Knowing your Body Mass Index (BMI) is key to keeping healthy and avoiding serious health issues. At Liv Hospital, we offer reliable advice based on international health standards. This helps you understand your health better.
BMI is a common way to measure weight. It sorts people into groups like underweight, healthy, overweight, and obese. By knowing your BMI, you can start making better choices for your health. A ‘body mass index 37’ is classified as Class 2 Obesity. Our simple guide explains the serious, shocking health risks and next steps.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding your BMI is key to knowing health risks.
- BMI sorts people into weight groups based on height and weight.
- A healthy BMI is between 18.5 and 24.9.
- Liv Hospital offers personalized health plans based on global health standards.
- Knowing your BMI helps you make better lifestyle choices.
What is Body Mass Index (BMI)?
Body Mass Index, or BMI, is a simple way to measure weight categories. It works the same for both men and women over 20. This makes it a key tool in healthcare.
Definition and Purpose
BMI is the body mass in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. It gives a number to check if a person’s weight is healthy for their height. The main goal of BMI is to quickly spot weight-related health issues.
We use BMI to find people at risk for health problems because of their weight. It’s not a final diagnosis but a first step for more checks.
History and Development of BMI
The idea of BMI started with Adolphe Quetelet, a Belgian mathematician, in the 19th century. It was first called the Quetelet Index. Later, Ancel Keys renamed it Body Mass Index in 1972. Even though it’s been around for a long time, BMI became a common health measure only recently.
Its simplicity and easy calculation helped make it popular in health care and public health.
How BMI is Used in Healthcare
In healthcare, BMI sorts people into weight categories like underweight, normal, overweight, and obese. These groups help doctors see the risk of health problems like diabetes and heart disease.
For example, a BMI of 35.1 or 38 means someone is obese, which raises health risks. Knowing BMI is key for making treatment plans and tracking weight changes.
How to Calculate Your BMI
Calculating your Body Mass Index (BMI) is easy. You just need your weight and height. We’ll show you how to do it with both metric and imperial systems. Plus, we’ll introduce you to online tools that make it even easier.
Standard BMI Formula
The formula for BMI is: BMI = Weight (kg) / Height² (m²). For example, if you weigh 70 kg and are 1.75 meters tall, your BMI is: BMI = 70 / (1.75)² = 70 / 3.0625 = 22.86. This tells you if your weight is healthy for your height.
To calculate your BMI, first, weigh yourself in kilograms. Then, measure your height in meters. Next, square your height. Lastly, divide your weight by the squared height. Your BMI score is the result.
Imperial vs. Metric Calculations
You can also use imperial units (pounds and inches) to calculate BMI. The formula is: BMI = (Weight in pounds / Height in inches²) * 703. For instance, if you weigh 154 pounds and are 68 inches tall, your BMI is: BMI = (154 / (68)²) * 703 = (154 / 4624) * 703 = 23.4.
Both methods give the same BMI score if you use the right conversion. This means you can calculate your BMI in the units you prefer.
Online BMI Calculators and Tools
If you struggle with math, online BMI calculators can help. Just enter your weight and height, and they’ll give you your BMI score. Many also categorize your BMI as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
Online BMI calculators are great for quick checks. Just search for “BMI calculator” online, and you’ll find many reliable tools.
