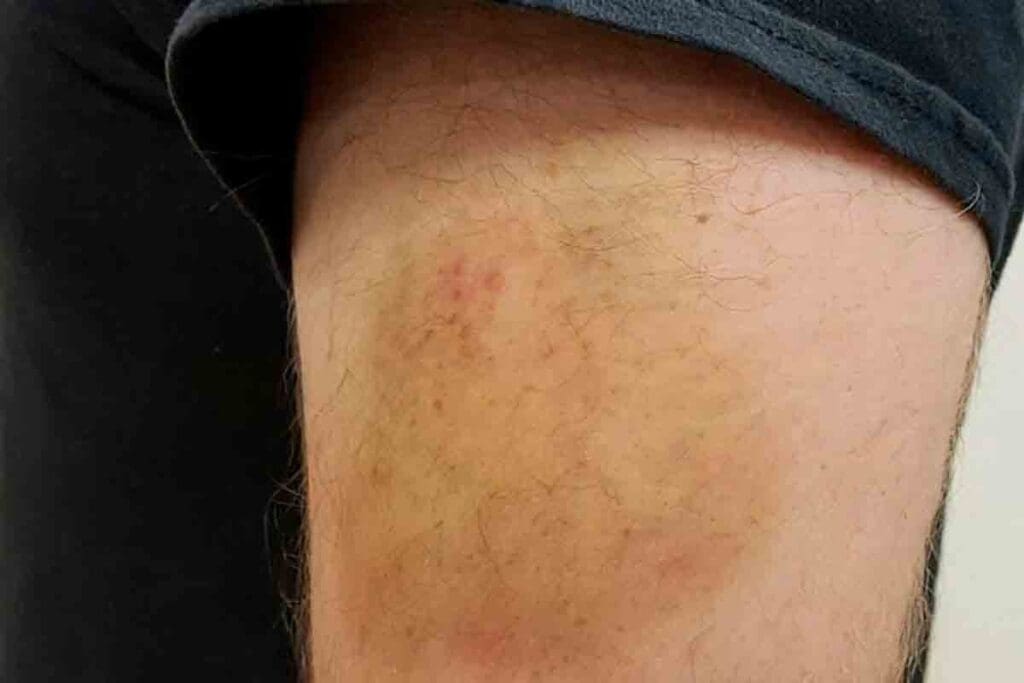
Blood clot in arm symptoms are important to recognize early to get the right medical help fast. At LivHospital, we emphasize understanding the warning signs of this serious condition.
A blood clot in the arm can occur when blood flow is blocked, leading to swelling, tenderness, pain, or cramping. While blood clots often form in the legs—affecting about 300,000 Americans each year—they can also appear in the arms with distinct symptoms. Common blood clot in arm symptoms include skin color changes, warmth, and visible veins.
Spotting these signs early is key to preventing serious complications. At LivHospital, we aim to educate patients about recognizing these symptoms and knowing when to seek immediate medical attention.
Key Takeaways
- Be aware of swelling, tenderness, and pain or cramping in the arm.
- Recognize skin discoloration and increased warmth as possible signs.
- Visible or bulging veins can mean a blood clot.
- Early detection is key for good treatment.
- Seek medical help if you notice any of these symptoms.
Understanding Blood Clots in the Arm: A Complete Overview
Blood clots in the arm are serious and need quick attention. Knowing what causes them and their symptoms is key. We’ll look at arm blood clots, their causes, types, and why they’re less common than leg clots.
What Causes Blood Clots in the Arm?
Several things can cause blood clots in the arm. Sitting for long periods, like on flights, or being in bed for too long increases the risk. Surgery, injuries, or trauma to the arm can also cause clots. Plus, conditions like cancer, heart disease, or genetic disorders can lead to arm clots.
Deep Vein Thrombosis vs. Superficial Thrombophlebitis
There are two main types of arm blood clots: Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Superficial Thrombophlebitis. DVT is a clot in the deep veins and is very dangerous. It can be life-threatening if it breaks loose and goes to the lungs. Superficial Thrombophlebitis is a clot in the superficial veins. It’s less severe but can be painful and serious.
