Aplastic anemia is a rare and serious condition. It happens when the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells. This leads to severe health problems.
At LivHospital, we know aplastic anemia is a complex issue. The bone marrow is key in making red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Without enough, the body can’t fight off infections, carry oxygen, or heal properly.
It’s important to understand aplastic anemia to diagnose and treat it well. We’re dedicated to using the latest treatments and care plans for those with this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Aplastic anemia is a rare and serious blood disorder.
- It is characterized by the failure of the bone marrow to produce blood cells.
- Understanding the condition is key for early detection and treatment.
- LivHospital offers complete care for patients with aplastic anemia.
- Effective treatment needs a team effort.
Understanding Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is a condition where the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. This is key for carrying oxygen, fighting off infections, and stopping bleeding. It’s a complex issue that has been studied for a long time.
Definition and Basic Concepts
Aplastic anemia happens when the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells. This leads to pancytopenia, a drop in red and white blood cells and platelets. It causes tiredness, more infections, and bleeding problems.
The main reason for aplastic anemia is damage to the stem cells in the bone marrow. This damage can come from autoimmune diseases, toxic chemicals, radiation, some medicines, or viruses.
It’s important to know that aplastic anemia is different from other anemias. While other anemias just lack red blood cells or hemoglobin, aplastic anemia affects all blood cells.
Historical Context and Prevalence
Aplastic anemia has been known for decades. It was once linked to toxic substances or radiation. The number of people with aplastic anemia varies worldwide. This is due to different environmental and genetic factors.
| Aspect | Description |
| Definition | Failure of bone marrow to produce blood cells, leading to pancytopenia |
| Causes | Autoimmune reactions, toxic chemical exposure, radiation, certain medications, viral infections |
| Historical Context | Recognized for decades, initially associated with toxic exposures or radiation |
| Prevalence | Varies globally, influenced by environmental and genetic factors |
Understanding aplastic anemia helps us see how complex its diagnosis and treatment are. This sets the stage for looking into its causes, symptoms, and treatment options in the next sections.
The Role of Bone Marrow in Blood Production

Bone marrow plays a key role in making blood. It’s the spongy tissue inside some bones. It makes blood cells through a process called hematopoiesis.
Normal Bone Marrow Function
Bone marrow is vital for our health. It makes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infections, and platelets help blood clot.
Recent studies show that immune attacks on marrow stem cells cause aplastic anemia. This shows how complex bone marrow function is and how it can be disrupted.
Hematopoiesis: The Blood Cell Formation Process
Hematopoiesis is how bone marrow makes blood cells. It starts with stem cells that can become different blood cells. Growth factors and cytokines control this process to keep the right blood cell balance.
When hematopoiesis is disrupted, it can lead to aplastic anemia. This means not enough blood cells are made. It can cause anemia, infections, and bleeding problems.
| Blood Cell Type | Function | Impact of Aplastic Anemia |
| Red Blood Cells | Carry oxygen throughout the body | Reduced oxygen delivery, leading to fatigue and weakness |
| White Blood Cells | Fight infections | Increased susceptibility to infections |
| Platelets | Help blood to clot | Increased risk of bleeding and bruising |
Knowing how bone marrow works is key to understanding aplastic anemia. It shows why bone marrow’s failure is so serious. It affects our health in many ways.
Bone Marrow Anemia: The Connection Explained
Bone marrow failure is a key factor in aplastic anemia. This condition happens when the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells. This leads to serious health problems.
How Bone Marrow Failure Leads to Aplastic Anemia
The bone marrow makes blood cells like red and white blood cells, and platelets. In aplastic anemia, it can’t do this well. This causes a lack of blood cells, leading to tiredness, infections, and bleeding issues.
Half the time, we don’t know what causes aplastic anemia. It’s called idiopathic aplastic anemia. But, it can be caused by chemicals, radiation, some medicines, and viruses. Knowing the cause helps doctors find the right treatment.
