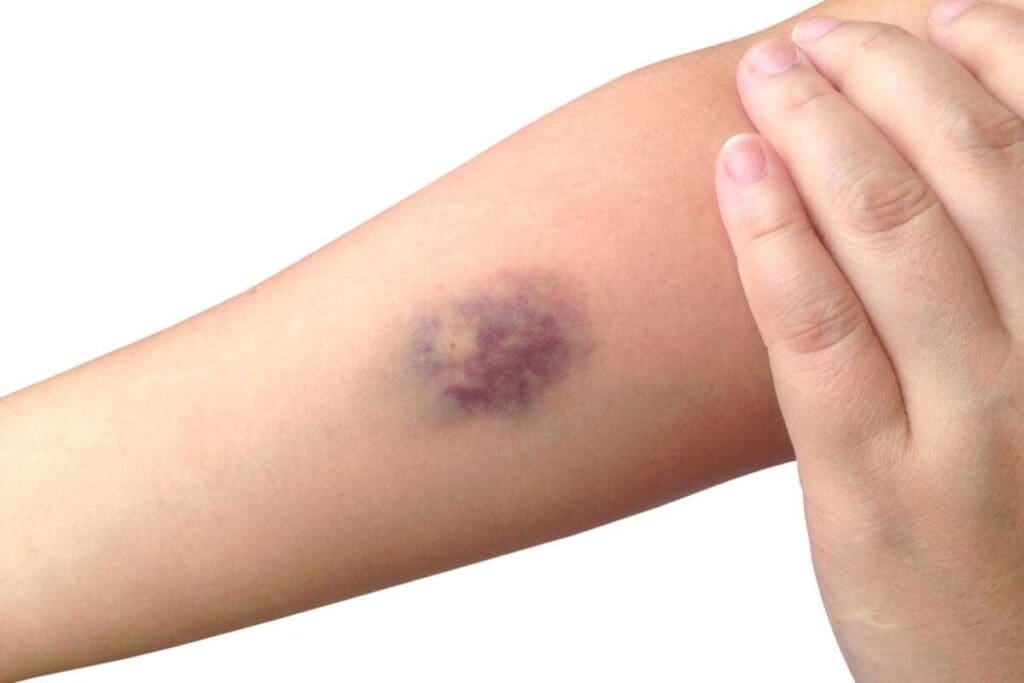
It’s vital to spot the signs of a blood clot in the arm early. At LivHospital, we stress the need to know the visual signs and risks of upper arm deep vein thrombosis (DVT).Explore blood clot arm pictures and learn to spot early signs, risks, and visible symptoms effectively.
Symptoms include swelling, pain, and cramping. You might also notice changes in skin color or temperature. Sometimes, veins can look bigger than usual. Knowing these signs can help you get medical help fast.
Our team at LivHospital is known worldwide for caring for our patients. In this article, we’ll look at the signs and symptoms of blood clots in the upper arm. We aim to help you understand the risks and what to watch for.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize the visual signs of a blood clot in the arm, such as swelling and skin discoloration.
- Understand the risks associated with upper extremity DVT.
- Learn about the importance of timely medical intervention.
- Discover how to identify visible vein enlargement.
- Find out how LivHospital’s expert team can support your care.
