Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a complex condition that affects many people. It’s important to know about the risks of brain AVM surgery. This knowledge helps patients make better choices about their care.
Dealing with AVM removal surgery can be scary. For example, Assem Elshaer had a stroke after surgery. This caused a lot of brain damage. It shows how vital it is to understand the possible side effects of these surgeries.
At Liv Hospital, we aim to give top-notch healthcare. We support international patients fully. In this article, we’ll look at 7 important facts about AVM surgery side effects. We’ll also talk about what you need to know about recovering.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the risks of AVM removal surgery is key for patient care.
- Brain AVM surgery can lead to various complications, like neurological problems.
- Patients might face seizures, headaches, and tiredness after surgery.
- Infection and stroke are serious risks with arteriovenous malformation surgery.
- Liv Hospital is committed to advanced, patient-centered care for AVM treatment.
Understanding Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
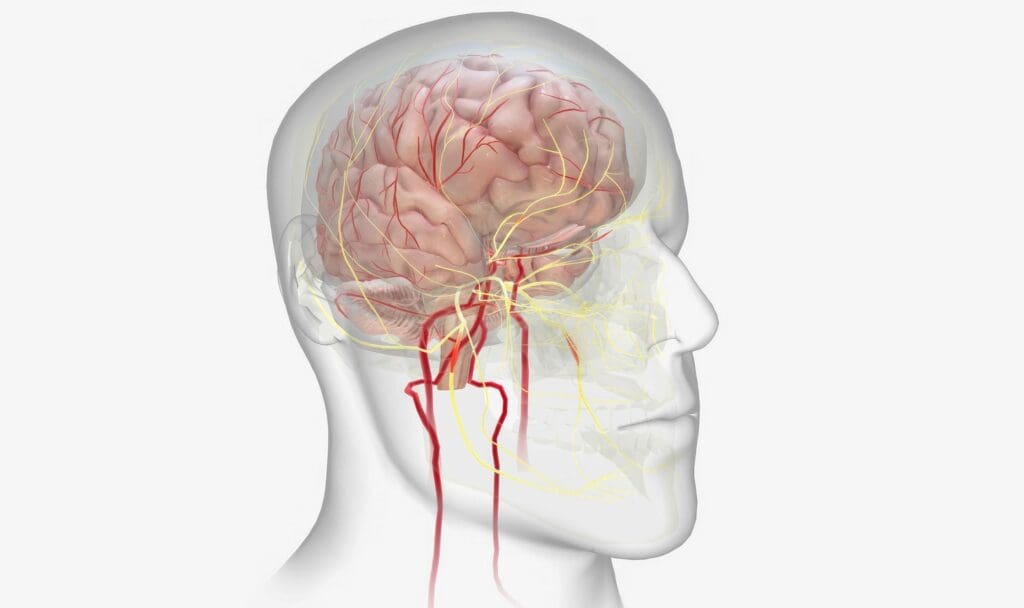
It’s important for patients to know about arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) before brain surgery. An AVM is a problem where arteries and veins connect directly, skipping the capillary system. This can cause health issues like neurological problems and bleeding.
What Is a Brain AVM?
A brain AVM is a mix of blood vessels in the brain that messes with blood flow and oxygen. Unlike regular blood vessels, AVMs lack a capillary bed. This can cause hemorrhaging or neurological damage. The exact cause of AVMs is not known, but they are thought to be present at birth.
Symptoms of a brain AVM can vary a lot. Some people might not show symptoms until the AVM ruptures, causing a hemorrhagic stroke. Others might have seizures, headaches, or neurological deficits because of the AVM. The condition can be found during a check-up for something else or after a rupture.
Why Surgical Intervention Is Often Necessary
Surgery is often needed to treat AVMs, mainly if they have ruptured or are likely to rupture. The main goal of AVM surgery is to stop bleeding and other problems by removing or closing the AVM. Whether to have surgery depends on the AVM’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
For some, like Assem Elshaer, surgery can change their life. Knowing the risks of AVMs and the benefits of surgery helps patients make good choices. We’ll look at the different surgery options for AVMs next.