Distinguishing Aplastic Anemia from Other Blood Disorders
Doctors must figure out if it’s aplastic anemia or something else. Other conditions can also cause low blood cell counts. These include myelodysplastic syndromes, leukemia, and infections.
To diagnose aplastic anemia, doctors use blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and other tests. The bone marrow biopsy is key. It lets doctors see how many cells are in the marrow and if there are any bad cells.
Diagnostic Criteria for Aplastic Anemia
| Diagnostic Test | Finding in Aplastic Anemia |
| Blood Tests | Pancytopenia (low counts of red and white blood cells and platelets) |
| Bone Marrow Biopsy | Hypocellular marrow (reduced cellularity) |
| Cytogenetic Analysis | Normal karyotype (absence of chromosomal abnormalities) |
It’s important to tell aplastic anemia apart from other blood disorders. This helps doctors choose the right treatment. For aplastic anemia, treatments like immunosuppressive therapy and bone marrow transplants are used. But, other conditions might need different treatments.
Types of Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia can be divided into two main types: acquired and inherited. Knowing these types helps doctors create better treatment plans.
Acquired Aplastic Anemia
Acquired aplastic anemia is the most common type. It happens when something outside the body damages the bone marrow. This damage stops the bone marrow from making blood cells.
Exposure to toxic chemicals, radiation, and certain medications can cause it. It can also be triggered by autoimmune reactions, where the body attacks its own bone marrow.
Sometimes, the cause of acquired aplastic anemia is unknown, called idiopathic. Treatment usually involves finding and fixing the cause. It may also include immunosuppressive therapy to stop the immune system’s attack.
Inherited Forms of Aplastic Anemia
Inherited aplastic anemia is caused by genetic mutations. These mutations affect the bone marrow’s ability to make blood cells. Fanconi anemia is an example of this type, where a person is born with a higher risk of bone marrow failure.
People with inherited aplastic anemia often have other health problems too. They might have leukemia or other congenital anomalies. Managing this type of aplastic anemia requires a detailed plan. This includes supportive care and sometimes bone marrow transplantation.
It’s important to diagnose aplastic anemia early and know its type. This helps doctors choose the best treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Causes of Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia happens when the bone marrow’s stem cells get damaged. This damage comes from different things. Knowing what causes it helps us find better ways to prevent and treat it.
Autoimmune Reactions
In some cases, aplastic anemia is caused by an autoimmune reaction. This is when the immune system attacks the bone marrow cells by mistake. This attack can greatly reduce blood cell production.
Toxic Chemical Exposure
Being exposed to harmful chemicals like pesticides and industrial solvents can lead to aplastic anemia. Expert says avoiding these chemicals can help prevent the condition.
Radiation and Medication-Induced Damage
High doses of radiation and some medicines, like chemotherapy, can harm the bone marrow. This can lead to aplastic anemia. The risk is higher with long or high doses.
Viral Infections and Idiopathic Cases
Viral infections, like hepatitis and HIV, can damage the bone marrow and cause aplastic anemia. But sometimes, the cause is unknown, and it’s called idiopathic aplastic anemia.
| Cause | Description | Examples |
| Autoimmune Reactions | Immune system attacks bone marrow cells | Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| Toxic Chemical Exposure | Exposure to harmful chemicals damages bone marrow | Pesticides, Industrial Solvents |
| Radiation and Medication | High doses of radiation or certain medications damage bone marrow | Chemotherapy, Certain Antibiotics |
| Viral Infections | Viral infections damage bone marrow | Hepatitis, HIV |
“Understanding the causes of aplastic anemia is key to managing and treating it well.”
— Expert
Recognizing the Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
It’s important to know the symptoms of aplastic anemia early. This is because getting medical help quickly can really help. Aplastic anemia happens when the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. This leads to symptoms that can be different for everyone.
Early Warning Signs
The first signs of aplastic anemia can be hard to spot. They might include:
- Fatigue and weakness, because of not enough red blood cells.
- Pale skin, from not having enough red blood cells.
- Shortness of breath, when the body can’t get oxygen to tissues.