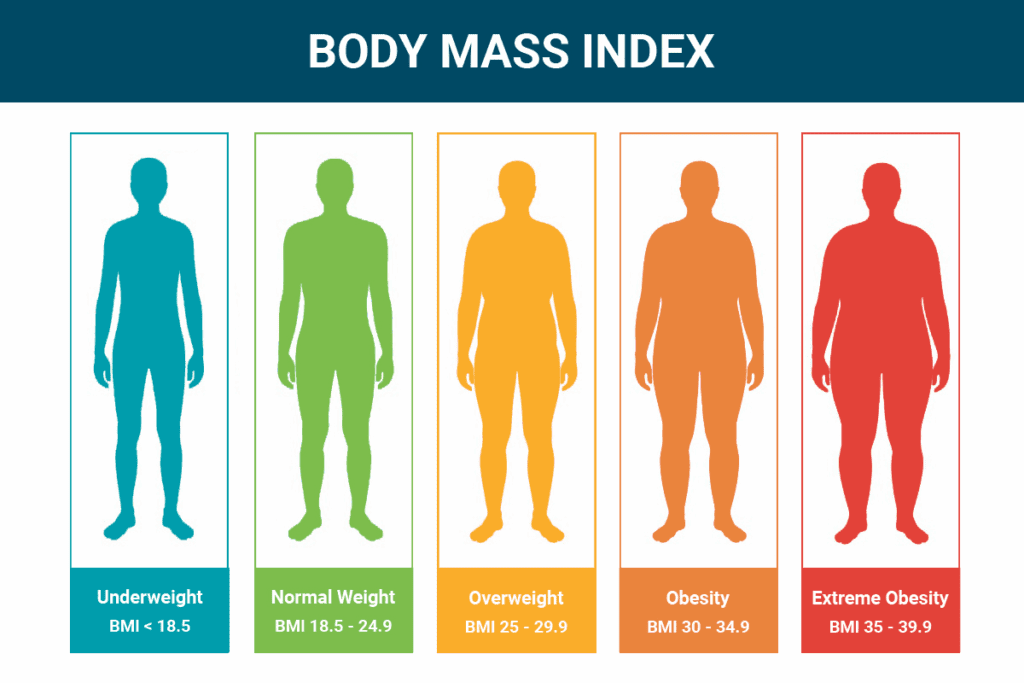
BMI Categories Explained
BMI categories help us understand our weight status and health risks. Knowing these categories is key to assessing our health.
Underweight: BMI Below 18.5
A BMI under 18.5 means you’re underweight. This can cause health problems like weak immune function and osteoporosis. It’s important to talk to a doctor if you’re underweight.
Healthy Weight: BMI 18.5-24.9
A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered healthy. This range lowers the risk of diseases like heart disease and diabetes. It shows you’re living a healthy lifestyle.
Overweight: BMI 25.0-29.9
Having a BMI of 25 to 29.9 means you’re overweight. This can lead to health issues like high blood pressure and diabetes. Changing your diet and exercise routine can help.
Obesity Classes: BMI 30 and Above
Obesity is a BMI of 30 or higher. It’s divided into classes based on risk. Class 1 has a moderate risk, Class 2 and Class 3 have higher risks. Obesity raises the risk of heart disease and cancer.
Knowing your BMI category is the first step to better health. Always consult with healthcare professionals for the best advice.
BMI Chart for Women: Understanding Female Body Composition
Understanding BMI for women means looking at weight, height, and body fat. Women’s body fat distribution is different from men’s. Age and pregnancy also change how BMI is seen.
Standard BMI Ranges for Women
Women, like men, have standard BMI categories. A BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 is normal. Below 18.5 is underweight, and above 24.9 is overweight. Staying in the normal range can lower health risks.
BMI is not a direct measure of body fat. It’s a general guide. It should be used with other health metrics to check overall health.
Age-Related BMI Considerations for Women
Women’s bodies change with age, gaining fat and losing muscle. This can change BMI readings. Hormonal shifts in postmenopausal women can also affect body composition.
It’s important to understand these age-related changes. Healthcare providers use this knowledge to assess health risks tied to BMI.
BMI During Pregnancy and Postpartum
Before pregnancy, BMI helps set weight gain goals. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has guidelines for healthy weight gain based on pre-pregnancy BMI.
After pregnancy, retained weight can affect BMI. Monitoring BMI postpartum helps spot health risks and guide weight management.
Every woman’s body is unique. Muscle mass, bone density, and body fat distribution are key to health. Using BMI charts wisely is a step towards a healthy lifestyle.
BMI Chart for Men: Male-Specific Considerations
Men can use BMI charts to check their weight status. But, it’s important to remember muscle mass too. The BMI chart for men helps show if their weight is healthy for their height.
Standard BMI Ranges for Men
For men, BMI ranges are the same as for women. They are underweight (BMI
Key Considerations:
- Muscle mass can increase BMI without showing fatness.
- Athletic men might have a high BMI without being overweight.
- BMI doesn’t tell the difference between lean muscle and fat.
Muscle Mass and BMI in Men
Men usually have more muscle than women, which affects their BMI. For example, a muscular man might have a high BMI without being overfat. It’s important to look at body composition when checking BMI scores.
For example: An athlete with a lot of muscle might be seen as overweight by BMI, even with low body fat.
Age-Related BMI Changes in Men
As men get older, their body composition changes. They might lose muscle and gain fat. This can change their BMI and health.
- Younger men (20-39 years) usually have more muscle.