Why Upper Limb Clots Are Less Common Than Leg Clots
Arms have smaller veins and less blood pooling than legs. This makes arm clots less likely. But, when they do happen, they’re serious and need quick medical care.
| Condition | Description | Risk Level |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Clot forms in deep veins | High |
| Superficial Thrombophlebitis | Clot forms in superficial veins | Moderate |
Blood Clot in Arm Symptoms: The Complete Guide
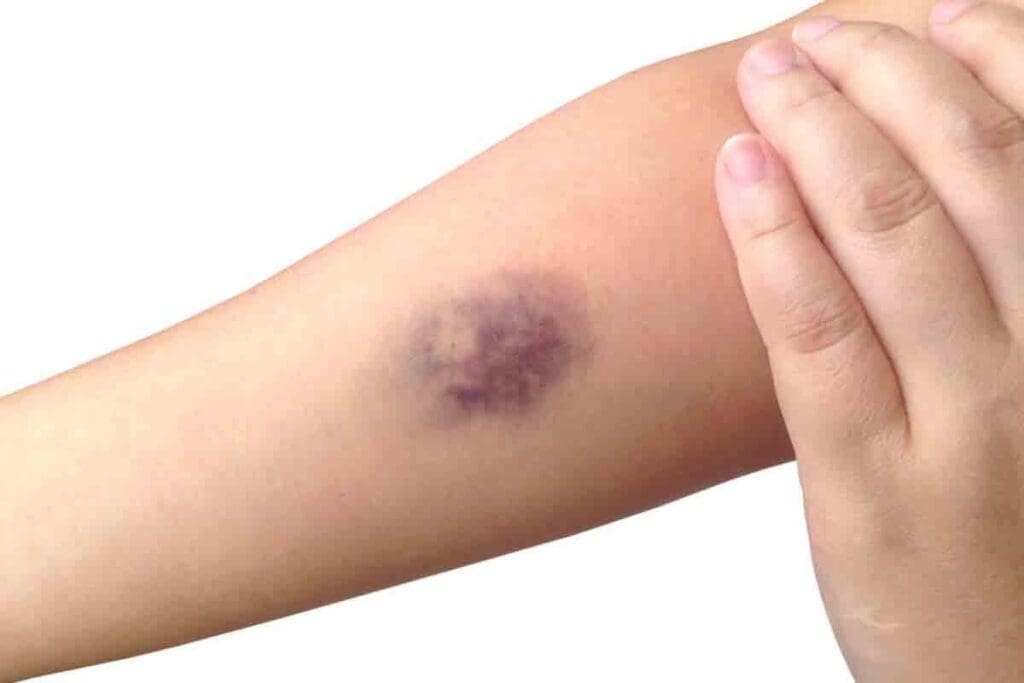
Knowing the signs of an arm blood clot is key to avoiding serious issues. A blood clot in the arm can show itself in different ways. Spotting these signs early can lead to quick medical help and might save a life.
How Blood Clot Symptoms Differ from Other Arm Conditions
Blood clot symptoms can be mistaken for other, less serious arm issues. Yet, there are clear differences. For example, while muscle soreness can cause pain and stiffness, a blood clot shows up with swelling, tenderness, and skin color changes. Knowing these differences is vital for catching it early.
Blood clots can happen without any injury or reason, making it important to watch for any unusual arm changes.
Why Early Detection Can Save Your Life
Finding a blood clot in the arm early is key because it can stop it from moving to the lungs. This could be deadly. Spotting symptoms early means quicker treatment, which greatly improves chances of recovery.
Quick action is vital for better treatment results. If you notice any odd symptoms, get medical help right away.
What Does a Blood Clot Feel Like?
A blood clot in the arm might feel like a constant, aching pain or tenderness along the vein. Some say it feels like a heavy or tight feeling in the arm. The area might also be warm, swollen, or have color changes.
The feeling of a blood clot can differ from person to person. But, it usually comes with other noticeable signs. If you’re feeling any of these, seeing a healthcare professional is a must.