Types of AVM Surgery Procedures
There are several ways to treat Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs). Each method has its own advantages and risks. The right choice depends on the AVM’s size, location, and how complex it is. It also depends on the patient’s health.
Traditional Open Surgery (Craniotomy)
Traditional open surgery, or craniotomy, is a common treatment for AVMs. It involves making an incision in the skull to remove the malformation. Craniotomy lets surgeons directly access and remove the AVM in many cases. But, it can lead to risks like infection, bleeding, and damage to brain tissue.
Embolization Techniques
Embolization is a less invasive method. It blocks blood flow to the AVM using materials like coils or glue. This technique can be used alone or with other treatments like surgery or radiosurgery. It reduces bleeding risks during surgery and can ease symptoms. But, it might not remove the AVM completely, and more treatments could be needed.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a precise radiation therapy. It targets the AVM with little harm to healthy tissue. SRS encourages the closure of abnormal blood vessels over years. It’s less invasive than surgery but depends on the AVM’s size and location. SRS is often chosen for hard-to-reach AVMs or when surgery is not suitable.
Each AVM surgery has its own use, benefits, and risks. The choice depends on the AVM’s details and the patient’s health.
AVM Surgery Side Effects: The 7 Most Common Complications
Knowing the side effects of AVM surgery is key to making good treatment choices. It’s important to think about both the short and long-term effects on a patient’s life.
Immediate vs. Long-Term Side Effects
AVM surgery side effects fall into two groups: immediate and long-term. Immediate effects happen right after surgery or during the hospital stay. Long-term effects can show up weeks, months, or even years later.
Right after surgery, you might feel neurological deficits like weakness or numbness. This is because the surgery touches delicate brain tissues and blood vessels.
“The risk of neurological deficits following AVM surgery is a significant concern, as it can impact a patient’s ability to perform daily activities.”
Long-term side effects might include headaches and seizures. These might need ongoing treatment with medicine. We’ll look at these more closely later.
Statistical Overview: Understanding Your Risk
To grasp the risks of AVM surgery, let’s look at some numbers. Research shows that 5-15% of patients face disabling neurological deficits after surgery.
| Complication | Risk Percentage |
|---|---|
| Disabling Neurological Deficits | 5-15% |
| Stroke Risk | 2-5% |
| Infection | 1-3% |
The 7 most common complications of AVM surgery are:
- Neurological deficits
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Infection
- Stroke risks
Knowing these common complications helps patients prepare for recovery. It also helps them make informed choices about their treatment.
Neurological Deficits: The Primary Concern
AVM surgery can lead to neurological deficits, a major worry for patients and doctors. These deficits mean a loss or reduction in brain function. This can greatly affect a person’s life quality.
Types of Possible Neurological Impairments
AVM surgery may cause different brain problems. These include motor, sensory, cognitive, and speech issues. The severity depends on the AVM’s location and size.
AVMs in key brain spots, like the motor cortex or speech areas, can cause big problems after surgery. Assem Elshaer, for example, faced serious brain challenges after his surgery. This shows the risks involved.
5-15% Risk of Disabling Neurological Deficits
Research shows a 5% to 15% chance of lasting brain damage after AVM surgery. This risk varies based on the AVM’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
| AVM Characteristic | Risk of Neurological Deficits |
|---|---|
| Small AVM (<3 cm) | Lower risk (<5%) |
| Large AVM (>6 cm) | Higher risk (10-15%) |
| AVM in critical brain areas | Higher risk (8-12%) |
Managing and Rehabilitating Neurological Issues
Dealing with brain problems after AVM surgery needs a team effort. This includes physical, occupational, speech, and cognitive therapy.
Rehab plans are made for each patient. They aim to help them recover and improve their life. Early start in therapy is key for the best results.
Headaches and Seizures After Brain AVM Removal
It’s important to know about headaches and seizures after AVM surgery. Patients often see big changes in their health after surgery. Knowing about these issues helps manage them better.
