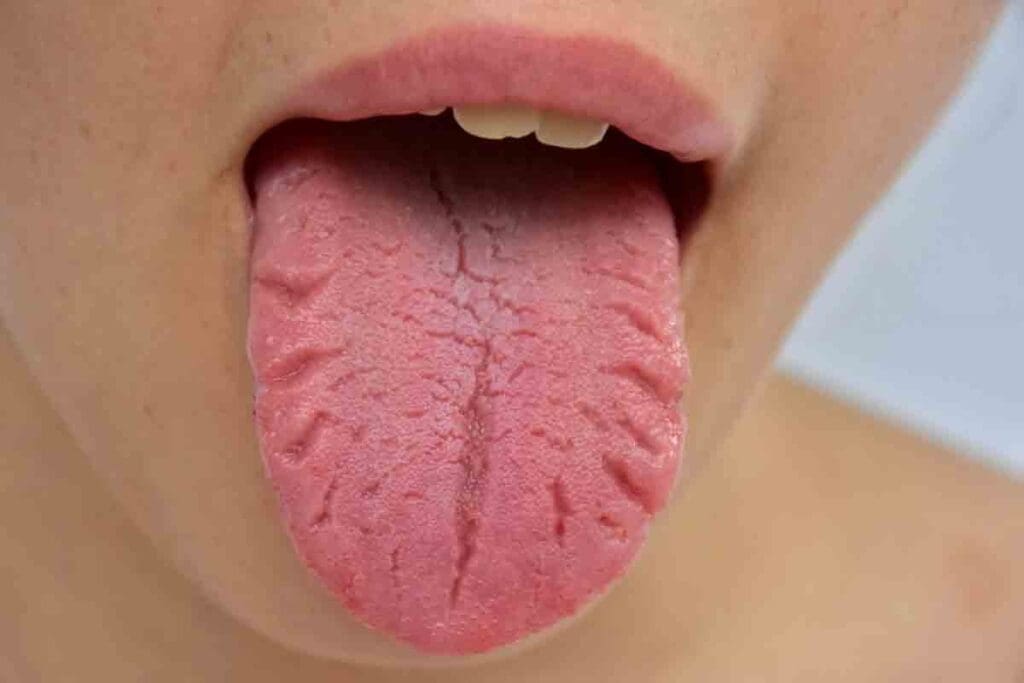
Changes in your tongue, like soreness or swelling, might show something’s off with your health. At Liv Hospital, we focus on you. We help you spot and deal with anemia-related tongue symptoms confidently.
Anemia tongue, or glossitis, makes your tongue swell, smooth, and sometimes hurts. It might look different shades of red. You might see inflammation, tenderness, and missing papillae. Sometimes, you’ll get ulcers or sores too. For more on how anemia impacts your mouth, check out Medical News Today.
Key Takeaways
- Identify the key signs of anemia-related tongue symptoms.
- Understand the importance of addressing iron deficiency.
- Discover practical remedies to restore tongue health.
- Learn how LivHospital’s patient-centered care can help.
- Explore the link between iron deficiency and oral health.
What Happens to Your Tongue When You Have Anemia

The tongue can show signs of health issues, like anemia. Anemia means not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. It affects many parts of the body, including our mouth.
The Connection Between Blood Health and Oral Tissues
Our blood health is key to keeping our mouth tissues healthy. It brings oxygen and nutrients to these areas. When we have anemia, our blood can’t carry enough oxygen.
This can cause problems in our mouth. The tongue, being very vascular, shows changes in blood health. Anemia can make the tongue pale, swollen, or smooth because of lost papillae. These signs can mean we’re not getting enough nutrients or have other health issues.
How Different Types of Anemia Affect the Tongue
Each type of anemia affects the tongue differently. Iron deficiency anemia often leads to a smooth, red tongue and mouth inflammation.
| Type of Anemia | Tongue Symptoms |
| Iron Deficiency Anemia | Smooth, red appearance; loss of papillae |
| Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia | Beefy red tongue; painful glossitis |
| Folate Deficiency Anemia | Similar to Vitamin B12 deficiency; oral ulcers |
Knowing how anemia types affect the tongue helps doctors treat it better. They can target treatments for both the anemia and its mouth symptoms.
Understanding Anemia Tongue: Causes and Mechanisms

It’s important to know what causes anemia tongue to manage it well. Anemia tongue happens when the tongue looks different because of a lack of nutrients, mainly iron.
