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Family history of aneurysms | Regular ultrasound or CT scans |
| History of smoking | Annual vascular check-ups |
| Hypertension | Regular blood pressure monitoring |
Working with Healthcare Providers
It’s important to work with healthcare providers if you’re at risk of carotid artery aneurysms. They can give you tailored advice, watch your risk factors, and suggest the right screenings and treatments.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into carotid artery aneurysms, including what causes them, their symptoms, how they’re diagnosed, and treatment options. Knowing about carotid artery aneurysms is key to avoiding serious issues like stroke or rupture.
Treatment options range from watching the aneurysm and managing it medically to surgery or endovascular procedures. The right treatment depends on the aneurysm’s size and the patient’s health.
Preventing carotid artery aneurysms involves making lifestyle changes, managing health conditions, and getting regular check-ups. By understanding the risks and taking action, people can lower their chance of getting an aneurysm.
Our talk shows the need for a complete plan to handle carotid artery aneurysms, from preventing them to treating them. By staying informed and working with doctors, people can face the challenges of this condition.
What is a carotid artery aneurysm?
A carotid artery aneurysm is a bulge in one of the carotid arteries. These arteries are in the neck and carry blood to the brain.
What are the symptoms of a carotid artery aneurysm?
Symptoms include a visible bulge or pulsation in the neck. You might also feel pain, have trouble swallowing, or experience hoarseness. Some people don’t show symptoms at all.
What causes carotid artery aneurysms?
Causes include atherosclerosis and plaque buildup. Trauma, infections, and genetic factors also play a role. Connective tissue disorders can contribute as well.
How are carotid artery aneurysms diagnosed?
Diagnosis starts with a physical exam. Then, ultrasound, CT, and MRI scans are used. Angiography and other imaging help confirm the aneurysm’s presence and details.
What are the treatment options for carotid artery aneurysms?
Treatment varies based on the aneurysm’s size and location. Options include monitoring, medical management, surgery, and endovascular procedures.
Can carotid artery aneurysms be prevented?
While prevention is not always possible, risk factors can be managed. Lifestyle changes and regular screenings are key. Working with your healthcare provider is also important.
What are the complications of untreated carotid artery aneurysms?
Untreated aneurysms can lead to stroke from clotting. Rupture and hemorrhage are also risks. Compression of nearby structures and carotid-cavernous fistula formation are other complications.
How can I manage daily activities with a carotid artery aneurysm?
Managing daily life means following your treatment plan. Make lifestyle changes to reduce risks. This helps maintain your overall health.
What is the difference between true and false aneurysms?
True aneurysms affect all layers of the artery wall. False aneurysms, or pseudoaneurysms, result from a leak or injury to the artery wall.
Are carotid artery aneurysms hereditary?
Yes, some aneurysms have a genetic link. This is more common in those with a family history of aneurysms or certain connective tissue disorders.
When should I seek emergency care for a carotid artery aneurysm?
Seek emergency care for severe symptoms. This includes sudden severe pain, trouble speaking or swallowing, or neurological deficits.
References
- Aurora Health Care (Extracranial Carotid Artery Aneurysm) : https://www.aurorahealthcare.org/services/heart-vascular/conditions/extracranial-carotid-artery-aneurysm
- MedStar Health (Carotid Aneurysms) : https://www.medstarhealth.org/services/carotid-aneurysms
- PMC – PubMed Central : https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6417903
- Tampa General Hospital (Carotid Artery Aneurysms) : https://www.tgh.org/institutes-and-services/conditions/carotid-artery-aneurysms
- Coastal Vascular & Vein Center (Carotid Artery Aneurysms) : https://coastalvvc.com/conditions/carotid-artery-aneurysms



