Warning Sign #1: Unexplained Swelling in the Affected Arm
Swelling in one arm without a clear reason might mean a blood clot. A clot in a deep vein can block blood flow. This leads to fluid buildup in the affected limb.
What Causes Clot-Related Swelling
Swelling from a blood clot happens because blood flow is blocked. A clot stops normal blood flow, causing fluid to gather in the area. This swelling might not hurt or might be a bit uncomfortable.
Key factors contributing to clot-related swelling include:
- Increased pressure in the veins due to the clot
- Inflammation caused by the clot
- Reduced blood flow
How to Measure and Monitor Arm Swelling
To track arm swelling, measure both arms at the same spot. This is usually the midpoint between the elbow and shoulder.
| Measurement Day | Affected Arm Circumference (cm) | Unaffected Arm Circumference (cm) |
| 1 | 30 | 28 |
| 2 | 31 | 28 |
| 3 | 32 | 28 |
Unilateral Swelling as a Key Indicator
Swelling in just one arm is a big warning sign of a blood clot. If one arm is much bigger than the other, get medical help right away.
Spotting blood clots early can really help with treatment. By noticing swelling, you can act fast and see a doctor.
Warning Sign #2: Pain and Tenderness Along the Arm
Pain or tenderness in the arm can be a sign of a blood clot. This pain is often different from muscle soreness. It can be constant and feel unique.
Characteristics of Blood Clot Pain
The pain from a blood clot can feel like a dull ache or a sharp stab. It might also feel heavy in your arm. The pain can be constant or may occur when the arm is moved or touched. Sometimes, you might also feel warmth or see redness in the area.
When Pain Occurs Without Other Symptoms
Pain in the arm can be the only sign of a blood clot. It’s important to notice any unusual or persistent pain that doesn’t seem to have a clear cause.
Differentiating from Muscle Soreness
Telling muscle soreness apart from blood clot pain can be hard. Blood clot pain usually stays in one spot and doesn’t get better with rest. If you’re not sure about your arm pain, see a doctor.
Warning Sign #3: Skin Discoloration and Color Changes
One of the key warning signs of a blood clot is a change in skin color. This can range from red to blue or purple. We’ll look at how to spot these changes and tell them apart from other conditions.
Red, Blue, or Purple Skin Tones
Skin discoloration from blood clots can show up in different ways. The skin might look red because of inflammation. Or it could turn blue or purple due to poor circulation or lack of oxygen. It’s important to notice these color changes early.
To understand the different skin tones linked to blood clots, let’s check out this table:
| Skin Tone | Possible Cause | Associated Symptoms |
| Redness | Inflammation | Warmth, swelling |
| Blue/Purple | Poor circulation, oxygen deprivation | Pain, tenderness |
| Bluish tint | Venous thrombosis | Swollen veins, pain |
How to Distinguish from Bruising
It’s important to tell the difference between skin discoloration from a blood clot and bruising. Bruises come from trauma and change color as they heal. They start blue/purple and turn green/yellow. But discoloration from a clot might not change color like that and can come with swelling or pain.
When Discoloration Indicates a Serious Problem
If you see significant skin discoloration, and it’s with pain, swelling, or warmth, get medical help right away. These signs can mean a serious problem that needs quick treatment.
In summary, skin discoloration and color changes are important warning signs. By knowing what they mean, you can take care of your health and get help when needed.
Warning Sign #4: Unusual Warmth in the Affected Area
One of the lesser-known symptoms of a blood clot is increased temperature in the affected area. This unusual warmth can be a significant indicator that something is amiss. When a blood clot forms, it can cause inflammation. This leads to increased blood flow to the area, making the skin feel warmer to the touch.
Why Blood Clots Cause Increased Temperature
Blood clots cause increased temperature due to the body’s natural response to the clot. Inflammation is a key factor here; when a clot forms, the body reacts by increasing blood flow to the affected area. This can result in warmth or heat.
The inflammation caused by a blood clot can lead to the release of various chemical mediators. These mediators cause the blood vessels to dilate. This dilation increases blood flow, contributing to the sensation of warmth.