The Role of Iron in Tongue Health
Iron is key for healthy tongue tissues. It helps make hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to the tongue and other parts of the body. Low iron can make the tongue pale, swollen, or inflamed, causing discomfort.
Iron deficiency means fewer healthy red blood cells. This makes the tongue look pale or white. It can also make the tongue’s surface smooth and shiny because of lost papillae.
How Nutrient Deficiencies Lead to Oral Symptoms
Lack of iron, vitamin B12, and folate can cause anemia tongue. These deficiencies change the tongue’s look, like making it pale or swollen. They can also cause pain or discomfort.
Without the right nutrients, our bodies can’t keep tissues healthy. For the tongue, this means symptoms like discomfort or changes in how it looks.
Risk Factors for Developing Anemia Tongue
Some things make it more likely to get anemia tongue. These include not getting enough iron or vitamin B12, having chronic diseases, or taking certain medicines. These can mess with how our body absorbs nutrients.
- Dietary deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, or folate
- Chronic diseases affecting nutrient absorption
- Certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors or anticonvulsants
- Pregnancy or menstruation, which can increase iron demands
Knowing these risk factors and how nutrient deficiencies cause anemia tongue helps us prevent and manage it.
7 Key Signs of Anemia Tongue to Watch For
The tongue can show signs of health issues, like anemia. Anemia can change the tongue in noticeable ways. Here are the 7 key signs to watch for.
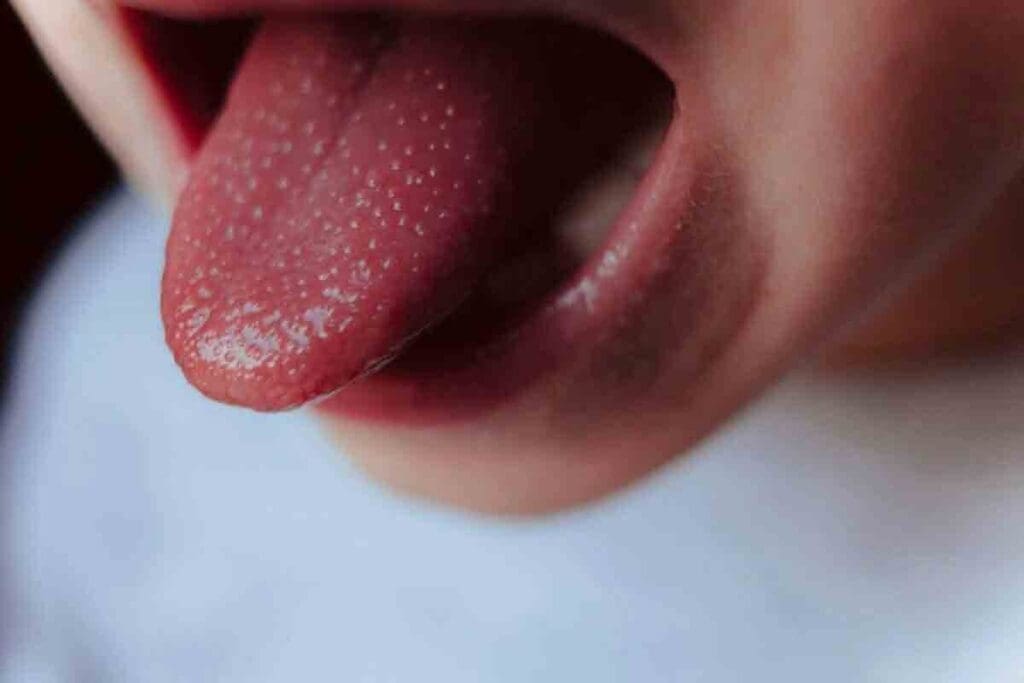
Pale or White Tongue Appearance
A pale or white tongue is a common sign of anemia. It happens when there’s not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. A pale tongue can be an early sign of iron deficiency anemia.
Swollen and Inflamed Tongue
Anemia can make the tongue swell and become inflamed. This can make the tongue look bigger and may hurt. Inflammation is the body’s way of trying to get more oxygen to the tissues.
Smooth, Glossy Surface (Loss of Papillae)
A smooth, glossy tongue is another sign of anemia. It happens when the small bumps on the tongue, called papillae, disappear. The loss of papillae makes the tongue shiny and smooth, and can cause a burning feeling.