- Older men (40+ years) might lose muscle and gain fat.
- Watching BMI over time can show these changes.
Understanding these points helps men use BMI charts better for health checks.
Understanding Body Mass Index 37 and Class 2 Obesity
BMI 37 falls into the Class 2 obesity category. This means a person needs a detailed health check and care plan. Class 2 obesity is when a person’s BMI is between 35 and 39.9, showing a big health risk.
What Classifies as BMI 35-39.9
A BMI of 35 to 39.9 is Class 2 obesity. It shows a person’s weight is much higher than what’s healthy for their height. This can lead to serious health problems.
To get a better idea, let’s look at BMI categories:
- A BMI below 18.5 is underweight.
- A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered normal weight.
- A BMI between 25 and 29.9 is overweight.
- A BMI between 30 and 34.9 is Class 1 obesity.
- A BMI between 35 and 39.9 is Class 2 obesity.
- A BMI of 40 or higher is Class 3 obesity.
Health Risks Associated with Class 2 Obesity
People with a BMI of 37 face a higher risk of serious health issues. These include:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypertension
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Certain types of cancer
It’s vital for those with Class 2 obesity to know these risks. They should work on reducing them through lifestyle changes and medical help.
Management Strategies for BMI 37
Managing a BMI of 37 needs a mix of diet changes, more exercise, and sometimes medical treatment.
Some good strategies are:
- Seeing a healthcare professional for a weight loss plan.
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that’s low in calories and full of nutrients.
- Doing regular physical activity, like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Joining weight loss programs or support groups for help and motivation.
- In some cases, medical treatments like bariatric surgery might be suggested.
By using these methods, people can lower their BMI and health risks. This improves their overall life quality.
Comparing Different BMI Values: From 20 to 45
Looking at BMI values from 20 to 45 shows how health changes. From being healthy to facing obesity risks, it’s all about understanding BMI. It helps us see health risks clearly.
Healthy Range: BMI 20.4 and BMI 22
A BMI of 20.4 or 22 means you’re at a healthy weight. This range lowers the risk of diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Eating well and staying active keeps you in this range.
For example, a BMI of 22 means better health than a higher BMI. Regular health checks and watching BMI help make smart health choices.
Overweight Range: Understanding the Implications
When BMI goes over 24.9, you’re considered overweight. A BMI of 25 or more means you’re at risk of obesity. Changing your lifestyle, like eating better and moving more, helps reduce these risks.
Knowing you’re overweight is key to preventing health problems. It’s not just about looks; extra weight can cause serious diseases like heart disease and some cancers.
Obesity Class 1: BMI 30-34.9
Obesity Class 1, with a BMI of 30 to 34.9, is a big health risk. People in this range face higher risks of diabetes and high blood pressure. Weight loss programs, like diet and exercise, are often suggested to lower these risks.
For someone with a BMI of 32, losing a little weight can greatly improve health. Doctors can help with safe weight loss plans.
Severe Obesity: BMI 35.1, 36, 38, and 39
Severe obesity, with a BMI of 35 or more, brings big health dangers. BMIs of 35.1, 36, 38, and 39 all fall into this high-risk group. Medical care, including surgery, may be needed for severe obesity.
A BMI of 45 is very high risk, with a huge chance of obesity-related health problems. People with a BMI of 45 or higher need careful medical care to manage health and plan for weight loss.
BMI Charts in Pounds and Inches: Practical Applications
BMI charts in pounds and inches are handy for figuring out your body mass index. They’re great for those who prefer imperial measurements.
Reading and Interpreting BMI Charts
To use a BMI chart, you need to know how to read it. BMI charts are tables or grids that show height and weight against BMI. Here’s how to understand them:
- Find your height on the chart, listed in inches or feet and inches.
- Look for your weight in pounds on the other side.
- Your BMI is where your height and weight meet.
For example, if you’re 5’8″ (68 inches) and weigh 150 pounds, find your BMI. Look at the row for 68 inches and the column for 150 pounds. The value there is your BMI.
Height-Weight Tables for Quick Reference
Height-weight tables help you see if your weight is healthy for your height. They’re based on BMI and useful for:
- Checking if you’re underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
- Setting weight goals for a healthy BMI.
- Tracking BMI changes as you lose or gain weight.
For instance, a 5’9″ person weighing 170 pounds has a BMI of about 25.1. This means they’re overweight, according to the table.