How to Check for Temperature Differences
To check for temperature differences between the affected and unaffected arms, you can use the back of your hand. Gently touch the back of your hand to both arms to compare their temperatures. If one arm feels significantly warmer than the other, it could be a sign of a blood clot.
Another method is to use a thermometer, though this is less common for checking arm temperature. If you notice a consistent difference in temperature, it’s worth consulting a healthcare professional.
When Warmth Accompanies Other Symptoms
When unusual warmth is accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, pain, or discoloration, it’s a strong indication that a blood clot might be present. It’s critical to seek medical attention if you experience a combination of these symptoms.
The presence of multiple symptoms can indicate a more serious condition. For instance, if you have a blood clot, the risk of it breaking loose and causing a pulmonary embolism increases. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital.
Warning Sign #5: Visible or Bulging Veins
When veins become more visible than usual, it could mean there’s a problem. This might be a sign of a blood clot. We’ll look into what causes this, its signs, and what it means for your health.
What Causes Veins to Become Prominent
Veins can look more noticeable if blood flow is blocked by a clot. A clot in a vein stops blood from flowing right. This makes the vein swell and stand out more.
“The presence of a blood clot can cause inflammation and swelling in the affected limb, further contributing to the visibility of the veins,” says a vascular specialist.
Distinguishing Normal Veins from Clot-Related Changes
Not all bulging veins mean you have a blood clot. Some people naturally have more visible veins. But, if your veins suddenly look different and you feel pain or swelling, you should see a doctor.
- Normal veins are typically not painful to the touch.
- Clot-related veins may be tender or painful.
- The skin around clot-related veins may be warm or discolored.
Using Visual Inspection to Identify Potencial Clots
Looking closely at your veins can help spot clots. Check for veins that are tender or swollen. If you see these signs, get a doctor’s opinion.
Spotting problems early is key to treating them well. Knowing the signs, like visible veins, helps you keep your blood vessels healthy.
Warning Sign #6: Weakness or Numbness in the Arm
Unexplained weakness or numbness in the arm can be a warning sign of a blood clot. This happens because the clot affects nerve function and the tissues around it.
How Blood Clots Affect Nerve Function
Blood clots can press on or damage nerves in the arm. This leads to feelings of weakness or numbness. The clot’s pressure on nerves can disrupt normal function.
This can cause a range of symptoms. These include mild tingling, complete numbness, or significant weakness.
Distinguishing from Other Neurological Issues
It’s important to tell the difference between numbness from a blood clot and other neurological problems. Conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or peripheral neuropathy can also cause numbness. But, a blood clot usually comes with other symptoms like swelling, pain, or skin color changes.
When Numbness Requires Emergency Care
If you have sudden or severe numbness, seek emergency medical care right away. This is true if you also have trouble speaking, facial drooping, or severe pain. Numbness in one arm or with weakness is a serious sign that needs quick attention.
Feeling weak or numb can be scary. If you’re worried about these symptoms, talk to a healthcare professional. They can give you a thorough check-up and the right care.
Warning Sign #7: Complications from Untreated Arm Clots
Untreated arm clots can cause severe and dangerous problems. We will look at the risks and why getting medical help is key.
Pulmonary Embolism: A Life-Threatening Danger
Pulmonary embolism is a big risk from untreated arm clots. It happens when a clot piece goes to the lungs and blocks blood flow. Pulmonary embolism is a medical emergency that needs quick action.
Symptoms include trouble breathing, chest pain, and a fast heart rate. If you have these, get to the emergency room fast.
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) can happen after a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the arm. PTS is when the clot damages veins, causing pain, swelling, and skin color changes.
PTS can really affect your life. Knowing the risks and taking steps to prevent it can help.
| Symptoms | Frequency | Impact on Quality of Life |
| Pain | Common | Significant |
| Swelling | Frequent | Moderate to Significant |
| Skin Discoloration | Less Common | Variable |
Long-Term Circulation Problems
Untreated arm clots can cause long-term circulation issues. The clot can damage blood vessels, leading to swelling, pain, and less mobility in the arm.