Beefy Red Tongue Appearance
In some cases, anemia can make the tongue look beefy red, often due to vitamin B12 deficiency. This can be painful or inflamed. A beefy red tongue is a sign of a serious deficiency and needs quick medical care.
Soreness or Pain
Soreness or pain in the tongue is common in anemia. This discomfort can be mild or severe and may get worse when eating or speaking.
Difficulty with Eating or Swallowing
Anemia can also make eating or swallowing hard. This is because of pain, swelling, or changes in the tongue’s surface. It’s important to address these issues to avoid malnutrition.
Changes in Taste
Lastly, anemia can change how things taste. Some people might taste metal or have trouble tasting certain foods. This symptom can be very upsetting and may affect nutrition.
Knowing these 7 signs of anemia tongue can help you get medical help if you notice them. Early treatment can greatly improve anemia outcomes.
How Different Types of Anemia Affect Your Tongue
Anemia can change how your tongue looks and feels. It happens when you don’t have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. Each type of anemia can show up differently in your mouth.
Iron Deficiency Anemia Tongue Symptoms
Iron deficiency anemia is very common. It can make your tongue look pale or white. Sometimes, your tongue might swell and get sore.
Your tongue might also feel smooth and shiny. This is because the tiny bumps on your tongue are gone. Eating spicy or sour foods can hurt your tongue even more.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency (Pernicious Anemia) Tongue Signs
Vitamin B12 deficiency makes your tongue look beefy red. It also feels smooth because the bumps on your tongue shrink. This can make eating and talking hard.
Folate Deficiency Anemia and the Tongue
Folate deficiency anemia makes your tongue red and sore. It’s because your body can’t make DNA and RNA properly. This affects the fast-growing cells in your mouth.
Hemolytic Anemia Tongue Manifestations
Hemolytic anemia destroys red blood cells too early. It’s not as common to see tongue symptoms with this type. But, it can make your tongue yellow from jaundice. You might also get mouth sores.
Knowing how anemia affects your tongue helps doctors treat it better. They can focus on the symptoms and find the root cause.
Diagnosing Anemia Through Tongue Examination
Healthcare providers often look at more than just blood tests to diagnose anemia. They also check for physical symptoms, like changes in the tongue. The tongue can show signs of anemia, helping in the diagnosis.
What Healthcare Providers Look For
During a tongue exam, doctors check for color, texture, and size changes. Signs of anemia in the tongue include pallor, inflammation, or a smooth surface. This is because of the loss of papillae.
A detailed look at these features helps doctors see if they match anemia symptoms. For example, a pale tongue might mean low red blood cells or hemoglobin. A swollen or inflamed tongue could point to a nutrient shortage.
Additional Tests to Confirm Diagnosis
Even with a tongue exam, more tests are needed to confirm anemia. These tests include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check red blood cell count and hemoglobin levels
- Blood smear to look at red blood cell shape
- Iron level tests to find iron deficiency
- Vitamin B12 and folate level tests for deficiencies
| Test | Purpose |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Checks red blood cell count and hemoglobin levels |
| Blood Smear | Looks at red blood cell shape |
| Iron Level Tests | Seeks iron deficiency |
Differentiating Anemia Tongue from Other Conditions
It’s important to tell anemia tongue symptoms from other conditions. Oral thrush, geographic tongue, or vitamin deficiencies can look similar. A full check is needed.
By combining tongue exam results with more tests, doctors can accurately diagnose anemia. They can then create a proper treatment plan.
Medical Treatments for Anemia Tongue Symptoms
Medical treatments for anemia tongue symptoms aim to fix the underlying issues, like iron or vitamin deficiencies. To manage anemia tongue, a mix of medical treatments and lifestyle changes is needed.
Iron Supplementation Approaches
Iron supplements are key for treating anemia tongue due to iron deficiency. The goal is to fill up iron stores and get hemoglobin levels back to normal. Oral iron supplements, like ferrous sulfate, are often the first choice.
It’s important to take iron supplements on an empty stomach to better absorb them. But, this can sometimes cause stomach problems. Taking the supplement with a bit of food or vitamin C can help lessen these side effects.