- Increased susceptibility to infections, from having too few white blood cells.
Advanced Symptoms
As aplastic anemia gets worse, symptoms can get more serious. These might include:
- Bleeding tendencies, like nosebleeds, bruising, or bleeding gums, from low platelet counts.
- Persistent infections, when the body can’t fight off infections well.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness, from anemia.
Emergency Symptoms Requiring Immediate Care
Some symptoms need help right away. These include:
- Severe bleeding that doesn’t stop.
- High fever or signs of a serious infection.
- Severe fatigue or shortness of breath when resting.
It’s key for patients and their caregivers to know these signs. This way, they can get medical help fast. Early treatment can greatly improve life for those with aplastic anemia.
Diagnostic Approaches for Aplastic Anemia
Healthcare experts use many tests to find aplastic anemia. Starting treatment early is key to managing the disease well.
Blood Tests and Complete Blood Count
Blood tests, like a complete blood count (CBC), are often the first step. A CBC checks the levels of red, white blood cells, and platelets. Low counts in aplastic anemia show a problem with making blood cells.
Key findings from a CBC in aplastic anemia include:
- Pancytopenia: A drop in red, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Anemia: Fewer red blood cells cause fatigue and weakness.
- Neutropenia: Low white blood cells make infections more likely.
- Thrombocytopenia: Fewer platelets lead to bruising and bleeding.
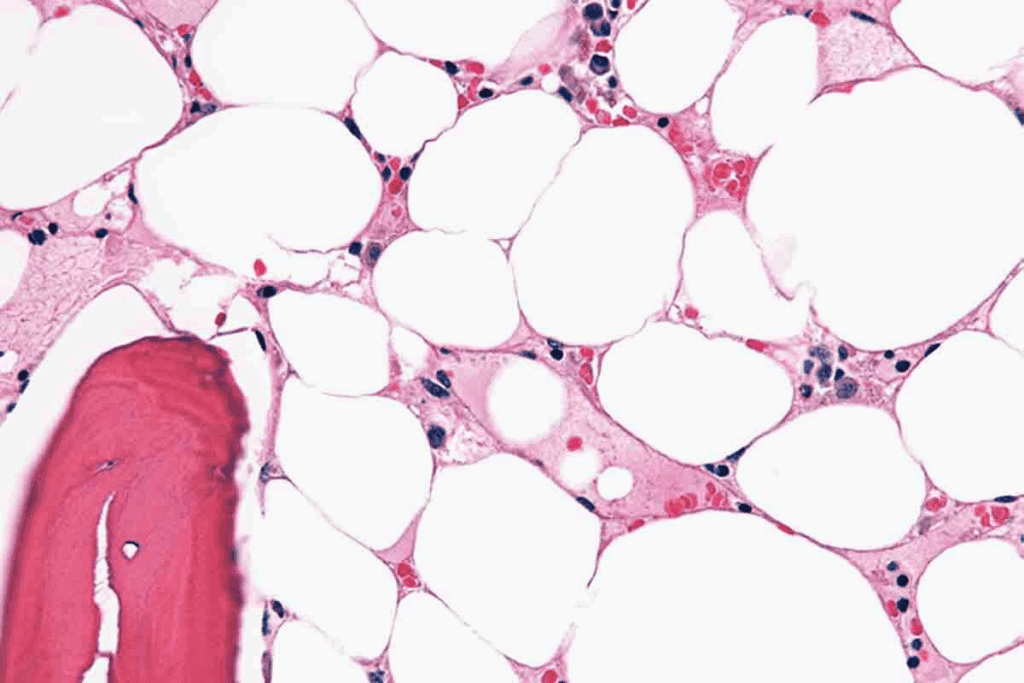
Bone Marrow Biopsy and Aspiration
A bone marrow biopsy and aspiration are key to confirming aplastic anemia. These take a bone marrow sample from the hipbone or sternum for study.