There’s also a chance of getting clots again, making circulation problems worse. Treating the first clot is key to avoiding these issues.
Knowing the risks of untreated arm clots helps people get medical help early. This can prevent serious health problems.
How to Tell If You Have a Blood Clot: Self-Assessment Guide
Figuring out if you have a blood clot involves checking your symptoms and risk factors. We’ll walk you through a simple process. This will help you figure out if you need to see a doctor.
Step-by-Step Evaluation Process
To see if you have a blood clot, follow these steps:
- Check for swelling in one arm or leg.
- Look for pain or tenderness that may feel like cramping or soreness.
- Inspect your skin for redness, warmth, or discoloration.
- Feel for a heavy or aching sensation in the affected limb.
If you notice any of these symptoms, think about your overall health and risk factors.
Risk Factor Analysis
Some things can make you more likely to get a blood clot. Consider these:
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Prolonged Inactivity | Long periods of immobility, such as during travel or bed rest. |
| Recent Surgery | Surgical procedures can increase the risk of clot formation. |
| Family History | A history of blood clots in close relatives. |
Knowing these risk factors can help you prevent blood clots and know when to see a doctor.
When to Trust Your Instincts and Seek Help
If you’re worried about your symptoms, trust your instincts and get help. As a doctor said,
“The best way to avoid complications from blood clots is early detection and treatment.”
Don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you notice any unusual symptoms or if you’re unsure about your condition.
By following this guide, you can understand your risk better. This will help you protect your health.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Arm Blood Clots
Diagnosing and treating arm blood clots needs a detailed plan. We will look at the tests, treatments, and care needed to manage these clots well.
Common Diagnostic Tests
Healthcare providers use imaging tests and blood work to find arm blood clots. Ultrasound uses sound waves to see blood vessels and find clots. The D-dimer blood test checks for a protein fragment when a clot dissolves.
Venography uses dye to see clots on an X-ray. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) gives detailed images of blood vessels and tissues.
Medication-Based Treatments
The main treatment for arm blood clots is anticoagulant medications. These stop the clot from growing and prevent new ones. Heparin and warfarin are common, with newer drugs like rivaroxaban and apixaban also used.
Thrombolytic therapy can dissolve the clot. It’s used for severe cases or when there’s a high risk of complications.
Surgical Interventions When Necessary
For big clots or high risk of pulmonary embolism, surgical intervention might be needed. This includes thrombectomy to remove the clot or a vena cava filter to stop clots from reaching the lungs.
Recovery and Follow-Up Care
After treatment, follow-up care is key. Patients are told to elevate the affected arm, wear compression stockings, and do regular physical activity to help circulation.
Knowing about diagnosis and treatment for arm blood clots helps patients take charge of their care. This improves outcomes and lowers the risk of complications.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Arm Blood Clots
To prevent arm blood clots, we need to know who’s at risk. By spotting high-risk groups and taking steps to prevent them, we can lower the risk of this serious condition.
Who’s Most at Risk for Developing Arm Clots
Some people are more likely to get arm blood clots. This includes:
- Those with a history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism
- People having major surgery, like orthopedic procedures
- Individuals with cancer or going through cancer treatment
- Those with genetic blood clotting disorders
- People with central venous catheters or pacemakers
Knowing these risk factors helps us take steps to prevent arm blood clots.
Preventive Measures for High-Risk Individuals
For those at high risk, there are steps to take:
| Preventive Measure | Description |
| Anticoagulant Medication | Prescribed to prevent clot formation |
| Compression Stockings | Used to improve blood flow |
| Regular Movement | Encouraged to prevent prolonged inactivity |
These steps can greatly lower the risk of arm blood clots.
Lifestyle Changes That Reduce Clot Risk
There are also lifestyle changes to help prevent arm blood clots:
- Staying hydrated to maintain blood flow
- Avoiding smoking, which damages blood vessels
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on veins
- Engaging in regular physical activity
By making these lifestyle changes, we can lower our risk of arm blood clots.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help for a blood clot in the arm is key. Some symptoms mean you need to go to the hospital right away. Knowing these can save lives.