Vitamin B12 and Folate Treatments
For anemia tongue caused by vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, taking these vitamins is vital. Vitamin B12 injections are often needed for those with pernicious anemia, as oral supplements may not be absorbed well.
Folate supplements are usually taken by mouth. It’s important to check folate levels to see if the treatment is working. Sometimes, high doses of folate are needed if the deficiency is severe.
Addressing Underlying Causes
While supplements are important, tackling the root causes of anemia tongue is also key. This might mean looking into and managing issues like celiac disease or stomach surgery.
Getting dietary advice is also a big part of treatment. It helps patients know which foods to eat and avoid to manage their condition well.
Timeline for Symptom Improvement
The time it takes for symptoms to get better varies based on how severe the anemia is and its cause. Generally, people start seeing improvements in tongue symptoms in a few weeks to a few months after starting treatment.
For example, iron supplements can show improvements in hemoglobin levels in 2-3 weeks. But, it might take several months to fully build up iron stores. Vitamin B12 injections can quickly improve symptoms, sometimes in just days.
It’s important to keep up with regular check-ups with healthcare providers. This helps track how well the treatment is working and makes any needed changes.
Dietary Remedies to Alleviate Sore Tongue from Iron Deficiency
To help a sore tongue from iron deficiency, focus on iron-rich foods and absorption enhancers. Changing your diet is key to managing anemia symptoms like sore tongue. Eating the right foods and avoiding those that block iron absorption can ease discomfort and aid in recovery.
Iron-Rich Foods to Include in Your Diet
Eating foods rich in iron is vital for treating iron deficiency anemia. Red meat, poultry, and seafood are great sources of iron. For example, clams, sardines, and organ meats like liver are very iron-rich. Plant-based options include beans, lentils, tofu, and fortified cereals. Also, dark leafy greens like spinach and kale are good for iron.
- Red meat (beef, lamb)
- Poultry (chicken, turkey)
- Seafood (clams, sardines, shrimp)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Nuts and seeds (pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds)
- Fortified cereals
Foods That Enhance Iron Absorption
Vitamin C boosts iron absorption, which is important for plant-based foods. Eat foods high in vitamin C like citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and tomatoes with iron-rich foods. For example, orange juice with your cereal can improve iron absorption.
| Food | Vitamin C Content |
| Orange | 100% DV per medium orange |
| Strawberries | 150% DV per cup |
| Bell Peppers | 125% DV per cup |
Foods to Avoid That Inhibit Iron Absorption
Some foods and drinks can lower iron absorption. Caffeine and tea, like black tea, can reduce iron absorption. Calcium-rich foods and supplements should be eaten at different times. Also, foods high in phytates like whole grains and legumes can lower iron absorption. But soaking, sprouting, or fermenting these foods can lessen this effect.
Sample Meal Plan for Anemia Recovery
Here’s a meal plan to help manage anemia and sore tongue:
| Meal | Food |
| Breakfast | Iron-fortified cereal with sliced banana and almond milk, glass of orange juice |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with spinach, bell peppers, and citrus vinaigrette |
| Dinner | Beef stir-fry with broccoli, carrots, and brown rice |
| Snack | Apple slices with almond butter |
By following these dietary tips, you can ease sore tongue from iron deficiency and help recover from anemia.
Practical Home Care for Anemia Tongue Relief
Home care is key to easing anemia tongue symptoms. We’ll explore how to do it right. It involves good oral hygiene, soothing remedies, and lifestyle changes.
Gentle Oral Hygiene Techniques
Good oral hygiene is vital for easing anemia tongue discomfort. Gentle brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush removes bacteria and debris without hurting the tongue.
- Use a mild, non-abrasive toothpaste.
- Brush your tongue gently from back to front.
- Replace your toothbrush regularly to maintain hygiene.
Soothing Remedies for Tongue Discomfort
Several remedies can ease anemia tongue discomfort. Cold or warm compresses offer quick relief.
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling.
- Use a warm compress to increase blood flow and comfort.
Natural Rinses and Topical Applications
Natural rinses and topical applications can offer extra relief. Saline rinses help keep the mouth clean and reduce inflammation.
- Mix 1/4 teaspoon of salt with 8 ounces of warm water.
- Rinse your mouth gently for 30 seconds.
- Spit out the solution and repeat as needed.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Support Recovery
Some lifestyle changes can help you recover from anemia tongue. A balanced diet rich in iron and vitamins is essential.