The bone marrow biopsy findings in aplastic anemia typically show:
| Characteristic | Normal Bone Marrow | Aplastic Anemia |
| Cellularity | Normal or increased cellularity | Hypocellularity, with a significant reduction in blood cell precursors |
| Blood Cell Precursors | Presence of various stages of blood cell development | Reduced or absent blood cell precursors |
| Fat Cells | Some fat cells present | Increase in fat cells, replacing the bone marrow space |
“The diagnosis of aplastic anemia is confirmed by the presence of pancytopenia and a hypocellular bone marrow.” –
Aplastic Anemia Foundation
Additional Diagnostic Tests
Other tests may be done to check for other conditions or find what caused aplastic anemia. These include:
- Flow cytometry to look at immune cells and find any issues.
- Cytogenetic analysis to find chromosomal problems.
- Imaging studies, like X-rays or CT scans, to see if the bone marrow or other organs are okay.
- Viral serology tests to find viruses linked to aplastic anemia.
By using these tests together, doctors can accurately diagnose aplastic anemia and plan the best treatment.
Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia
At LivHospital, we use many treatments for aplastic anemia to help patients. The right treatment depends on how severe the condition is and the patient’s health.
Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a key treatment for aplastic anemia. They help increase red and white blood cells and platelets. Regular transfusions can ease symptoms like fatigue and bleeding. But, they can also cause iron overload, needing extra treatment.
Immunosuppressive Therapy
Immunosuppressive therapy uses medicines to weaken the immune system. This method is based on the idea that aplastic anemia might be caused by an immune system problem. It aims to help the bone marrow work better.
Bone Marrow Transplantation
Bone marrow transplantation is a more serious treatment. It replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor. This treatment can cure aplastic anemia but has big risks, like graft-versus-host disease.
Supportive Care and Emerging Treatments
Supportive care is key in managing aplastic anemia. It focuses on easing symptoms and preventing problems. This includes antibiotics, medicines to boost blood cell production, and more. New treatments like gene therapy and novel immunosuppressive agents are being researched, giving hope for better care in the future.
At LivHospital, we follow the latest treatment plans for aplastic anemia. We make sure our patients get care that fits their needs.
Living with Aplastic Anemia
Living with aplastic anemia is tough. It affects not just the body but also the mind. Patients face many challenges that need a full plan to manage.
Managing Daily Life and Complications
Managing aplastic anemia means treating it medically and making lifestyle changes. Regular blood transfusions and immunosuppressive therapy are key. But, these treatments can make you more likely to get sick.
Every day, patients must watch for signs of infection or bleeding. These can be serious. Simple steps, like staying away from crowds or being careful when brushing teeth, are important. Getting used to these changes is hard but necessary.
Psychological Impact and Support Systems
The mental side of aplastic anemia is just as important. It can make you feel lonely, anxious, or depressed. Support systems, like family and friends, are key. They help you feel less alone.
Also, getting help for your mental health is important. Mental health professionals can teach you ways to handle stress. This helps you feel better overall. Living with aplastic anemia is more than just dealing with a disease; it’s about living a good life despite it.
Understanding aplastic anemia and using support systems can help patients live well. We aim to give the help and support needed on this journey.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook
The outlook for aplastic anemia depends on several important factors. These factors help doctors and patients make better treatment choices.
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Several things can change a patient’s outlook. These include:
- The severity of the condition at diagnosis
- The patient’s response to initial treatment
- The presence of any underlying health conditions
- The patient’s age and overall health status
Recent research shows that immune attacks on marrow stem cells are a big part of aplastic anemia. This knowledge has led to new treatments that aim to help patients more.
Survival Rates and Quality of Life
Thanks to better treatments, survival rates for aplastic anemia have gone up. The survival rate depends on how severe the condition is and how well it responds to treatment.
For those who get the right treatment, life quality can get much better. This means managing symptoms, avoiding complications, and dealing with the emotional side of the disease.
Every person with aplastic anemia has a different experience. Knowing what affects the prognosis and keeping up with new treatments helps patients and doctors work together. This way, they can aim for the best results.