Finding Your BMI on Standard Charts
Standard BMI charts are easy to use. To find your BMI on these charts:
- Make sure you know your exact height and weight.
- Use a reliable BMI chart in pounds and inches.
- Remember, BMI is just one health measure. It doesn’t consider muscle or body fat.
If your BMI is 44, which is obesity class III, the chart will show a high weight. For example, a 5’6″ person might weigh about 270 pounds for a BMI of 44.
By learning to use BMI charts in pounds and inches, you can easily check your weight status. This helps you make better health choices.
Limitations of BMI as a Health Measure
BMI is widely used but has big limitations. It doesn’t tell the difference between muscle and fat. It’s good for a general health check but doesn’t show the full picture of health.
Body Composition Not Considered
BMI doesn’t look at body composition. It uses weight and height, ignoring muscle and fat. This can make athletes with lots of muscle seem overweight, even if they’re not.
On the other hand, people with less muscle might seem fine but could be at risk from too much fat.
Ethnic and Racial Variations
BMI might not work the same for everyone because of body composition differences. Some groups might have more body fat at the same BMI. This can make BMI a bad way to judge health for everyone.
- Different ethnic groups may have varying body compositions.
- Racial differences can affect the relationship between BMI and body fat.
- Using BMI alone may lead to misclassification of health status in diverse populations.
Athletes and Muscular Individuals
Athletes and very muscular people often have high BMIs because of muscle, not fat. This shows a big problem with using BMI for them.
For athletes, looking at body fat percentage or waist size might be better. We need to think about these when checking the health of those with lots of muscle.
Elderly Population Considerations
The elderly face special challenges with BMI. As they age, they might lose muscle and gain fat, making BMI less accurate. They might also lose height because of bone loss, affecting BMI too.
For older adults, we need to look at more than just BMI to understand their health fully.
Conclusion: Using BMI as Part of Your Health Journey
Keeping a healthy BMI can lower health risks. We’ve seen how BMI charts for men and women are useful. They help you understand your body weight in relation to height.
Using these charts can spot weight-related health issues early. For example, a BMI of 100 is way above the healthy range. It shows severe obesity and health risks. We suggest using BMI as part of a bigger health check, looking at more than just weight and height.
Staying within a healthy BMI range can lower health risks. A balanced lifestyle, with good food and exercise, is key. This not only boosts your health but also supports it for the long term.
In short, BMI is a key tool for checking health risks tied to weight. We advise checking your BMI often and making smart choices to keep it healthy. This supports your health journey.
FAQ
What is Body Mass Index (BMI) and how is it calculated?
BMI is a simple way to check if you’re at a healthy weight. It’s calculated by dividing your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared (kg/m^2). You can also use online BMI calculators for an easy calculation.
What are the different BMI categories?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has defined BMI categories. These include underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity. Each category has a specific BMI range.
How is BMI used in healthcare settings?
BMI is used to spot health risks linked to weight. Doctors use it to check for diseases like diabetes and heart disease. It helps them decide on the best treatment.
What are the health implications of having a BMI of 36 or 37?
A BMI of 36 or 37 means you’re in class 2 obesity. This increases your risk of diseases like diabetes and heart disease. Lifestyle changes and medical help may be needed to reduce these risks.
How do BMI charts differ for men and women?
BMI is the same for both men and women. But, muscle mass and body composition can affect how BMI is seen. For example, athletes might have a high BMI without being obese.
Can BMI be used during pregnancy?
BMI isn’t reliable during pregnancy. It doesn’t account for pregnancy weight gain. Doctors use other measures to check health during pregnancy.
What are the limitations of using BMI as a health measure?
BMI has its limits. It doesn’t consider body composition, muscle mass, or ethnic differences. It’s not always accurate for athletes or the elderly.
How can I use BMI charts that are based on pounds and inches?
To use BMI charts based on pounds and inches, know your weight and height. Use a BMI chart or calculator to find your BMI. These charts help you quickly see your BMI category.
What is considered a healthy BMI range?
A healthy BMI range is 18.5 to 24.9. Being in this range lowers your risk of chronic diseases.
How does age affect BMI interpretation?
Age can change how BMI is seen. Muscle mass and body fat percentage change with age. This can affect BMI interpretation in older adults.
References
World Health Organization. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/topic-details/GHO/body-mass-index-bmi