- Include iron-rich foods like red meat, spinach, and fortified cereals.
- Consume vitamin C-rich foods to enhance iron absorption.
- Avoid spicy or acidic foods that can irritate the tongue.
When to See a Doctor About Anemia Tongue Swelling and Other Symptoms
Knowing when to see a doctor about anemia tongue symptoms is key. Anemia tongue swelling and other symptoms can show serious health problems. These need medical attention.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
Certain symptoms need quick medical check-ups. These include:
- Severe tongue swelling that makes breathing or swallowing hard
- Persistent or severe pain in the tongue
- Changes in tongue color, such as a beefy red or pale look
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing because of tongue discomfort
- Fever or chills with tongue symptoms
Tracking Your Symptoms Effectively
Keeping a symptom journal helps your doctor diagnose and treat anemia tongue. Track:
| Symptom | Date | Severity (1-10) | Additional Notes |
| Tongue swelling | 02/15 | 6 | Noticed after eating certain foods |
| Pain | 02/16 | 7 | Persistent throughout the day |
| Color change | 02/17 | 8 | Tongue appeared beefy red |
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
Being ready with questions helps you understand your condition better. Ask:
- What is the underlying cause of my anemia tongue symptoms?
- What treatment options are available for my condition?
- Are there any dietary changes I should make to alleviate symptoms?
- How can I manage tongue discomfort or pain?
- What follow-up care is necessary to monitor my condition?
Being informed and proactive helps you work well with your healthcare provider. Together, you can manage anemia tongue symptoms effectively.
Conclusion: Long-Term Management and Prevention of Anemia Tongue
Managing anemia tongue long-term means keeping iron levels up and tackling the root causes. It also involves making lifestyle changes. A diet full of iron and important nutrients is key to avoiding anemia tongue.
Regular health check-ups are vital to keep an eye on iron levels and overall health. Adding iron-rich foods and supplements when needed helps keep iron levels healthy.
Knowing what causes and shows anemia tongue helps us act early. This way, we can prevent and manage it, keeping our mouths and bodies healthy.
FAQ
What is anemia tongue?
Anemia tongue is when your tongue looks and feels different because of anemia. This usually happens because of a lack of iron or other nutrients.
How does iron deficiency cause anemia tongue?
When you don’t have enough iron, your body can’t make enough hemoglobin. This leads to changes in your tongue, like it becoming pale or swollen.
What are the symptoms of anemia tongue?
Signs of anemia tongue include a pale or white tongue. It might also be swollen or feel smooth. You could also notice it looks beefy red or hurts.
Can different types of anemia affect the tongue differently?
Yes, different anemias can change your tongue in different ways. For example, iron deficiency anemia might make your tongue pale, while vitamin B12 deficiency anemia could make it beefy red.
How is anemia tongue diagnosed?
Doctors check for anemia tongue by looking at your tongue and doing blood tests. They might do a complete blood count (CBC) and check your iron levels.
What are the treatments for anemia tongue?
To treat anemia tongue, doctors might give you iron supplements or vitamins like B12 and folate. They’ll also help you change your diet and manage any health issues.
Can dietary changes help alleviate anemia tongue symptoms?
Yes, eating foods rich in iron, B12, and folate can help. Avoiding foods that block iron absorption can also help your tongue feel better.
Are there any home remedies for anemia tongue relief?
Yes, you can try gentle mouth care and soothing remedies. Saltwater or baking soda rinses can help ease discomfort and aid in healing.
When should I see a doctor about anemia tongue symptoms?
If your symptoms are severe or don’t go away, see a doctor. Also, if you have trouble swallowing, breathing, or speaking, or if you’re worried about your symptoms or treatment.
How can I prevent anemia tongue?
To prevent anemia tongue, eat a balanced diet with enough iron. Manage any health conditions and address nutrient deficiencies quickly.
Can anemia tongue be a sign of an underlying health condition?
Yes, anemia tongue can mean you have a health issue like iron or vitamin B12 deficiency. It’s important to get checked by a healthcare provider.
Is anemia tongue a common symptom of anemia?
Yes, anemia tongue is a common sign of anemia, often seen in iron deficiency cases. It’s a key indicator of nutrient deficiencies.
Reference
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) – Pernicious anemia presenting as glossitis (tongue inflammation)