Understanding Blood Clots in the Arm
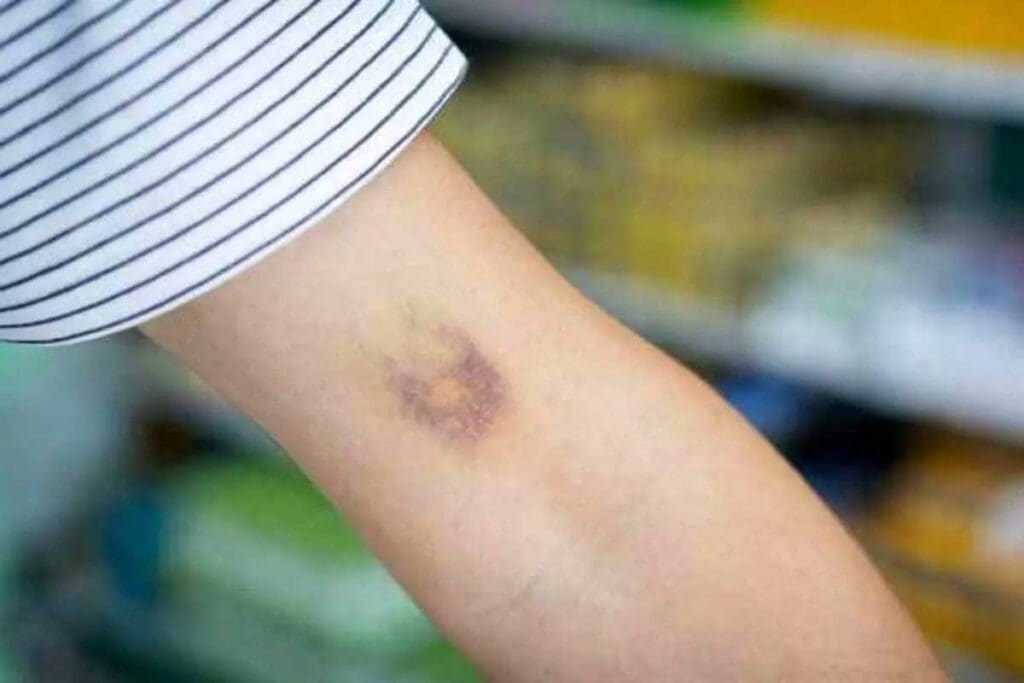
It’s important to know about blood clots in the arm to catch them early. These clots can form in different parts of the arm, like the upper arm, forearm, and elbow.
What Are Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Upper extremity DVT is a blood clot in the deep veins of the arm. It’s not as common as clots in the legs but can cause serious problems. It can happen for many reasons, like injury, medical procedures, or health issues.
How Common Are Arm Blood Clots?
Arm blood clots are not as common as leg clots. But, they are becoming more common because of medical devices. We’ll look at how often they happen and what increases the risk.
| Condition | Prevalence | Risk Factors |
| Upper Extremity DVT | Less common than lower extremity DVT | Central venous catheters, trauma, cancer |
| Arm Blood Clots | Increasing incidence | Medical devices, underlying health conditions |
Why Some People Don’t Notice Early Symptoms
Some people might not notice symptoms of arm blood clots early on. This is because up to 33-60 percent of cases go unnoticed. The reasons include where the clot is and how people feel pain.
It’s key for people to know the risks and watch for signs, mainly if they’ve had surgery or have health issues.
Blood Clot Arm Pictures: Visual Guide to Identification
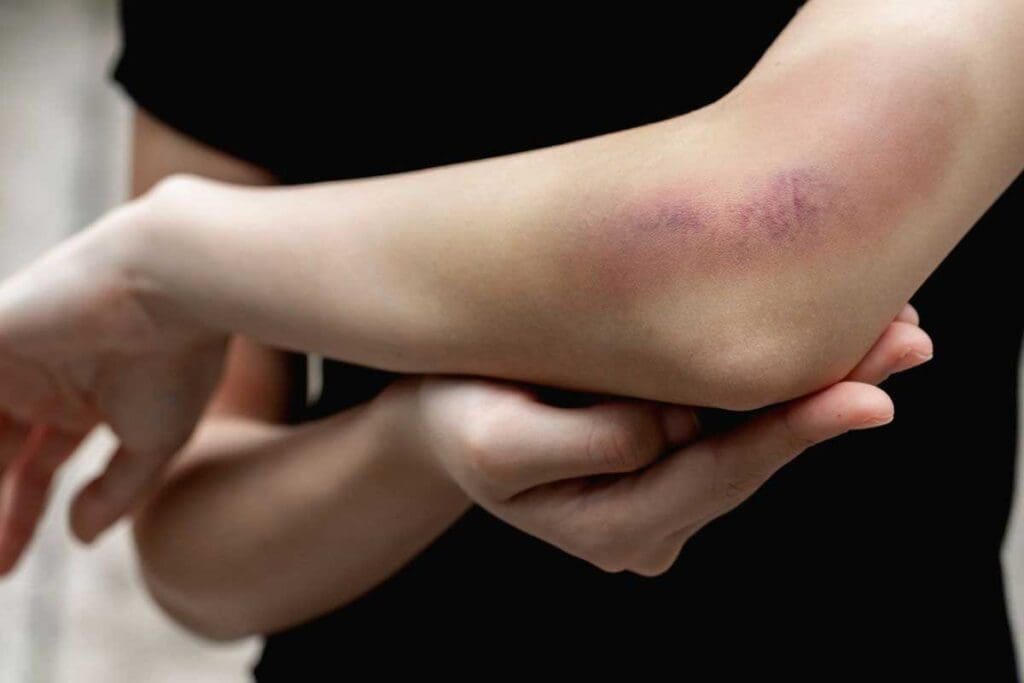
It’s important to know how to spot blood clots in the arm early. This can help prevent serious problems. Blood clots can look different, so it’s key to know what to look for.