Research Advances in Understanding and Treating Aplastic Anemia
Research has made big strides in understanding aplastic anemia. This has opened up new ways to treat it. It brings hope to people all over the world.
Recent Scientific Discoveries
Studies have uncovered how aplastic anemia works. They found that the immune system attacks the bone marrow. Immunosuppressive therapy is now key in treating it, by calming down this immune attack.
Genetic research has also made great progress. It has found certain genes linked to aplastic anemia. This discovery is helping create treatments that fit each patient’s genetic makeup.
Promising Clinical Trials and Future Directions
Many clinical trials are looking into new treatments for aplastic anemia. Eltrombopag, a drug that helps bone marrow, is showing great promise. Other trials are exploring gene therapy and stem cell transplants.
| Treatment Modality | Description | Potential Benefits |
| Immunosuppressive Therapy | Suppresses the immune system’s attack on bone marrow | Improved bone marrow function, reduced risk of infections |
| Eltrombopag | Stimulates bone marrow production | Increased platelet count, reduced need for transfusions |
| Gene Therapy | Corrects genetic mutations causing aplastic anemia | Potential cure, reduced risk of relapse |
As research keeps moving forward, we’ll see better treatments for aplastic anemia. The outlook for those with this condition is looking up. Ongoing studies and trials are leading to better care for patients.
Conclusion
Aplastic anemia is a complex condition where the bone marrow fails to make enough blood cells. This leads to a shortage of blood cells in the body. Managing this condition needs a team effort, using different treatments and care.
At LivHospital, we aim to give top-notch care to patients with aplastic anemia. Our team works closely with patients. We help them from the start of diagnosis to after treatment.
Treatment options include blood transfusions, medicines to suppress the immune system, and bone marrow transplants. The future looks bright for those with aplastic anemia. New research and medical technology are making treatments better and life quality higher.
We keep striving for medical excellence, dedicated to the best care for aplastic anemia patients. Our goal is to make life better for those affected. We believe a brighter future is ahead.
FAQ
What is aplastic anemia?
Aplastic anemia is a condition where the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells. This leads to serious health problems.
What is the role of bone marrow in blood production?
Bone marrow makes blood cells through a process called hematopoiesis. This process is broken in aplastic anemia.
How does bone marrow failure lead to aplastic anemia?
Bone marrow failure means it can’t make enough red, white blood cells, and platelets. This causes aplastic anemia.
What are the different types of aplastic anemia?
There are two types: acquired and inherited. Each has its own causes and signs.
What causes aplastic anemia?
Causes include autoimmune reactions, toxic chemicals, radiation, certain meds, viral infections, and some cases have no known cause.
What are the symptoms of aplastic anemia?
Symptoms start with fatigue and weakness. They can also include frequent infections and uncontrolled bleeding. Some symptoms are emergencies.
How is aplastic anemia diagnosed?
Doctors use blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and other tests to diagnose and understand the condition’s severity.
What are the treatment options for aplastic anemia?
Treatments include blood transfusions, immunosuppressive therapy, bone marrow transplants, and supportive care. New treatments offer hope.
How can patients manage daily life with aplastic anemia?
Patients cope with daily life by managing complications, dealing with the emotional impact, and using support systems.
What affects the prognosis of aplastic anemia?
The prognosis depends on how severe the condition is and how well it responds to treatment. This affects survival and quality of life.
What are the latest advances in understanding and treating aplastic anemia?
New discoveries and clinical trials are improving care for aplastic anemia patients, leading to better outcomes.
What is the connection between anemia and bone marrow?
Anemia happens when the bone marrow can’t make enough red blood cells. This is a key part of aplastic anemia.
How does aplastic anemia differ from other forms of anemia?
Aplastic anemia is unique because the bone marrow fails to produce all blood cells, not just red ones.
References
- DeZern, A. E., & Churpek, J. E. (2021). Approach to the diagnosis of aplastic anemia. Blood Advances, *5*(12), 2660–2671. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8233215/
