Post-Operative Headache Patterns and Management
Headaches are common after AVM surgery. They can be mild or severe. Many things can affect how bad they are, like the AVM’s size and where it is.
Managing Post-Operative Headaches: We use a few ways to help with headaches. This includes the right pain medicine, staying hydrated, and getting enough rest. Sometimes, we need to do more to find the cause.
Seizure Risk and Anti-Epileptic Medication Protocols
Seizures can also happen after AVM surgery. The chance of seizures depends on the AVM’s location and if the patient had seizures before.
Seizure Prevention and Management: To lower the chance of seizures, we might give anti-epileptic medicines. We pick the right medicine and amount based on the patient’s needs and history.
Watching for seizures and changing the medicine if needed is key. We work with patients to keep seizure risk low and improve their life quality.
Physical Side Effects: Nausea, Fatigue, and Infection
It’s important for patients to know about the physical side effects of AVM surgery. After surgery, patients often feel uncomfortable. These feelings can slow down their recovery.
Managing Post-Surgical Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common after AVM surgery. This is because of the anesthesia and pain meds. Effective management strategies include:
- Using anti-nausea medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider
- Staying hydrated with clear fluids like water or electrolyte-rich beverages
- Eating small, frequent meals that are bland and easy to digest
- Avoiding strong smells or foods that can trigger nausea
Following your doctor’s advice on managing nausea is key. It helps prevent dehydration and aids in a smoother recovery.
Expected Fatigue Patterns During Recovery
Fatigue is a common side effect after AVM surgery. It comes from the body’s response to surgery and healing. Patients usually feel tired for weeks to months. Key factors influencing fatigue include the surgery’s extent, the patient’s health, and their activity level before surgery.
To manage fatigue, patients should:
- Rest adequately, allowing the body to heal
- Gradually increase physical activity as recommended by healthcare providers
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support recovery
Infection Risks and Prevention Strategies
Infection is a risk after AVM surgery, like with any surgery. Preventive measures include:
- Following post-operative wound care instructions carefully
- Taking antibiotics as prescribed to prevent infection
- Monitoring for signs of infection, such as fever, redness, or swelling at the surgical site
- Attending follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing
By understanding these physical side effects and using the right strategies, patients can lessen their discomfort. This helps improve their recovery after AVM surgery.
Stroke Risk Following Arteriovenous Malformation Surgery
The risk of stroke after AVM surgery is a big worry for doctors and patients. Arteriovenous malformations are bad connections between arteries and veins. They can cause serious health problems if not treated right.
Surgery is a main way to treat AVMs, but it has risks. One of these risks is the chance of getting a stroke.
Hemorrhagic vs. Ischemic Stroke Complications
There are two main kinds of stroke that can happen after AVM surgery. Hemorrhagic stroke is when there’s bleeding in or around the brain. This can happen if an aneurysm or the AVM itself ruptures.
Ischemic stroke is when a blockage in a brain artery stops blood flow. This can be caused by a blood clot during or after surgery.
Both types of stroke can be very serious. They can lead to big disabilities or even death. It’s important to know the difference to manage and lessen their effects.
Prevention and Monitoring Protocols
To lower the chance of stroke after AVM surgery, we use several steps. We plan carefully before surgery, do the surgery with great care, and watch patients closely after. Patients often stay in the ICU to catch any problems early.
We also use MRI and CT scans to check the brain after surgery. These tests help us find any problems fast, so we can act quickly.
Emergency Response to Post-Operative Stroke Symptoms
It’s key to know the signs of stroke to get help fast. Symptoms include sudden weakness, trouble speaking, and vision problems. If you see these signs, act quickly.
If a stroke is suspected, we start a special response plan. A team of doctors, including neurologists and neurosurgeons, quickly assess the situation. We use emergency imaging to figure out what’s happening and how to treat it. This might include medicine for ischemic stroke or surgery for hemorrhagic stroke.