What Arm Blood Clots Look Like
Arm blood clots show up in several ways. Look out for:
- Swelling in the affected arm, which can be quite noticeable
- Redness or discoloration along the vein’s path
- Warmth or tenderness when touching the area of the clot
- Visible veins that seem more pronounced or hardened
Differentiating Blood Clots from Other Arm Conditions
It’s important to tell blood clots apart from other issues. For example:
- Muscle strain or injury can cause swelling and pain, but it doesn’t have vein-related symptoms like blood clots do
- Infections can cause redness and swelling, but they usually come with fever and other body-wide symptoms
Knowing these differences helps you figure out if you need to see a doctor.
Visible Changes in Arm Appearance
Blood clots can make your arm look different. Look out for:
- Swelling that doesn’t go away even when you elevate your arm
- Persistent pain or aching in the arm
- Discoloration that may look red, purple, or blue, depending on the clot’s size and location
These signs can be small or big, and it’s important to watch for them.
13 Key Signs and Symptoms of Arm Blood Clots
It’s important to know the signs of arm blood clots early. This helps in getting the right treatment quickly. Blood clots in the arm can show in different ways. It’s key to spot both visible signs and physical symptoms.
Visible Signs (First 6 Signs)
The visible signs of arm blood clots are quite clear. Here are the first six signs to watch for:
- Swelling: Swelling in the affected arm is a common sign.
- Redness or Blue Discoloration: The skin might look red or have a bluish tint.
- Warmth: The area might feel warmer than the rest of the skin.
- Visible Vein Enlargement: Veins might look bigger or more visible.
- Skin Changes: The skin could look shiny or tight, showing a clot.
- Discoloration: The arm might have patches of red to purple color.
Physical Symptoms (Next 7 Signs)
There are also physical symptoms to look out for. These include:
- Pain or Tenderness: Pain or tenderness in the arm, from mild to severe.
- Cramping: Muscle cramps or spasms in the affected arm.
- Heaviness: Feeling of heaviness or fatigue in the arm.
- Aching: Aching sensation, like a deep bruise.
- Tingling or Numbness: Some might feel tingling or numbness.
- Throbbing: A throbbing feeling, often with the pulse.
- Restricted Mobility: Stiffness or reduced mobility in the arm.
| Symptom | Description |
| Swelling | Swelling in the affected arm, often with pain. |
| Pain or Tenderness | Pain or tenderness in the arm, from mild to severe. |
| Redness or Blue Discoloration | The skin may appear red or have a bluish tint due to the clot. |
| Cramping | Muscle cramps or spasms in the affected arm. |
It’s vital to recognize these signs and symptoms. If you or someone you know has them, seek medical help right away. A healthcare professional can diagnose and treat the issue properly.
Locations of Blood Clots in the Arm
It’s important to know where blood clots can form in the arm. This knowledge helps in early detection and treatment. Clots can appear in the upper arm, forearm, and elbow, each with its own symptoms and risks.
Upper Arm Blood Clots
Blood clots in the upper arm are dangerous because they’re close to important structures. Look out for swelling, pain, and warmth in the area. Catching these signs early can prevent serious problems.