Emergency Warning Signs
If you notice any of these signs, go to the hospital fast:
- Severe pain or swelling in the arm
- Difficulty breathing or feeling short of breath
- Chest pain or pressure that spreads to the arm, neck, or jaw
- Rapid heartbeat or feeling like your heart is skipping beats
- Confusion or trouble speaking
These signs might mean you have a pulmonary embolism or another serious problem. You need to see a doctor right away.
What to Tell Your Healthcare Provider
When you go to the doctor, tell them everything about your symptoms:
| Information to Provide | Details to Include |
| Symptom description | Tell them when your symptoms started, how bad they are, and what makes them better or worse |
| Medical history | Share any past blood clots, recent surgeries, or times when you couldn’t move much |
| Current medications | Give them a list of all your medicines, including blood thinners if you take them |
What to Expect at the Hospital
When you get to the hospital, here’s what will happen:
- Initial assessment: Doctors will quickly check you to see how bad your symptoms are.
- Diagnostic tests: You might get imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans to find the blood clot.
- Treatment initiation: Based on what they find, they might start treatment right away. This could include medicine or other steps.
Knowing what to expect can help you feel less worried when you go to the emergency room.
Conclusion: Taking Action Against Blood Clots
It’s important to know the signs and risks of blood clots in the arm. We’ve looked at seven warning signs that can’t be ignored. These include swelling, pain, skin color changes, and warmth.
Knowing these signs helps people prevent blood clots and get medical help when needed. Preventing blood clots is key to staying healthy, even more so for those at high risk.
Preventing blood clots means being aware, making lifestyle changes, and getting medical help. We urge readers to take charge of their health. Understand your risk and work with doctors to create a prevention plan.
This way, we can lower the chance of serious problems like pulmonary embolism and post-thrombotic syndrome. Let’s focus on our health and take steps to stop blood clots.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a blood clot in the arm?
Signs include swelling, pain, and tenderness. You might also see skin discoloration or feel unusual warmth. Look for visible veins, weakness, or numbness in your arm.
How can I tell if I have a blood clot in my arm?
Check for 7 warning signs. These are swelling, pain, and tenderness. Also, watch for skin discoloration, warmth, and visible veins. Look for weakness or numbness too.
What causes blood clots in the arm?
Blood clots can come from injury, being immobile for too long, or certain health issues. Genetics also play a role.
What is the difference between deep vein thrombosis and superficial thrombophlebitis?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a clot in a deep vein, usually in the arm or leg. Superficial thrombophlebitis is a clot closer to the skin, causing inflammation and pain.
Can a blood clot cause pain?
Yes, a blood clot can cause pain and discomfort in the arm. The pain might be constant or worse when moving the arm.
How do I check for temperature differences in my arm?
Touch the affected arm and compare its warmth to the other arm. If it’s warmer, it could mean a blood clot.
What are the risk factors for developing arm blood clots?
Risk factors include a history of blood clots, recent surgery, or prolonged bed rest. Cancer and genetic conditions also increase risk.
How are arm blood clots diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, ultrasound, and sometimes blood tests. These confirm the presence of a clot.
What are the treatment options for arm blood clots?
Treatment includes anticoagulant medications and thrombolytic therapy. In some cases, surgery is needed to remove the clot.
Can I prevent arm blood clots?
Yes, you can prevent them. Stay active, avoid long periods of sitting or lying down, and keep a healthy weight. Manage any health conditions you have.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for a suspected blood clot?
Get medical help right away for severe symptoms. This includes trouble breathing, chest pain, or severe pain and swelling in your arm.
Reference
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). (2023). Blood Clot in Arm and Deep Vein Thrombosis.
Explains blood clot types in arm veins, symptoms such as swelling, tenderness, pain, and skin discoloration. Highlights the danger of embolism and need for urgent care.
