By knowing the risks and being ready to act, we can help patients do better after AVM surgery.
Risk Factors That Influence AVM Surgery Outcomes
Understanding the risks of AVM surgery is key for both doctors and patients. It helps them make smart choices. Knowing what can affect surgery results is very important.
AVM Size and Location: Impact on Complication Rates
The size and where an AVM is located matter a lot. Larger AVMs are riskier because they’re harder to operate on and can bleed more. Also, AVMs near important brain areas, like those for speech or movement, can lead to more problems after surgery.
Venous Drainage Patterns and Surgical Complexity
The way blood drains from an AVM also affects surgery success. AVMs with deep venous drainage are tougher to fix because of the risk of high blood pressure and bleeding. Knowing how blood drains helps doctors plan the surgery better and lower risks.
Patient-Specific Risk Factors to Consider
Things like age, health, and other health issues also matter. Older patients or those with other health problems might face more risks. A detailed check before surgery is needed to plan the best treatment.
By looking at these risks, doctors can guess possible problems and find ways to avoid them. This helps improve how well patients do after surgery.
Recovery Timeline After AVM Brain Surgery
The recovery after AVM brain surgery is complex. It includes immediate care and long-term rehab. Knowing this timeline helps patients plan and make informed choices about their care.
Hospital Stay and Immediate Post-Operative Period
Right after surgery, patients are watched closely in the hospital. How long they stay depends on the surgery’s complexity and their health. Usually, it’s a few days to a week.
Key aspects of the immediate post-operative period include:
- Close monitoring of vital signs and neurological function
- Management of pain and discomfort
- Prevention and early detection of possible complications
Long-Term Rehabilitation Process
After leaving the hospital, patients need rehab to get strong again. The rehab time and effort vary. It depends on the surgery’s extent and any health issues before.
Rehabilitation may include:
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and strength
- Occupational therapy to regain daily functioning skills
- Speech therapy if there are communication problems
Recovery from AVM Rupture vs. Elective Surgery
Recovery times differ for elective surgery and AVM rupture. Rupture patients often face a longer, harder recovery. This is because the rupture causes more damage.
Assem Elshaer’s recovery after surgery included a lot of rehab. He had physical therapy and counseling for emotional support. His story shows the value of personalized care during recovery.
Understanding the recovery timeline helps patients prepare. It’s key for patients and families to work with their healthcare team. Together, they can create a recovery plan that meets each person’s needs for the best results.
Success Rates and Long-Term Prognosis
AVM surgery success is not just about immediate results. It also looks at long-term health. We’ll dive into what affects AVM surgery success and patient outcomes.
Cure Rates for Different AVM Types and Locations
Cure rates for AVMs depend on their type, size, and where they are. Cure rates for these treatments can be 70% to 90% in 2-5 years, based on the AVM’s details.
A leading neurosurgeon says, “The location and size of the AVM are key to surgery success.”
“AVMs in deep or important brain areas have lower cure rates than those in easier-to-reach spots.”
Minor vs. Major Side Effects
It’s important to know the difference between minor and major side effects after AVM surgery. Minor side effects, like headaches or nausea, affect up to 40% of patients but are usually short-lived. Major side effects, like brain damage, are rarer but can greatly affect a patient’s life.
Factors That Improve Long-Term Survival Rates
Several things can help improve survival chances after AVM surgery. These include the patient’s age, health, and any other health issues. The skill of the surgical team and the use of new surgical methods also matter a lot.
Key factors for better long-term survival include:
- Complete removal of the AVM
- Using less invasive surgical methods
- Handling post-surgery problems well
- Good follow-up care
Understanding these factors helps patients and doctors make better choices about AVM treatment.
Advanced Treatment Options and Emerging Techniques
Medical technology is getting better, leading to new treatment options for Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs). We’re seeing a big change in how AVMs are treated. Now, treatments are more advanced and tailored to each patient.