A clot in the upper arm might make the arm swell and feel sore. It could also feel heavy or ache.
Forearm Thrombosis
Forearm thrombosis is when a blood clot forms in the forearm veins. It can happen due to injury, overuse, or health issues. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and trouble moving the forearm.
A study on deep vein thrombosis (DVT) shows how fast diagnosis and treatment are key.
Blood Clots in the Elbow
Blood clots in the elbow are rare but can be painful and serious. They might come from injury, repetitive strain, or conditions likethoracic outlet syndrome. Spotting elbow blood clot signs like pain and swelling is vital for quick action.
Can You Feel a Blood Clot in Your Arm?
Many times, you can feel a blood clot in your arm as a sore or painful spot. But some clots might not show symptoms until they grow big or cause trouble. Knowing the risks and watching for arm changes is key.
To understand blood clots in the arm better, let’s look at this table:
| Location | Common Symptoms | Potential Complications |
| Upper Arm | Swelling, pain, warmth | Pulmonary embolism, post-thrombotic syndrome |
| Forearm | Pain, swelling, limited mobility | Local tissue damage, chronic pain |
| Elbow | Localized pain, swelling | Chronic pain, limited mobility |
Common Causes of Blood Clots in Arms
Blood clots in the arm can come from many sources. These include injuries, medical procedures, and health issues. Knowing these causes helps us spot who’s at risk and how to prevent it.
Trauma and Injury
Getting hurt in the arm can lead to blood clots. The body tries to stop bleeding by forming a clot. But sometimes, this clot can move or stay in the arm, causing problems. Severe trauma, fractures, or intense exercise can cause these clots.
Medical Procedures and Devices
Some medical procedures and devices raise the risk of blood clots in the arm. For example, central venous catheters or peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs) can irritate blood vessel walls, causing clots. Also, surgeries, like those in the arm or shoulder, can increase the risk.
Underlying Health Conditions
Many health conditions can make you more likely to get blood clots in the arm. Conditions like cancer, heart disease, and clotting disorders can mess with blood clotting. Inflammatory diseases, like vasculitis, can also damage blood vessels, leading to clots.
Vigorous Activity and Overexertion
Doing too much physical activity can also cause blood clots. Activities that strain the arm can hurt blood vessels, leading to clots. While exercise is good, it’s important to know the risks of too much activity.
Risk Factors for Developing Arm Blood Clots
Knowing the risk factors for arm blood clots is key to preventing and catching them early. We’ve found several important factors that raise the chance of getting blood clots in the arm.
Medical Risk Factors
Some medical conditions and procedures can greatly up the risk of getting arm blood clots. These include:
- Surgery or trauma: Surgery, like operations on the arm or shoulder, can cause blood clots.
- Cancer: People with cancer, and those getting chemotherapy, are more likely to get blood clots.
- Central venous catheters: Having these catheters, used for meds or chemo, raises the risk.
- Certain medical conditions: Disorders like thrombophilia, which messes with blood clotting, increase the risk a lot.
| Medical Condition | Risk Level | Description |
| Cancer | High | Increases risk due to chemotherapy and tumor effects. |
| Thrombophilia | High | A condition that affects blood clotting. |
| Central Venous Catheters | Moderate | Presence of catheters can irritate veins and lead to clots. |
Lifestyle Risk Factors
Lifestyle choices also play a big part in getting arm blood clots. These include:
- Smoking: Smoking harms blood vessel linings, making them more prone to clots.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts more pressure on veins, mainly in arms and legs.
- Immobility: Long periods without moving, like on trips or in bed, can cause blood clots.
By knowing these risk factors, people can take steps to lower their chance of getting arm blood clots. It’s important to understand both medical and lifestyle factors to manage risk well.
Why Blood Clots in the Arms Are Dangerous
It’s important to know the risks of blood clots in the arm. These clots can lead to serious and life-threatening problems.
Potential for Pulmonary Embolism
One big danger of arm blood clots is they can travel to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism. It happens when a clot blocks blood flow to the lungs.
This is a medical emergency that needs quick action. It can cause sudden symptoms like trouble breathing and chest pain. If not treated fast, it can be deadly.
Local Complications
Arm blood clots can also cause problems close to the clot. These include post-thrombotic syndrome, which is chronic pain and swelling. The clot can also damage the surrounding tissues and veins.
These local issues can really affect your life. It’s key to treat the clot to prevent more harm.
Long-term Vascular Damage
A blood clot in the arm can also cause lasting damage. The clot can scar the vein, leading to chronic venous insufficiency. This makes it hard for the vein to send blood back to the heart.
This can cause ongoing swelling and pain. It’s a serious issue that needs attention.
Severity Comparison with Other Types of Blood Clots
Blood clots in the arm are more worrying than others. They have a high risk of breaking loose and going to the lungs.
Knowing how serious arm blood clots are helps us focus on treating them right away.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Understanding how to diagnose and treat arm blood clots is key. If a blood clot is suspected, quick medical action is needed. This ensures the right treatment starts right away.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If your arm swells, hurts, or turns color, see a doctor fast. Early action can greatly improve your chances of recovery. If your arm looks or feels off, don’t hesitate to get help.
“Prompt diagnosis and treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can prevent serious complications, including pulmonary embolism.”
American Heart Association
Diagnostic Procedures
Doctors use a mix of checks and scans to find blood clots in the arm. Ultrasound is a top choice to see the blood vessels and find clots. Sometimes, more tests like venography or MRI are needed to be sure.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for arm blood clots often means taking medicines to stop the clot from getting bigger. Anticoagulant medicines are common. Sometimes, a stronger treatment called thrombolytic therapy is used to break up the clot. We’ll pick the best treatment for you.
- Anticoagulation therapy
- Thrombolytic therapy
- Use of compression stockings
- In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary
It’s important to stick to your treatment plan and keep up with doctor’s visits. This helps keep an eye on your condition and makes sure your treatment works well.
Conclusion: Prevention Strategies and Outlook
It’s important to know the risks and signs of blood clots in the arm. This knowledge helps in preventing and treating them early. To lower the risk, stay active, avoid long periods of sitting, and manage health issues.
Preventing blood clots in the arm requires both lifestyle changes and medical care. People at high risk should watch for signs of swelling and seek help if they notice anything unusual.
FAQ
What does a blood clot in the arm look like?
A blood clot in the arm can make the area swell, turn red, and feel warm. The skin might look different, and touching it can hurt. Sometimes, you can’t see the clot, but the arm will be swollen and sore.
How to know if you have a blood clot in your arm?
Look for swelling, pain, redness, and warmth in your arm. You might also feel a heavy or sore feeling. If you think you have a blood clot, get medical help right away.
Can you get blood clots in your arm?
Yes, blood clots can happen in the arm, though it’s less common than in the legs. They can be caused by injury, medical procedures, or health issues.
Can you feel a blood clot in your arm?
Yes, you might feel a blood clot in your arm, like a hard lump or sore spot. It can hurt when you touch it.
What causes blood clots in the arms?
Blood clots in the arms can come from injury, medical procedures, or health problems. Being overweight or having a family history of blood clots can also increase your risk.
How dangerous are blood clots in the arm?
Blood clots in the arm can be dangerous if they break loose and go to the lungs. They can also harm the tissue and nerves nearby.
What are the signs and symptoms of a blood clot in the elbow?
The signs of a blood clot in the elbow are similar to others in the arm. You might see swelling, pain, redness, and warmth. The elbow might also feel stiff or hard to move.
What is thrombosis of the arm?
Thrombosis of the arm means a blood clot forms in a vein or artery. It can cause swelling, pain, and redness. It’s serious and needs quick treatment.
Are blood clots in the arms a sign of a more serious condition?
In some cases, blood clots in the arms can point to a bigger health issue, like cancer or a blood disorder. If you keep getting blood clots, see a doctor to check for any underlying conditions.
References:
- Sartori, M., & Lessiani, G. (2020). Superficial vein thrombosis: A current approach to management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 4069. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7765455/