Multimodal Approaches to Complex AVMs
One exciting new trend is multimodal approaches. This means using different treatments together, like embolization, surgery, and radiosurgery. It helps us create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
For example, a patient with a big AVM might first get embolization to shrink the blood flow. Then, radiosurgery might be used to get rid of the rest. This way, we can help patients more and lower the chance of problems.
Staged Procedures for High-Risk Cases
For AVMs that are high-risk, staged procedures are key. This means treating the AVM in parts, over time. It helps manage risks and is good for patients with big or tricky AVMs.
Staging treatment lets us watch how the patient does and change the plan if needed. It needs careful planning but can lead to better results for complex cases.
Research and Future Directions in AVM Treatment
The field of AVM treatment is always growing, with research and new techniques making things better. Better imaging tech helps us diagnose and plan treatments more accurately.
Looking ahead, we might see new embolization materials, better radiosurgery, and more effective surgery. As these new things come along, we’ll keep working to give our patients the best care possible.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About AVM Treatment
As we wrap up our talk on AVM surgery side effects and brain AVM removal, it’s clear that informed choices are key. Knowing the risks, benefits, and other options helps patients work well with their doctors.
We’ve looked at different AVM treatments, like surgery types, possible problems, and how long it takes to recover. This info helps patients make choices that fit their needs and situations.
Good decision-making about AVM treatment needs teamwork. Patients, families, and doctors must work together. With the latest medical info, we can help people with AVMs live better lives.
What are the common side effects of AVM surgery?
AVM surgery can lead to neurological issues, headaches, seizures, and nausea. Fatigue, infection, and stroke risks are also possible. The severity and frequency of these side effects vary by case and surgical method.
How long does it take to recover from AVM brain surgery?
Recovery time after AVM brain surgery varies. It depends on the surgery’s complexity and the patient’s health. Patients usually spend a few days to a week in the hospital. Then, they need several weeks or months of rehabilitation.
What are the risks associated with AVM surgery?
Risks include neurological deficits, stroke, infection, and death. The risk depends on the AVM’s size and location, the patient’s health, and the surgery type.
Can AVMs be treated without surgery?
Yes, some AVMs can be treated without surgery. Techniques like embolization or stereotactic radiosurgery are options. But, surgery is often needed for larger or more complex AVMs.
What is the success rate of AVM surgery?
Success rates vary by AVM size, location, and surgery type. Cure rates range from 50% to 90% for different AVM types.
How can I minimize the risks associated with AVM surgery?
To reduce risks, work with an experienced neurosurgical team. Follow their pre- and post-operative care advice. Be aware of risks and report any concerns to your healthcare provider.
What are the differences between hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke complications after AVM surgery?
Hemorrhagic stroke is bleeding in the brain. Ischemic stroke is a blockage of blood flow. Both can be serious. Quick medical attention is key if symptoms appear.
Can I expect to experience seizures after AVM surgery?
Seizures are a possible complication. The risk depends on the case and surgery type. Anti-epileptic medication can help manage this risk.
How can I manage post-operative headaches after AVM surgery?
Manage headaches with pain medication, rest, and other supportive measures. Follow your healthcare provider’s advice for headache management.
Are there any advanced treatment options or emerging techniques for AVMs?
Yes, there are advanced and emerging treatments for AVMs. These include multimodal approaches and staged procedures. They can help treat complex AVMs and improve outcomes.
What is the role of venous drainage patterns in AVM surgery outcomes?
Venous drainage patterns are key in AVM surgery outcomes. They affect procedure complexity and complication risk. Understanding these patterns is vital for optimal planning.
How does AVM size and location impact complication rates?
AVM size and location greatly affect complication rates. Larger and more complex AVMs have higher risks. Location also impacts the risk of neurological deficits and complications.
REFERENCES
- “Vascular Malformations of the Brain and Its Coverings.” J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2020;14(8):285‑294. DOI: 10.5797/jnet.ra.2020‑0020. PMC




































